Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
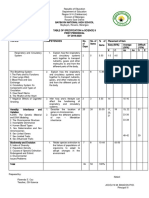
G-9 Mapeh
Enviado por
Honiel PagoboTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
G-9 Mapeh
Enviado por
Honiel PagoboDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
ST.
MICHAELS HIGH SCHOOL
Gandara, Samar
3rd Quarter Exam Music 9
Name: _______________________________ Grade & Section: ________________ Date: ___________
I. Identification
1. A German theologian who began a transformation in 1517 that was to
separate the Christian church into two main divisions.
2. The song to be sung by the church congregation.
3. A Swiss reformer who insisted on eliminating totally the use of Latin
language in church music.
4. A strophic form of madrigal.
5. A non-liturgical compositions based on religious text.
6. A composition set to French texts.
7. Originated from Italy, but usually employed a five voice texture set to
texts on pastoral and amorous subjects.
8. A four-part composition, predominantly homophonic with a regular metric
construction.
9. A four-voice texture with imitative counterpoint.
10. The leading composer of Spanish lute songs.
11. The period from 1450-1600.
12. An existing melody that is used as the basis of a composition with other
voice-parts.
13. Example of Lutheran chorales.
14. Noted for descriptive chansons
15. The principal composer of villancicos.
II. Enumeration
A. Different Kinds of Chanson (1-5)
B. Secular Music Composers in Italy (6-12)
C. Secular Music Composers in Germany (13-15)
D. Secular Music Composers in England (16-19)
ST. MICHAELS HIGH SCHOOL
Gandara, Samar
3rd Quarter Exam Arts 9
Name: _______________________________ Grade & Section: ________________ Date: ___________
I. Identification
1. An art mode that uses strong contrast between light and dark.
2. An art technique that uses gradient changes between color and the light
blending on the edges but retains the overall brilliance of the colors.
3. The painting mode blurs the edges of the outlines, creating tonal value.
4. The positioning of human figure where the weight is placed on one foot
while its shoulders and arms twist from the hips and legs.
5. An art period where people rediscovered the classical art and philosophy
of the Greeks and Romans.
6. A painting technique that renders shadows by replacing the color with a
different color.
7. A paint that was made of pigment and egg yolks as a binding agent.
8. A paint that was made of pigment and oils as a binding agent.
9. An art style that reacted against the renaissance, it is characterized by its
focus on emotions and distortion of figures.
10. A philosophy that true human potential is achieved though knowledge.
11. A rich and politically influential dynasty who commissioned hundreds of
paintings and sponsored many Renaissance artists.
12. Allows artist to draw figure in three dimensions on a two-dimensional
medium.
13. The lines that connect the objects towards the vanishing point.
14. An imaginary line that represents the eye level of the viewer.
15. An imaginary point where all object originate.
16. An architect, goldsmith, sculptor, engineer, and mathematician.
17. One of the most famous sculptural masterpieces of Michelangelo.
18. The pioneer of the renaissance style born in 1386 CE and died in
December 1466 CE.
19. He commissioned Michelangelo to paint the ceiling of the Sistine chapel.
20. An Italian artist born in 1452 CE and died in 1519 at the age of 67.
21. The famous work of Raphael.
22. The master in the medium of oil paint.
23. The artist who painted Madonna with a long neck.
24. An Italian artist born in 1475and died in 1564 CE.
25. A silk merchant who commissioned Da Vinci to paint his wife.
II. Enumeration
A. Characteristics of Renaissance (1-4)
B. Painting Modes of the Renaissance (5-8)
C. Artist of the Renaissance (9-14)
D. Great minds featured in the School of Athens (15-21)
E. Parts of the Linear Perspective (22-24)
ST. MICHAELS HIGH SCHOOL
Gandara, Samar
3rd Quarter Exam PE 9
Name: _______________________________ Grade & Section: ________________ Date: ___________
I. Identification
1. Commonly happen when playing a sport or doing an exercise.
2. Result from over using a body part while exercising or playing a sport over
a long period of time.
3. It happens while doing a physical activity such as sprains, strains, or
fractures.
4. The condition of a muscle which contracts involuntarily.
5. The stretch or a tear of ligament.
6. Develops rehabilitation program.
7. Specializing in the treatment and diagnosis of injuries related to
musculoskeletal system which includes the bones, muscles, joints, ligaments, tendons, and nerve
of the body.
8. A goal to improve physical fitness level.
9. The kind of exercise you will do to achieve specific benefits.
10. The number of times you need to exercise
II. Enumeration
A. Classification of Injuries (1-2)
B. Characteristics of a Good First-Aider (3-7)
C. Common Sports Injuries (8-10)
D. Primary Health Care Professionals (11-12)
E. Things to Consider in making Plan (13-15)
F. FITT Principle (16-19)
G. Levels of Intensity (20-22)
H. Types of Exercise (23-26)
I. Ways on How to Treat Sprain (27-30)
ST. MICHAELS HIGH SCHOOL
Gandara, Samar
3rd Quarter Exam Health 9
Name: _______________________________ Grade & Section: ________________ Date: ___________
I. Identification
1. The overuse of drugs.
2. Increased mental alertness, wakefulness, loss of appetite, and provide a
feeling of well-being.
3. Drugs which affect sensation, thinking, self-awareness, and emotion.
4. It acts to depress the central nervous system, thereby promoting
relaxation and sleep.
5. Drugs that relieve pain and often induce sleep.
6. Used by people who need sustained mental and physical alertness
pushing their physical endurance to the limit.
7. Known as poor mans cocaine.
8. Acts as a powerful stimulant of the central nervous system; active
component in tobacco.
9. Invented as a cure for opium and morphine addiction.
10. Used as a cough suppressant and to treat diarrhea.
11. Known as the king of drugs.
12. Valuable in the treatment of epilepsy and other forms of seizures.
13. An alkaloid hallucinogen extracted from the peyote cactus.
14. Potent pain-killer, cough depressant, and active component of anti-
diarrhea preparations.
15. Used to relieve severe pain, chest pain, and nervous tensions.
II. Enumeration
A. Factors which influence young people to use and abuse drugs (1-5)
B. Common Types of Depressant (6-9)
C. Common Types of Stimulant (10-14)
D. Common Types of Hallucinogen (15-17)
E. Common Types of Narcotics (18-20)
Você também pode gostar
- Summative Test 1st QuarterDocumento4 páginasSummative Test 1st QuarterChai BarcelonAinda não há avaliações
- WHLP g9 Mapeh 3rd QuarterDocumento6 páginasWHLP g9 Mapeh 3rd QuarterDianne PadillaAinda não há avaliações
- Entrep 9 q3 WK 3Documento3 páginasEntrep 9 q3 WK 3Kanon NakanoAinda não há avaliações
- LESSON PLAN 1st Cot HopeDocumento5 páginasLESSON PLAN 1st Cot HopeJunnel Mae Camacho Licor100% (1)
- COT1Documento2 páginasCOT1Marc Allen CadangAinda não há avaliações
- DLL Grade 10Documento2 páginasDLL Grade 10Phoebe Sudweste Quitaneg100% (1)
- Health 9Documento38 páginasHealth 9heraAinda não há avaliações
- Q1 Lesson1Documento4 páginasQ1 Lesson1Spencer NatarAinda não há avaliações
- Science 9 q1 Lamp v3Documento7 páginasScience 9 q1 Lamp v3Gerlie Velasco0% (3)
- Science 9 Week 2Documento9 páginasScience 9 Week 2Mary Joselyn BodionganAinda não há avaliações
- 3RD FD Cot 3 2023Documento4 páginas3RD FD Cot 3 2023Rowell TrinidadAinda não há avaliações
- Learning Competency Directory in Science 9 SY 2020 - 2021 First QuarterDocumento10 páginasLearning Competency Directory in Science 9 SY 2020 - 2021 First QuarterBerith Grace Magcalas-GallardoAinda não há avaliações
- Learners Directory in Science 7Documento4 páginasLearners Directory in Science 7jenny alla olayaAinda não há avaliações
- Philippine Festivals and Theatrical Forms Arts LessonDocumento10 páginasPhilippine Festivals and Theatrical Forms Arts LessonGeneAinda não há avaliações
- Science 10 Q3 Summative TestDocumento9 páginasScience 10 Q3 Summative Testpedro braulioAinda não há avaliações
- Spa Grade 8 Media Arts 3rd Quarter Week 5 8 For Language Editor RpmusngiDocumento22 páginasSpa Grade 8 Media Arts 3rd Quarter Week 5 8 For Language Editor RpmusngiDonna Shane ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- LCD Science 9Documento3 páginasLCD Science 9Alyssa NoroñaAinda não há avaliações
- Active Lifestyle Promotes HealthDocumento3 páginasActive Lifestyle Promotes HealthGenieva Dado AngcotAinda não há avaliações
- Science 10 Lesson PlanDocumento7 páginasScience 10 Lesson PlanThesairah Taule100% (1)
- Acitivty Sheets Q1W1 W2Documento8 páginasAcitivty Sheets Q1W1 W2Christian BejarinAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Curriculum GuideDocumento14 páginasDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Curriculum GuideJhaan CatorAinda não há avaliações
- Activity SheetDocumento11 páginasActivity SheetWinnie joy m. torresAinda não há avaliações
- Multiple Alleles-ABO Blood TypesDocumento2 páginasMultiple Alleles-ABO Blood TypesJoelynAinda não há avaliações
- Week 1Documento4 páginasWeek 1Werty Gigz DurendezAinda não há avaliações
- Co1 PPT - GemaimaDocumento43 páginasCo1 PPT - GemaimaGEMAIMA UNCLARAAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 9 - TOSDocumento1 páginaGrade 9 - TOSFlorenda CozAinda não há avaliações
- 3rd Grading Unit Test Module 1Documento2 páginas3rd Grading Unit Test Module 1Carlo ThornappleAinda não há avaliações
- Grade8 Health Q1 MODULE 3Documento12 páginasGrade8 Health Q1 MODULE 3EdrickLouise DimayugaAinda não há avaliações
- DNA and RNA Structure ComparisonDocumento4 páginasDNA and RNA Structure ComparisonEdzborbonAinda não há avaliações
- Dll. MATTER - DAY5.WEEK3.phase chane.3RDQDocumento4 páginasDll. MATTER - DAY5.WEEK3.phase chane.3RDQjunalyn franciscoAinda não há avaliações
- 7 E Instructional Model: Coastal ProcessesDocumento1 página7 E Instructional Model: Coastal ProcessesCharline A. RadislaoAinda não há avaliações
- Week2 - Q3 - Science 9Documento6 páginasWeek2 - Q3 - Science 9REYMART TANSIONGCOAinda não há avaliações
- 1st Quarter DLLDocumento3 páginas1st Quarter DLLVon Lloyd Ledesma LorenAinda não há avaliações
- 6 Types Secular Music LessonDocumento4 páginas6 Types Secular Music LessonEdalyn Despe MontemorAinda não há avaliações
- Schools Division of Himamaylan City: Third Grading Periodicaltest MAPEH Grade - 9Documento4 páginasSchools Division of Himamaylan City: Third Grading Periodicaltest MAPEH Grade - 9LORD IVAN PANCHOAinda não há avaliações
- DLL Biology FinalDocumento11 páginasDLL Biology FinalRUTH PIANGAinda não há avaliações
- Here are the answers to the multiple choice questions:1. c2. b 3. a4. b5. d6. b7. a8. c 9. a10. b11. b12. b13. a14. c15. b16. d17. b18. c19. b20. a21. c22. b23. c24. a25. d26. a27. a28. a29. bDocumento5 páginasHere are the answers to the multiple choice questions:1. c2. b 3. a4. b5. d6. b7. a8. c 9. a10. b11. b12. b13. a14. c15. b16. d17. b18. c19. b20. a21. c22. b23. c24. a25. d26. a27. a28. a29. bSher SherwinAinda não há avaliações
- TG Health 9Documento114 páginasTG Health 9shelley vibalAinda não há avaliações
- Volcano TypesDocumento5 páginasVolcano TypesJoahna Reena QuejadoAinda não há avaliações
- 2020 Tos Science 10Documento2 páginas2020 Tos Science 10Marvin ObraAinda não há avaliações
- Non-Mendelian Inheritance Practice ProblemsDocumento3 páginasNon-Mendelian Inheritance Practice ProblemsAnonymous 7NT1wDj100% (1)
- Parts and Functions of a Compound Microscope - S7 Module 1Documento69 páginasParts and Functions of a Compound Microscope - S7 Module 1AURORA () CARIAGAAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Scenario in the Philippines: Problems and SolutionsDocumento22 páginasDrug Scenario in the Philippines: Problems and SolutionsClaudine Joyce ValderamaAinda não há avaliações
- For Students Sci9 q3 Module3Documento22 páginasFor Students Sci9 q3 Module3Marian JanelleAinda não há avaliações
- SCIENCE 9 PERIODICAL EXAM REVIEWDocumento1 páginaSCIENCE 9 PERIODICAL EXAM REVIEWAnonymous PRyQ3MOAinda não há avaliações
- G 10 Science - QUARTER 3Documento58 páginasG 10 Science - QUARTER 3Aj Lyn AlferezAinda não há avaliações
- Division of Zambales First Periodic Test Mapeh 9 Direction: MULTIPLE CHOICES. Choose Theletter of The Appropriate Answer. I.MusicDocumento9 páginasDivision of Zambales First Periodic Test Mapeh 9 Direction: MULTIPLE CHOICES. Choose Theletter of The Appropriate Answer. I.MusicCecille MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Neoclassic and Romantic Period Arts and Music 3rd Periodical Test Table of SpecificationDocumento2 páginasNeoclassic and Romantic Period Arts and Music 3rd Periodical Test Table of SpecificationJhonabie Suligan CadeliñaAinda não há avaliações
- Q3 PPT Music9 (Violin - Strings Music)Documento17 páginasQ3 PPT Music9 (Violin - Strings Music)Gemma Marie PondolananAinda não há avaliações
- Science: Mahay Integrated Secondary SchoolDocumento8 páginasScience: Mahay Integrated Secondary Schoollavenia acdalAinda não há avaliações
- Microscope Parts and FunctionsDocumento3 páginasMicroscope Parts and Functionsangeline vacalaresAinda não há avaliações
- Guided Notes Lesson 4Documento4 páginasGuided Notes Lesson 4Raine RagadioAinda não há avaliações
- Cot Biodiversity 2022 - LeDocumento6 páginasCot Biodiversity 2022 - LeElaine MagpatagAinda não há avaliações
- Cot LP 2019-2020Documento9 páginasCot LP 2019-2020JESSICA ARNADOAinda não há avaliações
- DLL Science 9 Module 1 Unit 1 Week 1Documento5 páginasDLL Science 9 Module 1 Unit 1 Week 1Anna Mae Villanueva Luma-adAinda não há avaliações
- Health Grade9 Qtr1 Module1Documento17 páginasHealth Grade9 Qtr1 Module1Marchesa WitchtreuseAinda não há avaliações
- DLP Q1W4D3Documento3 páginasDLP Q1W4D3LA Lloyd Arvin MontesAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 1: Earthquakes and Faults (Introduction)Documento18 páginasLesson 1: Earthquakes and Faults (Introduction)Jacquilyn Castro TaganasAinda não há avaliações
- Grase 9 PT q2Documento4 páginasGrase 9 PT q2Israel MarquezAinda não há avaliações
- Summative Test 17-18Documento7 páginasSummative Test 17-18Jordan Miguel100% (1)
- Above All A#Documento2 páginasAbove All A#Honiel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- For All Fathers in The WorldDocumento1 páginaFor All Fathers in The WorldHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- 10 FMDocumento1 página10 FMHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- Purpose: RM 10-SU: Learning Advocacy Through Expert TestimonyDocumento6 páginasPurpose: RM 10-SU: Learning Advocacy Through Expert TestimonyHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- RM 2-MH: Healthy Lifestyle Practices For Mental-Emotional HealthDocumento2 páginasRM 2-MH: Healthy Lifestyle Practices For Mental-Emotional HealthHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- 13 FMDocumento2 páginas13 FMHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- 1 SuDocumento4 páginas1 SuHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- AdventDocumento7 páginasAdventHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- Where Am I Now? Physical ActivitiesDocumento2 páginasWhere Am I Now? Physical ActivitiesHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- 11 FMDocumento1 página11 FMHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- Reading 1: Thursday of The Fourth Week of Lent Lectionary: 247Documento2 páginasReading 1: Thursday of The Fourth Week of Lent Lectionary: 247Honiel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- 40 Doc 1Documento5 páginas40 Doc 1Honiel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- Religion 10Documento1 páginaReligion 10Honiel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- 3rd Monthly Exam Religion 10Documento1 página3rd Monthly Exam Religion 10Honiel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- Cert 1Documento1 páginaCert 1Honiel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- Module B Lesson 3Documento14 páginasModule B Lesson 3Honiel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 9-Mapeh 3rd QuarterDocumento40 páginasGrade 9-Mapeh 3rd QuarterHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- History of Sport MatchingDocumento2 páginasHistory of Sport MatchingHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- G-8 MapehDocumento5 páginasG-8 MapehHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- G-7 MapehDocumento5 páginasG-7 MapehHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- 3 FMDocumento10 páginas3 FMHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- G-11 PE and HealthDocumento1 páginaG-11 PE and HealthHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- 2 SuDocumento6 páginas2 SuHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- Situations Students Usually Do Not Have Control Over: RM 3-MH: Life Experiences Leading To Mental Health IssuesDocumento2 páginasSituations Students Usually Do Not Have Control Over: RM 3-MH: Life Experiences Leading To Mental Health IssuesHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- RM 2-SI: The Continuum of Physical Activity/Sport ParticipationDocumento1 páginaRM 2-SI: The Continuum of Physical Activity/Sport ParticipationHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- RM 2-FM: Process of Change: Tailoring Your ApproachDocumento3 páginasRM 2-FM: Process of Change: Tailoring Your ApproachHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- RM 2-MH: Healthy Lifestyle Practices For Mental-Emotional HealthDocumento2 páginasRM 2-MH: Healthy Lifestyle Practices For Mental-Emotional HealthHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- RM 2-PA: Where Am I Now?: Individually With Friends With Family MembersDocumento2 páginasRM 2-PA: Where Am I Now?: Individually With Friends With Family MembersHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- RM 2-MH: Healthy Lifestyle Practices For Mental-Emotional HealthDocumento2 páginasRM 2-MH: Healthy Lifestyle Practices For Mental-Emotional HealthHoniel PagoboAinda não há avaliações
- Burns Catalog Online PDFDocumento19 páginasBurns Catalog Online PDFjlee_296737Ainda não há avaliações
- Class and Race OptionsDocumento4 páginasClass and Race OptionsGeorge50% (2)
- Tivyside Classified 070615Documento3 páginasTivyside Classified 070615Digital MediaAinda não há avaliações
- PC power supply voltages in the form of DC currentDocumento8 páginasPC power supply voltages in the form of DC currentsoegyAinda não há avaliações
- Structuralist Analysis of Stage FX's The MousetrapDocumento2 páginasStructuralist Analysis of Stage FX's The Mousetrapsuperwee100Ainda não há avaliações
- 3 Point Problems: Which Figure Is Not in Each of Four Pictures?Documento7 páginas3 Point Problems: Which Figure Is Not in Each of Four Pictures?Daniel BarnesAinda não há avaliações
- The Mystic Class 11 Updated Psionics For 5eDocumento36 páginasThe Mystic Class 11 Updated Psionics For 5eShaadJackAinda não há avaliações
- Faq On Ivr 3d SecureDocumento2 páginasFaq On Ivr 3d SecureRio PopoffAinda não há avaliações
- Business Plan HotelDocumento36 páginasBusiness Plan Hoteldammika_077100% (7)
- Explosion BoxDocumento5 páginasExplosion BoxSiddhi PatwaAinda não há avaliações
- Hollywoodbets Greyville Polytrack@2021.11.22Documento4 páginasHollywoodbets Greyville Polytrack@2021.11.22Mitchlin Ryan PillayAinda não há avaliações
- Could - WorksheetDocumento2 páginasCould - WorksheetCristhina Anna0% (1)
- Pcnse PDFDocumento11 páginasPcnse PDFachraf trabelsiAinda não há avaliações
- Tribal DanceDocumento14 páginasTribal DanceTallieDrey100% (1)
- Pe 2 ExamDocumento2 páginasPe 2 ExamRodjan Moscoso100% (1)
- WL100-GA - Rev 01Documento1 páginaWL100-GA - Rev 01affendy roynAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar 3 - EOI MalagaDocumento69 páginasGrammar 3 - EOI MalagaDarioAinda não há avaliações
- Iron Kingdoms - Adventure - Fool's Errand (LVL 3-5) PDFDocumento29 páginasIron Kingdoms - Adventure - Fool's Errand (LVL 3-5) PDFnomad79Ainda não há avaliações
- Continuous Ink Supply System For Epson Stylus Photo R200/R210/R300/R310Documento8 páginasContinuous Ink Supply System For Epson Stylus Photo R200/R210/R300/R310Evan John O 'keeffeAinda não há avaliações
- Maturski Rad Melissa Mujezinovic W 03Documento30 páginasMaturski Rad Melissa Mujezinovic W 03Adnan Pyriel CelikAinda não há avaliações
- GMB Isp PDFDocumento29 páginasGMB Isp PDFmarkAinda não há avaliações
- Tales of The MoonDocumento1 páginaTales of The MoondollybreastsAinda não há avaliações
- The Forrester Wave™ Collaborative Work Management Tools, Q4 2020Documento15 páginasThe Forrester Wave™ Collaborative Work Management Tools, Q4 2020AbdelfattahHabibAinda não há avaliações
- Common Bar Supplies and Their UsesDocumento24 páginasCommon Bar Supplies and Their UsesNeslie ChoosyAinda não há avaliações
- SherlockDocumento4 páginasSherlockdash-watson-3695Ainda não há avaliações
- Data Management Accessories Guide: SoftwareDocumento2 páginasData Management Accessories Guide: Softwareأحمد قائدAinda não há avaliações
- NPL Casual Check Shirts-Benchmarking SS 24Documento167 páginasNPL Casual Check Shirts-Benchmarking SS 24chandan.niiftAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Marketing Online CourseDocumento22 páginasDigital Marketing Online CourseAnuj BajpaiAinda não há avaliações
- 7) Visual-Exploration-Round-Blue-3-masterDocumento14 páginas7) Visual-Exploration-Round-Blue-3-masterPreitee Ranjan PradhanAinda não há avaliações
- Hardware: The Physical Parts Hardware SoftwareDocumento2 páginasHardware: The Physical Parts Hardware SoftwareiqbalAinda não há avaliações