Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
MCQ Cardiology
Enviado por
vishaljairam100%(1)100% acharam este documento útil (1 voto)
924 visualizações2 páginasThe document contains 15 multiple choice questions related to cardiovascular physiology. Key points addressed in the questions include:
- The mechanism of action potential generation in the sinoatrial node.
- Pressure waves and events during the cardiac cycle such as the P wave, QRS complex, and heart sounds.
- Properties of the conducting system including the natural pacemaker and conduction pathways.
- Effects of the autonomic nervous system on the heart.
- Mechanisms that maintain arterial pressure following hemorrhage.
- Factors that decrease cardiac output such as hemorrhage.
- Events during the cardiac cycle including atrial and ventricular filling.
Descrição original:
Título original
Mcq Cardiology
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThe document contains 15 multiple choice questions related to cardiovascular physiology. Key points addressed in the questions include:
- The mechanism of action potential generation in the sinoatrial node.
- Pressure waves and events during the cardiac cycle such as the P wave, QRS complex, and heart sounds.
- Properties of the conducting system including the natural pacemaker and conduction pathways.
- Effects of the autonomic nervous system on the heart.
- Mechanisms that maintain arterial pressure following hemorrhage.
- Factors that decrease cardiac output such as hemorrhage.
- Events during the cardiac cycle including atrial and ventricular filling.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
100%(1)100% acharam este documento útil (1 voto)
924 visualizações2 páginasMCQ Cardiology
Enviado por
vishaljairamThe document contains 15 multiple choice questions related to cardiovascular physiology. Key points addressed in the questions include:
- The mechanism of action potential generation in the sinoatrial node.
- Pressure waves and events during the cardiac cycle such as the P wave, QRS complex, and heart sounds.
- Properties of the conducting system including the natural pacemaker and conduction pathways.
- Effects of the autonomic nervous system on the heart.
- Mechanisms that maintain arterial pressure following hemorrhage.
- Factors that decrease cardiac output such as hemorrhage.
- Events during the cardiac cycle including atrial and ventricular filling.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
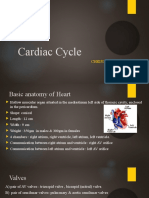
MCQ – CARDIOLOGY
Cardiovascular physiology MCQ S
Question 1: With respect to action potential in the sino-atrial node
F The resting membrane potential is more negative than for non-conducting
cardiac muscle
FDepolarisation is caused by activation of fast voltage gated sodium
channels
F There is dependence on vagal nerve stimulation for the generation of
action potentials
T Repolarisation is caused by increased potassium permeability
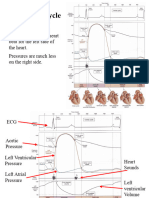
Question 2: During the cardiac cycle
F The T wave occurs after the end of ventricular contraction
T The a wave in the atrial pressure profile is caused by atrial contraction
F The c wave in the atrial pressure profile is caused by opening of the
atrio-ventricular valve
T The v wave in the atrial pressure profile is caused by venous return into the
Question 3: During the cardiac cycle
F Atrial contraction occurs during systole
T The P wave of the electrocardiogram represents atrial depolarisation
F The QRS complex represents ventricular repolarisation
F The T wave represents ventricular depolarisation
Question 4: Vasodilatation is caused by
F Increased pH
T Increased osmolarity
T Increased CO2 concentration
F Increased oxygen tension
Question 5: The following are associated with a decrease in cardiac output
F Increased blood volume
T Acute venous dilatation
T Venous obstruction
F Blood pressure of 160/100
Question 6: During the cardiac cycle
T The v wave in the atrial pressure profile is caused by venous return into the
atrium
T The notch in the aortic pressure profile is caused by closure of the aortic
valve
F The first heart sound is caused by opening of the atrio-ventricular valves
T The second heart sound is caused by closure of the aortic and pulmonary
Valves
Question 7: With respect to the conducting system of the heart
F The refractory period of the atrioventricular node is shorter than for normal
cardiac muscle fibres
F The sinoatrial node has an intrinsic rhythmic rate of 40-60 per minute
T The atrioventricular node has an intrinsic rhythmic rate of 40-60 per minute
T The Purkinje fibres have an intrinsic rhythmic rate of 15-40 per minute
Question 8: With respect to autonomic control of the heart
F Vagal stimulation has no effect on the rate of the rhythm of the sinoatrial
node
T Vagal stimulation decreases the excitability of the atrio-ventricular
junctional fibres
T Sympathetic stimulation increases the rate of the rhythm of the sinoatrial
node
F Sympathetic stimulation decreases the strength of myocardial contraction
Question 9: The following are important mechanisms in the short-term
maintenance of arterial pressure following haemorrhage
T Peripheral vasoconstriction
F Increased fluid retention by the kidneys
T Increased heart rate
F Increased venous return
Question 10: The following are produced locally in tissues and regulate
perfusion
T Prostaglandins
T Serotonin
F Adrenaline
F Noradrenaline
Question 11: With respect to the conducting system of the heart
T The sinoatrial node is the natural pacemaker
T Impulses are conducted from the sinoatrial node to the atrioventricular
node by three internodal pathways
F Impulses are conducted from the right atrium to the left atrium by the
Purkinje fibres
T There is a delay in the conduction of cardiac impulses at the atrioventricular
node
Question 12: During the cardiac cycle
F Pressure in the left ventricle must rise above 120mmHg to cause opening
of the aortic valve
F The period of rapid ejection occupies the first 70% of ventricular ejection
time
T The normal PR interval is about 0.16s
F The QT interval is the duration of ventricular relaxation
Question 13: Mean arterial pressure
T Is the average arterial pressure over a cardiac cycle
F Can be calculated from ½ (systolic minus diastolic pressure)
T Can be calculated from diastolic pressure + 1/3(pulse pressure)
F Can be calculated from the cardiac output X total peripheral resistance
Question 14: The following are associated with a decrease in cardiac output
F Pregnancy
F Anaemia
T Haemorrhage
F Hyperthyroidism
Question 15: During the cardiac cycle
F Blood flows into the atria only during atrial diastole
F Atrial contraction contributes 70% to ventricular filling
F Blood flows from the atria into the ventricles during systole
F Ventricular ejection occurs during the period of isometric contraction
Você também pode gostar
- Self-Assessment: BOFs for MRCP(UK) and MRCP(I) Part INo EverandSelf-Assessment: BOFs for MRCP(UK) and MRCP(I) Part IAinda não há avaliações
- Paper C 2019 With Key andDocumento28 páginasPaper C 2019 With Key andaizaz100% (1)
- L3,4-Cardiac Cycle Mcqs Fre, XBN.DDocumento7 páginasL3,4-Cardiac Cycle Mcqs Fre, XBN.DsajidAinda não há avaliações
- MCQDocumento20 páginasMCQAhmedabdo AbdoAinda não há avaliações
- Cvs MCQ Exam 2008Documento14 páginasCvs MCQ Exam 2008ZH. omg sarAinda não há avaliações
- MCQ CVS PDFDocumento22 páginasMCQ CVS PDFGovindaraju Subramani100% (1)
- Respiratory MCQDocumento3 páginasRespiratory MCQMarjina Khatoon NipuAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiology MCQDocumento7 páginasCardiology MCQNesma Adel100% (1)
- CVS MCQDocumento14 páginasCVS MCQNur Hamizah Md FuziAinda não há avaliações
- 04-CVS - Nader 6 2019+++++++Documento14 páginas04-CVS - Nader 6 2019+++++++Refan NajiAinda não há avaliações
- CVS MCQsDocumento21 páginasCVS MCQsMohammed Boyka100% (1)
- بنك الأسئلةDocumento775 páginasبنك الأسئلةسماح صلاح100% (1)
- Cardiology 2015-mcqsDocumento78 páginasCardiology 2015-mcqsAsif Newaz100% (1)
- CVS MCQsDocumento14 páginasCVS MCQsThana AlAnsari100% (2)
- MCQ On Cardiology IDocumento84 páginasMCQ On Cardiology IHarsh Oak50% (2)
- Quiz Cardiovascular Part 3 of 3Documento60 páginasQuiz Cardiovascular Part 3 of 3MedShare100% (7)
- Cardiology Mcq's Part - 1Documento31 páginasCardiology Mcq's Part - 1aymenAinda não há avaliações
- Cvs MCQDocumento52 páginasCvs MCQMiracle For NursesAinda não há avaliações
- A. Parasympathetic Stimulation of The HeartDocumento20 páginasA. Parasympathetic Stimulation of The HeartmuryumAinda não há avaliações
- CVS MCQDocumento11 páginasCVS MCQمصطفى حسن هاديAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiac Physiology MCQsDocumento13 páginasCardiac Physiology MCQsالعراقي الصامد100% (2)
- CardiologyDocumento29 páginasCardiologyVimal NishadAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz Cardiovascular Part 1 of 3Documento30 páginasQuiz Cardiovascular Part 1 of 3MedShare90% (10)
- Abdomen, Thorax, Embryology MCQsDocumento10 páginasAbdomen, Thorax, Embryology MCQsashok ashu100% (1)
- Respiration Physiology SEQs With KeyDocumento12 páginasRespiration Physiology SEQs With KeyMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- Path Cvs McqsDocumento33 páginasPath Cvs McqsShanzay KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Thorax ExamDocumento3 páginasThorax ExamMarera DomnicAinda não há avaliações
- CVS Trial ExamDocumento29 páginasCVS Trial ExamAssale Maen100% (1)
- CVS MCQsDocumento1 páginaCVS MCQsManisha JindalAinda não há avaliações
- Phys MCQDocumento21 páginasPhys MCQaerowong100% (2)
- MCQ RespiratoryDocumento6 páginasMCQ Respiratoryalemante100% (2)
- Hech MCQDocumento9 páginasHech MCQamol dahiphaleAinda não há avaliações
- MCQ CardioDocumento12 páginasMCQ CardioAhmed MahanaAinda não há avaliações
- Development of The Heart 'Mcq's and Note 'Documento3 páginasDevelopment of The Heart 'Mcq's and Note 'Florence BamigbolaAinda não há avaliações
- CARDIOVASDocumento18 páginasCARDIOVASVikash KushwahaAinda não há avaliações
- Blood MCQDocumento24 páginasBlood MCQBijay Kumar MahatoAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiology MCQsDocumento5 páginasCardiology MCQsTessa Neilson75% (4)
- Respiratory Medicine 151 200Documento31 páginasRespiratory Medicine 151 200Ahmed Kh. Abu Warda100% (2)
- MCQ IM DepDocumento183 páginasMCQ IM DepHesham A100% (3)
- 9 - Physiology MCQ of CardiovascularDocumento18 páginas9 - Physiology MCQ of CardiovascularMuhammad Javed GabaAinda não há avaliações
- XXX. MCQ Cardiovascular System Book 315-336Documento19 páginasXXX. MCQ Cardiovascular System Book 315-336Maria OnofreiAinda não há avaliações
- 012 CardiacDocumento41 páginas012 CardiacAhmed Zaghw100% (1)
- Quiz Cardiovascular Part 2 of 3Documento47 páginasQuiz Cardiovascular Part 2 of 3MedShare100% (8)
- 8th Finals McqsDocumento28 páginas8th Finals McqsMuhammad Uzair GujjarAinda não há avaliações
- Pharm Cvs McqsDocumento30 páginasPharm Cvs McqsSoodn Kang Soodn100% (3)
- Cardio MCQDocumento9 páginasCardio MCQtheonlymehul100% (2)
- MCQ RespiratoryDocumento6 páginasMCQ Respiratorynurulhudaabdulmuiez100% (2)
- Pathology Mcqs 2Documento6 páginasPathology Mcqs 2Numan Rox100% (5)
- Hemodynamics Practice QuestionsDocumento2 páginasHemodynamics Practice QuestionsMax HocksteinAinda não há avaliações
- Ganong Physiology Mcqs & SeqsDocumento193 páginasGanong Physiology Mcqs & SeqsRichardAinda não há avaliações
- Medicine Multiple Choise QuestionsDocumento61 páginasMedicine Multiple Choise QuestionsjuanmoraheAinda não há avaliações
- Rheumatic Fever - ICSDocumento17 páginasRheumatic Fever - ICSRachel SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory MCQsDocumento80 páginasRespiratory MCQsteenup9182% (11)
- Cardiovascular Physiology MCQsDocumento24 páginasCardiovascular Physiology MCQsKlarens Affana63% (8)
- MCQ Part 1 2005 "Example Questions"Documento3 páginasMCQ Part 1 2005 "Example Questions"RayC1977Ainda não há avaliações
- BLOOD MCQsDocumento27 páginasBLOOD MCQstyno Majon100% (3)
- Mcq-Heart Conducting SystemDocumento42 páginasMcq-Heart Conducting SystemDan BrightAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiac CycleDocumento31 páginasCardiac CycleAdwaitha KrAinda não há avaliações
- Cardaic DrugsDocumento57 páginasCardaic DrugsJyoti KathwalAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular Drugs - WsDocumento45 páginasCardiovascular Drugs - WsCowox Post PartumAinda não há avaliações
- Review and Update: Advanced Cardiac Life SupportDocumento55 páginasReview and Update: Advanced Cardiac Life SupportMartha Ullina TariganAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Management of Patients With Peripheral Vascular Disorders HypertensionDocumento17 páginasAssessment Management of Patients With Peripheral Vascular Disorders HypertensionJhosita Flora LarocoAinda não há avaliações
- The Physiologic Effects of Neuraxial BlocksDocumento5 páginasThe Physiologic Effects of Neuraxial BlocksSuresh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Syok NeurogenikDocumento12 páginasSyok NeurogenikFreddy PanjaitanAinda não há avaliações
- Unicare Product List (Oct. 2023)Documento3 páginasUnicare Product List (Oct. 2023)rizaie.azizuddin2022Ainda não há avaliações
- Myocardial Infraction ImprovedDocumento14 páginasMyocardial Infraction Improvedvikram yadavAinda não há avaliações
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocumento18 páginasNew Microsoft Word Documentapi-427712934Ainda não há avaliações
- Diabetes and Cardiovascular DiseaseDocumento119 páginasDiabetes and Cardiovascular DiseaseAlina PopaAinda não há avaliações
- Generic Name Brand Name Drug Class Mechanism of Action StructureDocumento4 páginasGeneric Name Brand Name Drug Class Mechanism of Action StructurenoelkiddoAinda não há avaliações
- ACUTE INFLAMMATION (Vascular Changes)Documento22 páginasACUTE INFLAMMATION (Vascular Changes)Ramesh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Pulmonary Hypertension: Annals of Internal MedicinetDocumento16 páginasPulmonary Hypertension: Annals of Internal MedicinetAlicia TGAinda não há avaliações
- T WaveDocumento15 páginasT WaveKay BristolAinda não há avaliações
- KMPLN Cara Menghitung RumusDocumento46 páginasKMPLN Cara Menghitung RumusLia SetiawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Adrenergic DrugsDocumento6 páginasAdrenergic DrugsbezaleeljonelAinda não há avaliações
- Common Problems in Cardiology (2016) (UnitedVRG)Documento332 páginasCommon Problems in Cardiology (2016) (UnitedVRG)Pisica ZmeuAinda não há avaliações
- The Golden Hour: Is The Time in Which Resuscitation of Severely Injured Patients Must Begin To Achieve Maximal SurviveDocumento17 páginasThe Golden Hour: Is The Time in Which Resuscitation of Severely Injured Patients Must Begin To Achieve Maximal SurviveJawahir SyahputraAinda não há avaliações
- Peripheral Arterial Blood Pressure Monitoring Adequately Tracks Central Arterial Blood Pressure in Critically Ill Patients An Observational StudyDocumento5 páginasPeripheral Arterial Blood Pressure Monitoring Adequately Tracks Central Arterial Blood Pressure in Critically Ill Patients An Observational StudyMARIANO ALEJANDRO MIGNINIAinda não há avaliações
- Fisiologi JantungDocumento30 páginasFisiologi JantungCecep Kurnia SAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiogenic ShockDocumento2 páginasCardiogenic ShockChristine QuironaAinda não há avaliações
- Icd 10Documento3 páginasIcd 10Ihsan Emille TheaAinda não há avaliações
- Contemporary Outcomes of Percutaneous Closure of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Adolescents and Adults PDFDocumento8 páginasContemporary Outcomes of Percutaneous Closure of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Adolescents and Adults PDFMuhammad IrfanAinda não há avaliações
- PQRST CapnografiaDocumento2 páginasPQRST CapnografiaFasta RamosAinda não há avaliações
- Pacemaker Timing & IntervalsDocumento124 páginasPacemaker Timing & IntervalsNiranjan Reddy100% (1)
- April 2021 - Pediatric Emergency CareDocumento128 páginasApril 2021 - Pediatric Emergency CareEdison Junior Juarez LaricoAinda não há avaliações
- Quick Reference GuideDocumento2 páginasQuick Reference GuideHoàng Anh NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- Daftar PustakaDocumento4 páginasDaftar PustakaDesi MardianiAinda não há avaliações
- Healing Touch Untuk KecemasanDocumento6 páginasHealing Touch Untuk KecemasanElvaAinda não há avaliações
- Wiggers Diagram SlidesDocumento15 páginasWiggers Diagram SlidesKuro ShiroAinda não há avaliações
- The Transport System IB Qq'sDocumento12 páginasThe Transport System IB Qq'sJohn OsborneAinda não há avaliações