Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Ship
Enviado por
Ashnee Sewock0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
29 visualizações3 páginasTítulo original
Ship.docx
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
29 visualizações3 páginasShip
Enviado por
Ashnee SewockDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 3
Name: Lekshmee Devi Sewock
Class: BOSHM/16B/FT
Module: Occupational Health
Module code: OSHM 1208
Lecturer: Dr. (Mrs.) J. Ramburn
Date Submitted: 15/03/17
Ship Breaking
Ship breaking is one among the most dangerous of occupations, with unacceptably
high levels of fatalities, injuries and work-related diseases. It is a difficult process
due to the structural complexity of the ships, and it generates many environmental
and safety and health hazards.
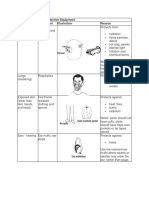
Workers usually lack personal protective equipment and have little training.
Inadequate safety controls, badly monitored work operations and high risk of
explosions create very dangerous work situations. Workers have very limited access
to health services and inadequate housing, welfare and sanitary facilities.
In addition, ship breaking is a highly polluting industry. Large amounts of toxic
substances (PVCs, mercury, lead, and sulfuric acid) not only intoxicate workers but
are also dumped into the soil and coastal waters. An average size ship contains up
to 7 tons of asbestos which is often sold in the local communities after scrapping. As
the majority of yards have no waste management systems or facilities to prevent
pollution, shipbreaking takes an enormous toll on the surrounding environment, the
local communities, fishery, agriculture, flora and fauna. This naturally causes
serious environmental damage with long-term effects for occupational, public and
environmental health.
The table below shows the hazards and the measures that must be taken to avoid
occupational accidents during the ship breaking process.
Hazards Actions & Preventions
Lack of PPE and training To ensure availability of PPE and
to train personnel
Exposure to asbestos fibres found Provide approved respirators/face
in hanger liners, mastic under shield/goggles
insulation, cloth over insulation,
cable, lagging and insulation on
pipes, especially through
inhalation.
Hazardous Materials Spills Provide spill kits containing
suitable material for spill
containment and cleanup.
Only fully qualified and properly
equipped personnel are allowed to
respond to hazardous material
spills.
Exposure to hazardous materials. These materials should be
segregated by substance and kept
separate to avoid any reaction
which may result in excessive
heat or fire.
Excess noiseassociated with Workers must be equipped
grinding, hammering and metal hearing protection such as ear
cutting muffs to avoid damaging their
ears.
Firefrom ignited insulation, Employers must have a written
matting, lagging, and residual fire watch policy that specifies the
fuel; and from lubricants and necessary training of workers,
other flammable liquids. their duties and personal
protective equipment (PPE) to be
used.
Provision of extinguishers, fire
hoses and standpipes, smoke
detectors, automatic sprinklers
and other fixed firefighting
systems
Injured when cutting metals Provision of sharp saw blades to
prevent malfunctions
Falls due to weakening of Wearing of safety harnesses and it
structures or sections during must be tied off when near open
continuous cutting holes and deck edges.
Você também pode gostar
- LP34 Personal Protective EquipmentDocumento2 páginasLP34 Personal Protective Equipmentglenn salandananAinda não há avaliações
- Plasma Cut Series: Operator ManualDocumento20 páginasPlasma Cut Series: Operator ManualprisilliawongAinda não há avaliações
- Personal Protection Elements For Mining: Sena Mining Center Supervision of Mining Works 811495Documento2 páginasPersonal Protection Elements For Mining: Sena Mining Center Supervision of Mining Works 811495NataliaVegaMolanoAinda não há avaliações
- Jasic MIG 200 Synergic MIG Welding Inverter Operation ManualDocumento18 páginasJasic MIG 200 Synergic MIG Welding Inverter Operation ManualFogarasiIstvánAinda não há avaliações
- Tig 200 Ac/Dc Analogseries: Operator ManualDocumento18 páginasTig 200 Ac/Dc Analogseries: Operator ManualAlejandro CKAinda não há avaliações
- Demo 1Documento27 páginasDemo 1Ferl Joy SedicolAinda não há avaliações
- Agri 7 Lesson 2.2 Personal Protective EquipmentDocumento20 páginasAgri 7 Lesson 2.2 Personal Protective EquipmentArianne Joy EsquivelAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 3 - Personal Protective EquipmentDocumento4 páginasLesson 3 - Personal Protective Equipmentmelanielampera17Ainda não há avaliações
- Occupational Health and Safety Procedure in Making Plastic BottlesDocumento9 páginasOccupational Health and Safety Procedure in Making Plastic Bottlesvworldpeace yanibAinda não há avaliações
- MIG Series: Operator ManualDocumento18 páginasMIG Series: Operator ManualAn VinhAinda não há avaliações
- Ppe-Guide - EnglishDocumento12 páginasPpe-Guide - EnglishUsman AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- PPE Match ActivityDocumento2 páginasPPE Match ActivityNicolas Andrés VargasAinda não há avaliações
- Adobe Scan 28 Mar 2022Documento24 páginasAdobe Scan 28 Mar 2022jyfthgrefdwsfghjAinda não há avaliações
- 7.PPE For Sanitation WorkersDocumento24 páginas7.PPE For Sanitation Workersvivek.sadevraAinda não há avaliações
- Personal Protective Equipment: Eye and Face Protection: Goggles, Safety Glasses or Face-Shields To Suit TheDocumento2 páginasPersonal Protective Equipment: Eye and Face Protection: Goggles, Safety Glasses or Face-Shields To Suit ThedeepakAinda não há avaliações
- TIG 200 Pulse AC/DC Mini Digital (JT-200DS)Documento32 páginasTIG 200 Pulse AC/DC Mini Digital (JT-200DS)bobisaAinda não há avaliações
- Safety Bulletin 31 SAFETY IN WELDING OR CUTTING (PART 1)Documento2 páginasSafety Bulletin 31 SAFETY IN WELDING OR CUTTING (PART 1)Trebor SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Eye and Face ProtectionDocumento2 páginasEye and Face Protectionhareesh.makesuAinda não há avaliações
- Ihom enDocumento3 páginasIhom enAkash Panchal 007Ainda não há avaliações
- Job Hazard AnalysisDocumento2 páginasJob Hazard AnalysisElisha JadormeoAinda não há avaliações
- Welding - Personal Protective Equipment Body Part Equipment Illustration ReasonDocumento3 páginasWelding - Personal Protective Equipment Body Part Equipment Illustration ReasonClark MercadoAinda não há avaliações
- Job Safety Analysis Worksheet: JGC Penthouse Extension BLDGDocumento2 páginasJob Safety Analysis Worksheet: JGC Penthouse Extension BLDGCherry BetonioAinda não há avaliações
- Samontina, Jeremiah John D - Activity #3 - PPEDocumento2 páginasSamontina, Jeremiah John D - Activity #3 - PPEjeremiah john samontinaAinda não há avaliações
- Safe Chemical HandlingDocumento23 páginasSafe Chemical HandlingUS KuntalAinda não há avaliações
- Ehs UvDocumento3 páginasEhs UvAdesh GurjarAinda não há avaliações
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Policy: PPE Requirements Used in These SituationsDocumento3 páginasPersonal Protective Equipment (PPE) Policy: PPE Requirements Used in These SituationsHelp Tubestar Crew100% (1)
- LE - Learning To Stick WeldDocumento36 páginasLE - Learning To Stick WeldDebye101Ainda não há avaliações
- Arc Ja140Documento19 páginasArc Ja140Александр ПанкратовAinda não há avaliações
- Addressed: DirigidoDocumento2 páginasAddressed: DirigidoAnonymous UEYVe55ZxAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation1 AutosavedDocumento18 páginasPresentation1 AutosavedMarissa MarianoAinda não há avaliações
- Precautions and Safe PracticesDocumento12 páginasPrecautions and Safe Practicesssmith2007Ainda não há avaliações
- HPCTTTTDocumento9 páginasHPCTTTTMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaAinda não há avaliações
- ENVIRONMENT & SUSTAINABILITY (Safety)Documento16 páginasENVIRONMENT & SUSTAINABILITY (Safety)nurul izzanyAinda não há avaliações
- Fact-Sheet-No.-41-Aug-2018 COMBUSTIBLE DUST HAZARDS IN THE WELDING AND CUTTING ENVIRONMENTDocumento3 páginasFact-Sheet-No.-41-Aug-2018 COMBUSTIBLE DUST HAZARDS IN THE WELDING AND CUTTING ENVIRONMENTCarlos BustamanteAinda não há avaliações
- Safety Reminders On Welding Practices: Group 2Documento26 páginasSafety Reminders On Welding Practices: Group 2Vinz Bryan AlmacenAinda não há avaliações
- fs33-201404 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) For Welding and CuttingDocumento4 páginasfs33-201404 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) For Welding and CuttingCarlos BustamanteAinda não há avaliações
- Safety Semis FinalsDocumento6 páginasSafety Semis FinalsMarvin Tan MaglinaoAinda não há avaliações
- Manual Del Operador - Alimetador NA-3Documento112 páginasManual Del Operador - Alimetador NA-3Edison Fernando CollaguazoAinda não há avaliações
- JSA New Line Installation 2012Documento2 páginasJSA New Line Installation 2012Deshbandhu Aman PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- MAXsa 10 ControllerDocumento52 páginasMAXsa 10 ControllerRiciu NickAinda não há avaliações
- PPE Training ModuleDocumento56 páginasPPE Training Modulehadeed shaikh100% (2)
- EPAS 8 Quarter 1 - Week 5-6Documento12 páginasEPAS 8 Quarter 1 - Week 5-6manolito mulatAinda não há avaliações
- Give One Example of A Personal Protective EquipmentDocumento1 páginaGive One Example of A Personal Protective EquipmentJoshua PincaAinda não há avaliações
- OM - VI 450 - Ltec - Power - Source - 15-099Documento28 páginasOM - VI 450 - Ltec - Power - Source - 15-099M. T. I. Ingenieria SASAinda não há avaliações
- TLE-EPAS Grade10 Q2 LAS5Documento3 páginasTLE-EPAS Grade10 Q2 LAS5JAMES HONRUBIAAinda não há avaliações
- IM279Documento58 páginasIM279mantenimiento steckerlAinda não há avaliações
- Manual SAE 400 G7Documento60 páginasManual SAE 400 G7america1591Ainda não há avaliações
- What Are Ppes? What Are Ppes?: Personal Protective Personal Protective Equipment Orientation Equipment OrientationDocumento16 páginasWhat Are Ppes? What Are Ppes?: Personal Protective Personal Protective Equipment Orientation Equipment OrientationKen FerrolinoAinda não há avaliações
- Physical HazardshhggDocumento3 páginasPhysical HazardshhggJhenard John Lansangan BeltranAinda não há avaliações
- Welding Safety: Amit Gola Assistant Director (Safety)Documento21 páginasWelding Safety: Amit Gola Assistant Director (Safety)Vishwash GoyalAinda não há avaliações
- Personal Protective Equipment (Ppe) : 3. Eye and Face ProtectionDocumento3 páginasPersonal Protective Equipment (Ppe) : 3. Eye and Face ProtectionMark DomingoAinda não há avaliações
- Job Hazard AnalysisDocumento1 páginaJob Hazard AnalysisArnold Roy Coballes ManaloAinda não há avaliações
- SWP-024 Usage of PPEDocumento5 páginasSWP-024 Usage of PPEadrianlim13Ainda não há avaliações
- M.Tech. AMC Lab ManualDocumento26 páginasM.Tech. AMC Lab ManualupenderAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 1: Safety Measures During Use and Preparation of Chemical SubstancesDocumento6 páginasExperiment 1: Safety Measures During Use and Preparation of Chemical SubstancesAliah AzizAinda não há avaliações
- Welding Safety - 2Documento1 páginaWelding Safety - 2kapsarcAinda não há avaliações
- SAFE USE GUIDE Submerged WeldingDocumento1 páginaSAFE USE GUIDE Submerged Weldingwealth osiobeAinda não há avaliações
- Safety Precautions in The LaboratoryDocumento6 páginasSafety Precautions in The LaboratoryDennis MuneneAinda não há avaliações
- Powerwave ManagerDocumento128 páginasPowerwave ManagerJackson Dias RochaAinda não há avaliações
- Workplace Vocabulary for Esl Students: With Exercises and TestsNo EverandWorkplace Vocabulary for Esl Students: With Exercises and TestsAinda não há avaliações
- Clena Floral Disinfectant MSDS - CERTDocumento5 páginasClena Floral Disinfectant MSDS - CERTcataztropherAinda não há avaliações
- Manual de Operador - Bucyrus - R30C PDFDocumento120 páginasManual de Operador - Bucyrus - R30C PDFPablo Maldonado100% (1)
- MSDS (NH4) 2c2o4Documento3 páginasMSDS (NH4) 2c2o4moazrilAinda não há avaliações
- Kera Tein NPNF (42-26EX) - MSDS - v1Documento4 páginasKera Tein NPNF (42-26EX) - MSDS - v1rafaeldelperu1982Ainda não há avaliações
- Lesson PlanDocumento10 páginasLesson Planmycoadante09Ainda não há avaliações
- GAV Gesipa ManualDocumento167 páginasGAV Gesipa Manual'Lampa'Ainda não há avaliações
- FDS Zinc Bromide Brine 20.5 PPGDocumento8 páginasFDS Zinc Bromide Brine 20.5 PPGnoe tellezAinda não há avaliações
- PMA SigmaDocumento6 páginasPMA SigmaCaerulus Fuad Abdul BaqiAinda não há avaliações
- MSDS BP Energol THB 46 PDFDocumento4 páginasMSDS BP Energol THB 46 PDFzaidan hadiAinda não há avaliações
- Crown Light CommissioningDocumento41 páginasCrown Light CommissioningAli AKAinda não há avaliações
- Material Safety Data SheetDocumento6 páginasMaterial Safety Data Sheetsehrish abidAinda não há avaliações
- 941112-001 Instal Q310 Rev4Documento72 páginas941112-001 Instal Q310 Rev4Sebin Kv0% (1)
- Paraffin MSDS: Section 1: Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDocumento5 páginasParaffin MSDS: Section 1: Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDevi M. Akliyah100% (1)
- Erythromycin Safety Data SheetDocumento5 páginasErythromycin Safety Data SheetsppAinda não há avaliações
- M05100028 200 KW Valve Recession (NGE 14 6 L) PDFDocumento17 páginasM05100028 200 KW Valve Recession (NGE 14 6 L) PDFManuel IzaquitaAinda não há avaliações
- Scaffolding Methodology-Skyrise 3A - 1Documento5 páginasScaffolding Methodology-Skyrise 3A - 1AdonisAinda não há avaliações
- Work Place SafetyDocumento21 páginasWork Place SafetyHitesh GulabaniAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 1: Before You Begin Determine Personal Support RequirementsDocumento20 páginasTopic 1: Before You Begin Determine Personal Support Requirementsdefa reyAinda não há avaliações
- Operating Manual Cleaning - General Safety InstructionsDocumento3 páginasOperating Manual Cleaning - General Safety InstructionsVitaliy SaparovAinda não há avaliações
- Revised Faryab Health and Safety Plan V2-ADB EditsDocumento40 páginasRevised Faryab Health and Safety Plan V2-ADB EditsZainullahAinda não há avaliações
- 0007 PpeDocumento66 páginas0007 PpeEGHAinda não há avaliações
- 1 (Hazard Analysis) For Earth Works Gurun Jsa G 001 Rev 002Documento3 páginas1 (Hazard Analysis) For Earth Works Gurun Jsa G 001 Rev 002nurul sarahAinda não há avaliações
- AnthropometryDocumento6 páginasAnthropometryNRheena NJane NSenidoAinda não há avaliações
- M - O3 - 6 Strruc STL ErctnDocumento30 páginasM - O3 - 6 Strruc STL ErctnalankrisherlpuAinda não há avaliações
- Manual Operador CAT529 PDFDocumento326 páginasManual Operador CAT529 PDFHeidi Cuevas VenegasAinda não há avaliações
- MelRhon Manila Elemi - MSDSDocumento6 páginasMelRhon Manila Elemi - MSDSantondegraciaAinda não há avaliações
- MN SVi1000 IOM GEA19527 RevFDocumento116 páginasMN SVi1000 IOM GEA19527 RevFMakiberAinda não há avaliações
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and The Company/UndertakingDocumento8 páginasSafety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and The Company/UndertakingA A OAinda não há avaliações
- COMPLIANCE in PHYSICS LABORATORYDocumento3 páginasCOMPLIANCE in PHYSICS LABORATORYReynan DulinayanAinda não há avaliações
- LaboratoryDocumento30 páginasLaboratoryAnggraghany Sanggrama WijayaAinda não há avaliações