Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Nursing Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer
Enviado por
SyafiqAziziDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Nursing Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer
Enviado por
SyafiqAziziDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
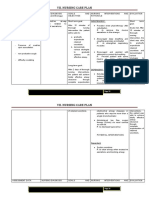
Nursing Diagnosis of Prostate Cancers Client.
1) Risk for infection related to invasive procedure.
Desired outcome: Experience no sign of infection.
Nursing Interventions Rationale
Maintain a sterile catheter system.
Provide regular catheter and meatal Measures to prevent introduction
care with soap and water. Apply of bacteria that may
antibiotic ointment around the cause infection or sepsis.
catheter site.
Avoids backward reflux of urine,
Ambulate with drainage bag
which may introduce bacteria into
dependent.
the bladder.
Patient who has had cystoscopy
Monitor vital signs, noting low-
and/or TURP is at increased risk
grade fever, chills, rapid pulse and
for surgical or septic shock related
respiration, restlessness, irritability,
to manipulation and
disorientation.
instrumentation.
Presence of drains, suprapubic
Observe drainage from wounds, incision increases risk of infection,
around suprapubic catheter. as indicated by erythema, purulent
drainage.
Change dressings frequently Wet dressings cause skin irritation
(suprapubic or retropubic and and provide media for bacterial
perineal incisions), cleaning and growth, increasing risk of wound
drying skin thoroughly each time. infection.
Provides protection for
surrounding skin, preventing
Use ostomy-type skin barriers.
excoriation and reducing risk of
infection.
May be given prophylactically
Administer antibiotics as indicated
because of increased risk of
by doctor.
infection with prostatectomy.
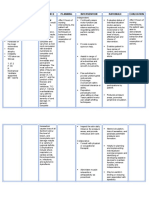
2) Risk for sexual dysfunction related to change in health status.
Desired outcome: Discuss concerns about the possible changes in body image with the partner.
Nursing Interventions Rationale
May have anxieties about the
Give opportunities or openings effects of surgery and may be
for patient and SO to talk about hesitant about asking necessary
concerns of incontinence and questions. Anxiety may have
sexual functioning. affected ability to access
information given previously.
The nerve plexus that controls
erection runs posteriorly to the
prostate through the capsule. In
Discuss basic anatomy. Be open procedures that do not involve the
and honest in answers to patients prostatic capsule, impotence and
questions. sterility usually are not
consequences. Surgical procedure
may not provide a permanent
cure, and hypertrophy may recur.
Physiological impotence occurs
when the perineal nerves are cut
during radical procedures; with
other approaches, sexual activity
Give accurate information about
can usually be resumed in 68
expectation of return of sexual
weeks Note: Penile prosthesis
function.
may be recommended to facilitate
erection and correct impotence
following radical perineal
procedure.
Seminal fluid goes into the
bladder and is excreted with the
Discuss retrograde ejaculation if
urine. This does not interfere with
transurethral or suprapubic
sexual functioning but will
approach is used.
decrease fertility and cause urine
to be cloudy.
Kegel exercises promote
Instruct in perineal and
regaining muscular control of
interruption and/or continuation
urinary continence and sexual
of urinary stream exercises.
function.
Persistent or unresolved problems
Refer to sexual counsellor as
may require professional
indicated.
intervention.
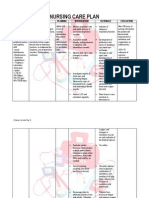
Discharge Plan for Client.
1. Assess and re-educate the client and his partner about the surgery procedure that has been
done, especially about the anatomy. Must using the common language and term with the client:
The prostate is the male sex gland that helps make semen. It is about the size of a walnut and
wraps around the urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the end of
the penis. In most cases, prostate cancer is slow growing.
2. Call 911 if this condition happens:
Leg feels warm, tender, and painful. It may look swollen and red.
Chest pain when take a deep breath or cough.
Feeling of lightheaded and short of breath.
Cough up blood.
3. Consult and follow with the urologist or oncologist if:
Fever occur.
Blood in the urine or have trouble urinating.
Pain that does not decrease or go away after taking up medicine.
Trouble of having an erection.
4. Medications:
Hormone therapy is medicine used to decrease testosterone (male hormone) levels.
Pain medicine may be given. Do not wait until the pain is severe.
Take your medicine as directed.
5. Do not smoke:
Nicotine can damage blood vessels and make it more difficult to manage your prostate cancer.
Smoking also increases your risk for new or returning cancer and delays healing after treatment.
Do not use e-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco in place of cigarettes or to help you quit. They still
contain nicotine. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need
help quitting.
Você também pode gostar
- Prostate Cancer NCPDocumento1 páginaProstate Cancer NCPKathleen Dimacali0% (1)
- Vii. Nursing Care Plan: Secretions in The AirwaysDocumento5 páginasVii. Nursing Care Plan: Secretions in The AirwaysJai - Ho100% (2)
- As Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Documento4 páginasAs Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Nicole GumolonAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implemantation Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 páginasAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implemantation Rationale EvaluationChloie Marie Rosalejos100% (1)
- Preoperative and Post Liver Transplant Nursing Care PlanDocumento5 páginasPreoperative and Post Liver Transplant Nursing Care PlanOctoober67% (6)
- NCP Modified Radical MastectomyDocumento5 páginasNCP Modified Radical MastectomyIvan Jules P. PALMARESAinda não há avaliações
- Spinal Cord Injury NCPDocumento2 páginasSpinal Cord Injury NCPEmmanuelRodriguez100% (1)
- Case Scenario: Prostate CancerDocumento5 páginasCase Scenario: Prostate Cancer24 PAULINO ALDRIN MUJARAinda não há avaliações
- Diarrhea Care PlanDocumento2 páginasDiarrhea Care Planzepoli_zepoly6232100% (1)
- NCP For Laryngeal CancerDocumento5 páginasNCP For Laryngeal CancerMădălina PinciucAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan and Diagnosis For MastectomyDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan and Diagnosis For MastectomyAngie Mandeoya100% (2)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento2 páginasIneffective Airway ClearancePatrick Arvin Ballesteros BarcarseAinda não há avaliações
- Drug NameDocumento4 páginasDrug Namecheanne003Ainda não há avaliações
- Final NCP LeptospirosisDocumento6 páginasFinal NCP LeptospirosisKeith Austin100% (1)
- Furosemid Citicoline Clexane, LevofloxacinDocumento9 páginasFurosemid Citicoline Clexane, Levofloxacincotyboy50% (2)
- Fistula NCPDocumento1 páginaFistula NCPHasna LisnaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP LymphedemaDocumento1 páginaNCP Lymphedemayasira50% (2)
- Breast Cancer Risk For InfectionDocumento6 páginasBreast Cancer Risk For Infectionam peAinda não há avaliações
- Ovarian Cancer NCPDocumento7 páginasOvarian Cancer NCPAsterlyn Coniendo100% (1)
- NCP LymphomaDocumento3 páginasNCP LymphomaJohn Emmanuel Tatad TudAinda não há avaliações
- Patient With Neutropenia Risk For Infection Related To Inadequate Secondary Defenses (Leukopenia, Neutropenia), Altered Response To MicrobialDocumento2 páginasPatient With Neutropenia Risk For Infection Related To Inadequate Secondary Defenses (Leukopenia, Neutropenia), Altered Response To MicrobialICa MarlinaAinda não há avaliações
- Discharge Planning ASTHMADocumento4 páginasDischarge Planning ASTHMANadja JamilahAinda não há avaliações
- Ortho NCPDocumento1 páginaOrtho NCPErjohn Vincent Lim100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Breast Cancer NCP PDFDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan For Breast Cancer NCP PDFMaina BarmanAinda não há avaliações
- Rani Ti Dine Tramadol Ketorolac in Paracetamol Drug StudyDocumento10 páginasRani Ti Dine Tramadol Ketorolac in Paracetamol Drug StudyIv'z TandocAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For Pre-Op Incision CaseDocumento8 páginasNCP For Pre-Op Incision CaseFAt TyAinda não há avaliações
- NCP LymphomaDocumento4 páginasNCP LymphomaRene John Francisco100% (2)
- NCPs For ParotidectomyDocumento8 páginasNCPs For ParotidectomyAcohCChao100% (1)
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasDocumento4 páginasNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Breast CancerDocumento1 páginaNursing Care Plan Breast CancerAhmed SalahAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired AdjustmentDocumento1 páginaNursing Care Plan Impaired Adjustmentderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For CamoxDocumento1 páginaNursing Care Plan For CamoxRolena Johnette B. PiñeroAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: Tetanus DateDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: Tetanus DateSheryl Ann Barit PedinesAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Pain Related To Inflammation of Tissues Secondary To AppendicitisDocumento2 páginasAcute Pain Related To Inflammation of Tissues Secondary To AppendicitisRachel SaavedraAinda não há avaliações
- Chiari - Frommel Syndrome - Sexual Dysfunction, Sexual Intercourse Discomfort & Loss of Sexual Desire Related To Dryness in The Vagina Secondary To Gal Actor RheaDocumento3 páginasChiari - Frommel Syndrome - Sexual Dysfunction, Sexual Intercourse Discomfort & Loss of Sexual Desire Related To Dryness in The Vagina Secondary To Gal Actor RheaLoord Vie Lu MondigoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Head InjuryDocumento3 páginasNCP Head InjuryAngel Mae Alsua100% (2)
- Discharge Plan For AppendicitisDocumento2 páginasDischarge Plan For Appendicitismclubert100% (3)
- FATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Documento4 páginasFATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Irene Grace BalcuevaAinda não há avaliações
- Doxofylline: D 400 MG TabletsDocumento33 páginasDoxofylline: D 400 MG TabletsBibek Singh Mahat100% (2)
- NCP CataractDocumento3 páginasNCP CataractKate ChavezAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocumento4 páginasNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternSeika SouiAinda não há avaliações
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento2 páginasImpaired Skin IntegrityBesael BaccolAinda não há avaliações
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDocumento6 páginasWord Ncp.......... TetanusaianrAinda não há avaliações
- NCP 2 and Soapie 1Documento5 páginasNCP 2 and Soapie 1narsD100% (1)
- NCP PancreatitisDocumento2 páginasNCP PancreatitisJeanelle Generoso100% (1)
- Tuano, Salma M. Bsn4-1 Acute PainDocumento2 páginasTuano, Salma M. Bsn4-1 Acute PainSALMA M. TUANOAinda não há avaliações
- Potts Disease NCP .. JustificationDocumento8 páginasPotts Disease NCP .. JustificationMicah SalesAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento5 páginasNursing Care Planruggero07100% (2)
- NCP - Acute Pain Stomach CancerDocumento2 páginasNCP - Acute Pain Stomach CancerJohn Michael TaylanAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Acute PainDocumento3 páginasNCP Acute PainDyanne BAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Cushing's SyndromeDocumento2 páginasNCP Cushing's SyndromeChristine LebicoAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Orthopedic Philipine CenterDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan Orthopedic Philipine CenterAnonymous NZTQVgjaAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento9 páginasNCPTracy Camille EscobarAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Acute PainDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan Acute PainAdelaine LorestoAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento5 páginasNursing Care PlanPaola Marie VenusAinda não há avaliações
- Fever Wound and Sprain NCPDocumento5 páginasFever Wound and Sprain NCProren100% (2)
- Assessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan NyaDocumento3 páginasAssessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan Nyaangel_pearl413100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeRozsy FakhrurAinda não há avaliações
- Prostatic CancerDocumento3 páginasProstatic CancerShakour El seifyAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing of Urinary System: Hema Malini, S.KP, MN, PHDDocumento4 páginasNursing of Urinary System: Hema Malini, S.KP, MN, PHDmutia ilhamAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Ventilation 8.2.17Documento41 páginasMechanical Ventilation 8.2.17SyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- Caring For Client With BurnsDocumento4 páginasCaring For Client With BurnsSyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 8 Common Hematological DisordersDocumento74 páginasLecture 8 Common Hematological DisordersSyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- Invitation Staff MGC13Documento3 páginasInvitation Staff MGC13SyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- Iium Kuantan 10km Run 2017Documento2 páginasIium Kuantan 10km Run 2017SyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- Other Profession For Diploma and Degree NursesDocumento2 páginasOther Profession For Diploma and Degree NursesSyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- CHECKLIST PREP 2015 "IIUM Kuantan 10 KM Run" Items Quantity: H2O Dispenser 3Documento1 páginaCHECKLIST PREP 2015 "IIUM Kuantan 10 KM Run" Items Quantity: H2O Dispenser 3SyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 3 Care of Pead ClientDocumento40 páginasLecture 3 Care of Pead ClientSyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- Stres ResponsesDocumento7 páginasStres ResponsesSyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- Midterm KEY 2014Documento12 páginasMidterm KEY 2014SyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- IIUM Academic Calendar 2015/2016Documento3 páginasIIUM Academic Calendar 2015/2016ZulaikhaEkaAinda não há avaliações
- Coping Strategies Geron (Aiman) (Aiman)Documento2 páginasCoping Strategies Geron (Aiman) (Aiman)SyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- Procedure 2 - Vaginal ExaminationDocumento2 páginasProcedure 2 - Vaginal ExaminationSyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- Group 5 ConstipationDocumento22 páginasGroup 5 ConstipationSyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- Wright State Final Version PDFDocumento8 páginasWright State Final Version PDFSyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- g3 Varicose Vein Nursing ManagementDocumento27 páginasg3 Varicose Vein Nursing ManagementSyafiqAzizi100% (2)
- Group 2Documento17 páginasGroup 2SyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- Group 6 Presentation Heartburn ObstetricDocumento21 páginasGroup 6 Presentation Heartburn ObstetricSyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- SOALANDocumento92 páginasSOALANSyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- Group 5 ConstipationDocumento22 páginasGroup 5 ConstipationSyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- Group 1 Oedema in PregancyDocumento11 páginasGroup 1 Oedema in PregancySyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- 1) Preparation & Technical and Security & Road MissionDocumento1 página1) Preparation & Technical and Security & Road MissionSyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- Group 1 Oedema in PregancyDocumento11 páginasGroup 1 Oedema in PregancySyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- SOALANDocumento92 páginasSOALANSyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- Bio StatDocumento3 páginasBio StatSyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- IIUM Academic Calendar 2015/2016Documento3 páginasIIUM Academic Calendar 2015/2016ZulaikhaEkaAinda não há avaliações
- 7/10/15 SR - Muzaitul Akma Mustapa Kamal Basha: Biostatistics NUR 3163Documento32 páginas7/10/15 SR - Muzaitul Akma Mustapa Kamal Basha: Biostatistics NUR 3163SyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- SOALANDocumento92 páginasSOALANSyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- Timetable Sem1year3 ColorDocumento1 páginaTimetable Sem1year3 ColorSyafiqAziziAinda não há avaliações
- WP-00068 HistoryDXADocumento4 páginasWP-00068 HistoryDXASehbaz SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Assisting in Patients Undergoing A ThoracentesisDocumento7 páginasAssisting in Patients Undergoing A Thoracentesiscoosa liquorsAinda não há avaliações
- The Aspects of Gene TherapyDocumento15 páginasThe Aspects of Gene TherapyLaleth Mendoza Ojales0% (1)
- RTI 17 Manual MOH R Central Ward-4Documento55 páginasRTI 17 Manual MOH R Central Ward-4SwarupaAinda não há avaliações
- Empanelled Hospital List MedicareDocumento608 páginasEmpanelled Hospital List Medicaresid mahalo100% (1)
- Post Term PregnancyDocumento22 páginasPost Term PregnancyDarianne HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Body Aches - 15 Possible CausesDocumento24 páginasBody Aches - 15 Possible Causesjbotha01Ainda não há avaliações
- Sample MCQ's of Bacteriology (MAC 221)Documento2 páginasSample MCQ's of Bacteriology (MAC 221)rajivkushwahAinda não há avaliações
- What Is The Metabolic Syndrome?Documento3 páginasWhat Is The Metabolic Syndrome?Yudha SavestilaAinda não há avaliações
- Week 3 TLE 101 Implementing and Monitoring Infection Control Policies and ProceduresDocumento3 páginasWeek 3 TLE 101 Implementing and Monitoring Infection Control Policies and ProceduresJoel Mamocod100% (1)
- MCC SaeDocumento98 páginasMCC SaeAllison100% (1)
- My New ThesisDocumento7 páginasMy New ThesisAlla Yeswanth Dilip KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Hyperthermia HIV NURSING CARE PLAN FLODocumento4 páginasHyperthermia HIV NURSING CARE PLAN FLOMicaela CrisostomoAinda não há avaliações
- Rita ProjectDocumento9 páginasRita ProjectRita GujarAinda não há avaliações
- Anemia, Acute Bronchitis and Adequate NutritionDocumento39 páginasAnemia, Acute Bronchitis and Adequate NutritionSetiawan DanuAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Vol22n15Documento65 páginasAdvanced Vol22n15Anderson Japa RibeiroAinda não há avaliações
- A Federal Type of Government Result inDocumento11 páginasA Federal Type of Government Result inIrene LetisiaAinda não há avaliações
- Maternal SepsisDocumento50 páginasMaternal SepsisMahmoud Abu Al AmrainAinda não há avaliações
- Code BlueDocumento18 páginasCode Blueandri100% (1)
- Rights of Sewage Workers InterviewDocumento8 páginasRights of Sewage Workers Interviewapi-541981758Ainda não há avaliações
- RotundaAmbulatoryHysteroscopyService at ConnollyHospitalDocumento34 páginasRotundaAmbulatoryHysteroscopyService at ConnollyHospitalAndreeaAinda não há avaliações
- Proposal For CSR Support of A Lifeline Express Project in The North-East or BiharDocumento13 páginasProposal For CSR Support of A Lifeline Express Project in The North-East or BiharSaurabh GuravAinda não há avaliações
- 3161 9711 1 SMDocumento3 páginas3161 9711 1 SMpuskesmas sidosermoAinda não há avaliações
- Hypertensive Emergency 3Documento45 páginasHypertensive Emergency 3saldy meirisandyAinda não há avaliações
- Joanne Marie Gomez ManaliliDocumento4 páginasJoanne Marie Gomez ManaliliJaira Marie Gomez Manalili100% (1)
- Emerging and Re-Emerging Disease in NepalDocumento25 páginasEmerging and Re-Emerging Disease in NepalBinayaAinda não há avaliações
- Health Optimizing Physical Education 1Documento22 páginasHealth Optimizing Physical Education 1Russel MejicoAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Related ProblemsDocumento25 páginasDrug Related ProblemsChristine GanAinda não há avaliações
- Session 4.1 Basic Concepts of Epidemiology: By: AS Ibrahim and NNH Mikhail, Ankara Cancer Epidemiology Course, April 2006Documento30 páginasSession 4.1 Basic Concepts of Epidemiology: By: AS Ibrahim and NNH Mikhail, Ankara Cancer Epidemiology Course, April 2006Benjamin PappuAinda não há avaliações
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocumento2 páginasCongenital Heart DiseaseZAY EMAinda não há avaliações