Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Procedure For Films: Medicalmicrobiology
Enviado por
muthiajayanti0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
7 visualizações1 páginakkk
Título original
035927_img028
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentokkk
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
7 visualizações1 páginaProcedure For Films: Medicalmicrobiology
Enviado por
muthiajayantikkk
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
652 M E D I C A L M I C R O B I O L O GY Methylated spirit (64 O.P.) . . .
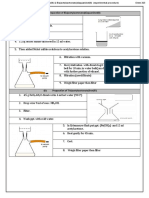
Procedure for films
These are made, dried and fixed in the usual manner. Ammonium oxalate, 1 per cent. in water .
(1)Stain with carbol gentian violet for 2-3 min. Z I E H L - N E E L S E N S TAI N 653
(2)Pour off stain, replace with Gram's iodine solution and allow to act for 1
mm. (2)Iodine solution Iodine . .
(3)Dry thoroughly by blotting. . 10 g.
. 20
(4)Decolourise with aniline-xylol, using several changes until the stain Potassium iodide . Distilled water . . 1000g.
ceases to be removed. ml.
Now examine at this stage under, the low power of the microscope; the (3)Liquor iodi fortis (BP)
nuclei of the pus cells should be of a pale-violet colour; if the nuclei are deeply Iodine . . . 10 g.
stained, then decolourisation is incomplete. . 6.
Potassium iodide . .
(5)Wash with several changes of xylol and dry. . 90 g ml. .
Methylated spirit (74 O.P.) . D istille d wa te r .
(6)Counterstain with dilute carbol fuchsin for 10-25 sec. Wash with . 10 ml. .
water and dry.
(4)Iodine-acetone. 35 ml. .
Procedure for sections Liquor iodi fortis Acetone .
965 ml.
Weigert's modification is specially recommended for the staining of (5)Dilute carbol fuchsin.
sections. . .
After removing the paraffin with xylol or benzol, treating with alcohol and Ziehl-Neelsen's (strong) carbol fuchsin (p. 654) 50 ml.
washing with water, counterstain first with carmalum for 10 min. and then Distilled water . . 950 ml.
proceed as above. After (5) the sections will be cleared and can at once be
mounted in Canada balsam or DPX. Procedure for films
(1)Cover slide with ammonium oxalate-crystal violet and allow to act for about
30 sec.
CLALTDIUS'S (1897) MODIFICATION OF GRAM'S METHOD (2)Pour off and wash freely with iodine solution . Cover with fresh
iodine solution and allow to act for about 30 sec.
(3)Pour off iodine solution and wash freely with iodine-acetone. Cover
(Counterstaining with picric acid) with fresh iodine-acetone and allow to act for about 30 sec.
(4)Wash thoroughly with water.
This method, which gives very pale, "transparent" counterstaining, is (5)Counterstain with dilute carbol fuchsin for about 30 sec.
recommended for the demonstration of fungi in tissue sections. (6)Wash with water, blot and dry.
(1)Stain with 1 per cent. aqueous methyl violet for 1-2 min. It is essential that the whole slide is flooded with each reagent in turn, and that
(2)Wash in water. the previous reagent is thoroughly removed at each step.
(3)Flood slide with a half-saturated watery solution of picric acid (i.e. 0.6 per
cent.). Cover slide with fresh picric acid and allow to act for 1-2 min.
(4)Remove excess picric acid solution with blotting paper.
(5)Decolourise with-Chloroform (or, preferably, aniline containing 0.1 per
cent. picric acid) until no more violet comes away in the decolouriser.
5 STAINING OF TUBERCLE AND OTHER ACID-FAST
BACILLI
(6)Rinse with xylol and mount in Canada balsam. 4. ZIEHL-NEELSEN METHOD
This method is a modification of Ehrlich's (1882) original method for the
differential staining of acid-fast bacilli with aniline-gentian violet followed by
PRESTON AND MORRELL'S (1962) MODIFICATION OF strong nitric acid. It incorporates improvements suggested, successively, by
Ziehl and Neelsen, and is described in a footnote in a paper by Johne (1885).
The ordinary aniline dye solutions do not readily penetrate the substance of
GRAM'S METHOD the tubercle bacillus and are therefore unsuitable for staining it. However, by
the use of a powerful staining solution that contains phenol, and the
(Decolourisation with iodine-acetone) application of heat, the dye can be made to penetrate the bacillus. Once
stained, the tubercle bacillus will withstand the action of powerful decolour ising
This method is recommended as giving reliable results without the need for agents for a considerable time and thus still retains the stain when everything
taking great care in adjusting the duration of decolourisation. else in the microscopic preparation has been decolourised.
The stain used consists of basic fuchsin, with phenol added. The dye is
Solutions required basic and its combination with a mineral acid produces a compound that is
(1) Ammonium oxalate-crystal violet. yellowish brown in colour and is readily dissolved out of all structures except
Crystal violet . . . . 20. acid-fast bacteria. Any strong acid can be used as a decolourising agent, but
. 200 g ml .
. 800 ml.
Você também pode gostar
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresNo EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Lesson-11 Staining Methods To Demonstrate Specialspecial TissueDocumento13 páginasLesson-11 Staining Methods To Demonstrate Specialspecial TissueSasa AbassAinda não há avaliações
- 44.1.16 AOAC of Fi Cial Method 906.03 in Vert Sugar in Sugars and SyrupsDocumento1 página44.1.16 AOAC of Fi Cial Method 906.03 in Vert Sugar in Sugars and Syrupsc2haAinda não há avaliações
- Gravimetric Determination ChlorideDocumento2 páginasGravimetric Determination ChlorideproferiveAinda não há avaliações
- Determination of Chloride Ion Concentration by GravimetryDocumento2 páginasDetermination of Chloride Ion Concentration by GravimetryMaam Jesecca JeckAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Hypochlorite in Bleach: Experiment 8Documento8 páginasAnalysis of Hypochlorite in Bleach: Experiment 8Nabilah HarisAinda não há avaliações
- SiO2 - MOLYBDOSILICIC ACID AND REDOX TITRATION OF MOLYBDENUM (III)Documento3 páginasSiO2 - MOLYBDOSILICIC ACID AND REDOX TITRATION OF MOLYBDENUM (III)Oscar BenimanaAinda não há avaliações
- Timms Staining ProtocolDocumento2 páginasTimms Staining ProtocolOLIVIA SANTAMARÍAAinda não há avaliações
- Ahmad Zakwan Bin Kassim - Lab 3 - CHM557Documento15 páginasAhmad Zakwan Bin Kassim - Lab 3 - CHM557Ahmad ZakwanAinda não há avaliações
- Titrimetric AnalysisDocumento3 páginasTitrimetric AnalysisKarthik BhatAinda não há avaliações
- Arsenic + AntimonyDocumento3 páginasArsenic + AntimonyTyroneAinda não há avaliações
- Bisacodyl Suppositories JPXVIIIDocumento2 páginasBisacodyl Suppositories JPXVIIITống Ái Linh NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- Iodoform: (Pilapil, Jean Diane Rose T.)Documento6 páginasIodoform: (Pilapil, Jean Diane Rose T.)Rashid KanetsaAinda não há avaliações
- Colour of Starch-Iodine Complex As Index of Retrogradability of Starch PastesDocumento5 páginasColour of Starch-Iodine Complex As Index of Retrogradability of Starch PastesSheni OgunmolaAinda não há avaliações
- Histamine PhosphateDocumento1 páginaHistamine Phosphategrace_febiantyAinda não há avaliações
- EtchingDocumento1 páginaEtchingSARSAN NDTAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Matters Textbook Answers Chapter 3Documento3 páginasChemistry Matters Textbook Answers Chapter 3MahamIsmail93% (15)
- Lab 9-4-Determination of Iodine Value of Oils and FatsDocumento3 páginasLab 9-4-Determination of Iodine Value of Oils and FatsDũng Nguyễn ViệtAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 6.2: Sample Potash FesoDocumento4 páginasExperiment 6.2: Sample Potash FesoShivam GusainAinda não há avaliações
- Bisacodyl-JP XVIIDocumento2 páginasBisacodyl-JP XVIITống Ái Linh NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- Separation of Antimony (Ii1) With Iodide andDocumento8 páginasSeparation of Antimony (Ii1) With Iodide andWi FuentesAinda não há avaliações
- The Case Study of Isothermal Adsorption of Phenol, O-Cresol On Natural Charcoal's and ApplicationsDocumento16 páginasThe Case Study of Isothermal Adsorption of Phenol, O-Cresol On Natural Charcoal's and ApplicationsIJRASETPublicationsAinda não há avaliações
- 3 - Gram StainingDocumento38 páginas3 - Gram StainingsummiyaAinda não há avaliações
- TUTORIAL SEPT 2021 (Combined) ChemDocumento44 páginasTUTORIAL SEPT 2021 (Combined) Chemmohamed magdyAinda não há avaliações
- Powdered Cellulose CodexDocumento2 páginasPowdered Cellulose CodexCarlo TierraAinda não há avaliações
- Blue Printing PDFDocumento3 páginasBlue Printing PDFanjuAinda não há avaliações
- Aoac 906.03 PDFDocumento2 páginasAoac 906.03 PDFAngie Cerinza AcostaAinda não há avaliações
- AOCS CD 1b-87Documento3 páginasAOCS CD 1b-87Luigi Avicenna100% (3)
- Chemistry Viva VoceDocumento12 páginasChemistry Viva VoceLight YagamiAinda não há avaliações
- Surface Preparation of MetalsDocumento24 páginasSurface Preparation of MetalsMilton EncaladaAinda não há avaliações
- Determination of Chemical Formulae: The Reaction of Zinc and IodineDocumento8 páginasDetermination of Chemical Formulae: The Reaction of Zinc and IodineJoseph LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Camposano, Airriel A. Week 7 12-Stem-C. Bernido Ms. Eds MatreoDocumento3 páginasCamposano, Airriel A. Week 7 12-Stem-C. Bernido Ms. Eds MatreoHAKDOWGAinda não há avaliações
- Iodine Value of Fats and Oils Cyclohexane-Acetic Acid MethodDocumento3 páginasIodine Value of Fats and Oils Cyclohexane-Acetic Acid MethodNovianto Nugroho100% (2)
- Iodine Value Aocs CD 1d-92Documento3 páginasIodine Value Aocs CD 1d-92Wynona Basilio75% (4)
- Aocs Method CD 1d-92 Índice Iodo (Ciclohexano-Acido Acético)Documento3 páginasAocs Method CD 1d-92 Índice Iodo (Ciclohexano-Acido Acético)JulianaAinda não há avaliações
- (I) Preparation of Bis (Acetylacetonato) Diaquanickel (II)Documento1 página(I) Preparation of Bis (Acetylacetonato) Diaquanickel (II)Nosayba M AlomariAinda não há avaliações
- Additive 151Documento2 páginasAdditive 151giorAinda não há avaliações
- Ibuprofen JP XVIDocumento1 páginaIbuprofen JP XVIcamilo.carrilloAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Hill ReactionDocumento5 páginas7 Hill ReactionMagnus JordanAinda não há avaliações
- Title of Experiment-1Documento6 páginasTitle of Experiment-1Utari Ika CahyaniAinda não há avaliações
- Ferrous Glycinate (Processed With Citric Acid) : SynonymsDocumento3 páginasFerrous Glycinate (Processed With Citric Acid) : SynonymsIfra AkhlaqAinda não há avaliações
- Appendix A Appendix A Standard Solutions and Reference Materials PDFDocumento8 páginasAppendix A Appendix A Standard Solutions and Reference Materials PDFFiorella MeoñoAinda não há avaliações
- Silica, Calorimetric, Molybd'ate Blue: 1. ApplicationDocumento2 páginasSilica, Calorimetric, Molybd'ate Blue: 1. ApplicationLượng Nguyễn VănAinda não há avaliações
- Kelm 203Documento8 páginasKelm 203Shantanu GhoshAinda não há avaliações
- Is 12308-7 - 1991 - 3Documento1 páginaIs 12308-7 - 1991 - 3Svapnesh ParikhAinda não há avaliações
- DR Davids Additional Chemistry Practical Work IDocumento79 páginasDR Davids Additional Chemistry Practical Work Iamr ahmed0% (1)
- Iron Content in FoodsDocumento5 páginasIron Content in FoodsPatrick Quiroz MorenoAinda não há avaliações
- Green Crystal LabDocumento16 páginasGreen Crystal LabRagingfist71Ainda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Practical FileDocumento26 páginasChemistry Practical FileAyushAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 62 Structured QuestionsDocumento23 páginasChapter 62 Structured QuestionsytAinda não há avaliações
- Separation and Purification of Organic CompoundsDocumento3 páginasSeparation and Purification of Organic CompoundsDonutHoshimiAinda não há avaliações
- Written ReportDocumento5 páginasWritten ReportHope CariñoAinda não há avaliações
- Farmacopea Japonesa 2021 4Documento237 páginasFarmacopea Japonesa 2021 4gerardoAinda não há avaliações
- 9362 Ifuhs303reticulinstainpackv16Documento2 páginas9362 Ifuhs303reticulinstainpackv16TanupreetAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment - 01: Engineering Chemistry - Laboratory ManualDocumento2 páginasExperiment - 01: Engineering Chemistry - Laboratory ManualDibyanshu AnandAinda não há avaliações
- CHEM 232 - Experiment No. 1 Spring 2018-2019Documento2 páginasCHEM 232 - Experiment No. 1 Spring 2018-2019Mohyeddine K. El SayedAinda não há avaliações
- Aluminium Ammonium Sulfate Fao CriteriaDocumento2 páginasAluminium Ammonium Sulfate Fao CriteriaVictor Hugo HinojosaAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal Percobaan Manufacture of Cis and Trans-Potassium Dioxalatodiacochromat (III)Documento3 páginasJurnal Percobaan Manufacture of Cis and Trans-Potassium Dioxalatodiacochromat (III)AnnisaAinda não há avaliações
- Jawaban Pretest Board VirusDocumento10 páginasJawaban Pretest Board VirusmuthiajayantiAinda não há avaliações
- Soal Pretest AnaerobDocumento4 páginasSoal Pretest AnaerobmuthiajayantiAinda não há avaliações
- Nyanyian PPT KulitDocumento6 páginasNyanyian PPT KulitmuthiajayantiAinda não há avaliações
- Nama Tanda Tangan: NO NO. StambukDocumento2 páginasNama Tanda Tangan: NO NO. StambukmuthiajayantiAinda não há avaliações
- 2018 Kuliah Absen - FIXDocumento3 páginas2018 Kuliah Absen - FIXmuthiajayantiAinda não há avaliações
- Img023Documento1 páginaImg023muthiajayantiAinda não há avaliações
- Ug Bact ExDocumento13 páginasUg Bact ExmuthiajayantiAinda não há avaliações
- 2016 Article 791 PDFDocumento24 páginas2016 Article 791 PDFmuthiajayantiAinda não há avaliações
- Daftar PustakaDocumento2 páginasDaftar PustakamuthiajayantiAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan in Advanced Chemistry AlcohoDocumento17 páginasLesson Plan in Advanced Chemistry AlcohoGlaiza Mapute CaringalAinda não há avaliações
- GPRSDocumento6 páginasGPRSRoberto CapchaAinda não há avaliações
- 5MF 10MFDocumento8 páginas5MF 10MFRodrigo Pessoa VespaAinda não há avaliações
- TIAC TechnologyDocumento13 páginasTIAC TechnologyPaul SunnyAinda não há avaliações
- Ets InternacionalDocumento72 páginasEts InternacionalRicardo MarquesAinda não há avaliações
- List of Accredited List of Accredited EIA Consultant Organizations (As On March 05, 2015) Organizations - 170Documento135 páginasList of Accredited List of Accredited EIA Consultant Organizations (As On March 05, 2015) Organizations - 170santhoshneo02@gmail.comAinda não há avaliações
- Solutios, Solutions of Non Electrolyte - 2019-2020 v2Documento80 páginasSolutios, Solutions of Non Electrolyte - 2019-2020 v2hazo hazAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment - CEP-534 - Team 04 PDFDocumento16 páginasAssignment - CEP-534 - Team 04 PDFshowravAinda não há avaliações
- Self-Operated Temperature Regulators Temperature Regulator Type 1Documento6 páginasSelf-Operated Temperature Regulators Temperature Regulator Type 1Pocola AdrianAinda não há avaliações
- Anti-Aromatase Activity of Phytochemicals in White Button Mushrooms (Agaricus Bisporus)Documento10 páginasAnti-Aromatase Activity of Phytochemicals in White Button Mushrooms (Agaricus Bisporus)Nimra Naveed ShaikhAinda não há avaliações
- BR Int LD Id Inspiration 55-70plusDocumento11 páginasBR Int LD Id Inspiration 55-70plustarkett tAinda não há avaliações
- Shades Eq Gloss Large Shade ChartDocumento2 páginasShades Eq Gloss Large Shade ChartmeganAinda não há avaliações
- Oxidation and Reduction Reactions in Organic ChemistryDocumento9 páginasOxidation and Reduction Reactions in Organic ChemistryTarun Lfc Gerrard100% (1)
- 905 3SDocumento4 páginas905 3SyasafyAinda não há avaliações
- ChE461-Course Outline and Teaching ScheduleDocumento2 páginasChE461-Course Outline and Teaching ScheduleAl JawadAinda não há avaliações
- Arihant 41 Years Chemistry (Crackjee - Xyz)Documento497 páginasArihant 41 Years Chemistry (Crackjee - Xyz)KaushikAinda não há avaliações
- Koerner. On The Creep GeosynteticDocumento6 páginasKoerner. On The Creep GeosynteticSergio Xexo Gonzalez RuizAinda não há avaliações
- 931 PDF PDFDocumento4 páginas931 PDF PDFChintamani VeerrajuAinda não há avaliações
- Borehole ProblemsDocumento10 páginasBorehole ProblemsMuh Andika Pratama WarisAinda não há avaliações
- Latihan Industri UiTM PDFDocumento28 páginasLatihan Industri UiTM PDFzzAinda não há avaliações
- Agave Biotechnology An OverviewDocumento15 páginasAgave Biotechnology An Overviewadrian perezAinda não há avaliações
- 自來水管埋設工程施說明書Documento187 páginas自來水管埋設工程施說明書富山Ainda não há avaliações
- Embuild BrochureDocumento38 páginasEmbuild BrochureKawish TamourAinda não há avaliações
- NuclearDocumento10 páginasNuclearUsman MunirAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocumento31 páginasBasic Concepts of ChemistryMohammadHussainKhan100% (1)
- Welding Technology NotesDocumento89 páginasWelding Technology NotesSanjay JangraAinda não há avaliações
- Paper 1Documento295 páginasPaper 1Shreyas TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- Identification of CarbohydratesDocumento2 páginasIdentification of CarbohydratesChristine Pearl Po0% (2)
- Nesrine-2021-2016 P4 QPDocumento686 páginasNesrine-2021-2016 P4 QPMostafa HaithamAinda não há avaliações
- Hot Work PermitDocumento2 páginasHot Work PermitRex UrbiztondoAinda não há avaliações
- ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideNo EverandICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideAndrew TeasdaleAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeNo EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (14)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincNo EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (137)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingNo EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (10)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsNo EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (3)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeNo EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodNo EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (20)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactNo EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (5)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeNo EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionNo EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (3)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeNo EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (90)
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsNo EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (1)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideAinda não há avaliações
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeAinda não há avaliações
- The Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesNo EverandThe Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesAinda não há avaliações
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactNo EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsAinda não há avaliações
- Essential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid DosagesNo EverandEssential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid DosagesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- Chemistry All-in-One For Dummies (+ Chapter Quizzes Online)No EverandChemistry All-in-One For Dummies (+ Chapter Quizzes Online)Ainda não há avaliações
- The Billion-Dollar Molecule: The Quest for the Perfect DrugNo EverandThe Billion-Dollar Molecule: The Quest for the Perfect DrugNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeNo EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (4)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolAinda não há avaliações