Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
New TSN Diarra Osi Layers in Automotive Networks 0313 v01
Enviado por
rahairiTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
New TSN Diarra Osi Layers in Automotive Networks 0313 v01
Enviado por
rahairiDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
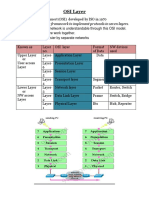
OSI Layers in Automotive Networks
OSI Layers in Automotive Networks
2013-03-20
IEEE 802.1 Plenary Meeting - Orlando
Aboubacar Diarra, Robert Bosch GmbH
1 2013-03-20 - IEEE 802.1 Plenary Meeting - Orlando
OSI Layers in Automotive Networks
Outline
OSI Reference Model
Simplified generic Architecture for Automotive Serial Busses
Basic Automotive E/E Architecture
Automotive Bus Systems in the OSI Model
Ethernet Impact on Automotive Bus Layering
2 2013-03-20 - IEEE 802.1 Plenary Meeting - Orlando
OSI Layers in Automotive Networks
OSI Reference Model
ECU 1 ECU 2
Application A
Data Application B
Application Protocol
7 Application 7 Application
6 Presentation 3 relevant Layers for 6 Presentation
5 Session Automotive Control Data 5 Session
Communication with Area
4 Transport Busses: Layers 1, 2 and 7 4 Transport
3 Network 3 Network
Communication Protocol
2 Data Link 2 Data Link
Bit Transmission Protocol
1 Physical 1 Physical
Transmission Medium
3 2013-03-20 - IEEE 802.1 Plenary Meeting - Orlando
OSI Layers in Automotive Networks
Simplified generic Architecture for Automotive
Serial Busses
Bus Node Bus Node
Application Application Layer 7
Communication Communication
Communication Communication
Controller Communication Protocol Controller Layer 1, 2
Transceiver Physical Layer Definition Transceiver
Layer 1
BUS
4 2013-03-20 - IEEE 802.1 Plenary Meeting - Orlando
OSI Layers in Automotive Networks
Basic Automotive E/E Architecture
Diagnosis
over CAN
Layer 4 *
Central
Gateway
CAN FlexRay
MOST
LIN
High
speed
CAN
Layer 1, 2, 4* Layer 1, 2, 4* Layer 1, 2, 4* Layer 1 to 7
* Layer 4 is used in this case for Diagnosis Services
5 2013-03-20 - IEEE 802.1 Plenary Meeting - Orlando
OSI Layers in Automotive Networks
Automotive Bus Systems in the OSI Model:
Example of the CAN Bus
Logical Link Control (LLC)
Acceptance Filtering
7 Application Overload Notification
Recovery Management
6 Presentation Medium Access control(MAC)
Data Encapsulation/Decapsulation
Frame Coding
5 Session
Error Detection/Signaling/Handling
4 Transport
Physical Signaling (PLS)
3 Network Bit Encoding/Decoding
Bit Time Synchronization
2 Data Link Physical Medium attachment(PMA)
Driver/Receiver Characteristics
Media Dependant Interface(MDI)
1 Physical Connectors
6 2013-03-20 - IEEE 802.1 Plenary Meeting - Orlando
OSI Layers in Automotive Networks
Automotive Bus Systems in the OSI Model:
Example of the FlexRay Bus
7 Application
Logical Link Control (LLC)
6 Presentation Protocol Operation Control
Medium Access control(MAC)
Message Framing
5 Session
Communication Cycle
4 Transport
Physical Signaling (PLS)
3 Network Bit Encoding/Decoding
Bit Time Synchronization
2 Data Link Physical Medium attachment(PMA)
Driver/Receiver Characteristics
Media Dependant Interface(MDI)
1 Physical Connectors
7 2013-03-20 - IEEE 802.1 Plenary Meeting - Orlando
OSI Layers in Automotive Networks
Automotive Bus Systems in the OSI Model:
Example of the MOST Bus
7 Application Application Programming Interface
6 Presentation Netservices Layer 2
5 Session
4 Transport
Netservices Layer 1
3 Network
2 Data Link MOST Transceiver
1 Physical Electrical PHY, FOTs Connectors and Plastic Fiber
8 2013-03-20 - IEEE 802.1 Plenary Meeting - Orlando
OSI Layers in Automotive Networks
Ethernet Impact on Automotive Bus Layering:
Example of On-Board Communication *
Remark:
Central Layer 3 and 4 can be
Gateway solicited for Car2X
Communication
Applications.
Switch
CAN FlexRay
LIN
High
speed
CAN
Ethernet
Layer 2
* Excepted On-Board Diagnosis (OBD)
which needs a Layer 4 support
9 2013-03-20 - IEEE 802.1 Plenary Meeting - Orlando
OSI Layers in Automotive Networks
Ethernet Impact on Automotive Bus Layering:
Example of Off-Board Communication
Diagnosis
Layer 3 / 4 over IP (DoIP)
Central
Gateway
Switch
CAN FlexRay
LIN
High
speed
CAN
Ethernet
Layer 3 / 4
Layer 4
10 2013-03-20 - IEEE 802.1 Plenary Meeting - Orlando
OSI Layers in Automotive Networks
Conclusion(1)
In reference to the OSI Data Communication Model, the Serial Interface
of CAN, FlexRay and LIN Busses typically needs 3 OSI Layers for On-
Board Communication excepted OBD: the Physical Layer, the Data
Link Layer and the Application Layer
The MOST Bus covers all the 7 OSI Layers for On-Board Communication
The Transport Layer is used for Off-Board Communication like
Diagnosis and also for OBD on these typical Automotive Area Networks.
The Layers 3 and 4 can be used for Vehicle On-Board Communication in
Car2X Communication Applications
11 2013-03-20 - IEEE 802.1 Plenary Meeting - Orlando
OSI Layers in Automotive Networks
Conclusion(2)
Therefore, for a Control Data Communication that occurs in an In-
vehicle closed Network, the need of the Layer 2 is justified.
On top of that, Layer 3 Routing Processes require more infrastructure
(eg. IP stack implementation, software implementation, memory need . .
.) and costs investments than Layer 2 solutions from an Automotive
Perspective
For In-vehicle Control Applications which require a very low Latency, a
Layer 2 solution is more pragmatic than a Layer 3 solution
However, Diagnosis over IP, Car2X and In-Car Wireless Communication
Applications need Layer 3 Routing Support
12 2013-03-20 - IEEE 802.1 Plenary Meeting - Orlando
OSI Layers in Automotive Networks
Thank You for your Attention
13 2013-03-20 - IEEE 802.1 Plenary Meeting - Orlando
Você também pode gostar
- Layer Encapsulation Devices or Components Keywords/DescriptionDocumento32 páginasLayer Encapsulation Devices or Components Keywords/DescriptionPranjal BarmanAinda não há avaliações
- Table - Osi and TCP - Ip ModelDocumento2 páginasTable - Osi and TCP - Ip ModelrskpsnaAinda não há avaliações
- Networking Market PrimerDocumento34 páginasNetworking Market Primercalypso_riAinda não há avaliações
- Ethernet Framing: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDDocumento20 páginasEthernet Framing: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDBahzadAinda não há avaliações
- 202 Networking ConceptsDocumento28 páginas202 Networking ConceptsVinay AroraAinda não há avaliações
- Networking Concepts and HardwareDocumento28 páginasNetworking Concepts and HardwareOrlando FelixAinda não há avaliações
- Networking DevicesDocumento4 páginasNetworking DevicesV VizAinda não há avaliações
- OSI Mode1Documento1 páginaOSI Mode1bushemmyAinda não há avaliações
- HCNA-HNTD V2.2 Training Material Ethernet FramingDocumento20 páginasHCNA-HNTD V2.2 Training Material Ethernet Framingmntesnot erkuAinda não há avaliações
- HC110110002 Ethernet FramingDocumento20 páginasHC110110002 Ethernet FramingjscansinoAinda não há avaliações
- Ethernet Framing: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDDocumento20 páginasEthernet Framing: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDmangla\Ainda não há avaliações
- 02 Ethernet FramingDocumento20 páginas02 Ethernet FramingPatrick WéryAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture OSI ModelDocumento4 páginasLecture OSI ModelShahzad AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- Ccna2 1Documento54 páginasCcna2 1Alok SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- HC110110002 Ethernet FramingDocumento20 páginasHC110110002 Ethernet Framingvince stacksAinda não há avaliações
- TCP Packet Encapsulation - DrawioDocumento1 páginaTCP Packet Encapsulation - DrawioparkallenbachAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 - OSI Model: ApplicationDocumento2 páginasChapter 2 - OSI Model: ApplicationKlokanAinda não há avaliações
- Segment Routing Technology and Use Cases: Alberto Donzelli 6 Nov 2018Documento30 páginasSegment Routing Technology and Use Cases: Alberto Donzelli 6 Nov 2018Anonymous NIkO5EI6Ainda não há avaliações
- Lecture 5 Transport (Compatibility Mode)Documento12 páginasLecture 5 Transport (Compatibility Mode)masih65Ainda não há avaliações
- This Study Resource WasDocumento5 páginasThis Study Resource WasJohn Lloyd A. CortezAinda não há avaliações
- 2.1.HC110110002 Ethernet FramingDocumento20 páginas2.1.HC110110002 Ethernet FramingStavros T.Ainda não há avaliações
- OSI and TCP/IP Networking Models ExplainedDocumento42 páginasOSI and TCP/IP Networking Models ExplainedSuds NariAinda não há avaliações
- Multiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...No EverandMultiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...Ainda não há avaliações
- 04 Data Link LayerDocumento118 páginas04 Data Link LayerLuận QuangAinda não há avaliações
- ASEAN IP Slide IPNetworkingV2.0Documento139 páginasASEAN IP Slide IPNetworkingV2.0Mg PoneAinda não há avaliações
- OSI Model Data Unit Layer Function: ApplicationDocumento6 páginasOSI Model Data Unit Layer Function: ApplicationSanyam JainAinda não há avaliações
- 103 Basic Network ConceptsDocumento46 páginas103 Basic Network ConceptslewalewaAinda não há avaliações
- CH 11Documento35 páginasCH 11abdalazeez shahateetAinda não há avaliações
- 2 - CCNA 200-301 # OSI and TCP-IP #Documento55 páginas2 - CCNA 200-301 # OSI and TCP-IP #ahmedabdelkareem191998Ainda não há avaliações
- OSI LayerDocumento4 páginasOSI LayerZuhairAhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 2-Network Reference ModelsDocumento29 páginasTopic 2-Network Reference Modelssamuel amareAinda não há avaliações
- osi-tcp cskDocumento28 páginasosi-tcp cskAngamuthuAinda não há avaliações
- 1.OSI Model Interview Questions and Answers (CCNA) - Networker InterviewDocumento5 páginas1.OSI Model Interview Questions and Answers (CCNA) - Networker InterviewSachin GudaAinda não há avaliações
- WK6 Lecture PTC Model PDFDocumento19 páginasWK6 Lecture PTC Model PDFStephen AdingoAinda não há avaliações
- OSI Model Explained for Networking BeginnersDocumento35 páginasOSI Model Explained for Networking BeginnersZaimeth ArqueroAinda não há avaliações
- CT1e 02 Standardization BodiesDocumento9 páginasCT1e 02 Standardization BodiesAmir ShahaniAinda não há avaliações
- Discuss The TCP/IP Model Into The World of TCP/IP Networking and Compare It With OSI ModelDocumento8 páginasDiscuss The TCP/IP Model Into The World of TCP/IP Networking and Compare It With OSI ModelInnocentAinda não há avaliações
- Zigbee Ex 1Documento15 páginasZigbee Ex 1Nene D TiAinda não há avaliações
- CN Lecture 11,12Documento73 páginasCN Lecture 11,12AMNA NAVEEDAinda não há avaliações
- Data Communication Theory: Wireless Case & Training DepartmentDocumento70 páginasData Communication Theory: Wireless Case & Training DepartmentChuks Etoh100% (1)
- The IP QoSDocumento56 páginasThe IP QoSHoney CharnaliaAinda não há avaliações
- New Structure in Deregulated EnvironmentDocumento98 páginasNew Structure in Deregulated EnvironmentIlaiyaa RajaAinda não há avaliações
- OSI Transport Layer: Network Fundamentals - Chapter 4Documento30 páginasOSI Transport Layer: Network Fundamentals - Chapter 4fun kollaAinda não há avaliações
- Data and Computer Communications LAN OverviewDocumento42 páginasData and Computer Communications LAN OverviewAngie Gaid TayrosAinda não há avaliações
- System and Network Administration Network EssentialsDocumento45 páginasSystem and Network Administration Network EssentialsArsalan JahaniAinda não há avaliações
- Patent Issues During IEEE Standards DevelopmentDocumento15 páginasPatent Issues During IEEE Standards DevelopmentIng. Armando OlveraAinda não há avaliações
- Week 1Documento149 páginasWeek 1gojan39660Ainda não há avaliações
- OSI Model & TCP/IP Layers ExplainedDocumento22 páginasOSI Model & TCP/IP Layers ExplainedADE SATRIOWIRAWANAinda não há avaliações
- OSI Model & TCP/IP ExplainedDocumento30 páginasOSI Model & TCP/IP ExplainedIng. Armando OlveraAinda não há avaliações
- The OSI Model & TCP/IP ModelDocumento19 páginasThe OSI Model & TCP/IP ModelJamaludin AfghanAinda não há avaliações
- OSI ModelDocumento23 páginasOSI ModelAmna ikhlaqAinda não há avaliações
- Supervisory Control & Data Acquisition: Communication TechnologyDocumento65 páginasSupervisory Control & Data Acquisition: Communication Technologyant7dotcomAinda não há avaliações
- Notes (EEE-D2) IoT Chapter-I (Part-2)Documento9 páginasNotes (EEE-D2) IoT Chapter-I (Part-2)116-Sravan KumarAinda não há avaliações
- OSI & TCP - IP ModelDocumento3 páginasOSI & TCP - IP ModelTamerlan MirzayevAinda não há avaliações
- ZigBee and IEEE 802.15.4Documento39 páginasZigBee and IEEE 802.15.4rsakm20019931100% (2)
- MODEL-MODEL REFERENSI PROTOKOLDocumento43 páginasMODEL-MODEL REFERENSI PROTOKOLJibril Hartri PutraAinda não há avaliações
- Data and Computer Communications: Tenth Edition by William StallingsDocumento42 páginasData and Computer Communications: Tenth Edition by William StallingsHasanAinda não há avaliações
- Connection-Oriented Networks: SONET/SDH, ATM, MPLS and Optical NetworksNo EverandConnection-Oriented Networks: SONET/SDH, ATM, MPLS and Optical NetworksAinda não há avaliações
- Personal Computer Local Networks ReportNo EverandPersonal Computer Local Networks ReportAinda não há avaliações
- An-ANI-1-115 HS Physical Layer ProblemsDocumento10 páginasAn-ANI-1-115 HS Physical Layer ProblemsrahairiAinda não há avaliações
- DelphiDocumento2 páginasDelphirahairiAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamental AnalysisDocumento52 páginasFundamental Analysisrahairi100% (4)
- Technical AnalysisDocumento92 páginasTechnical Analysisrahairi100% (11)
- Ecall Communications Test Bench - Structure and Content of MSD, Fds and Mds Messages 1 Ecall Test BenchDocumento14 páginasEcall Communications Test Bench - Structure and Content of MSD, Fds and Mds Messages 1 Ecall Test BenchrahairiAinda não há avaliações
- Productive Muslim EbookDocumento32 páginasProductive Muslim EbookMuhammadBagusPriambodo100% (1)
- TapeReadingAndMarketTactics PDFDocumento134 páginasTapeReadingAndMarketTactics PDFNenugrAinda não há avaliações
- ANSYS V11 Rotor Dynamics Web SeminarDocumento73 páginasANSYS V11 Rotor Dynamics Web Seminarbitconcepts9781Ainda não há avaliações
- (Ebook - PDF - Programming) Visual Basic 6 Black BookDocumento1.113 páginas(Ebook - PDF - Programming) Visual Basic 6 Black BookshivajayAinda não há avaliações
- F J Shark How To Be The Jerk Women LoveDocumento210 páginasF J Shark How To Be The Jerk Women LovepopeyeballinaAinda não há avaliações
- 100 TOP COMPUTER NETWORKS Multiple Choice Questions and Answers COMPUTER NETWORKS Questions and Answers PDFDocumento21 páginas100 TOP COMPUTER NETWORKS Multiple Choice Questions and Answers COMPUTER NETWORKS Questions and Answers PDFvaraprasad_ganjiAinda não há avaliações
- Wuhan Coronavirus in Hollywood Illuminati Predictive ProgrammingDocumento7 páginasWuhan Coronavirus in Hollywood Illuminati Predictive ProgrammingTazAinda não há avaliações
- Drama vs. MelodramaDocumento6 páginasDrama vs. MelodramaRajesh KarmakarAinda não há avaliações
- AGH Computer Configuration PDFDocumento10 páginasAGH Computer Configuration PDFAndrey MoraAinda não há avaliações
- LTI Sustainability Report FY 2017 18 PDFDocumento99 páginasLTI Sustainability Report FY 2017 18 PDFLatha Ramesh Institute of ManagementAinda não há avaliações
- EasyToon Animation Software Update NotesDocumento5 páginasEasyToon Animation Software Update NotesMaxAinda não há avaliações
- CiTRANS 610A Packet Transfer Platform User ManualDocumento286 páginasCiTRANS 610A Packet Transfer Platform User ManualShailendra Rawat0% (1)
- Guide Renewal PDFDocumento103 páginasGuide Renewal PDFka baraAinda não há avaliações
- Ch06 MAC Layer StandardsDocumento59 páginasCh06 MAC Layer StandardsvasanthmeAinda não há avaliações
- FortiOS 7.2.1 Log ReferenceDocumento1.643 páginasFortiOS 7.2.1 Log Referencemenap42333Ainda não há avaliações
- Lab Exercise 3 - SniffingDocumento4 páginasLab Exercise 3 - SniffingRyan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Impact of Social Media On YouthDocumento5 páginasImpact of Social Media On YouthNatAinda não há avaliações
- Jewellery JewelcadDocumento11 páginasJewellery Jewelcadaskar bhaiAinda não há avaliações
- ATCOR For IMAGINE 2013 - PC Installation PDFDocumento21 páginasATCOR For IMAGINE 2013 - PC Installation PDFChristian Javier Pinza JAinda não há avaliações
- Role of Computers in JournalismDocumento16 páginasRole of Computers in Journalismwiqi4love75% (12)
- Exemple Concours Master Finace d'Entreprise 2013-2014, Fsjes RABAT - منتدى كلية الحقوق أكادير - FSJES AGADIR FORUMDocumento3 páginasExemple Concours Master Finace d'Entreprise 2013-2014, Fsjes RABAT - منتدى كلية الحقوق أكادير - FSJES AGADIR FORUMSoukaina MoumenAinda não há avaliações
- Social Media The Importance of Social MediaDocumento11 páginasSocial Media The Importance of Social MediaLê Văn SơnAinda não há avaliações
- WPF Data Binding With Entity FrameworkDocumento12 páginasWPF Data Binding With Entity Frameworkthanhtrungcntt107Ainda não há avaliações
- Motorola Modem SB5120Documento74 páginasMotorola Modem SB5120Berks Homes100% (1)
- Knime Anomaly Detection VisualizationDocumento13 páginasKnime Anomaly Detection VisualizationFelipe MaximinoAinda não há avaliações
- The Java MagzineDocumento67 páginasThe Java Magzinesankalp.ims29310% (1)
- A10 Thunder Series and AX Series: System Configuration and Administration GuideDocumento178 páginasA10 Thunder Series and AX Series: System Configuration and Administration GuideAbrar Fazal RazzaqAinda não há avaliações
- ATC-850 User's ManualDocumento2 páginasATC-850 User's ManualMaitry ShahAinda não há avaliações
- DfirDocumento20 páginasDfirAndrei StefanAinda não há avaliações
- Rhel 7Documento22 páginasRhel 7gmasayAinda não há avaliações
- This Text Is Emphasized This Text Is ItalicDocumento14 páginasThis Text Is Emphasized This Text Is ItalicSathish ArukondaAinda não há avaliações
- Monitor and Control Weather Station with LabVIEWDocumento16 páginasMonitor and Control Weather Station with LabVIEWAlba O'GalivanAinda não há avaliações
- CCIE 100 Success SecretsDocumento134 páginasCCIE 100 Success Secretsnegev2005100% (3)
- WWW Olegsych Com 2008 09 t4 Tutorial Creatating Your First Code GeneratDocumento11 páginasWWW Olegsych Com 2008 09 t4 Tutorial Creatating Your First Code GeneratTu NamAinda não há avaliações
- Resume-Jennifer GordonDocumento1 páginaResume-Jennifer Gordonapi-454343923Ainda não há avaliações