Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Benadryl Drug Study
Enviado por
Cheezy BreadDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Benadryl Drug Study
Enviado por
Cheezy BreadDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Benadryl Drug Study
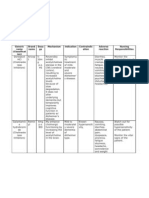
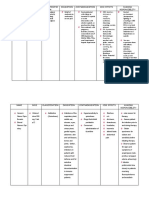
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride
Brand Name: Benadryl, Tusstat
Pregnancy Category B
Drug classes: Antihistamine, Anti-motion sickness agent,
Sedative/hypnotic, Antiparkinsonian agent, Cough suppressant
Therapeutic actions
Competitively blocks the effects of histamine at H1-receptor sites, has
atropine-like, antipruritic, and sedative effects.
Indications
Relief of symptoms associated with perennial and seasonal allergic
rhinitis; vasomotor rhinitis; allergic conjunctivitis; mild,
uncomplicated urticaria and angioedema; amelioration of allergic
reactions to blood or plasma; dermatographism; adjunctive therapy in
anaphylactic reactions
Active and prophylactic treatment of motion sickness
Nighttime sleep aid
Parkinsonism (including drug-induced parkinsonism
and extrapyramidal reactions), in the elderly intolerant of more potent
agents, for milder forms of the disorder in other age groups, and in
combination with centrally acting anticholinergicantiparkinsonian drugs
Suppression of cough due to colds or allergy (syrup formulation)
Contraindications
Contraindicated with allergy to any antihistamines, third trimester of
pregnancy, lactation.
Adverse effects
Drowsiness, sedation, dizziness, disturbed coordination, fatigue, confusion,
restlessness, excitation, nervousness, tremor, headache, blurred
vision, diplopia
Hypotension, palpitations, bradycardia, tachycardia, extrasystoles
Epigastric distress, anorexia, increased appetite and weight gain, nausea,
vomiting, diarrhea or constipation
Urinary frequency, dysuria, urinary retention, early menses, decreased libido,
impotence
Hemolytic anemia, hypoplastic anemia,
thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia
Thickening of bronchial secretions, chest tightness, wheezing, nasal
stuffiness, dry mouth, dry nose, dry throat, sore throat
Urticaria, rash, anaphylactic shock, photosensitivity, excessive
perspiration
Drug Interactions:
Possible increased and prolonged anticholinergic effects with MAO
inhibitors
Nursing considerations
Administer with food if GI upset occurs.
Administer syrup form if patient is unable to take tablets.
Monitor patient response, and arrange for adjustment of dosage to
lowest possible effective dose.
Você também pode gostar
- Theophylline Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasTheophylline Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (5)
- Diphenhydramine HydrochlorideDocumento1 páginaDiphenhydramine Hydrochloridegita24203965100% (1)
- Drug Study TramadolDocumento2 páginasDrug Study TramadolLiana Louisse JoseAinda não há avaliações
- Penicillin Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasPenicillin Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- DiphenhydramineDocumento1 páginaDiphenhydramineYanejoulce SacanleAinda não há avaliações
- Dimenhydrinate PDFDocumento2 páginasDimenhydrinate PDFWindy SengiAinda não há avaliações
- IsoketDocumento2 páginasIsoketJaessa FelicianoAinda não há avaliações
- Losartan Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasLosartan Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Risperidone Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasRisperidone Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Verapamil HCL Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasVerapamil HCL Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Carbidopa-Levodopa (SINEMET CR)Documento1 páginaCarbidopa-Levodopa (SINEMET CR)Amanda CoadAinda não há avaliações
- diphenhydrAMINE (BENADRYL)Documento1 páginadiphenhydrAMINE (BENADRYL)Amanda CoadAinda não há avaliações
- Difflam Drug StudyDocumento1 páginaDifflam Drug StudyDanlee EstandaAinda não há avaliações
- Tetracycline HCL Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasTetracycline HCL Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Diazepam Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasDiazepam Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Ranitidine Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasRanitidine Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- FluticasoneDocumento4 páginasFluticasonevanAinda não há avaliações
- Levetiracetam PDFDocumento3 páginasLevetiracetam PDFShaira TanAinda não há avaliações
- Warfarin Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasWarfarin Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (2)
- Warfarin Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasWarfarin Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (2)
- Simvastatin Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasSimvastatin Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Simvastatin Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasSimvastatin Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Nitroglycerine Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasNitroglycerine Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Name of Drug FinalDocumento7 páginasName of Drug FinalJaessa FelicianoAinda não há avaliações
- Arixtra Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasArixtra Drug StudyEdelweiss Marie Cayetano100% (1)
- Prednisone Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasPrednisone Drug StudyCheezy Bread67% (3)
- Drug Stidy TramadolDocumento2 páginasDrug Stidy TramadolRez ApegoAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Card PropofolDocumento1 páginaDrug Card PropofolBenAinda não há avaliações
- OfloxacinDocumento2 páginasOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- Phenobarbital Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasPhenobarbital Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasDrug StudygayskieAinda não há avaliações
- Phenytoin Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasPhenytoin Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- 4th Rot Drug StudyDocumento3 páginas4th Rot Drug StudyAaron GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasOfloxacin Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasMetoprolol Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaAinda não há avaliações
- DiphenhydramineDocumento10 páginasDiphenhydramineFebry Dian SinagaAinda não há avaliações
- XareltoDocumento2 páginasXareltoMichael Kuzbyt100% (1)
- AeknilDocumento2 páginasAekniljaycey24Ainda não há avaliações
- Generic Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsDocumento2 páginasGeneric Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsAinda não há avaliações
- Propylthiouracil DSDocumento6 páginasPropylthiouracil DSAlexandrea MayAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study 2Documento1 páginaDrug Study 2Blitz KriegAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study EntecavirDocumento4 páginasDrug Study EntecavirClarimae AwingAinda não há avaliações
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol)Documento2 páginasAcetaminophen (Tylenol)amelia hearonAinda não há avaliações
- AMINOPHYLLINEDocumento2 páginasAMINOPHYLLINEmusiclover017100% (1)
- Drug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolDocumento1 páginaDrug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolmikErlh100% (2)
- Drug Study NewDocumento4 páginasDrug Study NewJehannah Dayanara Berdan HayudiniAinda não há avaliações
- ZonisamideDocumento2 páginasZonisamideRo-anne AkuAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing InterventionsDocumento5 páginasDrug Study Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing InterventionsYvonne AgathaAinda não há avaliações
- AmlodipineDocumento2 páginasAmlodipineMika Kudo100% (2)
- Aerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFADocumento3 páginasAerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFAGwyn RosalesAinda não há avaliações
- ALZHEIMER's - Drug Study.Documento2 páginasALZHEIMER's - Drug Study.Christian UretaAinda não há avaliações
- DiphenhydramineDocumento6 páginasDiphenhydramineAndrea BroccoliAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study FORTDocumento3 páginasDrug Study FORTLysa Mae EleazarAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study For MGDocumento1 páginaDrug Study For MGSandra MedinaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - VancomycinDocumento2 páginasDrug Study - VancomycinKhatlen BagaresAinda não há avaliações
- Catapres Clonidine Drug CardDocumento1 páginaCatapres Clonidine Drug CardSheri490Ainda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento6 páginasDrug StudyMa R DyAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocumento2 páginasDrug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NamehahahaAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocumento3 páginasClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsEAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study ICUDocumento5 páginasDrug Study ICUEcko MoawiaAinda não há avaliações
- Tramadol UltramDocumento2 páginasTramadol UltramatchiekAinda não há avaliações
- MetoclopramideDocumento3 páginasMetoclopramideapi-3797941100% (1)
- ChlorpromazineDocumento2 páginasChlorpromazineFay Dominguez100% (1)
- Drug AnalysisDocumento18 páginasDrug AnalysisArt Christian RamosAinda não há avaliações
- IsosorbideDocumento2 páginasIsosorbideSAinda não há avaliações
- Digoxin DrugstudyDocumento1 páginaDigoxin DrugstudyJustine GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasAmlodipine Drug StudyKevin Aliasas100% (3)
- Buspar (Buspirone)Documento1 páginaBuspar (Buspirone)EAinda não há avaliações
- PropranololDocumento6 páginasPropranololanon_678895677Ainda não há avaliações
- New Singulair MontelukastDocumento1 páginaNew Singulair MontelukastCassie100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasDrug StudyAimee GutierrezAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocumento2 páginasDrug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NamehahahaAinda não há avaliações
- Antihistamine and DecongestantDocumento22 páginasAntihistamine and DecongestantAngeline de GalaAinda não há avaliações
- DiphenhydramineDocumento9 páginasDiphenhydramineFhey Bernadette BeltranAinda não há avaliações
- BenaxilDocumento2 páginasBenaxilHavier EsparagueraAinda não há avaliações
- Risperdone and Lithium CarbonateDocumento4 páginasRisperdone and Lithium CarbonateFionah RetuyaAinda não há avaliações
- Nystatin Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasNystatin Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Nifedepine Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasNifedepine Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Benicar Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasBenicar Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Lansoprazole Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasLansoprazole Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Potassium Salts Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasPotassium Salts Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Ramipril Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasRamipril Drug StudyCheezy Bread0% (1)
- Simvastatin Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasSimvastatin Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações
- Tramadol HCL Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasTramadol HCL Drug StudyCheezy BreadAinda não há avaliações