Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
CVA
Enviado por
nursing concept mapsDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CVA
Enviado por
nursing concept mapsDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
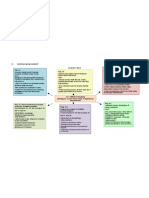
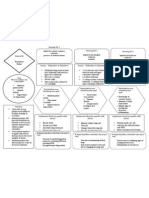
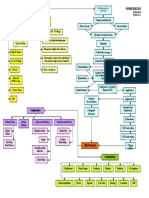
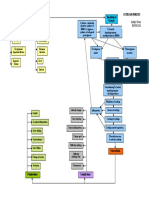
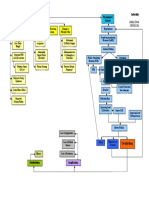
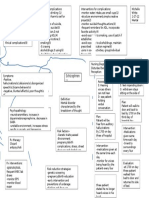
CEREBROVASCULAR
ACCIDENT (CVA)
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY PREVENTION
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
CAUSES
d by gradual, rapid onset of neurologic deficits due to compromised cerebral blood flow Stop smoking
RISK FACTORS
ASSESSMENT
Thrombosis Maintaining a healthy weight
CLINICAL MANIFESTATION CT Scan
Embolism
ow and oxygenation of cerebral neurons or interrupted; changes occur in 4-5 min. Hypertension Signs and symptoms of ICP
Hemorrhage Arteriography Following a healthy diet
Diabetes Mellitus
Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIA) Weakness of the face, arm, leg, especially on one side of the body defects
Perceptual MRI
Atherosclerosis Exercise Daily
blood vessels swell which blood flow; vasospasm and blood viscosity further impede blood flow
Aphasia Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
Substance Abuse
Obesity, sedentary lifestyle, heart disease, previous transientTrouble
ischemicspeaking
attacks Hemianopsia
Single-photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT)
s a central core of dead and dying cells surrounded by band of minimally perfused cells Confusion
Visual disturbance
Women: oral contraceptive use, pregnancy, menopause
Loss of balance and coordination
c deficits occur on opposite side where stroke occurred in brain: contralateral deficit
Sudden severe headache
Motor, sensory, cranial nerve, cognitive and other functions may be disrupted
Christine Marie S. Barce
BSN-3A
Você também pode gostar
- Bipolar Concept MapDocumento3 páginasBipolar Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (2)
- Emphysema Pathophysiology ExplainedDocumento1 páginaEmphysema Pathophysiology ExplainedGil AswiguiAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Map TemplateDocumento1 páginaConcept Map Templatenursing concept mapsAinda não há avaliações
- Hip FractureDocumento3 páginasHip Fracturenursing concept mapsAinda não há avaliações
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure OverviewDocumento7 páginasPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure Overviewnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Concept Map BlankDocumento2 páginasConcept Map Blanknursing concept mapsAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnostics: Disorder & Basic Patho/Etiology: Clinical ManifestationsDocumento1 páginaDiagnostics: Disorder & Basic Patho/Etiology: Clinical Manifestationsnursing concept mapsAinda não há avaliações
- Physiological ChangesDocumento1 páginaPhysiological ChangesJilian McGuganAinda não há avaliações
- Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation BAIAE Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocumento3 páginasBronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation BAIAE Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramVictor Angelo VeraAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramDocumento1 páginaDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramJhe Lyn82% (11)
- Mental Health Concept MapDocumento2 páginasMental Health Concept Mapnursing concept mapsAinda não há avaliações
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus PathophsyiologyDocumento3 páginasPatent Ductus Arteriosus Pathophsyiologynursing concept mapsAinda não há avaliações
- Pituitary Adenoma Concept MapDocumento1 páginaPituitary Adenoma Concept Mapnursing concept mapsAinda não há avaliações
- ESRD PathophysiologyDocumento2 páginasESRD Pathophysiologynursing concept mapsAinda não há avaliações
- PATHODocumento2 páginasPATHOmycoclitAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Management Concept MapDocumento1 páginaNursing Management Concept MapXy-Za Roy Marie100% (1)
- Sleep Apnea Concept MapDocumento1 páginaSleep Apnea Concept Mapashleydean100% (2)
- Critical Care Concept MapDocumento1 páginaCritical Care Concept Mapkonniep69100% (1)
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocumento3 páginasAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsAinda não há avaliações
- Bipolar Disorder Concept MapDocumento1 páginaBipolar Disorder Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Schizophrenia MapDocumento1 páginaSchizophrenia Mapnursing concept mapsAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Burn InjuryDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology of Burn InjuryAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (1)
- Pathophysio CRF2 - RevisedDocumento1 páginaPathophysio CRF2 - Reviseddeborah malnegroAinda não há avaliações
- Degenerative Disc Disease Concept MapDocumento1 páginaDegenerative Disc Disease Concept Mapnursing concept mapsAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of BREAST CANCERDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology of BREAST CANCERAlinor Abubacar100% (6)
- Hypertension Concept MapDocumento1 páginaHypertension Concept Mapashleydean100% (7)
- ARF PathophysiologyDocumento2 páginasARF Pathophysiologykathy100% (9)
- Osteoarthritis Concept MapDocumento1 páginaOsteoarthritis Concept Mapnursing concept maps0% (1)
- Infertility Concept MapDocumento1 páginaInfertility Concept Mapnursing concept maps50% (2)
- Concept MapDocumento1 páginaConcept Mapnursing concept mapsAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Sean Barnett-Nurs362resumeDocumento2 páginasSean Barnett-Nurs362resumeapi-252467227Ainda não há avaliações
- GVP Annex V AbbreviationsDocumento5 páginasGVP Annex V AbbreviationsSilvia PeroniAinda não há avaliações
- Nres1dm-Chapter I and IIDocumento35 páginasNres1dm-Chapter I and IImlmmandapAinda não há avaliações
- "GIANT CELL TUMOR": CASE PRESENTATION - at Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh.Documento37 páginas"GIANT CELL TUMOR": CASE PRESENTATION - at Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh.Dr. Mohammad Nazrul IslamAinda não há avaliações
- Cervical CancerDocumento5 páginasCervical Cancerjinoop100% (1)
- Common TestsDocumento8 páginasCommon Testsapi-84383303Ainda não há avaliações
- Risks of Elective Cesarean SectionDocumento11 páginasRisks of Elective Cesarean SectionLutfiAnny Rahman HakimAinda não há avaliações
- VenesectionDocumento2 páginasVenesectionMorounshayo OshodiAinda não há avaliações
- QuizzesDocumento6 páginasQuizzesJafinAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of Management of Poisoned Patient: 09/09/1440 DR Abdelmonem G. Madboly 1Documento19 páginasPrinciples of Management of Poisoned Patient: 09/09/1440 DR Abdelmonem G. Madboly 1JyotiAinda não há avaliações
- AAOS Abstracts GuidelinesDocumento6 páginasAAOS Abstracts GuidelinesNuno PaisAinda não há avaliações
- Kimberly Mcneil ResumeDocumento3 páginasKimberly Mcneil ResumeKim Floyd McneilAinda não há avaliações
- Annotated Bibliography FormatDocumento2 páginasAnnotated Bibliography FormatJohn TerryAinda não há avaliações
- Annotated BibliographyDocumento4 páginasAnnotated Bibliographyapi-317390500Ainda não há avaliações
- NCP For Laryngeal CancerDocumento5 páginasNCP For Laryngeal CancerMădălina PinciucAinda não há avaliações
- Appstat PDFDocumento197 páginasAppstat PDFrfactor0976Ainda não há avaliações
- Dermato CHDocumento10 páginasDermato CHSuthan KaveriAinda não há avaliações
- Ex Harvard Medical School Personal Statement ExampleDocumento3 páginasEx Harvard Medical School Personal Statement ExamplekikyAinda não há avaliações
- Ventilation Mini ManualDocumento44 páginasVentilation Mini ManualKhusnul DwinitaAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Cardio Physiotherapy 1Documento318 páginasLecture Cardio Physiotherapy 1Nurse GhanemAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetes PharmacologyDocumento14 páginasDiabetes PharmacologyRich JeongAinda não há avaliações
- Tracheostomy Care GuideDocumento4 páginasTracheostomy Care GuideSuchismita SethiAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Nursing Manual PDFDocumento93 páginasClinical Nursing Manual PDFVatau FlorinAinda não há avaliações
- Common HCC Codes and Diabetes Manifestations SheetDocumento2 páginasCommon HCC Codes and Diabetes Manifestations SheetmeikaizenAinda não há avaliações
- Qip Project 1Documento13 páginasQip Project 1api-508609843Ainda não há avaliações
- Bio StatisticsDocumento21 páginasBio StatisticsanaeshklAinda não há avaliações
- Person of Interest S02E07 720p Bluray demaNDDocumento48 páginasPerson of Interest S02E07 720p Bluray demaNDJack CooperAinda não há avaliações
- GlaukomaDocumento41 páginasGlaukomadanufarandiAinda não há avaliações
- Pregnancy Terms ExplainedDocumento4 páginasPregnancy Terms Explainedعبدالرحمن الزيودAinda não há avaliações
- Journal Club: Dr. Shereen S. LucmanDocumento36 páginasJournal Club: Dr. Shereen S. LucmanShereen DS LucmanAinda não há avaliações