Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Assessment Algorithm: Is Patient at Risk For CKD?
Enviado por
Sirsefti Anggi0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
201 visualizações1 páginaThis document outlines an algorithm for identifying and referring patients at risk for chronic kidney disease (CKD). It involves assessing patients for CKD risk factors, evaluating kidney function through estimated GFR and urine tests, and referring patients to different levels of care depending on the severity of any abnormalities found. The goal is to detect CKD early and provide education to help preserve kidney function.
Descrição original:
farmakoterapi ginjal
Título original
ALGORITMA GINJAL
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThis document outlines an algorithm for identifying and referring patients at risk for chronic kidney disease (CKD). It involves assessing patients for CKD risk factors, evaluating kidney function through estimated GFR and urine tests, and referring patients to different levels of care depending on the severity of any abnormalities found. The goal is to detect CKD early and provide education to help preserve kidney function.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
201 visualizações1 páginaChronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Assessment Algorithm: Is Patient at Risk For CKD?
Enviado por
Sirsefti AnggiThis document outlines an algorithm for identifying and referring patients at risk for chronic kidney disease (CKD). It involves assessing patients for CKD risk factors, evaluating kidney function through estimated GFR and urine tests, and referring patients to different levels of care depending on the severity of any abnormalities found. The goal is to detect CKD early and provide education to help preserve kidney function.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
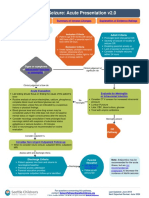
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Assessment Algorithm
Identification and Referral
Emergency
Room
Visit
Is patient at risk for CKD?
Age > 60 years Exposure to drugs/contrast Systemic infections Family history of CKD
High blood pressure Urinary tract infection Drug toxicity Autoimmune diseases
Urinary stones Lower urinary tract obstruction Diabetes Hx acute renal failure
Yes
Evaluate patients at increased risk for CKD
Consider:
-Serum creatinine to determine estimated eGFR
-Assessment of proteinuria
-Urinalysis for presence of white & red blood cells
Does patient have abnormal eGFR?
http://www.kidney.org/professionals/kdoqi/gfr_calculator.cfm
Yes
Is eGFR 45 60? Is eGFR < 45?
Refer patient to primary
Refer patient to
care physician or internist
nephrologist for follow-up
for follow-up
Provide Patient Education on Preserving Kidney Function
Avoid all NSAIDS
Avoid Milk of Magnesia
Avoid oral & enema sodium phosphate products
Avoid needle punctures and blood pressures in non-dominant arm
Avoid subclavian central lines
Avoid gladolinium-based contrast if eGFR < 30 or acute kidney injury
CAUTIOUS USE OF IV/MRI CONTRAST DYECONSULT NEPHROLOGY
The Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (KDOQI)
Prepared by the Renal Network of the Upper Midwest, Inc.
recommendations for Chronic Kidney Disease: Evaluation,
Please call 1-800-973-3773 for questions or reprint
Classification, and Stratification were used to develop
requests.
portions of this document.
Você também pode gostar
- Aitc 1506 Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocumento32 páginasAitc 1506 Chronic Kidney DiseaseDhenokAinda não há avaliações
- RetrieveDocumento6 páginasRetrieveSillieteAinda não há avaliações
- 02-50-4079 ABB ManagingTransRecipBk PC PDFDocumento12 páginas02-50-4079 ABB ManagingTransRecipBk PC PDFjulma1306Ainda não há avaliações
- Best Practices in Renal Dosing: Bruce A. Mueller, PharmdDocumento47 páginasBest Practices in Renal Dosing: Bruce A. Mueller, PharmdRuqayya AdamuAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Kidney Injury Review 2017Documento20 páginasAcute Kidney Injury Review 2017Eduardo MoraesAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacotherapy in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients Presenting With Acute Coronary SyndromeDocumento27 páginasPharmacotherapy in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients Presenting With Acute Coronary SyndromeaudiAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal Dr. Tri Hadi-29 Des 2021Documento17 páginasJurnal Dr. Tri Hadi-29 Des 2021aldyAinda não há avaliações
- Living Donor Kidney Transplantation - Jonathon Oldsburgh - UOM 21.8.19Documento106 páginasLiving Donor Kidney Transplantation - Jonathon Oldsburgh - UOM 21.8.19Renal Association MauritiusAinda não há avaliações
- AKI Child W NS 2018Documento4 páginasAKI Child W NS 2018Indah Nur LathifahAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Kidney Injury Prevention & Early Detection With Novel BiomarkersDocumento37 páginasAcute Kidney Injury Prevention & Early Detection With Novel Biomarkerssapphire_asaphAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Kidney Injury: Current Concepts and New Insights: Key WordsDocumento5 páginasAcute Kidney Injury: Current Concepts and New Insights: Key WordsIHAinda não há avaliações
- Aki AcpDocumento21 páginasAki AcpAndrés FelipeAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnostic Approach To Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocumento3 páginasDiagnostic Approach To Chronic Kidney DiseaseBlomblom Pow00Ainda não há avaliações
- Primary Care Approach To Management of CKD: February 2018Documento15 páginasPrimary Care Approach To Management of CKD: February 2018AbedDabajaAinda não há avaliações
- ADPKDDocumento22 páginasADPKDAbira KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Neurological Complications of CKDDocumento10 páginasNeurological Complications of CKDHalim Muhammad SatriaAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetic Conference 2 (1) RenalDocumento20 páginasDiabetic Conference 2 (1) RenalWarren DonaldsonAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic Kidney Disease Bhakti MuliaDocumento24 páginasChronic Kidney Disease Bhakti MuliaCOVID RSHJAinda não há avaliações
- An Overview of CKD ProfessionalsDocumento15 páginasAn Overview of CKD ProfessionalsabhigyanAinda não há avaliações
- Aki in Heart PatientDocumento12 páginasAki in Heart PatientVivek GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Aca 19 225Documento6 páginasAca 19 225M Ali AdrianAinda não há avaliações
- Albumin:Creatinine Ratio (Urine) - ACR: Description Indication Why Measure ACR?Documento2 páginasAlbumin:Creatinine Ratio (Urine) - ACR: Description Indication Why Measure ACR?Ebtisam alfakhriAinda não há avaliações
- SUPER - Recom - Vaccin-ESRD-AJKD-2019Documento9 páginasSUPER - Recom - Vaccin-ESRD-AJKD-2019Ioana PanculescuAinda não há avaliações
- RG 220116Documento20 páginasRG 220116Yo MeAinda não há avaliações
- The Challenge of Kidney Damage During Interventional Cardiology ProceduresDocumento6 páginasThe Challenge of Kidney Damage During Interventional Cardiology ProceduresIJAR JOURNALAinda não há avaliações
- AKI Perioperatif 3Documento6 páginasAKI Perioperatif 3Kevin JohanesAinda não há avaliações
- 00014Documento9 páginas00014Gardênia GurgelAinda não há avaliações
- Falla Renal en UCI Chest-2012Documento13 páginasFalla Renal en UCI Chest-2012Alexander CasillaAinda não há avaliações
- Serum Uric Acid To Albumin Ratio Can Predict Contrast-Induced Nephropathy in ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Patients Undergoing Primary Percutaneous Coronary inDocumento9 páginasSerum Uric Acid To Albumin Ratio Can Predict Contrast-Induced Nephropathy in ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Patients Undergoing Primary Percutaneous Coronary intinatobingAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S0085253822009085 MainDocumento10 páginas1 s2.0 S0085253822009085 MainRezky Faried HidayatullahAinda não há avaliações
- Risk Factors For Heart Failure in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease: The CRIC (Chronic Renal Insuf Ficiency Cohort) StudyDocumento10 páginasRisk Factors For Heart Failure in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease: The CRIC (Chronic Renal Insuf Ficiency Cohort) StudyMarilia Cruz PoloAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Pericarditis: Clinical PracticeDocumento8 páginasAcute Pericarditis: Clinical PracticeGaby Alejandra Ordonez AndradeAinda não há avaliações
- Feline Acute Kidney Injury. 2. Approach To Diagnosis, Treatment and PrognosisDocumento9 páginasFeline Acute Kidney Injury. 2. Approach To Diagnosis, Treatment and PrognosisMartín QuirogaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesion Renal Aguda y SX Hepatorrenal en Cirrosis NEJM 2023-1-5Documento5 páginasLesion Renal Aguda y SX Hepatorrenal en Cirrosis NEJM 2023-1-5marss06cvAinda não há avaliações
- Jcem 3266Documento16 páginasJcem 3266dasdAinda não há avaliações
- Should All Patients Have A Resting 12-Lead ECG Before Elective Noncardiac SurgeryDocumento3 páginasShould All Patients Have A Resting 12-Lead ECG Before Elective Noncardiac Surgerytsiko111Ainda não há avaliações
- Jurnal ANCADocumento22 páginasJurnal ANCAMuthia FaurinAinda não há avaliações
- Cirrhosis and Elective Non-Hepatic Surgery 2023Documento12 páginasCirrhosis and Elective Non-Hepatic Surgery 2023ctsakalakisAinda não há avaliações
- Febrile Seizures PathwayDocumento10 páginasFebrile Seizures PathwayFerry Abu Irsyad AtthaillahAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocumento10 páginasAcute Kidney InjuryMaya_AnggrainiKAinda não há avaliações
- Acute On Chronic Liver Failure: Ulva Yogia GuslafDocumento19 páginasAcute On Chronic Liver Failure: Ulva Yogia GuslafSyahrul AdzimAinda não há avaliações
- Viteri2018 Prevalensi 5Documento17 páginasViteri2018 Prevalensi 5adrian revoAinda não há avaliações
- Boala Cronica de Rinichi Adrian CovicDocumento85 páginasBoala Cronica de Rinichi Adrian CovicLorenaAinda não há avaliações
- Onconephrology Core Curriculum 2023Documento19 páginasOnconephrology Core Curriculum 2023jogutiro01Ainda não há avaliações
- Inequity of Access To Investigation and Effect On Clinical Outcomes: Prognostic Study of Coronary Angiography For Suspected Stable Angina PectorisDocumento7 páginasInequity of Access To Investigation and Effect On Clinical Outcomes: Prognostic Study of Coronary Angiography For Suspected Stable Angina PectorisAna LemesAinda não há avaliações
- VN 132 Study Guide FinalDocumento2 páginasVN 132 Study Guide FinalLupita SolorzanoAinda não há avaliações
- GatroDocumento48 páginasGatronainggolan Debora15Ainda não há avaliações
- PReVerse Nefropatia Por ContrasteDocumento13 páginasPReVerse Nefropatia Por ContrasteRaziel CamachoAinda não há avaliações
- 1406b1f8cc PDFDocumento1 página1406b1f8cc PDFAs RifahAinda não há avaliações
- CKD Full GuidelineDocumento11 páginasCKD Full Guidelinenaty77777Ainda não há avaliações
- Practice Guidelines: Diagnosis of Stable Ischemic Heart Disease: Recommendations From The ACPDocumento2 páginasPractice Guidelines: Diagnosis of Stable Ischemic Heart Disease: Recommendations From The ACPicarosalernoAinda não há avaliações
- 2022 NEJM Uses of GFR and Albuminuria LevelDocumento9 páginas2022 NEJM Uses of GFR and Albuminuria LevelPeter Albeiro Falla CortesAinda não há avaliações
- Contrast Induced Nephropathy in Cardiac Patients: Update On Prevention and TreatmentDocumento60 páginasContrast Induced Nephropathy in Cardiac Patients: Update On Prevention and TreatmentZorica DAinda não há avaliações
- Polyarteritis NodosaDocumento6 páginasPolyarteritis NodosaEkaAinda não há avaliações
- Study of Clinical Profile of Patient With Acute Kidney DiseaseDocumento7 páginasStudy of Clinical Profile of Patient With Acute Kidney DiseaseIJAR JOURNALAinda não há avaliações
- DRC e USO de ESTATINASDocumento2 páginasDRC e USO de ESTATINASdramorimcostaAinda não há avaliações
- Manajemen PVCDocumento11 páginasManajemen PVCHarie CiptaAinda não há avaliações
- Alogaritma CKDDocumento2 páginasAlogaritma CKDChairunnisa SiamAinda não há avaliações
- Statin in CKDDocumento10 páginasStatin in CKDKartika RahmawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Pediatric Liver Intensive CareNo EverandPediatric Liver Intensive CareNaresh ShanmugamAinda não há avaliações
- 18 Dec SLSDocumento16 páginas18 Dec SLSSirsefti AnggiAinda não há avaliações
- Stok 26032022Documento26 páginasStok 26032022Sirsefti AnggiAinda não há avaliações
- Spreiying of AnimalDocumento3 páginasSpreiying of AnimalSirsefti AnggiAinda não há avaliações
- November 2017: Senin Selasa Rabu Kamis Jum'At SabtuDocumento11 páginasNovember 2017: Senin Selasa Rabu Kamis Jum'At SabtuSirsefti AnggiAinda não há avaliações
- CH 04Documento80 páginasCH 04flock_duxAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory SyncytialDocumento32 páginasRespiratory Syncytialtummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (1)
- Clinical Bacteriology by DR Agwu EzeraDocumento116 páginasClinical Bacteriology by DR Agwu EzeraRodgers Bazigu100% (1)
- Contoh Naskah Pidato Bahasa Inggris SingkatDocumento4 páginasContoh Naskah Pidato Bahasa Inggris SingkatYuyunajulAinda não há avaliações
- Klatt 2005 Pathology of AIDSDocumento290 páginasKlatt 2005 Pathology of AIDSMaya RustamAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology: Morphology of BacteriaDocumento18 páginasMicrobiology: Morphology of BacteriaABHISHEK AGRAWAL100% (1)
- Choanephora RobertDocumento2 páginasChoanephora RobertSusan Fabio TeaAinda não há avaliações
- Universal PrecautionsDocumento4 páginasUniversal PrecautionsRasheena Alaja JainalAinda não há avaliações
- Infection With Toxoplasma Gondii Can Promote Chronic Liver Diseases in HIV-infected IndividualsDocumento7 páginasInfection With Toxoplasma Gondii Can Promote Chronic Liver Diseases in HIV-infected IndividualsVerena AlvesAinda não há avaliações
- Leptospirosis FactsDocumento1 páginaLeptospirosis FactsZenitha FauziaAinda não há avaliações
- Pathognomonic SignsDocumento1 páginaPathognomonic SignsRodessa Mandac TarolAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Infection Control: Phlebotomy, 5e (Booth)Documento13 páginasChapter 3 Infection Control: Phlebotomy, 5e (Booth)Carol Reed100% (1)
- Ii: Fungi: D. Fungal PathogenecityDocumento4 páginasIi: Fungi: D. Fungal PathogenecitybirukmelkAinda não há avaliações
- Ticks: Ixodidae - Hard Ticks Argasidae - Soft TicksDocumento20 páginasTicks: Ixodidae - Hard Ticks Argasidae - Soft TickssanthiyasandyAinda não há avaliações
- Asepsis and InfectionDocumento6 páginasAsepsis and InfectionMabes100% (1)
- Black DeathDocumento6 páginasBlack Deathapi-308366238Ainda não há avaliações
- How Effective Are COVIDDocumento4 páginasHow Effective Are COVIDMARHUMA HAPSIN. ABBASAinda não há avaliações
- Impact Defense Core - Michigan7 2013 HJPPDocumento221 páginasImpact Defense Core - Michigan7 2013 HJPPdeabtegoddAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of IV TherapyDocumento15 páginasFundamentals of IV TherapyMilo AlmirolAinda não há avaliações
- Detecting Oral CancerDocumento2 páginasDetecting Oral CancerRamon Jose Arandia SarmientoAinda não há avaliações
- Penicillins - KatzungDocumento6 páginasPenicillins - KatzungKarl CAinda não há avaliações
- Define EpiglottisDocumento10 páginasDefine EpiglottisAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dAinda não há avaliações
- List of Civil Surgeons in Islamabad, PakistanDocumento5 páginasList of Civil Surgeons in Islamabad, PakistanArooj FarooqAinda não há avaliações
- Copar PDFDocumento8 páginasCopar PDFAngelica100% (1)
- Date Report Date Name Age/Sex Lab No. Reg. No. Panel Name Slide No. Ref. Dr. Report StatusDocumento2 páginasDate Report Date Name Age/Sex Lab No. Reg. No. Panel Name Slide No. Ref. Dr. Report StatusSaurabh SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Febrile Neutropenia Care GuidelineDocumento2 páginasFebrile Neutropenia Care GuidelinedenokayuMRAinda não há avaliações
- 18C Medical3 (PDF Library)Documento28 páginas18C Medical3 (PDF Library)Michael KnightsAinda não há avaliações
- Public Health Reviews: Effectiveness of Condoms in Preventing Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDocumento11 páginasPublic Health Reviews: Effectiveness of Condoms in Preventing Sexually Transmitted InfectionsKhairul WaraAinda não há avaliações
- Retrospective Serology Survey of Leptospirosis and Viral Hepatitis in Patients of Acute Febrile Illness With Jaundice - A Study From Tertiary Care Hospital of Sub-Himalayan RegionDocumento3 páginasRetrospective Serology Survey of Leptospirosis and Viral Hepatitis in Patients of Acute Febrile Illness With Jaundice - A Study From Tertiary Care Hospital of Sub-Himalayan RegionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyAinda não há avaliações
- PharyngitisDocumento20 páginasPharyngitisPutri ClaraAinda não há avaliações