Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Advantages and Disadvantages of Floating Exchange Rates
Enviado por
SyedAshirBukhari50%(2)50% acharam este documento útil (2 votos)
1K visualizações3 páginasAdvantages and Disadvantages of Floating Exchange Rates
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoAdvantages and Disadvantages of Floating Exchange Rates
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
50%(2)50% acharam este documento útil (2 votos)
1K visualizações3 páginasAdvantages and Disadvantages of Floating Exchange Rates
Enviado por
SyedAshirBukhariAdvantages and Disadvantages of Floating Exchange Rates
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 3
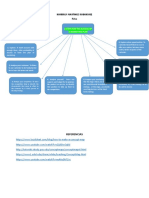
ADVANTAGES AND
DISADVANTAGES OF
FLOATING EXCHANGE
RATES
Floating exchange rates have these main advantages:
No need for international management of exchange
rates: Unlike fixed exchange rates based on a metallic standard,
floating exchange rates dont require an international manager
such as the International Monetary Fund to look over current
account imbalances. Under the floating system, if a country has
large current account deficits, its currency depreciates.
No need for frequent central bank intervention: Central banks
frequently must intervene in foreign exchange markets under the
fixed exchange rate regime to protect the gold parity, but such is
not the case under the floating regime. Here theres no parity to
uphold.
No need for elaborate capital flow restrictions: It is difficult to
keep the parity intact in a fixed exchange rate regime while
portfolio flows are moving in and out of the country. In a floating
exchange rate regime, the macroeconomic fundamentals of
countries affect the exchange rate in international markets,
which, in turn, affect portfolio flows between countries.
Therefore, floating exchange rate regimes enhance market
efficiency.
Greater insulation from other countries economic
problems: Under a fixed exchange rate regime, countries export
their macroeconomic problems to other countries. Suppose that
the inflation rate in the U.S. is rising relative to that of the Euro-
zone.
Under a fixed exchange rate regime, this scenario leads to an
increased U.S. demand for European goods, which then
increases the Euro-zones price level. Under a floating exchange
rate system, however, countries are more insulated from other
countries macroeconomic problems. A rising U.S. inflation
instead depreciates the dollar, curbing the U.S. demand for
European goods.
Floating exchange rates also have disadvantages:
Higher volatility: Floating exchange rates are highly volatile.
Additionally, macroeconomic fundamentals cant explain
especially short-run volatility in floating exchange rates.
Use of scarce resources to predict exchange rates: Higher
volatility in exchange rates increases the exchange rate risk that
financial market participants face. Therefore, they allocate
substantial resources to predict the changes in the exchange
rate, in an effort to manage their exposure to exchange rate risk.
Tendency to worsen existing problems: Floating exchange
rates may aggravate existing problems in the economy. If the
country is already experiencing economic problems such as
higher inflation or unemployment, floating exchange rates may
make the situation worse.
For example, if the country suffers from higher inflation,
depreciation of its currency may drive the inflation rate higher
because of increased demand for its goods; however, the
countrys current account may also worsen because of more
expensive imports.
Você também pode gostar
- What Are The Main Advantages and Disadvantages of Fixed Exchange RatesDocumento4 páginasWhat Are The Main Advantages and Disadvantages of Fixed Exchange RatesGaurav Sikdar0% (1)
- Factors Affecting Money SupplyDocumento3 páginasFactors Affecting Money Supplycuriben100% (5)
- Limitations of Harrod-Domar Models for Underdeveloped NationsDocumento3 páginasLimitations of Harrod-Domar Models for Underdeveloped NationsprabindraAinda não há avaliações
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Marginal CostingDocumento4 páginasAdvantages and Disadvantages of Marginal CostingnileshmsawantAinda não há avaliações
- If MCQ 40 Nos.Documento7 páginasIf MCQ 40 Nos.gowthamAinda não há avaliações
- Theories of Interest RateDocumento10 páginasTheories of Interest RateAshutoshAinda não há avaliações
- Imsb T6Documento5 páginasImsb T6Lyc Chun100% (2)
- International Portfolio Management Unit 2Documento12 páginasInternational Portfolio Management Unit 2Omar Ansar Ali100% (1)
- Conduct of Monetary Policy Goal and TargetsDocumento12 páginasConduct of Monetary Policy Goal and TargetsSumra KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Exchange Rates ForecastingDocumento25 páginasExchange Rates ForecastingBarrath RamakrishnanAinda não há avaliações
- Interest RatesDocumento8 páginasInterest RatesMuhammad Sanawar ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Factors Affecting Exchange RatesDocumento12 páginasFactors Affecting Exchange RatesHaritha JayanAinda não há avaliações
- Investments and Portfolio ManagementDocumento5 páginasInvestments and Portfolio ManagementFedrick BuenaventuraAinda não há avaliações
- Characteristics of Undeveloped NationsDocumento2 páginasCharacteristics of Undeveloped Nationspdalingay100% (1)
- Big Push Theory of Economic DevDocumento2 páginasBig Push Theory of Economic DevsukandeAinda não há avaliações
- CH 5 Security Market IndexesDocumento12 páginasCH 5 Security Market IndexesMoin khanAinda não há avaliações
- The Foreign Exchange MarketDocumento16 páginasThe Foreign Exchange Marketmanojpatel5167% (3)
- International FinanceDocumento56 páginasInternational FinanceSucheta Das100% (1)
- How Inflation, Interest Rates, Debt, and More Impact Currency ExchangeDocumento2 páginasHow Inflation, Interest Rates, Debt, and More Impact Currency ExchangeTikitaka TitiAinda não há avaliações
- Crowding out explainedDocumento3 páginasCrowding out explainedsattysattuAinda não há avaliações
- Devlopment and DependencyDocumento7 páginasDevlopment and Dependencygangadhar119Ainda não há avaliações
- International Finance Chapter 3Documento40 páginasInternational Finance Chapter 3Mehrab Jami Aumit 1812818630Ainda não há avaliações
- The Global Financial CrisisDocumento35 páginasThe Global Financial CrisisSamya MittalAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1 - IFM Meaning, Nature & ScopeDocumento3 páginasModule 1 - IFM Meaning, Nature & ScopeSandeep Patil100% (2)
- Concept of RiskDocumento40 páginasConcept of Riskemba2015Ainda não há avaliações
- Foreign ExchangeDocumento25 páginasForeign ExchangeArti SainiAinda não há avaliações
- National Income Accounting ExplainedDocumento10 páginasNational Income Accounting ExplainedExcel Joy Marticio100% (1)
- Multinational CompaniesDocumento5 páginasMultinational CompaniesAhmed D. RamihAinda não há avaliações
- Adam Smiths Theory of Economic DevelopmentDocumento4 páginasAdam Smiths Theory of Economic DevelopmentSazin MahmudAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 1.1 International Finance ManagementDocumento15 páginasLesson 1.1 International Finance Managementashu1286Ainda não há avaliações
- Quantity Theory of MoneyDocumento20 páginasQuantity Theory of MoneyRucha Tandulwadkar100% (1)
- Macro Economic Policy, Monetary and Fiscal PolicyDocumento48 páginasMacro Economic Policy, Monetary and Fiscal Policysujata dawadiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 IntroDocumento14 páginasChapter 1 IntroliyayudiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter - 2 (International Flow of Funds)Documento23 páginasChapter - 2 (International Flow of Funds)shohag30121991100% (1)
- Answers To End of Chapter Questions and Applications: 3. Imperfect MarketsDocumento2 páginasAnswers To End of Chapter Questions and Applications: 3. Imperfect Marketssuhayb_1988Ainda não há avaliações
- Government Intervention in International BusinessDocumento8 páginasGovernment Intervention in International Businessਹਰਸ਼ ਵਰਧਨAinda não há avaliações
- Public Debt Lesson 6 and 7Documento19 páginasPublic Debt Lesson 6 and 7BrianAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment On Foreign Exchange Market.Documento6 páginasAssignment On Foreign Exchange Market.Sadman Skib.0% (1)
- 6 Key Factors That Influence Exchange RatesDocumento9 páginas6 Key Factors That Influence Exchange RatesRizwan BashirAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Markets and Institutions 1Documento29 páginasFinancial Markets and Institutions 1Hamza Iqbal100% (1)
- Balance of PaymentsDocumento16 páginasBalance of PaymentsShipra SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Markets With Asymmetric InformationDocumento8 páginasMarkets With Asymmetric InformationJessica PariñasAinda não há avaliações
- Nelson's Low Level Equilibrium Trap Theory ExplainedDocumento3 páginasNelson's Low Level Equilibrium Trap Theory ExplainedKris Sara Sajiv100% (1)
- International Financial Markets Chapter 3 SummaryDocumento22 páginasInternational Financial Markets Chapter 3 SummaryFeriel El IlmiAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Markets in India ClassificationDocumento49 páginasFinancial Markets in India ClassificationNew OldAinda não há avaliações
- International Economics Chapter 8-12Documento13 páginasInternational Economics Chapter 8-12Alfred Martin50% (2)
- Case Study 5.2Documento5 páginasCase Study 5.2Jessa Beloy100% (6)
- Evaluate The Effectiveness of Australia's Monetary Policy in Addressing The Economic Issues Resulting From The Global Financial Crisis of 2008-2009Documento5 páginasEvaluate The Effectiveness of Australia's Monetary Policy in Addressing The Economic Issues Resulting From The Global Financial Crisis of 2008-2009yingy0116Ainda não há avaliações
- Capital and Money MarketDocumento17 páginasCapital and Money MarketBalamanichalaBmcAinda não há avaliações
- Rostow's ModelDocumento2 páginasRostow's Modelonlyfordocs595100% (2)
- Exchange Rate RegimeDocumento5 páginasExchange Rate RegimeNaman DugarAinda não há avaliações
- Importance of Money Markets for Economic DevelopmentDocumento1 páginaImportance of Money Markets for Economic DevelopmentchandranilAinda não há avaliações
- ICC Curve Slope and Inferior GoodsDocumento4 páginasICC Curve Slope and Inferior GoodsGhalib HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Liquidity Preference Theory PDFDocumento12 páginasLiquidity Preference Theory PDFgaurav singhAinda não há avaliações
- International Finance - 1Documento109 páginasInternational Finance - 1Mohamed Fathy100% (1)
- Bretton Woods system explainedDocumento12 páginasBretton Woods system explainedAadi SarinAinda não há avaliações
- Free FloatDocumento5 páginasFree FloatHinaJhambAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 11Documento23 páginasChapter 11Fazila AzharAinda não há avaliações
- Explaining Exchange Rate RegimesDocumento9 páginasExplaining Exchange Rate RegimesBP JoshieAinda não há avaliações
- Exchange Rate and It's TypeDocumento4 páginasExchange Rate and It's Typeanish-kc-8151Ainda não há avaliações
- Code BBA Couse DetailsDocumento44 páginasCode BBA Couse DetailsSaddamHusSainAinda não há avaliações
- GWOT Costs Pakistan is PayingDocumento16 páginasGWOT Costs Pakistan is PayingSyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- Unpaid Bills Detail: Ch10 Lynn's Music StudioDocumento1 páginaUnpaid Bills Detail: Ch10 Lynn's Music StudioSyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- The Examination Will Include The Following Subjects and Each Subject Will Carry The Marks Shown Against ItDocumento5 páginasThe Examination Will Include The Following Subjects and Each Subject Will Carry The Marks Shown Against ItSyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- Advantage of Acquisition AreDocumento4 páginasAdvantage of Acquisition AreSyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- Theresearchproposal 100303013047 Phpapp02Documento37 páginasTheresearchproposal 100303013047 Phpapp02SyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- Audit UnileverDocumento19 páginasAudit UnileverSyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- John KotterDocumento3 páginasJohn KotterSyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- Strategic Management: Life-Cycle StrategiesDocumento7 páginasStrategic Management: Life-Cycle StrategiesSyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- ACCTG222Documento4 páginasACCTG222SyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Quality AuditingDocumento34 páginasAdvanced Quality AuditingNando EriawanAinda não há avaliações
- University of The Punjab Gujranwala CampusDocumento3 páginasUniversity of The Punjab Gujranwala CampusSyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- ZHP CleanerDocumento3 páginasZHP CleanerSyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- 2013 Whistleblowing SupportOurWork enDocumento16 páginas2013 Whistleblowing SupportOurWork enSyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- Shariah FMR Dec 2016Documento8 páginasShariah FMR Dec 2016SyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- English WHISTLE BLOWERDocumento2 páginasEnglish WHISTLE BLOWERSyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Anmol Khazaney by Hakeem Muhammad Tariq MahmoodDocumento34 páginas2 Anmol Khazaney by Hakeem Muhammad Tariq MahmoodSharifa SorathiaAinda não há avaliações
- 1 2Documento20 páginas1 2SyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus Corporate GovernanceDocumento8 páginasSyllabus Corporate GovernanceBrinda HarjanAinda não há avaliações
- BSC Maths Derivative FormulaDocumento1 páginaBSC Maths Derivative Formulamati ullah73% (30)
- The Marketing Environment: - PESTE AnalysisDocumento12 páginasThe Marketing Environment: - PESTE AnalysisSyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- AuditDocumento23 páginasAuditSyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- Development of A Scale To Measure Professional Skepticism PDFDocumento24 páginasDevelopment of A Scale To Measure Professional Skepticism PDFSyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- Research Proposal SampleDocumento24 páginasResearch Proposal Sampleatevhanz_bcAinda não há avaliações
- AccountingDocumento74 páginasAccountingSyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- Audit FinalDocumento39 páginasAudit FinalmalleshAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Accounting Course 1st LecturerDocumento19 páginasFinancial Accounting Course 1st LecturerSyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Accounting Course 1st LecturerDocumento19 páginasFinancial Accounting Course 1st LecturerSyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- Classwise 2Documento21 páginasClasswise 2SyedAshirBukhariAinda não há avaliações
- Market testing of Joyline's Durian SpreadDocumento2 páginasMarket testing of Joyline's Durian SpreadRC CRAinda não há avaliações
- Accounts Manipulation A Literature Review and Proposed Conceptual FrameworkDocumento12 páginasAccounts Manipulation A Literature Review and Proposed Conceptual FrameworkafdtlgezoAinda não há avaliações
- Business Case - Amy Baker Nature's CureDocumento19 páginasBusiness Case - Amy Baker Nature's CurerasyidazmiAinda não há avaliações
- 1 - Demomstration On Replacement Theory Part IDocumento6 páginas1 - Demomstration On Replacement Theory Part IAshim SahaAinda não há avaliações
- Formlabs Case - 311Documento8 páginasFormlabs Case - 311Jake MarzoffAinda não há avaliações
- Accounts Receivable q3Documento3 páginasAccounts Receivable q3Omnia HassanAinda não há avaliações
- Bajaj TheoryDocumento5 páginasBajaj TheoryNikhil IngaleAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Supply Chain OPME005 PDFDocumento46 páginasAdvanced Supply Chain OPME005 PDFNageshwar SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Common Size Income Statements 2Documento7 páginasCommon Size Income Statements 2Aniket KedareAinda não há avaliações
- CRMDocumento39 páginasCRMSwathi AjayAinda não há avaliações
- Finra Bond InfoDocumento151 páginasFinra Bond InfoPropertywizzAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT: 07 "Organizational Structure & Its Planning": PLC: Product Life CycleDocumento5 páginasUNIT: 07 "Organizational Structure & Its Planning": PLC: Product Life CycleTabish KhanAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Strategic Business Analysis?: Vision, Mission, and ValuesDocumento6 páginasWhat Is Strategic Business Analysis?: Vision, Mission, and ValuesJoseph VillartaAinda não há avaliações
- Cirque Du Soleil (Blue Ocean Strategy) : - by Group 6Documento7 páginasCirque Du Soleil (Blue Ocean Strategy) : - by Group 6KHALKAR SWAPNILAinda não há avaliações
- Clarins Business CaseDocumento16 páginasClarins Business CaseAkshit AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Marketing Plan For FTTHDocumento5 páginasMarketing Plan For FTTHsheinmin thuAinda não há avaliações
- Audit and Assurance June 2009 Past Paper Answers (ACCA)Documento15 páginasAudit and Assurance June 2009 Past Paper Answers (ACCA)Serena JainarainAinda não há avaliações
- Mapa ConceptualDocumento2 páginasMapa Conceptualcamila fotanarosaAinda não há avaliações
- Strategic Management Assignment 5Documento23 páginasStrategic Management Assignment 5Jabri JuhininAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals OF Accounting: Ms. Maryvin M. Maluya, CPA, CTTDocumento35 páginasFundamentals OF Accounting: Ms. Maryvin M. Maluya, CPA, CTTAmalia Tamayo YlananAinda não há avaliações
- Why Might Share Price Follow A Random Walk by Senior SophisterDocumento13 páginasWhy Might Share Price Follow A Random Walk by Senior SophisterHu ShanxiongAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Accounting IiDocumento39 páginasFundamentals of Accounting IiMintayto TebekaAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Notes 1&2Documento19 páginasLecture Notes 1&2VanillaheroineAinda não há avaliações
- Consumer and Business Markets: Lesson 3.4Documento22 páginasConsumer and Business Markets: Lesson 3.4willsonjohndrewfAinda não há avaliações
- VTC Telemarketing Database and Order Entry SystemDocumento2 páginasVTC Telemarketing Database and Order Entry SystemMaricar PinedaAinda não há avaliações
- Test 3 ReviewDocumento3 páginasTest 3 ReviewOmarSalehAinda não há avaliações
- CAT 1 Module (NIAT Encoded)Documento245 páginasCAT 1 Module (NIAT Encoded)UFO CatcherAinda não há avaliações
- Gitman pmf13 ppt11Documento53 páginasGitman pmf13 ppt11Sajjad AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Demographic Report by MatthDocumento2 páginasDemographic Report by Matthngoctuan_ntdAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Marketing Mix of Life InsuranceDocumento19 páginasChapter 3 Marketing Mix of Life Insurancerahulhaldankar0% (1)
- Kleptopia: How Dirty Money Is Conquering the WorldNo EverandKleptopia: How Dirty Money Is Conquering the WorldNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (25)
- Look Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereNo EverandLook Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (3)
- Narrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsNo EverandNarrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (94)
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumNo EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (12)
- Nudge: The Final Edition: Improving Decisions About Money, Health, And The EnvironmentNo EverandNudge: The Final Edition: Improving Decisions About Money, Health, And The EnvironmentNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (92)
- The War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesNo EverandThe War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (8)
- The Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaNo EverandThe Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaAinda não há avaliações
- Vulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomNo EverandVulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomAinda não há avaliações
- University of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingNo EverandUniversity of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (97)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyNo EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (227)
- The Genius of Israel: The Surprising Resilience of a Divided Nation in a Turbulent WorldNo EverandThe Genius of Israel: The Surprising Resilience of a Divided Nation in a Turbulent WorldNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (16)
- Second Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenNo EverandSecond Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenAinda não há avaliações
- The Lords of Easy Money: How the Federal Reserve Broke the American EconomyNo EverandThe Lords of Easy Money: How the Federal Reserve Broke the American EconomyNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (69)
- The Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetNo EverandThe Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetAinda não há avaliações
- Economics 101: From Consumer Behavior to Competitive Markets—Everything You Need to Know About EconomicsNo EverandEconomics 101: From Consumer Behavior to Competitive Markets—Everything You Need to Know About EconomicsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- Financial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassNo EverandFinancial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassAinda não há avaliações
- Principles for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailNo EverandPrinciples for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (237)
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationNo EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (46)
- Doughnut Economics: Seven Ways to Think Like a 21st-Century EconomistNo EverandDoughnut Economics: Seven Ways to Think Like a 21st-Century EconomistNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (37)
- Kaizen: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Continuous Improvement And Transforming Your Life With Self DisciplineNo EverandKaizen: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Continuous Improvement And Transforming Your Life With Self DisciplineNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (36)
- The Ascent of Money: A Financial History of the WorldNo EverandThe Ascent of Money: A Financial History of the WorldNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (132)
- Against the Gods: The Remarkable Story of RiskNo EverandAgainst the Gods: The Remarkable Story of RiskNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (352)
- How an Economy Grows and Why It Crashes: Collector's EditionNo EverandHow an Economy Grows and Why It Crashes: Collector's EditionNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (102)