Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Respratory Drugs I-II
Enviado por
Tyler Lawrence CoyeTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Respratory Drugs I-II
Enviado por
Tyler Lawrence CoyeDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Respiratory Drugs Part I-II
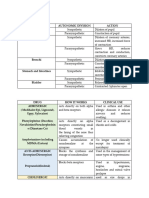
Drugs Class Mechanism
Guaifenesin (OTC) Expectorant
Opiod derivative
Dextromethrophan (OTC) Antitussive whichlacks analgesic or
addictive properties
Mucous membrane
Phenyephrine (OTC) Alpha-antagonist
Decongestant
Central acting,
OpioidsLaudanum
analgesicdepresses both
Codine ( only one really used) Antitussive
the respiratory center
Hydrocodone
and the cough reflex
-Exerts antitussive action on
stretch or cough receptors
Benzonatate Antitussive
in the lung
-Peripheral acting
Active sulfhydral
groupopens disulfide
Acetylcysteine
Mucolytic linkagesin mucus therby
( oral or inhaled)
lowering its viscosity thus
facilitating its expulsion
Epinephrine
Alpha-adrenergic receptor
Sympathomimetic
activators
Ephedrine
Beta-adrenergic agonist;
activateadenyl cyclase
Isoproterenol Sympathomimetic
coupling w/ Gs increase
cAMP
Beta 2 adrenergic
Albuterol Sympathomimetic receptor agonist( same
mech as isoproterenol)
Theophylline Methyxanthine relax bronchial Sm Musc
Zileuton 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor
Leukotriene Pathway
Zafirulkast LTD4 receptor
Inhibitors
Montelukast antagonists
Anti-inflammatory, inhibit
cytokine production,
Prednisone prevent infiltration of
Corticosteroids
Certolizumab lymphocytes, eosinophils
and mast cells into
asthmatic airways
Activated by esterase in
Ciclesonide Corticosteroids
bronchial epithelial cells
Atropine inhibit of Ach causes
Muscarinic Antagonists
Ipratropium Br smooth muscles to relax
Alter chloride channels
Mast cells inhibition =>
Cromolyn decreased histamine
Mast cell Stabilizers
Nedocromil release
Eosinophil inhibition =>
decreased allergic response
Anti-IgE mAb => decrease
Omalizumab Monoclonal Ab
IgE in plasma
Respiratory Drugs Part I-II
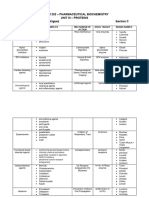
Side Effects
Hallucinagenic @ high doses
-Histamine release
-Resistance to cough suppresison
-Mucus accumulation
Caustic to esophagus if pill broken
Tachycardia, arrhythmia, angina
pectoris
high doses can cause cardiac
arrhythmias
tremor, nervousness, headache,
muscle cramps,dry mouthand
palpitations
High doses in pts on diuretics,
xanthine derivatives, or renal failure
=>hypokalaemia
clearance increasedby induction of
hepatic enzymes (smoking; dietary
effects)
Systemic Effx:Adrenal
suppresion,oropharnygeal
candidiasis( tx by rinsing mouth with
water after medication), osteoporosis,
cataracts, glucose intoleranceLocal
Effx:Vocal cords, hoarseness
minor, localized to deposition sites
Throat irritation, cough and mouth
dryness
Notes
Often used w/ anti-histamines (H2),
decongestants and antitussives in many
combination products
Drug-Drug interactions:MAO
inhibitors:isocarboxazid, phenelzine, selegiline,
tranylcypromineSerotonin reuptake
inhibitors:fluoxetine and paroxetine
Adults only
Contraindicated:Asthmatics, MAO
inhibitorsHydrocodone: semi-synthetic opiod; used
to treat acetaminophen, alcohol related toxicity
Contraindicated:patients who cannot swallow
whole pill
Needs to beswallowed whole
Indications:adjuvant for pts with chronic
bronchopulmonary disease, acute
bronchopulmonary disease, pulmonary
complications of cystic fibrosis, acetaminphen
overdoseContraindications:patient
hypersensitivity
Sc or inhalation administration, rapid acting
less potent, more centrally acting, not used as much
for treating asthma
potent bronchodilator, administered by inhalation
administered by inhalation, see effect after 5-20
minutes
Most effective Xanthine bronchodilator ( others:
Theobromine and caffeine),oraladministration,
narrow therapeutic window
oral administration
oral and pharnygeal
Aerosol tx most effective = avoid systemic effects
pro drug
lower dose so no increased HR
High dose = does not enter CNS
Clinical indications:pretreatment with either agent
blocked bronchoconstriction caused by allergen
inhalation, exercise,sulfur dioxide, occupation
asthmaRestrictions:not as effective as inhaled
corticosteroids, decreased use in childhood
reduces degree of both early and late
bronchiospastic response to Ag challenge
Reduction of the severity of asthma exacerbation =
reduction in corticosteroid requirements
Lots of $$, cancer chemo
Você também pode gostar
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)No EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Medicinal Chemistry of Drugs Affecting the Nervous SystemNo EverandMedicinal Chemistry of Drugs Affecting the Nervous SystemAinda não há avaliações
- Class of Drug Generic Drug Name Brand Name UseDocumento14 páginasClass of Drug Generic Drug Name Brand Name Useeducatemeplease100% (1)
- RespiratoryDocumento2 páginasRespiratoryJohn SmithAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory System Pharmacology NotesDocumento15 páginasRespiratory System Pharmacology NotesAli Rahimi100% (1)
- Dr. Elly Nurus Sakinah 2010Documento23 páginasDr. Elly Nurus Sakinah 2010udunk adhinkAinda não há avaliações
- Pharm Drugs ChartsDocumento21 páginasPharm Drugs ChartsTris100% (1)
- Ings Pre MedsDocumento1 páginaIngs Pre MedsIngrid LarobisAinda não há avaliações
- Anti Asthmatic Drugs (1) AnanyaDocumento23 páginasAnti Asthmatic Drugs (1) AnanyaSiddharth Shekhar SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 05: Drugs Acting On The Respiratory System Drugs Acting On The Upper Respiratory TractDocumento8 páginasUnit 05: Drugs Acting On The Respiratory System Drugs Acting On The Upper Respiratory TractDental LecturesMMQAinda não há avaliações
- Lange Smart Charts: Pharmacology, 2e Pharmacologic SuffixesDocumento2 páginasLange Smart Charts: Pharmacology, 2e Pharmacologic SuffixesSolAinda não há avaliações
- Module 7 Pharmacology of Autocoids-1Documento35 páginasModule 7 Pharmacology of Autocoids-1Cyrill sorianoAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology, II SemDocumento186 páginasPharmacology, II SemSheba RoymonAinda não há avaliações
- Histamine 5-ht Angiotensin Kinin Endothelins Eicosanoids Interleukins TNF Interferones Growth FCDocumento57 páginasHistamine 5-ht Angiotensin Kinin Endothelins Eicosanoids Interleukins TNF Interferones Growth FCFaisal 'arifAinda não há avaliações
- Sem 5/unit-3 Autocoids & Related DrugsDocumento28 páginasSem 5/unit-3 Autocoids & Related DrugsDARSHAN BhirudAinda não há avaliações
- Effector OrganDocumento2 páginasEffector OrganCamille De JesusAinda não há avaliações
- How to Optimize Your Website for Search EnginesDocumento5 páginasHow to Optimize Your Website for Search EnginesMarisa Deana Pontrelli100% (1)
- Antiasthmatic DrugsDocumento36 páginasAntiasthmatic DrugsJannah ZahraaAinda não há avaliações
- Parasympathomimetics - Direct "-Chol", Indirect "-Stigmine" or "Stigmime"Documento3 páginasParasympathomimetics - Direct "-Chol", Indirect "-Stigmine" or "Stigmime"mclAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 30 NotesDocumento4 páginasChapter 30 NotesMariah Jane TaladuaAinda não há avaliações
- Defn: Periodic Spasm of Bronchial Smooth Muscles, Increased Secretion, andDocumento5 páginasDefn: Periodic Spasm of Bronchial Smooth Muscles, Increased Secretion, andSambit BeheraAinda não há avaliações
- Bronchial Asthama and COPDDocumento37 páginasBronchial Asthama and COPDAyesha AlamAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Suffixes Cheat Sheet Sorted AlphabeticallyDocumento3 páginasDrug Suffixes Cheat Sheet Sorted Alphabeticallystudynote155Ainda não há avaliações
- Top 200 Expanded 1Documento27 páginasTop 200 Expanded 1Dean HarperAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs Acting On The Upper Respiratory TractDocumento12 páginasDrugs Acting On The Upper Respiratory TractPrincess C. SultanAinda não há avaliações
- Medications TackledDocumento3 páginasMedications TackledAl-Khan HadjailAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment Proteins 2023 2024Documento4 páginasAssignment Proteins 2023 2024Kiana RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- Bronchodilators and Corticosteroids Mechanisms of ActionDocumento3 páginasBronchodilators and Corticosteroids Mechanisms of ActionOdyAinda não há avaliações
- AlphafreqrxDocumento27 páginasAlphafreqrxapi-431095797Ainda não há avaliações
- Veterinary CNS DrugsDocumento8 páginasVeterinary CNS DrugsLaureece Salm ApduhanAinda não há avaliações
- CNS DrugsDocumento8 páginasCNS DrugsLaureece Salm ApduhanAinda não há avaliações
- Antiemetic Drugs: PHR Sangita ShakyaDocumento26 páginasAntiemetic Drugs: PHR Sangita ShakyaCurex QAAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of agents on bronchus smooth muscleDocumento16 páginasEffect of agents on bronchus smooth muscleNym Angga SantosaAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology SummaryDocumento14 páginasPharmacology SummaryteddyjolinAinda não há avaliações
- Autonomic Nervous System AgentsDocumento23 páginasAutonomic Nervous System AgentsCarlo GaradoAinda não há avaliações
- AntihistaminesDocumento16 páginasAntihistaminesdanielgy376Ainda não há avaliações
- Autacoids: Local Hormones Acting Near Their Site of SynthesisDocumento20 páginasAutacoids: Local Hormones Acting Near Their Site of SynthesisDeia ArahmanAinda não há avaliações
- Name of Drug Dosage/Route Mechanism of Action/ Classification Indication/Contraindication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocumento3 páginasName of Drug Dosage/Route Mechanism of Action/ Classification Indication/Contraindication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMonica Gagarin CortezAinda não há avaliações
- 8respiratory DrugsDocumento2 páginas8respiratory DrugsSOFIA ALYSSA MARIE ABUDEAinda não há avaliações
- Asthma ManagemntDocumento13 páginasAsthma Managemntapi-26215965Ainda não há avaliações
- Opioids & MSK TreatmentDocumento6 páginasOpioids & MSK TreatmentNashrah HusnaAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs For AsthmaDocumento1 páginaDrugs For Asthmakamil malikAinda não há avaliações
- Adrenergic Drugs: Pharmacological Department Medical School - UNPAD Ike HusenDocumento33 páginasAdrenergic Drugs: Pharmacological Department Medical School - UNPAD Ike HusenHendra EfendiAinda não há avaliações
- Albuterol SalbutamolDocumento2 páginasAlbuterol SalbutamolPePpER29Ainda não há avaliações
- Copia Di Drugs That Cause or Prolong Delirium - UpToDateDocumento2 páginasCopia Di Drugs That Cause or Prolong Delirium - UpToDateAFA.BLSAinda não há avaliações
- Cholinoreceptor Blocking AgentsDocumento38 páginasCholinoreceptor Blocking AgentsAassh DcmbrAinda não há avaliações
- Hmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, InteractionsDocumento28 páginasHmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, InteractionsolswnhAinda não há avaliações
- Moonlighting GuideDocumento14 páginasMoonlighting GuideJulienneAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and GlucocorticoidsDocumento56 páginasPharmacology of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and GlucocorticoidsRidhaAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs Class Mechanism: Guaifenesin (OTC)Documento10 páginasDrugs Class Mechanism: Guaifenesin (OTC)Tyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory Patho PhysDocumento1 páginaRespiratory Patho PhysTori IkeharaAinda não há avaliações
- Adrenergic Drugs-New PDFDocumento69 páginasAdrenergic Drugs-New PDFKuldeep ChaudhariAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology Finals Review GuideDocumento8 páginasPharmacology Finals Review GuideJered OlarveAinda não há avaliações
- Share 1. Ranitidine i-WPS OfficeDocumento6 páginasShare 1. Ranitidine i-WPS OfficeJADE ASHLEY TORRESAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Alpha Adrenergic BlockersDocumento34 páginas5 Alpha Adrenergic Blockersmatchees-gone rogueAinda não há avaliações
- Modul Muskuloskeletal - NSAIDs 2017Documento56 páginasModul Muskuloskeletal - NSAIDs 2017khairunnisanurainiAinda não há avaliações
- ANS2Documento16 páginasANS2yaya mohaAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs Used in Neuro PharmacologyDocumento3 páginasDrugs Used in Neuro PharmacologyNabeel Kouka, MD, DO, MBA, MPH100% (1)
- Neuropharmacology ANSDocumento47 páginasNeuropharmacology ANSnezifzenu2023Ainda não há avaliações
- Sympathomimetic Drugs PharmacologyDocumento10 páginasSympathomimetic Drugs PharmacologyHaroon JavedAinda não há avaliações
- Dfa 6 29629Documento12 páginasDfa 6 29629Tyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 3 Capsule Tendon Balance ProceduresDocumento19 páginasLecture 3 Capsule Tendon Balance ProceduresTyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Accuracy With Mada: Philipp Doebler Heinz HollingDocumento21 páginasMeta-Analysis of Diagnostic Accuracy With Mada: Philipp Doebler Heinz HollingTyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- Jfas Original ResearchDocumento12 páginasJfas Original ResearchTyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- Wound and Skin Ulcer Management Care Guide PDFDocumento21 páginasWound and Skin Ulcer Management Care Guide PDFAdriel Chandra AngAinda não há avaliações
- Ankle Instability 2017-2018Documento44 páginasAnkle Instability 2017-2018Tyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- Anki Data Folder Location and Backup GuideDocumento1 páginaAnki Data Folder Location and Backup GuideTyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- Operative Techniques in Foot and Ankle Surgery - (Axial Screw Technique For Midfoot Arthrodesis in Charcot Foot Deformit... )Documento7 páginasOperative Techniques in Foot and Ankle Surgery - (Axial Screw Technique For Midfoot Arthrodesis in Charcot Foot Deformit... )Tyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- Luke Vetti - NBPME Part 1 - LEA - Anterior Hip + Gluteal Muscles 1Documento3 páginasLuke Vetti - NBPME Part 1 - LEA - Anterior Hip + Gluteal Muscles 1Tyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- AntipsychoticsDocumento29 páginasAntipsychoticsTyler Lawrence Coye100% (4)
- Podiatry Institute ManualDocumento301 páginasPodiatry Institute ManualTyler Lawrence Coye100% (2)
- Anti EpilepticsDocumento46 páginasAnti EpilepticsTyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- Treatment of Lisfranc Fracture-Dislocations With PDocumento8 páginasTreatment of Lisfranc Fracture-Dislocations With PTyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- Penn Presby Residency Manual PodiatryDocumento400 páginasPenn Presby Residency Manual PodiatryTyler Lawrence Coye100% (1)
- Trauma Manual (Podiatry)Documento403 páginasTrauma Manual (Podiatry)QuantumjanitorAinda não há avaliações
- Trauma Workshop 1Documento10 páginasTrauma Workshop 1Tyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture-12-2 22 17Documento7 páginasLecture-12-2 22 17Tyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- The Principles of Antibiotic Therapy: S. Aureus Streptococcus PneumoniaeDocumento16 páginasThe Principles of Antibiotic Therapy: S. Aureus Streptococcus PneumoniaeDianne Chua100% (7)
- Venous DiseaseDocumento19 páginasVenous DiseaseTyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- AnticoagulantsDocumento47 páginasAnticoagulantsTyler Lawrence Coye100% (1)
- Principles of ankle and foot CT imaging and applicationsDocumento48 páginasPrinciples of ankle and foot CT imaging and applicationsTyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- 09 Vascular TraumaDocumento36 páginas09 Vascular TraumaTyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- CROZER-KEYSTONE RESIDENCY MANUAL SECOND EDITIONDocumento219 páginasCROZER-KEYSTONE RESIDENCY MANUAL SECOND EDITIONTyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- USMLE STEP 1 and STEP 2 Highly Tested Topics Gold CollectionDocumento36 páginasUSMLE STEP 1 and STEP 2 Highly Tested Topics Gold CollectionTyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs Class Mechanism: Guaifenesin (OTC)Documento10 páginasDrugs Class Mechanism: Guaifenesin (OTC)Tyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- The Ohio Book - LEA DiagramsDocumento168 páginasThe Ohio Book - LEA DiagramsTyler Lawrence Coye100% (2)
- Chapter 8 - Head and Neck 2015Documento72 páginasChapter 8 - Head and Neck 2015Tyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy RecallDocumento337 páginasAnatomy RecallTyler Lawrence Coye100% (2)
- Mit PDFDocumento106 páginasMit PDFTyler Lawrence CoyeAinda não há avaliações
- Citizens Response and Arguments Against Closing Muhlenberg HospitalDocumento15 páginasCitizens Response and Arguments Against Closing Muhlenberg HospitalDeborah Joyce DoweAinda não há avaliações
- Fetal Surgery - The Ochsner Experience With in Utero Spina Bifida RepairDocumento6 páginasFetal Surgery - The Ochsner Experience With in Utero Spina Bifida RepairJusten ThompsonAinda não há avaliações
- Bedside BrochureDocumento2 páginasBedside Brochureapi-438607141100% (1)
- Products Anti Diabetes For Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Natto Roots Momordica Balsamina Caju Bark Artemisia Afra TinctureDocumento5 páginasProducts Anti Diabetes For Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Natto Roots Momordica Balsamina Caju Bark Artemisia Afra TinctureNile Valley MedicineAinda não há avaliações
- Practice TestDocumento6 páginasPractice TestJulie May SuganobAinda não há avaliações
- Cup of Kindness: NHS Greater Glasgow and ClydeDocumento16 páginasCup of Kindness: NHS Greater Glasgow and ClydecrispypataAinda não há avaliações
- Tech MagDocumento44 páginasTech Magcarambola88Ainda não há avaliações
- Cranial Manipulative TherapyDocumento6 páginasCranial Manipulative Therapypurple112650% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan GoiterDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan Goiterdee_day_8100% (4)
- Measles MorbiliDocumento16 páginasMeasles MorbiliRegyna SusantiAinda não há avaliações
- Full Avanto BrochureDocumento30 páginasFull Avanto BrochureMas NoAinda não há avaliações
- Literatur Pasien SafetyDocumento11 páginasLiteratur Pasien SafetyRisky SetyoAinda não há avaliações
- Amniotic Band SyndromeDocumento6 páginasAmniotic Band SyndromeVít DrochýtekAinda não há avaliações
- Abdominal HerniaDocumento2 páginasAbdominal HerniaMichael BoadoAinda não há avaliações
- Test Bank For Nursing Assistant 11th Edition by Acello PDFDocumento8 páginasTest Bank For Nursing Assistant 11th Edition by Acello PDFa605415410Ainda não há avaliações
- Worksheets - Isbar Week 4 x1Documento3 páginasWorksheets - Isbar Week 4 x1api-631170779Ainda não há avaliações
- Morton Ch01Documento11 páginasMorton Ch01headepartmentAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter II - Anemia and Hypovolemic Shock Secondary To An Upper Gastrointestinal BleedingDocumento3 páginasChapter II - Anemia and Hypovolemic Shock Secondary To An Upper Gastrointestinal BleedingKn VelasquezAinda não há avaliações
- Treatment Aspects in Perioperative NursingDocumento51 páginasTreatment Aspects in Perioperative NursingShibin Jacob100% (2)
- Interpretation of The Reptile Blood ProfileDocumento8 páginasInterpretation of The Reptile Blood ProfileAndre NgoAinda não há avaliações
- Patient Diary Leaflet FINALDocumento3 páginasPatient Diary Leaflet FINALerika motosAinda não há avaliações
- Self-Assessment Colour Review of Small Animal Soft Tissue SurgeryDocumento194 páginasSelf-Assessment Colour Review of Small Animal Soft Tissue Surgerymiliindianu100% (3)
- ZEISS AngioPlex Case Reports US 31 150 0032IDocumento12 páginasZEISS AngioPlex Case Reports US 31 150 0032Idarkspawn69Ainda não há avaliações
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)Documento3 páginasAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)akish4uAinda não há avaliações
- Customer Satisfaction - Literature Review - FinalDocumento28 páginasCustomer Satisfaction - Literature Review - FinalSaumya SarkarAinda não há avaliações
- Triptico HTAi Bilbao EnglishDocumento2 páginasTriptico HTAi Bilbao EnglishaaaznarezAinda não há avaliações
- Doctors Nurses Overcome Workplace HierarchiesDocumento6 páginasDoctors Nurses Overcome Workplace HierarchiesAndres CarreraAinda não há avaliações
- Tamsulosin Hydro ChlorideDocumento2 páginasTamsulosin Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (3)
- Addition and DeletionDocumento10 páginasAddition and DeletionNikkaMontilAinda não há avaliações