Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Assign4 1
Enviado por
Zavier AguilaTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Assign4 1
Enviado por
Zavier AguilaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
1
ENSC 380
Assignment 4
Due: Dec 5, 2016 (4 pm)
Problem 1.
The impulse response of a CT-LTI system is
h(t ) 10e 10t u (t ) 100e 100t u (t )
Sketch the asymptotic Bode magnitude plot of the system. Use radian frequency.
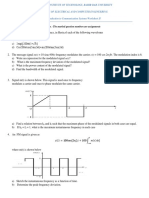
Problem 2
The message transmitted by a DSBSC modulator has a bandwidth of 5 Hz and a Fourier
Transform of
1, 5 f 5;
X(f )
0, otherwise
The transmitted signal is y (t ) x (t ) cos 2 f c t , where f c is the carrier frequency (and is
much higher than the bandwidth of the message).
A synchronous demodulator is used to recover x(t ) from y (t ) . The low pass filter in the
demodulator is an ideal low-pass filter with a bandwidth of 5 Hz. Due to imperfection in
the implementation, the local carrier in the demodulator has a frequency of f c 1 Hz
(instead of the correct value of f c Hz).
Let X ( f ) be the CTFT of the demodulated signal (the one that appears at the output of
the ideal low-pass filter). Sketch X ( f ) .
Problem 3
A common problem in over-the-air television signal transmission is multipath distortion of
the received signal due to the transmitted signal bouncing off structures. Typically a
strong main signal arrives at some time and a weaker ghost signal arrives later. So if the
transmitted signal is xt t the recieved signal is
xr t Km x t t tm Kg xt t tg ,
where K m K g and tg tm .
1.
2.
What is the transfer function of this communication channel?
What would be the transfer function of an equalization system that would
compensate for the effects of multipath?
Problem 4
Find the Nyquist rates for these signals.
(a)
xt 15rect 300tcos104 t
(d)
x t 4sinc500t comb 200t
(b)
xt 7sinc40t cos150t
Problem 5
Sample the CT signal,
1
t
xt 15 sinc 5t comb sin32 t
2
2
to form the DT signal, xn . Sample at the Nyquist rate and then at the next higher rate
for which the number of samples per cycle is an integer. Plot the magnitude of the CTFT
of the CT signal and the DTFT of the DT signal.
Problem 6
Let X ( F ) be the DTFT of the signal x[n] below
x[3] 1, x[2] 0, x[1] 1, x[0] 2,
x[1] 1,
x[2] 2,
x[3] 1,
x[4] 2,
x[5] 1,
x[6] 0,
x[7] 1, all other x[n] 0.
(a) Evaluate X ( F )
F 0
(b) Evaluate X ( F )
F 1/2
Você também pode gostar
- Digital Communications Exercise Solution for Zero ISI ConditionDocumento2 páginasDigital Communications Exercise Solution for Zero ISI ConditiondebealAinda não há avaliações
- Sampling and ReconstructionDocumento40 páginasSampling and ReconstructionHuynh BachAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Signal Processing - 1Documento77 páginasDigital Signal Processing - 1Sakib_SL100% (1)
- ECE341 Midterm Practice Questions Communication SystemsDocumento3 páginasECE341 Midterm Practice Questions Communication SystemsAdam SummersAinda não há avaliações
- Ch7 FourierTransform Continuous-Time Signal AnalysisDocumento43 páginasCh7 FourierTransform Continuous-Time Signal AnalysisNat RajAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction to Digital Signal ProcessingDocumento77 páginasIntroduction to Digital Signal Processingkarthik0433Ainda não há avaliações
- Digital Communication Systems Lecture-2: Sampling and QuantizationDocumento73 páginasDigital Communication Systems Lecture-2: Sampling and QuantizationSyed Abdullah Hasan ChishtiAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Communication Theory (EE503) Assignment 4Documento3 páginasAdvanced Communication Theory (EE503) Assignment 4EarthNandanAinda não há avaliações
- What is OFDMDocumento15 páginasWhat is OFDMRajib MukherjeeAinda não há avaliações
- DSP-Chapter1 Student 28062015Documento45 páginasDSP-Chapter1 Student 28062015NguyenThaoAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 10 PDFDocumento5 páginasLecture 10 PDFMehdi RabbaniAinda não há avaliações
- Examples Fourier - PsDocumento3 páginasExamples Fourier - PsAntonio MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- VI Sem ECE AssignmentsDocumento11 páginasVI Sem ECE AssignmentsManoj VarmaAinda não há avaliações
- EC - CE11 - Communications (1) : Test SummaryDocumento16 páginasEC - CE11 - Communications (1) : Test Summarysaravanababu jayapalAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment DSP 1Documento1 páginaAssignment DSP 1vankhoakmtAinda não há avaliações
- 1-Sampling and ReconstructionDocumento27 páginas1-Sampling and ReconstructionQuyen TranAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture #5, Fall 2003: ECE 6602 Digital CommunicationsDocumento12 páginasLecture #5, Fall 2003: ECE 6602 Digital Communicationsshakr123Ainda não há avaliações
- Digital Communication 601 - TutorialDocumento12 páginasDigital Communication 601 - TutorialHemanth Vinay Kumar0% (1)
- Comm AssntIIDocumento6 páginasComm AssntIIkalAinda não há avaliações
- Calculating Bandwidth of a Composite Channel Using Frequency Division MultiplexingDocumento25 páginasCalculating Bandwidth of a Composite Channel Using Frequency Division MultiplexingHunain AKAinda não há avaliações
- Total GMAT Math ExcerptDocumento18 páginasTotal GMAT Math ExcerptvinothAinda não há avaliações
- CH 5Documento42 páginasCH 5Monirul IslamAinda não há avaliações
- Problem Set 1Documento3 páginasProblem Set 1venkatesh pasumarthiAinda não há avaliações
- Sampling Theorem and Pulse ModulationDocumento27 páginasSampling Theorem and Pulse ModulationPavan PrakashAinda não há avaliações
- 9-MC Modulation and OFDMDocumento36 páginas9-MC Modulation and OFDMAbdul AzeezAinda não há avaliações
- Section A: Attempt All Questions. Property Table For Fourier Transform Is On The Last PageDocumento3 páginasSection A: Attempt All Questions. Property Table For Fourier Transform Is On The Last PageNasirAinda não há avaliações
- Linear EqualizerDocumento39 páginasLinear EqualizerVicky PatelAinda não há avaliações
- FM ExercisesDocumento5 páginasFM ExercisesanililhanAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 4Documento1 páginaAssignment 4Ilian A DeeringAinda não há avaliações
- Data Transmission ExercisesDocumento23 páginasData Transmission ExercisesSubash PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 - dsp1 - Co Thuc - Full, dsp1, Co Thuc, Xu Li Tin Hieu, BKDN, DSPDocumento120 páginasChapter 5 - dsp1 - Co Thuc - Full, dsp1, Co Thuc, Xu Li Tin Hieu, BKDN, DSPXP2009Ainda não há avaliações
- The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Department of Electronic and Information EngineeringDocumento6 páginasThe Hong Kong Polytechnic University Department of Electronic and Information EngineeringSandeep YadavAinda não há avaliações
- 2022 (E.s.) - 2Documento2 páginas2022 (E.s.) - 2Nikhil Kumar JaiswalAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 02Documento8 páginasLab 02Joevane B. EscrupoloAinda não há avaliações
- Sampling theorem: lowpass filter 1 −) (ωDocumento2 páginasSampling theorem: lowpass filter 1 −) (ωMohammed Hamid RasheedAinda não há avaliações
- Fall Semester 2019-20 ECE4001 Digital Communication Systems Digital Assignment 1 Due Date: 09/09/2019Documento4 páginasFall Semester 2019-20 ECE4001 Digital Communication Systems Digital Assignment 1 Due Date: 09/09/2019Grace ARORAAinda não há avaliações
- Fall Semester 2019-20 ECE4001 Digital Communication Systems Digital Assignment 1 Due Date: 09/09/2019Documento4 páginasFall Semester 2019-20 ECE4001 Digital Communication Systems Digital Assignment 1 Due Date: 09/09/2019PRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Ainda não há avaliações
- Mobile Communications Handbook: Stuber, G.L. "Modulation Methods" Ed. Suthan S. Suthersan Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 1999Documento16 páginasMobile Communications Handbook: Stuber, G.L. "Modulation Methods" Ed. Suthan S. Suthersan Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 1999Sai RamAinda não há avaliações
- n (t) × cos (2πf t + φ) Low-pass filterDocumento3 páginasn (t) × cos (2πf t + φ) Low-pass filterkhawasikarAinda não há avaliações
- HW 3Documento3 páginasHW 3Zero ChengAinda não há avaliações
- Essential Components of Digital Signal Processing SystemsDocumento4 páginasEssential Components of Digital Signal Processing SystemsMd. Asaduzzaman RazAinda não há avaliações
- COMM 401: Signals & Systems Theory: SamplingDocumento20 páginasCOMM 401: Signals & Systems Theory: SamplingNesma GamalAinda não há avaliações
- Solved Problems: EE160: Analog and Digital CommunicationsDocumento145 páginasSolved Problems: EE160: Analog and Digital CommunicationsJoseSimoes100% (1)
- Tutorial 1Documento1 páginaTutorial 1Sumadhur SaxenaAinda não há avaliações
- Partial response signalling achieves 2 symbols per HzDocumento4 páginasPartial response signalling achieves 2 symbols per HzDr-Muhammad RizwanAinda não há avaliações
- DSP-7 (Multirate) (S)Documento58 páginasDSP-7 (Multirate) (S)Jyothi JoAinda não há avaliações
- Effects of Sampling and Aliasing in Discrete Time SinusoidsDocumento7 páginasEffects of Sampling and Aliasing in Discrete Time SinusoidsJuman RehmanAinda não há avaliações
- Communication SystemsDocumento35 páginasCommunication SystemsSudhamsh Maddala100% (1)
- Practice QuestionsDocumento4 páginasPractice Questionspratik shuklaAinda não há avaliações
- Sampling and ReconstructionDocumento63 páginasSampling and ReconstructionHermyraJ RobertAinda não há avaliações
- CH 5Documento43 páginasCH 5ubyisismayilAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 9: M - Ary Amplitude and Frequency Shift Keying, Signal SpaceDocumento19 páginasLab 9: M - Ary Amplitude and Frequency Shift Keying, Signal SpaceAyman YounisAinda não há avaliações
- End-Semester Exam Questions in Communication SystemsDocumento4 páginasEnd-Semester Exam Questions in Communication SystemsYash YashAinda não há avaliações
- Mobile Communications Tutorial: Rayleigh Fading and its EffectsDocumento3 páginasMobile Communications Tutorial: Rayleigh Fading and its EffectsIhthisham KalidhAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 7Documento3 páginasTutorial 7Ali AlabidAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsAinda não há avaliações
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Ainda não há avaliações
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportAinda não há avaliações