Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Apple
Enviado por
nikhilDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Apple
Enviado por
nikhilDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
APPLE
The apple tree (Malus pumila, commonly and erroneously called Malus domestica) is a deciduous tree in
the rose family best known for its sweet. It is cultivated worldwide as a fruit tree, The tree originated
in Central Asia. Apple trees are large if grown from seed. Generally apple cultivars are propagated
by grafting onto rootstocks, which control the size of the resulting tree. There are more than 7,500
known cultivars of apples, resulting in a range of desired characteristics. Different cultivars are bred for
various tastes and uses, including cooking, eating raw and cider production.
Mango
Mangoes are juicy stone fruit (drupe) from numerous species of tropical trees belonging to the flowering
plant genus Mangifera, cultivated mostly for their edible fruit. The majority of these species are found in
nature as wild mangoes. The genus belongs to the cashew family Anacardiaceae. Mangoes
are native to South Asia,[2][3] from where the "common mango" or "Indian mango", Mangifera indica, has
been distributed worldwide to become one of the most widely cultivated fruits in the tropics.
Other Mangifera species (e.g. horse mango, Mangifera foetida) are also grown on a more localized basis.
It is the national fruit of India, Pakistan, and the Philippines, and the national tree of Bangladesh.[4]
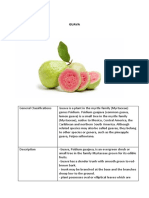
Guava
Guavas (singular guava /w.v/)[1] are common tropical fruits cultivated and enjoyed in many tropical
and subtropical regions.
Psidium guajava (common guava, lemon guava) is a small tree in the Myrtle family (Myrtaceae), native
to Mexico, Central America, and northern South America. Although related species may also be called
guavas, they belong to other species or genera, such as the "pineapple guava" Acca sellowiana.
Grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus Vitis.
Grapes can be eaten fresh as table grapes or they can be used for making wine, jam, juice, jelly, grape seed
extract, raisins, vinegar, and grape seed oil. Grapes are a non-climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in
clusters.
Manilkara zapota
Manilkara zapota, commonly known as the sapodilla (/spdl/),[1] is a long-lived, evergreen tree native
to southern Mexico, Central America and the Caribbean.[2] An example natural occurrence is in coastal
Yucatn in the Petenes mangroves ecoregion, where it is a subdominant plant species.[3] It was introduced to
the Philippines during Spanish colonization. It is grown in large quantities
in Pakistan, India, Thailand, Malaysia, Cambodia, Indonesia, Bangladesh and Mexico.
The name "zapota" from the Spanish zapote [apote] ultimately derives from the Nahuatl word tzapotl.
Você também pode gostar
- The Common Fruits in The Philippines: Hezikea Lavaine P. LabordoDocumento4 páginasThe Common Fruits in The Philippines: Hezikea Lavaine P. LabordoMa. Lexieni LabordoAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Tree: Appletree MangotreeDocumento3 páginasTypes of Tree: Appletree MangotreeNeha parveenAinda não há avaliações
- MangoDocumento1 páginaMangodilwale puchAinda não há avaliações
- Types: Guavas AreDocumento12 páginasTypes: Guavas AreJesa Rose Tingson100% (1)
- Mangifera: Mangoes Are JuicyDocumento3 páginasMangifera: Mangoes Are JuicyAbrahamAinda não há avaliações
- MangoDocumento1 páginaMangoKyle BrianAinda não há avaliações
- Guava GGLDocumento3 páginasGuava GGLAshwini24111997Ainda não há avaliações
- Mango: Mangifera, Consisting of Numerous Tropical Fruiting Trees, CultivatedDocumento1 páginaMango: Mangifera, Consisting of Numerous Tropical Fruiting Trees, CultivatedharishAinda não há avaliações
- The MangoDocumento1 páginaThe MangoSaleh RehmanAinda não há avaliações
- GGGGGDocumento1 páginaGGGGGPenny LowAinda não há avaliações
- Guava: 2 Etymology and Regional NamesDocumento6 páginasGuava: 2 Etymology and Regional NamesdivyaAinda não há avaliações
- The Different Kind of FruitDocumento1 páginaThe Different Kind of Fruitbuenlyndon92Ainda não há avaliações
- MangoDocumento13 páginasMangodane567Ainda não há avaliações
- Real LifeDocumento4 páginasReal LifeIlyas Raj ControversywalaAinda não há avaliações
- AvocadoDocumento2 páginasAvocadonikhilAinda não há avaliações
- AmpalayaDocumento1 páginaAmpalayaapi-240801339Ainda não há avaliações
- Citrus FruitsDocumento11 páginasCitrus FruitsymonnlopezAinda não há avaliações
- Pomaceous Fruit Tree Family Rosaceae Cultivated Genus Deciduous Central AsiaDocumento1 páginaPomaceous Fruit Tree Family Rosaceae Cultivated Genus Deciduous Central Asiaelectronics0109Ainda não há avaliações
- Etymology: MangiferaDocumento5 páginasEtymology: MangiferaElena AlonAinda não há avaliações
- 225 228 1 SMDocumento15 páginas225 228 1 SMsantosh kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Fauna and Flora of The UeprimDocumento12 páginasFauna and Flora of The UeprimQQAinda não há avaliações
- Plants For Major Highways and Major Roads: Landscape ArchitectureDocumento41 páginasPlants For Major Highways and Major Roads: Landscape ArchitectureCapao PadillaAinda não há avaliações
- This Article Is About Bananas GenerallyDocumento2 páginasThis Article Is About Bananas GenerallyHana PrasatthongAinda não há avaliações
- MangoDocumento12 páginasMangothippliAinda não há avaliações
- Mango 1Documento3 páginasMango 1BrianAinda não há avaliações
- FruitsDocumento10 páginasFruitsHarshika BhagourAinda não há avaliações
- Apple: For The Technology Company, See For Other Uses, See - "Apple Tree" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocumento5 páginasApple: For The Technology Company, See For Other Uses, See - "Apple Tree" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeelathaprabhuAinda não há avaliações
- AppleDocumento1 páginaAppleharishAinda não há avaliações
- Guava: 1.report TextDocumento3 páginasGuava: 1.report TextKevin Rosibel100% (2)
- India Shrub Euphorbiaceae South America Crop Tropical Subtropical Starchy Tuberous Root Carbohydrates Yucca Asparagaceae Tapioca Garri Maize NigeriaDocumento1 páginaIndia Shrub Euphorbiaceae South America Crop Tropical Subtropical Starchy Tuberous Root Carbohydrates Yucca Asparagaceae Tapioca Garri Maize Nigeriaben-jAinda não há avaliações
- AratilesDocumento6 páginasAratilesMarlene Roullo100% (1)
- EdiblePalms NotasDocumento13 páginasEdiblePalms Notascesar3126Ainda não há avaliações
- INTRODUCTIONDocumento1 páginaINTRODUCTIONaman546455Ainda não há avaliações
- Chap 2Documento7 páginasChap 2PriyankaAinda não há avaliações
- Apple: Pomaceous Fruit Tree Family Rosaceae Cultivated Genus Deciduous Central AsiaDocumento1 páginaApple: Pomaceous Fruit Tree Family Rosaceae Cultivated Genus Deciduous Central AsiaslyothersAinda não há avaliações
- Ziziphus Mauritiana PDFDocumento6 páginasZiziphus Mauritiana PDFRiky SetiawanAinda não há avaliações
- Banana: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocumento2 páginasBanana: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchErwin SesioAinda não há avaliações
- India Shrub Euphorbiaceae South America Crop Tropical Subtropical Starchy Tuberous Root Carbohydrates Yucca Asparagaceae Tapioca Garri MaizeDocumento1 páginaIndia Shrub Euphorbiaceae South America Crop Tropical Subtropical Starchy Tuberous Root Carbohydrates Yucca Asparagaceae Tapioca Garri MaizeRind Bergh DevelosAinda não há avaliações
- Your Guide To Identifying PalmsDocumento10 páginasYour Guide To Identifying PalmsrickomamaAinda não há avaliações
- 17 Medicinal Plants HWDocumento5 páginas17 Medicinal Plants HWKirsten Alexandra MerrittAinda não há avaliações
- Azadirachta Indica (Neem) : Scientific ClassificationDocumento7 páginasAzadirachta Indica (Neem) : Scientific ClassificationVishnu RamanAinda não há avaliações
- Guava Wikipedia enDocumento10 páginasGuava Wikipedia envitaAinda não há avaliações
- AppleDocumento1 páginaAppleAmaya AcelynAinda não há avaliações
- Sour SopDocumento4 páginasSour Sopclint_mystarAinda não há avaliações
- NeemDocumento8 páginasNeemwindow_7Ainda não há avaliações
- Mammea AmericanaDocumento5 páginasMammea AmericanavitazzoAinda não há avaliações
- Banana Dessert BananasDocumento1 páginaBanana Dessert BananasJorge Domingo YlloaAinda não há avaliações
- Musa Species Are Native To Tropical South and Southeast Asia, and Are Likely ToDocumento1 páginaMusa Species Are Native To Tropical South and Southeast Asia, and Are Likely ToSumeet DudaniAinda não há avaliações
- Mango: Navigation Search Merged DiscussDocumento13 páginasMango: Navigation Search Merged Discussakashyap87Ainda não há avaliações
- Edible Shrubs: Amelanchier Species: Juneberries Produce Blackcurrant-SizeDocumento7 páginasEdible Shrubs: Amelanchier Species: Juneberries Produce Blackcurrant-SizeMaria MariAinda não há avaliações
- Flora at Sanjay Gandhi ParkDocumento9 páginasFlora at Sanjay Gandhi ParkMahesh TejaniAinda não há avaliações
- Plantation and Adoption For A Tree-1-1Documento8 páginasPlantation and Adoption For A Tree-1-1Preetham M. C Preetham M. CAinda não há avaliações
- RambutanDocumento13 páginasRambutanIhsan1991 YusoffAinda não há avaliações
- Cashew AppleDocumento16 páginasCashew AppleJon AvnetAinda não há avaliações
- Fungsi Dari SapodillaDocumento17 páginasFungsi Dari SapodillaSri Yuni HaninanaAinda não há avaliações
- Annonaceous Fruits: P Padmanabhan and G Paliyath, University of Guelph, Guelph, ON, CanadaDocumento5 páginasAnnonaceous Fruits: P Padmanabhan and G Paliyath, University of Guelph, Guelph, ON, CanadaharlentAinda não há avaliações
- Muntingia CalaburaDocumento12 páginasMuntingia CalaburaLailaAinda não há avaliações
- Moringa (Genus)Documento1 páginaMoringa (Genus)Ignacio AllamiAinda não há avaliações
- Mango: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocumento12 páginasMango: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchVicces P. EstradaAinda não há avaliações
- Tipu SultanDocumento4 páginasTipu SultannikhilAinda não há avaliações
- Agriculture: Agriculture Is The Cultivation and BreedingDocumento2 páginasAgriculture: Agriculture Is The Cultivation and BreedingnikhilAinda não há avaliações
- AvocadoDocumento2 páginasAvocadonikhilAinda não há avaliações
- Saina Nehwal: Personal LifeDocumento5 páginasSaina Nehwal: Personal LifenikhilAinda não há avaliações
- Ilovepdf MergedDocumento10 páginasIlovepdf MergedperwirapertanianindonesiaAinda não há avaliações
- TCM Food Therapy E-BookDocumento19 páginasTCM Food Therapy E-BookCinqMarsAinda não há avaliações
- PranaMAMA Food Brochure Vata Kapha 3 FoldDocumento2 páginasPranaMAMA Food Brochure Vata Kapha 3 FoldHidayathulla SkAinda não há avaliações
- Manual de Utilizare Storcator Moulinex JU585GDocumento44 páginasManual de Utilizare Storcator Moulinex JU585GTiberiu IonescuAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition Therapy: Low FodmapsDocumento2 páginasNutrition Therapy: Low FodmapsVaidehi UlaganathanAinda não há avaliações
- 2016 Cassandra Donoian. All Rights ReservedDocumento46 páginas2016 Cassandra Donoian. All Rights ReservedSchen NgAinda não há avaliações
- Calorii LegumeDocumento13 páginasCalorii Legumeadisan777Ainda não há avaliações
- Eat Right For Your Blood Type: Meat & PoultryDocumento7 páginasEat Right For Your Blood Type: Meat & PoultryEjaz HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 4 - Application - at The RestaurantDocumento5 páginasLesson 4 - Application - at The RestaurantAndreea VasileAinda não há avaliações
- Gulayan report-SNES-pictures-2018Documento36 páginasGulayan report-SNES-pictures-2018Jojo Ofiaza GalinatoAinda não há avaliações
- Classification of VegetablesDocumento8 páginasClassification of VegetablesMakee MckayAinda não há avaliações
- Lectins in Food PDFDocumento27 páginasLectins in Food PDFnedcordovaAinda não há avaliações
- Product ListDocumento20 páginasProduct ListAfzal RAinda não há avaliações
- Name: Kamala Age: 44 BMI: 29.05 Weight: 82.0 Diet Preference: Non-VegetarianDocumento3 páginasName: Kamala Age: 44 BMI: 29.05 Weight: 82.0 Diet Preference: Non-Vegetarianinstallationsap1Ainda não há avaliações
- How To Succeed 2 2014 Exotic VegetablesDocumento25 páginasHow To Succeed 2 2014 Exotic VegetablesBryanaAinda não há avaliações
- Materi Kelas KopiDocumento3 páginasMateri Kelas KopiHSE SentulAinda não há avaliações
- Data Buyer Go4worldbussinessDocumento683 páginasData Buyer Go4worldbussinessTeuku Safrizal100% (1)
- Chettinad Kalyana Vatha KuzhambuDocumento7 páginasChettinad Kalyana Vatha Kuzhambunila100% (1)
- List of Root VegetablesDocumento6 páginasList of Root VegetablesAlarm GuardiansAinda não há avaliações
- Description HerbariumDocumento8 páginasDescription HerbariumShella Mae Duclayan RingorAinda não há avaliações
- The Complete Indian Rice Cookbook Master - Rekha SharmaDocumento697 páginasThe Complete Indian Rice Cookbook Master - Rekha SharmaMayurAinda não há avaliações
- June PlumDocumento1 páginaJune PlumCharo StewartAinda não há avaliações
- LATIHAN SOAL PTS Grade 2Documento1 páginaLATIHAN SOAL PTS Grade 2Selah AL - GhaziyahAinda não há avaliações
- Ayurveda MDocumento28 páginasAyurveda MhajihalviAinda não há avaliações
- Rate List (07.07.2023) SouthDocumento4 páginasRate List (07.07.2023) Southsubra1032Ainda não há avaliações
- Catalogue Mahana Coffee - 6 Sep 2022Documento17 páginasCatalogue Mahana Coffee - 6 Sep 2022Hua hin International corporation Co LtdAinda não há avaliações
- Soal PTS Kelas 7Documento5 páginasSoal PTS Kelas 7Hj. ArisahAinda não há avaliações
- Juice Plus Complete SmoothiDocumento38 páginasJuice Plus Complete SmoothiMaria GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Kitchen GlossaryDocumento23 páginasKitchen Glossaryvpv433Ainda não há avaliações
- Plants InventoryDocumento10 páginasPlants InventorySheikh XafarAinda não há avaliações