Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Ranitidine Drug Study
Enviado por
Cheezy BreadDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Ranitidine Drug Study
Enviado por
Cheezy BreadDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Ranitidine Drug Study
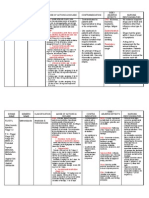
In making a Drug Study, the following elements must be present: Generic Name and the
Brand name (not all brands, just the brand used by the patient), Action, Indication,
Pregnancy Category, Drug Classification, and Contraindication, Adverse Effect, Drug
interaction and Nursing Consideration/Intervention. Most clinical instructors preferred this
to be in a long bond paper in printed or handwritten with paper in landscape.
Ranitidine hydrochloride
Brand Name: Alti-Ranitidine (CAN), Novo-Ranidine (CAN), Nu-Ranit (CAN),
Zantac, Zantac EFFERdose, Zantac GELdose, Zantac 75
Pregnancy Category B
Drug class: Histamine2 (H2) antagonist
Therapeutic actions
Competitively inhibits the action of histamine at the histamine 2 (H2)
receptors of the parietal cells of the stomach, inhibiting basal gastric acid
secretion and gastric acid secretion that is stimulated by food, insulin,
histamine, cholinergic agonists, gastrin, and pentagastrin.
Indications
Short-term treatment of active duodenal ulcer
Maintenance therapy for duodenal ulcer at reduced dosage
Short-term treatment of active, benign gastric ulcer
Short-term treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease
Pathologic hypersecretory conditions (eg, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome)
Treatment of erosive esophagitis
Treatment of heartburn, acid indigestion, sour stomach
Contraindications
Contraindicated with allergy to ranitidine, lactation.
Use cautiously with impaired renal or hepatic function.
Adverse effects
Headache, malaise, dizziness, somnolence, insomnia, vertigo,
Tachycardia, bradycardia, PVCs (rapid IV
administration), Rash, alopecia, Constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting,
abdominal pain, hepatitis, increased ALT levels, Gynecomastia, impotence or
decreased libido, Leukopenia, granulocytopenia,
thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, Pain at IM site, local burning or itching at
IV site, Arthralgias
Drug Interactions:
Increased effects of warfarin, TCAs
Decreased effectiveness of diazepam
Decreased clearance and possible increased toxicity
of lidocaine, nifedipine
Nursing considerations
Administer oral drug with meals and at bedtime.
Decrease doses in renal and liver failure.
Provide concurrent antacid therapy to relieve pain.
Administer IM dose undiluted, deep into large muscle group.
Arrange for regular follow-up, including blood tests, to evaluate
effects.
Você também pode gostar
- Ranitidine HydrochlorideDocumento2 páginasRanitidine HydrochlorideIvan Liquiran AvenadoAinda não há avaliações
- Ranitidine, Famotidine, Essentiale, Paracetamol, Xyzal, AeknilDocumento12 páginasRanitidine, Famotidine, Essentiale, Paracetamol, Xyzal, AeknilJenivic Empig Puedan100% (1)
- Drug Study TramadolDocumento14 páginasDrug Study TramadolBianca Freya Porral85% (13)
- Zantac Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasZantac Drug StudyCee Kaye Gee0% (1)
- Drug Study - Tamiflu, FlagylDocumento2 páginasDrug Study - Tamiflu, Flagylmark_gain100% (1)
- RanitidineDocumento1 páginaRanitidineMcmac YangoAinda não há avaliações
- Vii. Drug Study Drug Indication Action Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Date Ordered: Generic Name: SpecificDocumento1 páginaVii. Drug Study Drug Indication Action Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Date Ordered: Generic Name: SpecificnuraAinda não há avaliações
- Benadryl Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasBenadryl Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study (Ranitidine, Metoclopramide, Ketorolac, and Omeprazole)Documento8 páginasDrug Study (Ranitidine, Metoclopramide, Ketorolac, and Omeprazole)Akisan0% (1)
- Chlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Documento4 páginasChlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Nurginayah RusliAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study Ranitidine TramadolDocumento10 páginasDrug Study Ranitidine TramadolSitti Zhainab0% (1)
- Drug Study MetronidazoleDocumento2 páginasDrug Study MetronidazoleJha NetAinda não há avaliações
- PantoprazoleDocumento1 páginaPantoprazoleKC Ignacio100% (1)
- Heparin InjectionDocumento2 páginasHeparin InjectiongagandipkSAinda não há avaliações
- FamotidineDocumento1 páginaFamotidineMäc LäntinAinda não há avaliações
- Carisoprodol (Drug Study)Documento2 páginasCarisoprodol (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888Ainda não há avaliações
- Drug Routes Side Effects Co4Ntraindications Nursing Responsibility Brand Name: Inhalation: CoughDocumento2 páginasDrug Routes Side Effects Co4Ntraindications Nursing Responsibility Brand Name: Inhalation: CoughChristianne Janella PagadorAinda não há avaliações
- Ranitidine Drug StudyDocumento1 páginaRanitidine Drug StudyJen Alhambra100% (14)
- MetoclopramideDocumento3 páginasMetoclopramideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocumento23 páginasDrug StudyReiche GomezAinda não há avaliações
- Name of Drug FinalDocumento7 páginasName of Drug FinalJaessa FelicianoAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study Atenolol, Cefuroxime, SimvastatinDocumento4 páginasDrug Study Atenolol, Cefuroxime, Simvastatinpaupaulala100% (4)
- Drug StudyDocumento1 páginaDrug StudyJojelyn Yanez Balili100% (2)
- NitrofurantoinDocumento3 páginasNitrofurantoinapi-3797941Ainda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - Furosemide (Lasix)Documento2 páginasDrug Study - Furosemide (Lasix)mikErlh80% (5)
- DrugsDocumento5 páginasDrugsdeepika kushwah100% (1)
- Drug Study TramadolDocumento2 páginasDrug Study TramadolGrace Stephanie100% (13)
- PhenobarbitalDocumento2 páginasPhenobarbitalJeremy_Fabio_5332100% (2)
- LansoprazoleDocumento2 páginasLansoprazoleGeorley Lobrido100% (1)
- Ranitidine Drug SummDocumento1 páginaRanitidine Drug SummWarren100% (3)
- Drug StudyDocumento5 páginasDrug StudyLizeth Querubin93% (15)
- Drug Study PantoprazoleDocumento2 páginasDrug Study PantoprazoleFlauros Ryu Jabien100% (3)
- Omeprazole Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasOmeprazole Drug StudyFeliza Therese A. DeloriaAinda não há avaliações
- LevofloxacinDocumento3 páginasLevofloxacinkezia_reyes67% (3)
- MetronidazoleDocumento2 páginasMetronidazoleJm RomancapAinda não há avaliações
- PantoprazoleDocumento2 páginasPantoprazoleMargaret Cortinas0% (1)
- Generic Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento1 páginaGeneric Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesmaemalabonAinda não há avaliações
- Chlorthalidone HygrotonDocumento2 páginasChlorthalidone HygrotonLIEZEL GRACE VELAYOAinda não há avaliações
- KetorolacDocumento1 páginaKetorolacAngela Tenorio100% (1)
- MetronidazoleDocumento2 páginasMetronidazolehauteanicoleAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study Diclofenac KDocumento3 páginasDrug Study Diclofenac KCarl Julienne Masangcay100% (1)
- AmilorideDocumento1 páginaAmilorideRox San100% (1)
- OndansetronDocumento2 páginasOndansetronhauteanicoleAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento6 páginasDrug StudyAko Si Vern ÖAinda não há avaliações
- Acetazolamide/diamoxDocumento3 páginasAcetazolamide/diamoxjedisay1100% (1)
- CefazolinDocumento1 páginaCefazolinernestjohn67% (3)
- Contraindications: DRUG STUDY: MetronidazoleDocumento1 páginaContraindications: DRUG STUDY: MetronidazoleCrystal Ann Monsale TadiamonAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento8 páginasDrug StudyMaria Charlene Orpilla0% (1)
- BuscopanDocumento1 páginaBuscopanPhine Santos Tabas100% (1)
- Drug StudiesDocumento4 páginasDrug StudiesgyantuazonAinda não há avaliações
- DrugsDocumento27 páginasDrugspeterjongAinda não há avaliações
- KetorolacDocumento4 páginasKetorolacx483xDAinda não há avaliações
- Ramipril Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasRamipril Drug StudyCheezy Bread0% (1)
- Ranitidine HCLDocumento3 páginasRanitidine HCLdanny17phAinda não há avaliações
- Medication: Captopril (Capoten) Is An ACE Inhibitor and A Common Antihypertensive. Captopril Generic Name Contents (Hide)Documento43 páginasMedication: Captopril (Capoten) Is An ACE Inhibitor and A Common Antihypertensive. Captopril Generic Name Contents (Hide)Kath Rubio0% (1)
- Rani Ti DineDocumento2 páginasRani Ti DineCarl Sagisabal IbascoAinda não há avaliações
- 13 Drug StudyDocumento6 páginas13 Drug StudyRachel Yvonne Cabacungan100% (1)
- Ma. Patricia R. de Leon Bsn-Iv: Drug Indications Contraindicatio Ns Action Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento6 páginasMa. Patricia R. de Leon Bsn-Iv: Drug Indications Contraindicatio Ns Action Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesTricia_De_Leon_6494Ainda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento24 páginasDrug StudyMc Joewell HudencialAinda não há avaliações
- Drug OrderDocumento3 páginasDrug OrderSaima BataloAinda não há avaliações
- Nifedepine Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasNifedepine Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Nystatin Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasNystatin Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Nitroglycerine Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasNitroglycerine Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Lansoprazole Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasLansoprazole Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Diazepam Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasDiazepam Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Benicar Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasBenicar Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Benadryl Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasBenadryl Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Phenytoin Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasPhenytoin Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Phenobarbital Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasPhenobarbital Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasOfloxacin Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Penicillin Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasPenicillin Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Potassium Salts Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasPotassium Salts Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Verapamil HCL Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasVerapamil HCL Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Simvastatin Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasSimvastatin Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Ramipril Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasRamipril Drug StudyCheezy Bread0% (1)
- Prednisone Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasPrednisone Drug StudyCheezy Bread67% (3)
- Risperidone Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasRisperidone Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Tetracycline HCL Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasTetracycline HCL Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Simvastatin Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasSimvastatin Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Theophylline Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasTheophylline Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (5)
- Tramadol HCL Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasTramadol HCL Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Warfarin Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasWarfarin Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (2)
- Warfarin Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasWarfarin Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (2)
- Losartan Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasLosartan Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Humss Diass Module 3-4Documento4 páginasHumss Diass Module 3-4Rojelyn ConturnoAinda não há avaliações
- BmjvudxxzdrtyyhDocumento14 páginasBmjvudxxzdrtyyhsoud aladwani100% (1)
- And Personality Psychology Compass,: Daftar PustakaDocumento7 páginasAnd Personality Psychology Compass,: Daftar PustakadimasAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7Documento11 páginasChapter 7Jehanne Marie, Tiongson JamiroAinda não há avaliações
- Sex Usually Comes To Mind When We Hear The WordsDocumento1 páginaSex Usually Comes To Mind When We Hear The WordsCheryl PetersenAinda não há avaliações
- Saes B 008Documento5 páginasSaes B 008Anonymous a4Jwz14WAinda não há avaliações
- First Aid For Snake BitesDocumento15 páginasFirst Aid For Snake BitesMary Grace OgatisAinda não há avaliações
- 701 W. 51st Street Austin, Texas 78751 Phone-512-438-4800Documento2 páginas701 W. 51st Street Austin, Texas 78751 Phone-512-438-4800api-550348575Ainda não há avaliações
- Module 6 Incentive ProgramDocumento34 páginasModule 6 Incentive ProgramKavin RajAinda não há avaliações
- Metrx PDFDocumento22 páginasMetrx PDFGeomar LaraAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Leadership and Management Practice TestDocumento1 páginaNursing Leadership and Management Practice TestMikhaela GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- The Transradial Approach To Percutaneous Coronary InterventionDocumento9 páginasThe Transradial Approach To Percutaneous Coronary InterventionDeebanshu GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- PNS 293 National Food Control SystemDocumento24 páginasPNS 293 National Food Control SystemSherry SalazarAinda não há avaliações
- Textbook of RehabilitationDocumento7 páginasTextbook of RehabilitationSomesh GadekarAinda não há avaliações
- Bahan Kemas - Selisih SO Vs Sistem FY2020 - 291220Documento17 páginasBahan Kemas - Selisih SO Vs Sistem FY2020 - 291220Idan RidwanAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study - HR - GeneraDocumento6 páginasCase Study - HR - GeneraArianne Araica de VelásquezAinda não há avaliações
- Task 4Documento3 páginasTask 4Muhammad Azam AzmiAinda não há avaliações
- Healthy Parks Healthy PeopleDocumento23 páginasHealthy Parks Healthy PeopleMailey GanAinda não há avaliações
- Wet My Pantys and Have Pulsating OrgasmDocumento1 páginaWet My Pantys and Have Pulsating OrgasmIbrahimovic HelenaAinda não há avaliações
- 3 (NCORT) Guidelines For Resuscitation Training in Ministry of Health Malaysia Hospitals & Healthcare Facilities PDFDocumento66 páginas3 (NCORT) Guidelines For Resuscitation Training in Ministry of Health Malaysia Hospitals & Healthcare Facilities PDFDzarrinAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluación Diagnóstica Inglés - 5 QuintoDocumento6 páginasEvaluación Diagnóstica Inglés - 5 Quintonadia cespedes cruzAinda não há avaliações
- Week 4 DiscussionDocumento1 páginaWeek 4 DiscussionJacob YorgAinda não há avaliações
- Pahang Medical Update 2024Documento3 páginasPahang Medical Update 2024dropzslimmingAinda não há avaliações
- How To Build Muscle On A Raw Food DietDocumento35 páginasHow To Build Muscle On A Raw Food DietTiago Matos100% (2)
- (PHARMACEUTICS-II, 2131) : Diploma in Pharmacy 2Nd Year: E-Learning ContentDocumento2 páginas(PHARMACEUTICS-II, 2131) : Diploma in Pharmacy 2Nd Year: E-Learning Contentkamlesh singhAinda não há avaliações
- Rescue 177 Waiver March 4 2023 1Documento1 páginaRescue 177 Waiver March 4 2023 1Johnjohn MarfalAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial - Sheets - Week 2Documento3 páginasTutorial - Sheets - Week 2kimblendarkwah01Ainda não há avaliações
- Dela Fuente V Dela FuenteDocumento5 páginasDela Fuente V Dela FuenteDominic EstremosAinda não há avaliações
- Legalizing The Use of Euthanasia in The PhilippinesDocumento11 páginasLegalizing The Use of Euthanasia in The PhilippinesGAMEPORIUMAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1Documento89 páginasUnit 1Rudra Sai SandeepAinda não há avaliações
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)No EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Nota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNo EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (404)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsAinda não há avaliações
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNo EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (32)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (42)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDNo EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (3)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNota: 2 de 5 estrelas2/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNo EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (82)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryNo EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (46)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNo EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsNo EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (4)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNo EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (6)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesNo EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (1412)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNo EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.No EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (110)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNo EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsNo EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (170)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisNo EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (8)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessNo EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (328)
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassNo EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (27)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingNo EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1138)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeNo EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (254)