Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
RPT 2017 Fizik Form 4
Enviado por
shshshchinTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
RPT 2017 Fizik Form 4
Enviado por
shshshchinDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
RANCANGAN PENGAJARAN TAHUNAN FIZIK TING.
4 2017
YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2017
PHYSICS FORM 4
SMK SERI BINTANG SELATAN, KUALA LUMPUR
Week
Date
Learning Area
Learning Objectives
Learning Outcomes
A student is able to :
- Explain what Physics is.
- Recognize the Physics in every day life
1.1 Understanding Physics
1.2 Understanding base quantities
and
derived quantities
3/1 6/1
9/1 13/1
I-THINK/HOTS/PDP
Explain what base quantities and derive quantities are.
List base quantities and their units
List some derived quantities and their units
Express quantities using prefixes
Express quantities using scientific notation
Express derived quantities as well as their units in terms of base
quantities and base units
- Solve problems involving conversion of units.
KBAT: EVALUATE
SOURCE: YOUTUBE
INTRODUCTION
TO
PHYSICS
KBAT: APPLYING
16/1 -20/1
1.3 Understanding scalar and
vector quantities
- Define scalar and vector quantities
- Give examples of scalar and vector quantities
1.4
Understanding
measurements
1.5 Analysing scientific
investigations
4
23/1 27/1
26/1 131/1
1/2
RPT/NORMALA/2017
measure physical quantities using appropriate
explain accuracy and consistency
explain sensitivity
explain types of experimental error
use appropriate techniques to reduce errors.
- identify variables in a given situation
- identify a question suitable for scientific
investigation
- form hypothesis
- design and carry out a simple experiment to test
the hypothesis
- record and present data in a suitable form
- interpret data to draw a conclusion
- write a report of the investigation
KBAT: APPLYING
KBAT: ANALYZING
SOURCE: EXP
CUTI PERAYAAN2CUTI SEMPENA PERAYAAN TAHUN BARU CINA
CUTI HARI WILAYAH
RANCANGAN PENGAJARAN TAHUNAN FIZIK TING.4 2017
Week
Date
Learning Area
Learning Objectives
2.1 Analysing linear motion
1/2 - 5/2
FORCES AND
MOTION
9/2
6/2 - 10/2
8
9
20/2 24/2
27/2 3/3
10
6/3 -10/3
FORCES AND
MOTION
13/3 -17/3
18/3 -26/3
RPT/NORMALA/2017
KBAT: APPLYING
- plot and interpret displacement time and velocity-time
graphs
- deduce from the shape of a displacement-time graph
when a body is :
i.
at rest
ii.
moving with uniform velocity
iii.
moving with non-uniform velocity
- determine distance, displacement and velocity frm a displacement-time
graph.
- Deduce from the shape of velocity-time graph when a body is :
i.
at rest
ii.
moving with uniform velocity
iii.
moving with non-uniform velocity
- determine distance, displacement, velocity and acceleration from a
velocity-time graph.
- Solve problems on linear motion with uniform acceleration.
KBAT: ANALYZING
PENILAIAN KURIKULUM 1 / 2017
PENILAIAN KURIKULUM 1 / 2017
PERBINCANGAN PEPERIKSAAN PENILAIAN KURIKULUM 1/2017
2.3
11
- define distance and displacement
- define speed and velocity and state that average
velocity ,
v = s/t
- define acceleration and deceleration and state that
a= vu
t
(Experiment using ticker timer)
- calculate speed and velocity
- calculate acceleration/deceleration
- solve problems on linear motion with uniform acceleration using
i . v = u + at
ii
s = ut + at
iii v = u + 2as
I-THINK/HOTS/PDP
CUTI HARI THAIPUSAM
2.2 Analysing motion graph
Learning Outcomes
FORCES AND
MOTION
Understanding Inertia
Explain what inertia is
Relate mass to inertia
Give examples of situation involving inertia
Suggest ways to reduce the negative effects of inertia.
[experiment]
KBAT: CREATING
SOURCE: EXP
CUTI PERTENGAHAN PENGGAL1
RANCANGAN PENGAJARAN TAHUNAN FIZIK TING.4 2017
Week
Date
Learning Area
Learning Objectives
2.4
12
Analysing momentum
Define the momentum of an object
Define momentum (p) as the product of mass (m ) and velocity (v ) i.e. p
= mv
State the principle of conservation of momentum
Describe application of conservation of momentum.
Solve problems involving momentum
[experiment]
Describe the effects of balanced forces acting on an object
Describe the effects of unbalanced forces acting on an object
Determine the relationship between force, mass and acceleration i.e.
F=ma
Solve problems using F=ma
[experiment]
27/3 - 31/3
FORCES AND
MOTION
2.5
13
Learning Outcomes
Understanding the effects of
force
3/4 7/4
2.6
Analysing impulse and
impulsive force
Explain what an impulsive force means
Give examples of situations involving impulsive force.
Define impulse as a change in momentum, i.e.
F = mv - mu
t
Explain the effect on increasing or decreasing time of impact on the
magnitude of the impulsive force.
Describe situations where an impulsive force needs to be reduced and
suggest ways to reduce it.
Describe the situation where an impulsive force is beneficial.
Solve problem involving impulsive forces.
demonstration
Describe the importance of safety features in vehicles
explain acceleration due to gravity
state what a gravitational field is
define gravitational field strength
determine the value of acceleration due to gravity
define weight (W) as the product of mass (m) and acceleration due
to gravity (g) i.e. W = mg
solve problem involving acceleration due to gravity
describe situations where forces are in equilibrium
state what a resultant force is
add two forces are to determine the resultant force
resolve a force into the effective component forces.
- Solve problems involving forces in equilibrium.
14
10/4- 14/4
FORCES AND
MOTION
2.7 Being aware of need for safety
feature in vehicles
I-THINK/HOTS/PDP
KBAT: APPLYING
SOURCE: EXP
KBAT: APPLYING
SOURCE:
COMPETITION EGG
PARACHUTTE
KBAT: ANALYZING
2.8 Understanding gravity
15
17/4 -21/4
FORCES AND
MOTION
16
24/4 - 28/4
RPT/NORMALA/2017
2.9 Analysing forces in equilibrium
(part I)
2.9 Analysing forces in equilibrium
(part II)
KBAT: APPLYING
SOURCE: YOUTUBE
KBAT: APPLYING
KBAT: APPLYING
RANCANGAN PENGAJARAN TAHUNAN FIZIK TING.4 2017
Week
Date
Learning Area
Learning Objectives
Learning Outcomes
2.10 Understanding work energy,
power and efficiency
17
1/5 -5/5
2.11 Appreciating the importance of
maximizing the efficiency of devices
18
19
20
21
8/5 12/5
15/5 19/5
22/5 226/5
27/5 11/6
12/6 -16/6
I-THINK/HOTS/PDP
KBAT: ANALYZING
SOURCE: YOUTUBE
Recognize the importance for maximizing efficiency of device in
conserving resources.
Mid Year Examination 2017
Mid Year Examination 2017
Mid Year Examination 2017
-------------------------------------------------------------------- Mid Year Holiday 2017-----------------------------------------------------------DISCUSSION OF EXAM PAPER / PERBINCANGAN KERTAS JAWAPAN PPT 2017
2.12 Understanding elasticity
22
Define work (W) as the product of an applied force (F) and displacement
(s) of an object in the direction of the applied force i.e. W = Fs
State that when work is done energy is transferred from one object to
another.
Define kinetic energy and state that Ek = mv
Define gravitational potential energy and state that Ep = mgh
State the principle of conservation of energy
Define power and state that P = W/t
Explain what efficiency of a device is
Solve problems involving work, energy, power and efficiency
19/6 23/6
Define elasticity
Define Hookes Law
Define elastic potential energy and state that Ep = kx
Determine the factor effect elasticity
Describe applications of elasticity
Solve problem involving elasticity
[experiment]
KBAT: APPLYING
SOURCE: EXP
23
23/6
26/6 30/6
3.1 Understanding pressure
24
HARI DISKUSI 1
CUTI SEMPENA PERAYAAN HARI RAYA PUASA
- Define pressure and state that P = F
A
- Describe application of pressure
- Solve the problems involving pressure
KBAT: APPLYING
SOURCE: EXP
3/7 7/7
3.2 Understanding pressure in liquid
FORCE AND
PRESSURE
Relate depth to pressure in liquid
Relate density to pressure in liquid
Explain pressure in liquid and state that P = hg
Describe applications of pressure in liquids
Solve problems involving pressure in liquids
[experiment]
25
KBAT: APPLYING
SOURCE: EXP
KBAT: APPLYING
SOURCE: EXP
10/6 14/7
RPT/NORMALA/2017
RANCANGAN PENGAJARAN TAHUNAN FIZIK TING.4 2017
Week
Date
Learning Area
Learning Objectives
3.3 Understanding gas pressure and
atmospheric pressure
26
18/7 - 22/7
Learning Outcomes
-
I-THINK/HOTS/PDP
Explain gas pressure.
Explain atmospheric pressure
Describe the applications of atmospheric pressure
Solve problems involving atmospheric pressure and gas pressure
KBAT: APPLYING
SOURCE: EXP
FORCE AND
PRESSURE
3.4 Applying Pascals principle
State Pascals Principle
Explain hydraulic systems
Describe applications of Pascals Principle
Solve problems involving Pascals Principle
KBAT: APPLYING
SOURCE: EXP
3.5 Applying Archimedes principle
27
25/7 - 29/7
FORCE AND
PRESSURE
3.6 Understanding Bernoullis
Principle
Explain Buoyant Force
Relate buoyant force to the weight of the liquid displaced
State Archimedes Principle
Describe application of Archimedes Principle
Solve problem involving Archimedes Principle
State Bernoullis Principle
Explain the resultant force exist due to difference in fluid pressure
Describe applications of Bernoullis Principle
Solve problems involving Bernoullis Principle
KBAT: APPLYING
SOURCE: EXP
KBAT: APPLYING
SOURCE: EXP
28
4.1 Understanding thermal equilibrium
31/7 - 5/8
4.2 Understanding specific heat
capacity
29
7/8 -11/8
HEAT
4.3 Understanding specific latent
heat
30
14/8 - 18/8
RPT/NORMALA/2017
- Explain thermal equilibrium
- Explain how liquid-in- glass thermometer works
- Define specific heat capacity (c)
- State that c = Q
m
- Determine the specific heat capacity of a liquid
- Determine the specific heat capacity of a solid
- Describe application of specific heat capacity
- Solve problems involving specific heat capacity
- State that transfer of heat during a change of phase does not cause a
change in temperature
- Define specific latent heat (l )
- State that l = Q
m
- Determine the specific latent heat of fusion.
- Determine the specific latent heat of vaporization
- Solve problems involving specific latent heat.
KBAT: ANALYZING
SOURCE: EXP
KBAT: APPLYING
SOURCE: EXP
KBAT: APPLYING
SOURCE: EXP
RANCANGAN PENGAJARAN TAHUNAN FIZIK TING.4 2017
Week
31
Date
21/8 25/8
26 /8 1/9
32
4/8 8/9
Learning Area
Learning Objectives
I-THINK/HOTS/PDP
KBAT: ANALYZING
SOURCE: EXP
KBAT: ANALYZING
SOURCE: EXP
LIGHT
5.2 Understanding refraction of light
5.3 Understanding total internal
reflection of light
33
11/9 - 15/9
LIGHT
Week
Date
Learning Area
RPT/NORMALA/2017
Learning Outcomes
- Explain gas pressure, temperature and volume in terms of the behaviour
4.4 Understanding the gas laws
of gas molecules.
- Determine the relationship between pressure and volume at constant
temperature for a fixes mass of gas i.e
pV = constant
- Determine the relationship between relationship between volume and
temperature at constant pressure for a fixed mass of gas i.e V =
constant or V T
T
- Determine the relationship between pressure and temperature at constant
volume for a fixed mass of gas i.e p = constant or p T
T
- Explain absolute zero
- Explain the absolute /Kelvin scale of temperature
- Solve problem involving pressure, temperature and volume of a fixed
mass of gas.
------------------------------------------------------------------------- Mid Semester 2 Holiday ------------------------------------------------------------- Describe the characteristics of image formed by reflection of light
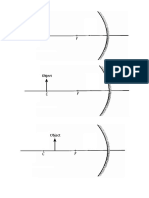
5.1 Understanding Reflection of Light
- State the laws of reflection of light
- Draw ray diagram \a to show the position and characteristics of the
image formed by a
iplane mirror
iiconvex mirror
iiiconcave mirror
- describe application of reflection of light.
- Construct a device based on the application of reflection of light.
Learning Objectives
- Explain refraction of light
- Define n = sin i
sin r
- Determine the refractive index of glass or Perspex block.
- State the refractive index, n, as
Speed of light in vacuum
Speed of light in a medium
- Describe phenomena due to refraction
- Solve problems involving the refraction of light.
- Explain total internal reflection of light
- Define critical angle (c)
- Relate the critical angle to the refractive index i.e.
n = _1_
sin c
- Describe natural phenomenon involving total internal reflection
- Describe applications of total internal reflection
- Solve problems involving total internal reflection
Learning Outcomes
KBAT: APPLYING
SOURCE: YOUTUBE
KBAT: APPLYING
SOURCE: EXP
I-THINK/HOTS/PDP
RANCANGAN PENGAJARAN TAHUNAN FIZIK TING.4 2017
5.4 Understanding lenses
34
18/9 22/9
LIGHT
-
Explain focal point and focal length
Determine the focal point and focal length of a convex lens
Determine the focal point and focal length of a concave lens
Draw a ray diagrams to show the positions and characteristics of the
images formed by a convex lens.
Draw ray diagrams to show the position and characteristics of the images
formed by a concave lens
Define magnification as m = v
u
Relate focal length (f) to the object distance (u) and image distance (v),
i.e
1 = 1 + 1
f
u
v
Solve problems involving lenses
35
25/9 -29/9
36
3/10 7/10
Final Examination 2017
37
38
10/10 14/10
16/10 -20/10
Final Examination 2017
CUTI SEMPENA PERAYAAN DEEPAVALI
39
23/10 28/10
Final Examination 2017
40
30/10 3/11
DISCUSSION
41
6/11 - 10/11
DISCUSSION
42
13/11 17/11
CHECKING MARKSHEET
43
20/11 24/11
HARI DISKUSI 2
KBAT: APPLYING
SOURCE: EXP
REVISION
End of Year Holiday
RPT/NORMALA/2017
Você também pode gostar
- Elements and Compounds ExplainedDocumento9 páginasElements and Compounds ExplainedshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- Econsave OilDocumento2 páginasEconsave OilshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- f1 Chapter 4 ReproductionDocumento22 páginasf1 Chapter 4 ReproductionshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- f1 Chapter 7 AirDocumento12 páginasf1 Chapter 7 AirshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- FireInsuranceProposalForm PDFDocumento4 páginasFireInsuranceProposalForm PDFshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- 三年级Documento1 página三年级CHIN SOK HONG MoeAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Topik 1 Kertas 1 - Jawapan BARUDocumento1 páginaTopik 1 Kertas 1 - Jawapan BARUshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- RAC2021 Live Coding ChallengeDocumento1 páginaRAC2021 Live Coding ChallengeshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Topik 1 Kertas 1 - Jawapan BARUDocumento1 páginaTopik 1 Kertas 1 - Jawapan BARUshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- Skema t4 TuitionDocumento20 páginasSkema t4 TuitionshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Following Information May Be Useful. The Symbols Have Their Usual Meaning. U VDocumento2 páginasThe Following Information May Be Useful. The Symbols Have Their Usual Meaning. U VshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- TreasurehuntDocumento18 páginasTreasurehuntAhmad OmarAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Sample For Micro:bit: This Sample Questions Is Created With The Objective BelowDocumento6 páginasSample For Micro:bit: This Sample Questions Is Created With The Objective BelowshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Absorption of HeatDocumento6 páginasAbsorption of HeatshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- Parts and Use of a Basic Light MicroscopeDocumento9 páginasParts and Use of a Basic Light MicroscopeshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Am Bon Use CatalogueDocumento19 páginasAm Bon Use CatalogueshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- ANALISIS KEPUTUSAN FIZIK 5KRK 2015Documento2 páginasANALISIS KEPUTUSAN FIZIK 5KRK 2015shshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- Ray Diagram Curved MirrorDocumento2 páginasRay Diagram Curved MirrorshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- ACFrOgBsXVgiX0jQESasasa0yWP3PFxzFdLrkEM3B8r3ULrDrXc-ujzdAJS8hgBHU HyRHPIpl3sYDOVeLUvHPWcLEJDMs4XekHvLu8Z3SFkYQ0qWZA4DimJFrXysZneGnkIDocumento12 páginasACFrOgBsXVgiX0jQESasasa0yWP3PFxzFdLrkEM3B8r3ULrDrXc-ujzdAJS8hgBHU HyRHPIpl3sYDOVeLUvHPWcLEJDMs4XekHvLu8Z3SFkYQ0qWZA4DimJFrXysZneGnkIshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry SPM NotesDocumento12 páginasChemistry SPM NotesArthas Rhee HermanAinda não há avaliações
- Class Teacher Approbation ContractDocumento18 páginasClass Teacher Approbation ContractshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- 面包材料华英对照称呼Documento2 páginas面包材料华英对照称呼ailinleeAinda não há avaliações
- Command WordsDocumento4 páginasCommand WordsshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Molar Calculations: Converting Between Moles, Mass, Volume, and ParticlesDocumento1 páginaMolar Calculations: Converting Between Moles, Mass, Volume, and ParticlesshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- Characteristics of A 21st Century Classroom - SampleDocumento8 páginasCharacteristics of A 21st Century Classroom - SampleMyers RicaldeAinda não há avaliações
- University Monsters PackDocumento42 páginasUniversity Monsters PackshshshchinAinda não há avaliações
- Projectile Motion LabDocumento8 páginasProjectile Motion LabAAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 13-4Documento35 páginasLecture 13-4Mapalo faith ChamaAinda não há avaliações
- Leaching and Evap ProblemsDocumento9 páginasLeaching and Evap ProblemsValerie Ann FranciscoAinda não há avaliações
- Thermal Energy Storage Technologies PDFDocumento21 páginasThermal Energy Storage Technologies PDFMohammed Nafis NAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 01 PPT IrDocumento34 páginasUnit 01 PPT Irapi-237496924Ainda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- HSSRPTR - Plus One Physics Focus Point Part 2 Chapter 9-15Documento55 páginasHSSRPTR - Plus One Physics Focus Point Part 2 Chapter 9-15AswithAinda não há avaliações
- Paramount Physics Cafe Teaching A2 Physics SkillsDocumento5 páginasParamount Physics Cafe Teaching A2 Physics SkillsMahbub KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Thermal Concepts1Documento6 páginasThermal Concepts1api-288721232Ainda não há avaliações
- IGCSE Coordinated Science Review Notes-Physics PDFDocumento95 páginasIGCSE Coordinated Science Review Notes-Physics PDFNishi ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Physics IX WORKSHEETDocumento8 páginasPhysics IX WORKSHEETShahidul Hassan MontiAinda não há avaliações
- MCQ Questions Bank ThermodynamicsDocumento31 páginasMCQ Questions Bank Thermodynamicsahmed mohamed hassanAinda não há avaliações
- Prueba 2 Conceptos T RmicosDocumento26 páginasPrueba 2 Conceptos T RmicosjosueAinda não há avaliações
- Properties of Pure Substance - Spring 2020Documento83 páginasProperties of Pure Substance - Spring 2020Hamza AliAinda não há avaliações
- FKCH 8 HHM BYSJxe F8 ZG 74Documento45 páginasFKCH 8 HHM BYSJxe F8 ZG 74MahaAinda não há avaliações
- Piping 30000Documento14 páginasPiping 30000Prasanta Kumar BeheraAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Food EngineeringDocumento59 páginasIntroduction To Food EngineeringMaryam SarAinda não há avaliações
- MERC MATERIAL For Power PlantDocumento58 páginasMERC MATERIAL For Power PlantDurga Prasad SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Drying Is One of The Oldest Methods of Preserving FoodbfdDocumento7 páginasDrying Is One of The Oldest Methods of Preserving FoodbfdJefrie RonaldAinda não há avaliações
- Calorimetry and Thermal Expansion PDFDocumento54 páginasCalorimetry and Thermal Expansion PDFshyla100% (2)
- Exergy analysis of latent heat storage systems with sensible heating and subcooling of PCMDocumento16 páginasExergy analysis of latent heat storage systems with sensible heating and subcooling of PCMAngieRinconOrtegaAinda não há avaliações
- Tables and Index Thermodynamics Cengel 7E-2Documento118 páginasTables and Index Thermodynamics Cengel 7E-2tomtom9649Ainda não há avaliações
- 3 Thermodynamics TDEEDocumento129 páginas3 Thermodynamics TDEENikhilAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Pure SubstanceDocumento52 páginasChapter 2 Pure SubstanceSyafiq AimanAinda não há avaliações
- 3rd Quarter Science 8Documento50 páginas3rd Quarter Science 8John Ryan PiolAinda não há avaliações
- A Predictive Model For Confined and Unconfined Nucleate Boiling Heat Transfer CoefficientDocumento11 páginasA Predictive Model For Confined and Unconfined Nucleate Boiling Heat Transfer CoefficientBotao QiaoAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Revision ChecklistDocumento36 páginasPhysics Revision Checklistapi-3723991100% (5)
- Ch-01 Matter in Our Surroundings SQ PDFDocumento5 páginasCh-01 Matter in Our Surroundings SQ PDFParamita KaranAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4Documento20 páginasChapter 4DertySulistyowatiAinda não há avaliações
- Review of Mathematical Modeling On Latent Heat Thermal Energy Storage Systems Using Phase-Change MaterialDocumento33 páginasReview of Mathematical Modeling On Latent Heat Thermal Energy Storage Systems Using Phase-Change MaterialabinayajothiAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry With Physics Reviewer PDFDocumento69 páginasChemistry With Physics Reviewer PDFRJ JRAinda não há avaliações