Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Labour Markets Cheat Sheet
Enviado por
jeremythaman0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
403 visualizações2 páginasLabour markets involve individuals seeking employment to earn income interacting with employers seeking workers for production. Many labour markets exist for each industry and occupation. The demand for labour is derived from consumer demand and is affected by factors like a firm's output, productivity, economic conditions, and the cost of capital. The supply of labour is influenced by wages, working conditions, skills/education, mobility, labour force participation rates, and social attitudes. Recent trends in Australia include unemployment stabilizing at 5.7% while underutilization and insecure work have increased, and part-time work is growing while full-time work declines.
Descrição original:
Economics stats 2016
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoLabour markets involve individuals seeking employment to earn income interacting with employers seeking workers for production. Many labour markets exist for each industry and occupation. The demand for labour is derived from consumer demand and is affected by factors like a firm's output, productivity, economic conditions, and the cost of capital. The supply of labour is influenced by wages, working conditions, skills/education, mobility, labour force participation rates, and social attitudes. Recent trends in Australia include unemployment stabilizing at 5.7% while underutilization and insecure work have increased, and part-time work is growing while full-time work declines.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
403 visualizações2 páginasLabour Markets Cheat Sheet
Enviado por
jeremythamanLabour markets involve individuals seeking employment to earn income interacting with employers seeking workers for production. Many labour markets exist for each industry and occupation. The demand for labour is derived from consumer demand and is affected by factors like a firm's output, productivity, economic conditions, and the cost of capital. The supply of labour is influenced by wages, working conditions, skills/education, mobility, labour force participation rates, and social attitudes. Recent trends in Australia include unemployment stabilizing at 5.7% while underutilization and insecure work have increased, and part-time work is growing while full-time work declines.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
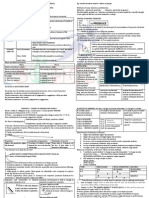
Labour market is a factor market and crucial part of economy, which involves the
interaction between individuals seeking employment to earn income and employers
who want to find workers (with appropriate skill) for production process. Many labour
markets for each industry, firm, occupation in economy. No single; price for labour and
Conditions.
FACTORS EFFECTING DEMAND: Firms demand labour by offering wages; this is
different to product market cause Labour is derived demand. (Based of consumer
needs)
- The output of firms
- Productivity of Labour (economy wide UP 1.4%)(Market Sector UP 2.5%)
(Multifactor UP 0.4%) differ w industryAffects employment (depends on
aggregate demand)(Total Output/Input)
- Economic conditions (aggregate demand)(Reaching Recession)(RBA promote
growth decrease AUD about 74.4 US cents and RBA Lowered interest rate 1.75%)
(Promote economic activity)(Increase derived demand for Labour) e.g realestate
boom
- Cost of Capital RBA I.R (1.75%), encouraging investment in capital goods.
FACTORS EFFECTING SUPPLY:
- Wages
- Working conditions
- Skills and Education
- Mobility of Labour Occupational (end mining boom) Geographical (peak mining
boom) reskilling
- Labour force participation (64.7%) lower than (65.9%) -Portion of the population
that decides to supply its labour (can and willing) workforce/population aged 15
up to 65 * 100.
- state of economy can encourage increase
- Ageing population (GOVT. increase retirement to 70/offer incentives to firms for
keeping elderly workers.)
- Social Attitudes gender empowerment (more women in workforce)
- School retention rates (growing trend for young people to pursue tertiary
education)
- Gillard Govt. increase tax free threshold from 6,000 to 18,000 make people want
to pursue work
WORFORCE: above the age of 15 and actively working or seeking work. = unemployed
+ employed
- Population currently 23.13 million (natural increase + migrants (fill skilled jobs in
low supply)
- Age distribution (ageing population)
- Education patterns (increasingly more people chasing tertiary education)
TRENDS
Unemployment is currently settled at 5.7% and has slightly increased but otherwise
fairly stable decreasing since 6% peak late 2014/ early 2015
Underutilisation rate 14.5% is on increase 16.5% with hidden employment
Casualisation and contracted labour on the increaseCasual (23.9%) Contract (9%)
Insecure work and usually contributes to underutilization
Government investing in industry to increase hours worked and creates employment
opportunities with reskilling as well.
Part-time work is increasing steadily and Full time work fluctuating but downward trend
Firms tend to have an over-capacity of labour
- Labour Market institutionsAustralia becoming more decentralized wage system,
- encourages allocative efficiency:
o Awards are industry specific
o Encourages supply to better industries
- If you are unskilled or skilled in a poor industry then living conditions can
decrease and makes it less practical e.g shut down of manufacturing in Australia
vs boom of minerals
Você também pode gostar
- Multiple Choiice 2nd SemDocumento119 páginasMultiple Choiice 2nd SemMudit RokzzAinda não há avaliações
- 1-2 National IncomeDocumento33 páginas1-2 National IncomeSupratik DattaAinda não há avaliações
- Chap11 12 Extra PDFDocumento8 páginasChap11 12 Extra PDFpuspa khanalAinda não há avaliações
- Economic IndicatorsDocumento2 páginasEconomic IndicatorsShamsiyyaUAinda não há avaliações
- MacroEconomics Written Assignment 2Documento6 páginasMacroEconomics Written Assignment 2Thais HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Macsg12: Aggregate Demand in The Money Goods and Current MarketsDocumento30 páginasMacsg12: Aggregate Demand in The Money Goods and Current MarketsJudithAinda não há avaliações
- 178.200 06-4Documento34 páginas178.200 06-4api-3860979Ainda não há avaliações
- Sri Sharada Institute of Indian Management - Research: "GDP, Unemployment & Inflation of Russia "Documento12 páginasSri Sharada Institute of Indian Management - Research: "GDP, Unemployment & Inflation of Russia "Rahul RanaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Eco561Documento55 páginasChapter 2 Eco561norshaheeraAinda não há avaliações
- EC101 Revision Questions - Graphical Analysis - SolutionsDocumento10 páginasEC101 Revision Questions - Graphical Analysis - SolutionsZaffia AliAinda não há avaliações
- Aggregate Demand-Supply Practice WorksheetDocumento1 páginaAggregate Demand-Supply Practice WorksheetRoberto Velasco MabulacAinda não há avaliações
- HRM Final Cheat Sheet (All)Documento3 páginasHRM Final Cheat Sheet (All)Jeffery KaoAinda não há avaliações
- Inflation, Activity, and Nominal Money Growth: Prepared By: Fernando Quijano and Yvonn QuijanoDocumento31 páginasInflation, Activity, and Nominal Money Growth: Prepared By: Fernando Quijano and Yvonn QuijanoRizki Praba NugrahaAinda não há avaliações
- The Difference Between Solow and HarrodDocumento14 páginasThe Difference Between Solow and HarrodbrenAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 8 Review Questions With AnswersDocumento9 páginasChapter 8 Review Questions With AnswersDiamante Gomez0% (1)
- Chapter 2 Macro SolutionDocumento11 páginasChapter 2 Macro Solutionsaurabhsaurs100% (1)
- Economics For Ca-Cpt - Quick Revision VersionDocumento14 páginasEconomics For Ca-Cpt - Quick Revision VersionCA Suman Gadamsetti75% (4)
- Research Proposal PDFDocumento36 páginasResearch Proposal PDFHassan MaganAinda não há avaliações
- Class 2 Measuring Macro Variables - GDP and InflationDocumento66 páginasClass 2 Measuring Macro Variables - GDP and InflationKaia LorenzoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Macro SolutionDocumento14 páginasChapter 2 Macro Solutionsaurabhsaurs100% (1)
- The IS-LM Model: Equilibrium: Goods and Money Markets Understanding Public PolicyDocumento37 páginasThe IS-LM Model: Equilibrium: Goods and Money Markets Understanding Public PolicyShashank Shekhar SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5Documento79 páginasChapter 5Nokulunga ManyangaAinda não há avaliações
- Kaldor Model - Group 3Documento12 páginasKaldor Model - Group 3Dairy Of PeaceAinda não há avaliações
- Question Paper PDFDocumento17 páginasQuestion Paper PDFSaianish KommuchikkalaAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 1 Nature of Regression AnalysisDocumento26 páginasChap 1 Nature of Regression AnalysisSamina AhmeddinAinda não há avaliações
- 5f461726 7d5c 42411c 96d2 75d219e1d8aaDocumento15 páginas5f461726 7d5c 42411c 96d2 75d219e1d8aaMuhammed EmbabyAinda não há avaliações
- Argument Analysis ExampleDocumento4 páginasArgument Analysis ExampleJ VAinda não há avaliações
- International Economics: Foreign Exchange Markets and Exchange RatesDocumento50 páginasInternational Economics: Foreign Exchange Markets and Exchange RatesMa Shareen Joy SaleAinda não há avaliações
- Types of UnemploymentDocumento22 páginasTypes of UnemploymentKusantha Rohan WickremasingheAinda não há avaliações
- Inflation Causes and Effects RevisionDocumento26 páginasInflation Causes and Effects RevisionData AnalystAinda não há avaliações
- Economic IDocumento24 páginasEconomic ICarlo Widjaja100% (1)
- Imsb T6Documento5 páginasImsb T6Lyc Chun100% (2)
- Unit 11 - Lesson 1 - Economic GrowthDocumento12 páginasUnit 11 - Lesson 1 - Economic Growthapi-260512563Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Macro SolutionDocumento11 páginasChapter 2 Macro Solutionsaurabhsaurs100% (1)
- Tutorial Set 7 - SolutionsDocumento5 páginasTutorial Set 7 - SolutionsChan Chun YeenAinda não há avaliações
- Econ 112: Review For Final ExamDocumento9 páginasEcon 112: Review For Final ExamOmar RaoufAinda não há avaliações
- End Term MEP 16 With AnswersDocumento9 páginasEnd Term MEP 16 With AnswersVimal AnbalaganAinda não há avaliações
- Instructions: Students May Work in Groups On The Problem Set. Each Student Must Turn in His/her OWNDocumento16 páginasInstructions: Students May Work in Groups On The Problem Set. Each Student Must Turn in His/her OWNHamna AzeezAinda não há avaliações
- Namma Kalvi Economics Unit 4 Surya Economics Guide emDocumento34 páginasNamma Kalvi Economics Unit 4 Surya Economics Guide emAakaash C.K.Ainda não há avaliações
- Impacts of Capital Control by Malaysian Government During 1997 Asian Financial Crisis On Malaysian Corporate SectorsDocumento4 páginasImpacts of Capital Control by Malaysian Government During 1997 Asian Financial Crisis On Malaysian Corporate SectorsCherylynne EddyAinda não há avaliações
- Consumption FunctionDocumento39 páginasConsumption FunctionAnku SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Advance Heterodox Economics - Lectures On ProductionDocumento9 páginasAdvance Heterodox Economics - Lectures On Productionoscrend39Ainda não há avaliações
- Classical Macroecon and Keynesian AggregateDocumento23 páginasClassical Macroecon and Keynesian Aggregatessregens820% (1)
- Macsg09: The Government and Fiscal PolicyDocumento24 páginasMacsg09: The Government and Fiscal PolicyJudith100% (1)
- Consumption & Saving FunctionDocumento31 páginasConsumption & Saving FunctionAshish Singh100% (1)
- Autocorrelation: What Happens If The Error Terms Are Correlated?Documento18 páginasAutocorrelation: What Happens If The Error Terms Are Correlated?Nusrat Jahan MoonAinda não há avaliações
- Mec 101 (E)Documento20 páginasMec 101 (E)Aslam BohemiaAinda não há avaliações
- Mankiw Chapter 5 Open Economy InvestmentDocumento59 páginasMankiw Chapter 5 Open Economy InvestmentYusi PramandariAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter-4 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyDocumento55 páginasChapter-4 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supplycarl jaffersonAinda não há avaliações
- Measuring A Nation'S Income: Questions For ReviewDocumento4 páginasMeasuring A Nation'S Income: Questions For ReviewNoman MustafaAinda não há avaliações
- Trade Policy in Developing CountriesDocumento14 páginasTrade Policy in Developing CountriesFarhan NoorAinda não há avaliações
- Theory of Production 1 0Documento22 páginasTheory of Production 1 0Suthan Dinho సుతాన్ దళినైడుAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 01Documento29 páginasChap 01mnadiriAinda não há avaliações
- Macroeconomics Final Exam NotesDocumento24 páginasMacroeconomics Final Exam NotesThomas Bryant100% (1)
- Did United Technologies Overpay For Rockwell CollinsDocumento2 páginasDid United Technologies Overpay For Rockwell CollinsRadAinda não há avaliações
- Public EconomicsDocumento11 páginasPublic EconomicsAzvemberAinda não há avaliações
- Employment and UnemploymentDocumento40 páginasEmployment and Unemploymentandrew.collananAinda não há avaliações
- SDKLJKWLN K WDocumento32 páginasSDKLJKWLN K WDeepak R GoradAinda não há avaliações
- The Labour Market Demand and SupplyDocumento29 páginasThe Labour Market Demand and SupplyNafis SiddiquiAinda não há avaliações
- Unemployment:: The Labour Force Is Defined As The Number of People Employed Plus The Number Unemployed But SeekingDocumento8 páginasUnemployment:: The Labour Force Is Defined As The Number of People Employed Plus The Number Unemployed But SeekingsczameeAinda não há avaliações
- Assess The Effectiveness of Fiscal Policy On Distribution of Income and WealthDocumento4 páginasAssess The Effectiveness of Fiscal Policy On Distribution of Income and WealthjeremythamanAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 3 NotesDocumento7 páginasTopic 3 NotesjeremythamanAinda não há avaliações
- Jock Palfreeman Essay NotesDocumento3 páginasJock Palfreeman Essay NotesjeremythamanAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Markets EconomisDocumento5 páginasFinancial Markets EconomispoAinda não há avaliações
- Related Text WorksheetDocumento3 páginasRelated Text WorksheetjeremythamanAinda não há avaliações
- Jock PalfreemanDocumento2 páginasJock PalfreemanjeremythamanAinda não há avaliações
- AS MacroDocumento61 páginasAS MacroAhmed AliAinda não há avaliações
- Full Download Ebook Ebook PDF Macroeconomics Australia in The Global Environment 1st Australia PDFDocumento42 páginasFull Download Ebook Ebook PDF Macroeconomics Australia in The Global Environment 1st Australia PDFshiela.martinez137100% (42)
- Damodaram Sanjivayya National Law University Visakhapatnam, A.P., IndiaDocumento32 páginasDamodaram Sanjivayya National Law University Visakhapatnam, A.P., IndiaKaushik NanduriAinda não há avaliações
- NCERT-class 12-Eco-Summary (Part 2) PDFDocumento26 páginasNCERT-class 12-Eco-Summary (Part 2) PDFrahul pawarAinda não há avaliações
- AS Economics Revision NotesDocumento16 páginasAS Economics Revision NotesAlexandru Huțu100% (1)
- ECO 372 Final Exam GuideDocumento15 páginasECO 372 Final Exam GuideECO 372 Week 5 Final ExaminationAinda não há avaliações
- Ebook Economics 11Th Edition Arnold Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocumento36 páginasEbook Economics 11Th Edition Arnold Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFkhondvarletrycth100% (11)
- 111 Struct1Documento8 páginas111 Struct1Tamar LaliashviliAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 4 Open Economy MacroeconomicsDocumento36 páginasChap 4 Open Economy MacroeconomicsDương Quốc TuấnAinda não há avaliações
- Subject CT7 - Economics: Institute of Actuaries of IndiaDocumento7 páginasSubject CT7 - Economics: Institute of Actuaries of IndiaSomya AgrawalAinda não há avaliações
- Most Important Question - 18504280 - 2023 - 05 - 04 - 23 - 39Documento20 páginasMost Important Question - 18504280 - 2023 - 05 - 04 - 23 - 39TanishkaAinda não há avaliações
- Is LM PDFDocumento9 páginasIs LM PDFShivam SoniAinda não há avaliações
- Full Download Ebook Ebook PDF Macroeconomics Global Edition 13th Edition PDFDocumento41 páginasFull Download Ebook Ebook PDF Macroeconomics Global Edition 13th Edition PDFcarol.martinez79498% (41)
- Recessionary and Inflationary GapsDocumento7 páginasRecessionary and Inflationary GapsKasili MasilikaniAinda não há avaliações
- Macro Tutor2u BDocumento20 páginasMacro Tutor2u BdAinda não há avaliações
- General Measurement Aptitude TestDocumento207 páginasGeneral Measurement Aptitude TestEDUCATED MIND100% (1)
- macroeconfIChapter 9Documento14 páginasmacroeconfIChapter 9meghapraveen82% (11)
- CH 28Documento35 páginasCH 28bus242Ainda não há avaliações
- Examen Ener 2016 (Ing) ADocumento4 páginasExamen Ener 2016 (Ing) AManuel GranadosAinda não há avaliações
- Macroeconomics - Definition, Scope and OthersDocumento9 páginasMacroeconomics - Definition, Scope and OthersNishtha BansalAinda não há avaliações
- Summary of Monetary Policy in AlgeriaDocumento3 páginasSummary of Monetary Policy in AlgerialaykaireAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 15: Monetary Policy: I. The Money MarketDocumento4 páginasChapter 15: Monetary Policy: I. The Money MarketVanu VanujanAinda não há avaliações
- The Short-Run Tradeoff Between Inflation and UnemploymentDocumento29 páginasThe Short-Run Tradeoff Between Inflation and UnemploymentWening RestiyaniAinda não há avaliações
- Parkin 8e TIF Ch26Documento40 páginasParkin 8e TIF Ch26Pranta SahaAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 3 Review Practice Set (Modules 16-21)Documento9 páginasUnit 3 Review Practice Set (Modules 16-21)Samuel JayAinda não há avaliações
- Inflation: Definitions, Kinds, and Causes of InflationDocumento5 páginasInflation: Definitions, Kinds, and Causes of InflationAbnmsAinda não há avaliações
- Wage-Led Growth: An Equitable Strategy For Economic RecoveryDocumento51 páginasWage-Led Growth: An Equitable Strategy For Economic RecoveryAAinda não há avaliações
- ZICA T5 - TaxationDocumento521 páginasZICA T5 - TaxationMongu Rice95% (42)
- Microeconomics and KeynesDocumento248 páginasMicroeconomics and KeynesSudeep Mirza100% (16)
- Aggregate Demand & Aggregate SupplyDocumento41 páginasAggregate Demand & Aggregate SupplyAlison FernandesAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassNo EverandFinancial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassAinda não há avaliações
- A History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationNo EverandA History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (11)
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumNo EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (12)
- Look Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereNo EverandLook Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (3)
- The War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesNo EverandThe War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (8)
- Narrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsNo EverandNarrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (94)
- The New Elite: Inside the Minds of the Truly WealthyNo EverandThe New Elite: Inside the Minds of the Truly WealthyNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (10)
- The Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaNo EverandThe Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaAinda não há avaliações
- When Helping Hurts: How to Alleviate Poverty Without Hurting the Poor . . . and YourselfNo EverandWhen Helping Hurts: How to Alleviate Poverty Without Hurting the Poor . . . and YourselfNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (36)
- High-Risers: Cabrini-Green and the Fate of American Public HousingNo EverandHigh-Risers: Cabrini-Green and the Fate of American Public HousingAinda não há avaliações
- The Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetNo EverandThe Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetAinda não há avaliações
- Workin' Our Way Home: The Incredible True Story of a Homeless Ex-Con and a Grieving Millionaire Thrown Together to Save Each OtherNo EverandWorkin' Our Way Home: The Incredible True Story of a Homeless Ex-Con and a Grieving Millionaire Thrown Together to Save Each OtherAinda não há avaliações
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyNo EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (227)
- Principles for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailNo EverandPrinciples for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (237)
- The Meth Lunches: Food and Longing in an American CityNo EverandThe Meth Lunches: Food and Longing in an American CityNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (5)
- Nudge: The Final Edition: Improving Decisions About Money, Health, And The EnvironmentNo EverandNudge: The Final Edition: Improving Decisions About Money, Health, And The EnvironmentNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (92)
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationNo EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (46)
- University of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingNo EverandUniversity of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (97)
- Doughnut Economics: Seven Ways to Think Like a 21st-Century EconomistNo EverandDoughnut Economics: Seven Ways to Think Like a 21st-Century EconomistNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (37)