Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Bert Katrina Lesson Dec 2nd Science
Enviado por
api-349755868Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Bert Katrina Lesson Dec 2nd Science
Enviado por
api-349755868Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Name: Katrina Bert Cohort: I/S
Lesson Plan
Lesson Title: The Respiratory System- Anatomy Grade: 10 Date:
Subject: Grade 10 Applied Science (SNC2P) Strand: Biology- Tissues, Organs, And Systems
Location: Time: 75 minutes
Lesson Plan Description:
This is an introductory lesson to the respiratory system. In this lesson, the students will learn about the
process of breathing, and how oxygen moves through your mouth and through the respiratory system and how
carbon dioxide moves out. The students will also be taught about how your chest rises and falls from the work
of your diaphragm. They will also look at the affects of smoking on the lungs and how it impacts the process
of breathing.
CURRICULUM CONNECTIONS
Ontario Curricular Overall Expectations:
A1. Demonstrate scientific investigation skills (related to both inquiry and research) in the four areas of skills
(initiating and planning, performing and recording, analyzing and interpreting, and Communicating)
B2. Investigate cell division, cell specialization, and the organization of systems in animals, including
humans, using various laboratory techniques;
B3. Demonstrate an understanding of the hierarchical organization of cells, from tissues, to organs, to systems
in animals, including humans
Ontario Curricular Specific Expectations:
A1.1. Formulate scientific questions about observed relationships, ideas, problems, and/or issues, make
predictions, and/or formulate hypotheses to focus inquiries or research
A1.10. Draw conclusions based on inquiry results and research findings, and justify their conclusions
B2.1. Use appropriate terminology related to human cells, tissues, organs, and systems,
B3.4. Explain the general function of some of the systems in the human body (e.g., the function of the
circulatory system is to transport materials through the body; the function of the digestive system is to absorb
nutrients; the function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into and remove carbon dioxide from the
body)
Learning Goals:
Today I will learn
How oxygen moves through the respiratory system
How carbon dioxide moves out of the respiratory system
What role the diaphragm plays in breathing
How smoking impacts my lungs and my breathing process
ASSESSMENT and EVALUATION
Success Criteria
I can: explain the steps/ process that oxygen goes through as it travels through my body
Drafted by Lakehead University Orillia Faculty of Education Team-August 2013
I can: explain the steps/ process that carbon dioxide goes through as it out of my body
I can: understand what role the diaphragm plays in breathing
I can: understand the impact that smoking has on my lungs and process of breathing
Assessment:
Achievement Chart Categories: Knowledge and Understanding; Thinking; Communication; Application
Assessment For, As, Of Learning:
Assessment Mode: Assessment Assessment Tool
Written, Oral, Performance Strategy Instrument used to
Specific task for record data
students
Assessment For Learning Write Exit Tickets After students leave
they will fill out an
exit card on what
they learned and if
there was anything
they would like to
look into further
Assessment As Learning Write/Do Booklet Students will be
given booklet of
readings and
questions on
respiratory system
that they must read
and answer.
Assessment Of Learning Oral Discussion of Discussing parts of
Dissection lungs as we go over
the dissection of the
lung pluck from a
pig.
CONSIDERATIONS FOR PLANNING
Prior Learning: Prior to this lesson, students will have
* A basic understanding of the respiratory system
* A basic understanding of the parts of how breathing works
Differentiation:
Students can work with a partner/ or a group if they are struggling to complete the activity
Learning Skills/Work Habits
Highlight/circle ones that are addressed: responsibility, organization, independent work, collaboration,
initiative, self-regulation
Highlight/circle ones that are assessed: responsibility, organization, independent work, collaboration,
initiative, self-regulation
Vocabulary:
All definitions are in action section
Drafted by Lakehead University Orillia Faculty of Education Team-August 2013
Resources and Materials /Technology Integration:
YouTube video showing difference between healthy lungs and those of a smoker
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Wa6l4r73pIE
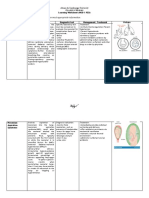
Pictures of respiratory system anatomy to show as parts and functions are explained
Pictures of lungs to show lobes
Learning Environment:
Work on their own or in groups of 2
Cross Curricular Links:
Health- making healthy lifestyle choices
Lesson Delivery Format
What Teachers Do: What Students do:
Action: Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Investigation
**Go through parts and explain what they are, their function, and Students listen and take notes on
where they are (also show on diagram** important information stated
Ask any and all questions
Pathway of Respiration:
1. Mouth and nose
a. Draws in air through nostrils and mouth
b. Filters, warms, and moistens the air
c. Then travels to the
2. Pharynx (throat)
a. Passage way for air and food
3. Larynx
a. Connects the pharynx to the trachea
b. Voice box (voice production, vocal cords)
4. Trachea (windpipe)
a. Rings of flexible cartilage to support it and keep it
open if pressure changes
5. Bronchi
a. Division of trachea into lungs
b. Subdivide into smaller and smaller branches
c. Also clean, warm, and moisten air
6. Lungs
a. Divided into lobes by fissures (or lines)
i. Left lung has 2 lobes
ii. Right lung has 3 lobes
7. Bronchioles
a. Smallest branches of the bronchi
b. The end bronchioles end in
8. Alveoli (air sacs)
a. Millions of clustered alveoli which look like
bunches of grapes
Drafted by Lakehead University Orillia Faculty of Education Team-August 2013
b. This is where gas exchange takes place
c. This also ties into the respiratory membrane or the
air-blood membrane
i. This is where the air from the alveoli is
flowing past the walls of the capillaries and
being fused into the membranes
1. Capillaries have walls that are as
thin as tissue paper
2. Oxygen enters the blood and the
carbon dioxide from the blood enters
the alveoli
Most people think that when you breath your chest moves because Students listen and take notes on
your lungs are expanding, but really, your chest expands to make important information stated
room for your lungs. This is done by the muscle that lies below Ask any and all questions
your lungs your diaphragm
When you breathe in (inhale) your diaphragm tightens
(contracts) and flattens to allow for your lungs to fill with
air
When you breath out (exhale) your diaphragm relaxes and
allows the air to move out of the lungs
Smoking and your lungs: Students listen and take notes on
Chemicals from cigarettes inflame the lungs and lead to an important information stated
overproduction of mucus (this is why most smokers have Ask any and all questions
a smokers cough)
The chemicals also break down the elastic walls of the
lungs causing them to not expand as well
Within weeks of quitting smoking the affects can start to
reverse, your lungs start to repair themselves. It is never to
late to quit!
Show YouTube Video
Consolidation & Connection: Reflection Questions
Lung Pluck Investigation and Dissection: Ask and answer questions
Bring out lung pluck, discuss and show all parts Put on gloves and investigate
Ask students what they think certain parts are
Cut into some parts and allow them to see the inside
Allow student to place on gloves and touch and investigate
different parts
Personal Reflection:
The Lesson:
The Teacher:
Drafted by Lakehead University Orillia Faculty of Education Team-August 2013
Você também pode gostar
- First Quarter Science 9 DLLDocumento29 páginasFirst Quarter Science 9 DLLAriane Ace de Guzman95% (58)
- Pathophysiology of TuberculosisDocumento3 páginasPathophysiology of TuberculosisMonica Marie Morales86% (14)
- SCI9-Q1-W1-2-L1-The Respiratory and The Circulatory SystemsDocumento5 páginasSCI9-Q1-W1-2-L1-The Respiratory and The Circulatory SystemsOliver VillanuevaAinda não há avaliações
- Science 9 Teachers' GuideDocumento336 páginasScience 9 Teachers' GuideMaragatas Integrated School100% (1)
- CPAP Cannulaide Pocket GuideDocumento2 páginasCPAP Cannulaide Pocket GuidepacsolanoAinda não há avaliações
- Q1 Lesson1Documento4 páginasQ1 Lesson1Spencer NatarAinda não há avaliações
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan Using 5esDocumento2 páginasSemi Detailed Lesson Plan Using 5esrondariopearldawnAinda não há avaliações
- DLP-Bohol - Science9 Q1 W1 D1Documento3 páginasDLP-Bohol - Science9 Q1 W1 D1Jen Lorejas100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledg e Skills Attitudes Values Reference SDocumento3 páginasDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledg e Skills Attitudes Values Reference SAndrie Vonn Perocho Nerpiol100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Identify The Key Parts of The Breathing System Skills Attitudes ValuesDocumento3 páginasDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Identify The Key Parts of The Breathing System Skills Attitudes ValuesAndrie Vonn Perocho NerpiolAinda não há avaliações
- Daily Lesson LogDocumento18 páginasDaily Lesson LogApple SamoyAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Curriculum GuideDocumento14 páginasDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Curriculum GuideJhaan CatorAinda não há avaliações
- September 4-8, 2023Documento3 páginasSeptember 4-8, 2023rosemalyn pahamtangAinda não há avaliações
- DAY: 4 I. Objectives: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofDocumento5 páginasDAY: 4 I. Objectives: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofGinalynMaacAinda não há avaliações
- SCIENCE 9 (1) - MELC 1 - Reviewed by CommitteeDocumento13 páginasSCIENCE 9 (1) - MELC 1 - Reviewed by CommitteeBayani VicencioAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Simple FormDocumento2 páginasLesson Plan Simple FormShaNe BesaresAinda não há avaliações
- Sci 9-dlp 1Documento8 páginasSci 9-dlp 1elsie tequinAinda não há avaliações
- RespirationDocumento6 páginasRespirationuzmaAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory System LessomDocumento7 páginasRespiratory System LessomDaliah Wedderburn100% (1)
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan. Renante S. Cruz Science Teacher ApplicantDocumento5 páginasSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan. Renante S. Cruz Science Teacher ApplicantRenante Cruz100% (1)
- Q1 Lesson4&5Documento3 páginasQ1 Lesson4&5Spencer NatarAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson PlanDocumento2 páginasLesson PlanJustine Mae Sevilla SimbeAinda não há avaliações
- DLL For Respiratory SystemDocumento4 páginasDLL For Respiratory SystemJuvilla BatrinaAinda não há avaliações
- Sci9 - Mod1Documento4 páginasSci9 - Mod1KaiAinda não há avaliações
- Sci 9-DLP 2Documento5 páginasSci 9-DLP 2elsie tequinAinda não há avaliações
- The Respiratory System and Circulatory System The Respiratory System and Circulatory SystemDocumento2 páginasThe Respiratory System and Circulatory System The Respiratory System and Circulatory SystemalvinPaboresAinda não há avaliações
- DLL bioSEPT4Documento3 páginasDLL bioSEPT4Rosallie Caaya-NuezAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan - 3Documento5 páginasLesson Plan - 3api-320427440Ainda não há avaliações
- DLL Science 9 JuneDocumento8 páginasDLL Science 9 JuneElma Ortega CamionAinda não há avaliações
- Q1 Lesson2Documento2 páginasQ1 Lesson2Spencer NatarAinda não há avaliações
- 1st-quarter-PART 1 DLLDocumento34 páginas1st-quarter-PART 1 DLLAngelicque EserAinda não há avaliações
- ACTIVITY 3-Week 3, Quarter 1, DLL-September 05, 2022Documento4 páginasACTIVITY 3-Week 3, Quarter 1, DLL-September 05, 2022Jessica Manawes NavorAinda não há avaliações
- Q1 Lesson3Documento3 páginasQ1 Lesson3Spencer NatarAinda não há avaliações
- DAY: 2 I. Objectives: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofDocumento4 páginasDAY: 2 I. Objectives: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofGinalynMaacAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan No. 3Documento6 páginasLesson Plan No. 3Pineda RenzAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 9 Science Biology 1 DLPDocumento13 páginasGrade 9 Science Biology 1 DLPManongdo AllanAinda não há avaliações
- Technology Integration Lesson Plan 1Documento4 páginasTechnology Integration Lesson Plan 1api-320427440Ainda não há avaliações
- 1st-quarter-PART 1 DLLDocumento32 páginas1st-quarter-PART 1 DLLErwinAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 10 Bio Respiration 2020 2Documento8 páginasGrade 10 Bio Respiration 2020 2Nicketa AndersonAinda não há avaliações
- DAY: 3 I. Objectives: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofDocumento5 páginasDAY: 3 I. Objectives: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofGinalynMaacAinda não há avaliações
- SCI9 - Q1 - MELC1 - Respiratory SystemDocumento10 páginasSCI9 - Q1 - MELC1 - Respiratory SystemCRESELDA VANGUARDIAAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan in Science 9: I. ObjectivesDocumento8 páginasLesson Plan in Science 9: I. ObjectivesmarichuAinda não há avaliações
- 1st-quarter-PART 1 DLLDocumento33 páginas1st-quarter-PART 1 DLLTeremiejoseph ObadoAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 9 DLL ScienceDocumento30 páginasGrade 9 DLL ScienceSpencer GudinAinda não há avaliações
- DLP-Bohol - Science9 Q1 W1 D2Documento3 páginasDLP-Bohol - Science9 Q1 W1 D2Jhapz SalvillaAinda não há avaliações
- Ukanteach 2 Lesson Plan: Title of Lesson: The Amazing Respiratory SystemDocumento16 páginasUkanteach 2 Lesson Plan: Title of Lesson: The Amazing Respiratory Systemapi-340827160Ainda não há avaliações
- DLL On Respiratory System Irah Jane L. Valentino San Teodoro Nhs Grade 9Documento3 páginasDLL On Respiratory System Irah Jane L. Valentino San Teodoro Nhs Grade 9Sher-ann May Labaguis Abo100% (2)
- 1st-quarter-PART 1 DLLDocumento33 páginas1st-quarter-PART 1 DLLAngelicque EserAinda não há avaliações
- Science 9 ODL IDEA WK1 L1 PRINTEDDocumento3 páginasScience 9 ODL IDEA WK1 L1 PRINTEDClarice Jenn MaltoAinda não há avaliações
- Schools Division of Negros Oriental: Republic of The Philippines Region VII, Central VisayasDocumento2 páginasSchools Division of Negros Oriental: Republic of The Philippines Region VII, Central VisayasSharna Flynn SolonAinda não há avaliações
- Daily Lesson LOG: Stem 12 A Session 1 Session 2Documento2 páginasDaily Lesson LOG: Stem 12 A Session 1 Session 2alvinPaboresAinda não há avaliações
- Edited DLL First QuarterDocumento4 páginasEdited DLL First QuarterMarie VicAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan For Grade 9 Science Quarter 1 Week 2Documento3 páginasLesson Plan For Grade 9 Science Quarter 1 Week 2Windie M. BemidaAinda não há avaliações
- DAY: 1 I. Objectives: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofDocumento4 páginasDAY: 1 I. Objectives: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofGinalynMaac100% (2)
- LTE TG Module 1 Respiratory PDFDocumento26 páginasLTE TG Module 1 Respiratory PDFAnnEviteAinda não há avaliações
- Science Collab UpDocumento5 páginasScience Collab Upapi-600452845Ainda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan in Science 10Documento3 páginasLesson Plan in Science 10Phranxies Jean BlayaAinda não há avaliações
- Science9 TGDocumento327 páginasScience9 TGEmma rebellonAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 9 DLL ScienceDocumento30 páginasGrade 9 DLL ScienceEmerson RosalAinda não há avaliações
- Grade Level Quarter / Domain Week & Day No. Page No.: (9LT-Ia-b-26) Respiratory System (Structure and Functions)Documento5 páginasGrade Level Quarter / Domain Week & Day No. Page No.: (9LT-Ia-b-26) Respiratory System (Structure and Functions)Fermin Fedillaga Celada Jr.Ainda não há avaliações
- Inquire, Investigate, Integrate!: Making Connections to the K-2 Science Standards and the Common CoreNo EverandInquire, Investigate, Integrate!: Making Connections to the K-2 Science Standards and the Common CoreAinda não há avaliações
- How to Use Your Mind A Psychology of Study: Being a Manual for the Use of Students and Teachers in the Administration of Supervised StudyNo EverandHow to Use Your Mind A Psychology of Study: Being a Manual for the Use of Students and Teachers in the Administration of Supervised StudyAinda não há avaliações
- Bones of The Human BodyDocumento21 páginasBones of The Human Bodyapi-349755868Ainda não há avaliações
- 1st Days of SchoolDocumento9 páginas1st Days of Schoolapi-349755868Ainda não há avaliações
- Esl Facilitation PresentationDocumento16 páginasEsl Facilitation Presentationapi-349755868Ainda não há avaliações
- Rubric For Physical EducationDocumento1 páginaRubric For Physical Educationapi-349755868Ainda não há avaliações
- Case Study For EmphysemaDocumento5 páginasCase Study For EmphysemaGabbii CincoAinda não há avaliações
- MSDS Carestream Dental Developer MTR Alc enDocumento7 páginasMSDS Carestream Dental Developer MTR Alc enGustavo AlcântaraAinda não há avaliações
- Module Cardiovascular SystemDocumento14 páginasModule Cardiovascular SystemVynz Morales CosepAinda não há avaliações
- Cough: Adilah: PhysiotherapistDocumento19 páginasCough: Adilah: PhysiotherapistAleen ZakiAinda não há avaliações
- Dialogue Nursing EnglishDocumento4 páginasDialogue Nursing EnglishSri Ayu Lestari100% (1)
- Gambaran Usia Pada Kejadian Covid-19: Rosyada Elviani Chairil Anwar Rico Januar SitorusDocumento6 páginasGambaran Usia Pada Kejadian Covid-19: Rosyada Elviani Chairil Anwar Rico Januar SitorusRizka ZahroAinda não há avaliações
- Case Analysis 9,10Documento4 páginasCase Analysis 9,10Jhia TorreonAinda não há avaliações
- Synovent E-Series: VentilatorDocumento4 páginasSynovent E-Series: VentilatorArboAinda não há avaliações
- Oxamyl 10%Gr: Safety Data SheetDocumento6 páginasOxamyl 10%Gr: Safety Data SheetAgung RiswantoAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Management of COVID-19 Patients - v1Documento18 páginasClinical Management of COVID-19 Patients - v1rohitAinda não há avaliações
- GeadsDocumento21 páginasGeadsshivaniAinda não há avaliações
- Educational Series in Congenital Heart DISEASE: Tetralogy of Fallot: Diagnosis To Long-Term Follow-UpDocumento15 páginasEducational Series in Congenital Heart DISEASE: Tetralogy of Fallot: Diagnosis To Long-Term Follow-UpDr Mohammed Nizam UddinAinda não há avaliações
- Chest ProtocolsDocumento82 páginasChest ProtocolsTanveer AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- OMD552 Hospital Waste Management UNIT-3Documento22 páginasOMD552 Hospital Waste Management UNIT-3Saravanakumar MAinda não há avaliações
- Echocardiography in Fontan PhysiologyDocumento30 páginasEchocardiography in Fontan PhysiologyNavojit ChowdhuryAinda não há avaliações
- Sanathana Sai Sanjeevini: ...... Healing FragrancesDocumento25 páginasSanathana Sai Sanjeevini: ...... Healing Fragrancesamane72Ainda não há avaliações
- Worksheet Pedia (Sanaani)Documento4 páginasWorksheet Pedia (Sanaani)Nur SanaaniAinda não há avaliações
- Active RelaxationDocumento1 páginaActive RelaxationrohailAinda não há avaliações
- Nitrogen SafetyDocumento4 páginasNitrogen SafetyrahulAinda não há avaliações
- 1910.252 - General Requirements. - Occupational Safety and Health AdministrationDocumento17 páginas1910.252 - General Requirements. - Occupational Safety and Health AdministrationIne NuristaAinda não há avaliações
- SDS 175 BEST ONE SeriesDocumento6 páginasSDS 175 BEST ONE SeriesWitara SajaAinda não há avaliações
- Babylog 8000plusDocumento126 páginasBabylog 8000plusMohamed AbdulaalAinda não há avaliações
- How To Collect Anterior Nasal Specimen For COVID 19Documento2 páginasHow To Collect Anterior Nasal Specimen For COVID 19Ghouri ToufeequeAinda não há avaliações
- Bio2Flow - Catalogue - EN 2021Documento20 páginasBio2Flow - Catalogue - EN 2021Ujung DuniaAinda não há avaliações
- Cluster 2 Gathered by MakilingDocumento5 páginasCluster 2 Gathered by MakilingKeziah Kaye ManogAinda não há avaliações
- Blastomycosis Life CycleDocumento1 páginaBlastomycosis Life CyclethescarletpimpernelsAinda não há avaliações
- Hold Your Breath For 5 MinutesDocumento57 páginasHold Your Breath For 5 MinutesAlínio José100% (5)
- Assessment of The Respiratory SystemDocumento49 páginasAssessment of The Respiratory SystemMariana Mikaela AlagarAinda não há avaliações