Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Lab Intro
Enviado por
api-328029949Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Lab Intro
Enviado por
api-328029949Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Lab Introduction
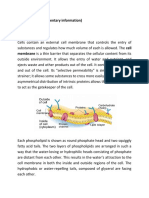
According to IHW (2005), there are different ways substances can pass through the
membrane, whether it is to enter or leave the cells. They are mainly divided into 2 ways ; active
and passive. Osmosis is one special type of passive transport which is a diffusion of water through
a selectively permeable membrane without using energy, in which it moves from the side of lower
solute concentration to the higher solute concentration. Because this selectively permeable
membrane only allows some substances to pass through, not every solute can pass through it as
water can. Normally, each side will have different concentration of a solute, therefore, there will be
a movement of water from the side with less solute (hypotonic) to the side with more solute
(hypertonic). But if the solute can cross the membrane, there would be a balance of the two sides,
which is called an Isotonic solution. So these types of solutions are very important to living
things ,to the patients in the hospital , to the plants absorption of water , also freshwater and
seawater animals could not survive without this.(Saucedo,2012)
To get a clearer picture and also a better understanding of how the water moves in
osmosis, conducting an experiment would be a great way. In this experiment, we will be soaking a
jelly and potato in both hypertonic and hypotonic solution. So after the experiment, we will be able
to observe the change in volume and mass, which can tell us the movement of water whether it
goes in or out of the jelly/potato.
References
IHW (March,2005). Movement across membranes. Retrieved 06 March 2017 from http://
www.biologymad.com/resources/diffusionrevision.pdf
Saucedo, J. (May 1,2012). Osmosis. Retrieved 06 March 2017 from http://
www.brighthubeducation.com/science-homework-help/111424-guide-to-hypotonic-hypertonic-
and-isotonic-solutions/
Você também pode gostar
- Bio Lab IntroDocumento2 páginasBio Lab Introapi-327731714Ainda não há avaliações
- Lab Intro OsmosisDocumento2 páginasLab Intro Osmosisapi-327826901Ainda não há avaliações
- Osmosis Lab IntroDocumento1 páginaOsmosis Lab Introapi-327726527Ainda não há avaliações
- Jelly IntroDocumento1 páginaJelly Introapi-341690050Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport Lesson 5.2: Cell Transport-Passive and ActiveDocumento10 páginasChapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport Lesson 5.2: Cell Transport-Passive and ActiveVanshika VermaAinda não há avaliações
- Osmosis Lab Report IntroductionDocumento2 páginasOsmosis Lab Report Introductionapi-327823961100% (1)
- Lab Report Introduction Tanat Sangwong 5961121: OsmosisDocumento2 páginasLab Report Introduction Tanat Sangwong 5961121: Osmosisapi-327827118Ainda não há avaliações
- Gene103Lab DiffusionandOsmosisDocumento5 páginasGene103Lab DiffusionandOsmosisbodurr571Ainda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2 - Diffusion and OsmosisDocumento11 páginasLecture 2 - Diffusion and Osmosiskinza yasirAinda não há avaliações
- Gr9 - Movement of SubstancesDocumento40 páginasGr9 - Movement of SubstancesKara NewmanAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisDocumento6 páginasActivity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisThea Calyn WalicanAinda não há avaliações
- Bios - Transport of MaterialDocumento46 páginasBios - Transport of MaterialNeseriani AndersonAinda não há avaliações
- 5.7 Cell TransportDocumento6 páginas5.7 Cell TransportMonica B. BautistaAinda não há avaliações
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocumento3 páginasDiffusion and Osmosisshaniah100% (1)
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocumento6 páginasDiffusion and OsmosisCharlesAinda não há avaliações
- Osmosis IntroductionDocumento2 páginasOsmosis Introductionapi-335117665Ainda não há avaliações
- Bio IntroDocumento1 páginaBio Introapi-327847414Ainda não há avaliações
- Las-Q3-Wk6.1 2Documento12 páginasLas-Q3-Wk6.1 2Jhude JosephAinda não há avaliações
- 4.transport MechanismsDocumento94 páginas4.transport MechanismsHyacinth RaeAinda não há avaliações
- Biochem Laboratory Activity 2Documento4 páginasBiochem Laboratory Activity 2Kristine PangahinAinda não há avaliações
- Water Ang Ingon Sa Isa Ka Source: Semipermeable MembraneDocumento1 páginaWater Ang Ingon Sa Isa Ka Source: Semipermeable MembranemarielAinda não há avaliações
- Intro Osmosis LabDocumento1 páginaIntro Osmosis Labapi-327696239Ainda não há avaliações
- Biology Grade 10 Lesson Plan March 6 - March 10Documento5 páginasBiology Grade 10 Lesson Plan March 6 - March 10Nicketa AndersonAinda não há avaliações
- Diffusion Vs OsmosisDocumento3 páginasDiffusion Vs OsmosisK TanAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanism: Osmosis Is The Spontaneous Net Movement ofDocumento4 páginasMechanism: Osmosis Is The Spontaneous Net Movement ofm bilalAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7Documento20 páginasChapter 7criselledalipe12Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Doc 4Documento4 páginasChapter 1 Doc 4Enju ChipepeAinda não há avaliações
- Osmosis Lab IntroductionDocumento2 páginasOsmosis Lab IntroductionPaperless TwnAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Membrane Structure-And FunctionDocumento5 páginasCell Membrane Structure-And FunctionEmmanuel MwaleAinda não há avaliações
- GRADE 11 (Supplementary Information)Documento3 páginasGRADE 11 (Supplementary Information)EleinaAinda não há avaliações
- Diffusion Osmosis and Active TransportDocumento18 páginasDiffusion Osmosis and Active TransportThompson Ta Ta JevonAinda não há avaliações
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocumento30 páginasMovement in and Out of CellsEmy AnkrahAinda não há avaliações
- Theory: 1 Plant Water RelationsDocumento11 páginasTheory: 1 Plant Water RelationsalekhyaAinda não há avaliações
- Osmosis Active TransportDocumento25 páginasOsmosis Active Transportyasser yousriAinda não há avaliações
- REVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDocumento4 páginasREVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDavé TranAinda não há avaliações
- Osmosis: Diffusion Is The Process Where Molecules of Two or More Substances Move AboutDocumento3 páginasOsmosis: Diffusion Is The Process Where Molecules of Two or More Substances Move AboutizzahAinda não há avaliações
- Cell MembranesDocumento5 páginasCell MembranesTiaraHadiAshariAinda não há avaliações
- 7-4 Cell TransportDocumento24 páginas7-4 Cell Transportapi-342334216Ainda não há avaliações
- Group 6 Written ReportDocumento4 páginasGroup 6 Written ReportLuckyGuy25Ainda não há avaliações
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocumento4 páginasMovement in and Out of CellsIndah ParamithaAinda não há avaliações
- 19031121-Abeto-Difusi Molekul Di Dalam AirDocumento29 páginas19031121-Abeto-Difusi Molekul Di Dalam AirZhafiraAinda não há avaliações
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocumento2 páginasDiffusion and OsmosisMera FunportalAinda não há avaliações
- Lect 2 Membrane TransportDocumento29 páginasLect 2 Membrane Transportramadan100% (1)
- Cell Transport Powerpoint NotesDocumento33 páginasCell Transport Powerpoint Notesapi-644325383Ainda não há avaliações
- Osmosis: For Other Uses, SeeDocumento4 páginasOsmosis: For Other Uses, SeeMisrai FaraukAinda não há avaliações
- DiffusionDocumento32 páginasDiffusionAce Mhac TeñidoAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology 1Documento15 páginasGeneral Biology 1Beejae ApalisAinda não há avaliações
- Laboratory Experiment No. 11 - Transport Across MembranesDocumento4 páginasLaboratory Experiment No. 11 - Transport Across MembranesMary Rose CatalbasAinda não há avaliações
- Biotech Module2Documento12 páginasBiotech Module2Aldrin M. ObiasAinda não há avaliações
- OsmosisDocumento19 páginasOsmosisdamyangdcsAinda não há avaliações
- Diffusion & OsmosisDocumento19 páginasDiffusion & Osmosishugo roblesAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Transport Powerpoint NotesDocumento33 páginasCell Transport Powerpoint Notesapi-644325383Ainda não há avaliações
- Passive and Active Cell Transport MechanismsDocumento4 páginasPassive and Active Cell Transport MechanismsAlan VargheseAinda não há avaliações
- BS 1Documento12 páginasBS 1JAHANZEB NAZIRAinda não há avaliações
- OsmosisDocumento3 páginasOsmosisGayathriAinda não há avaliações
- OsmosisDocumento4 páginasOsmosisSOUMYA RANJAN NATHAinda não há avaliações
- Osmosis - WikipediaDocumento37 páginasOsmosis - WikipediaBashiir NuurAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Transport NotesDocumento10 páginasCell Transport NotesReyad BarbarAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 10 Diffusion, Osmosis and Transport - TeacherDocumento20 páginasChap 10 Diffusion, Osmosis and Transport - TeacherSulochana Devi PalanisamyAinda não há avaliações
- Black DeathDocumento18 páginasBlack Deathapi-328029949Ainda não há avaliações
- Black DeathDocumento1 páginaBlack Deathapi-328029949Ainda não há avaliações
- AssyriaDocumento29 páginasAssyriaapi-328029949Ainda não há avaliações
- Facebooks HistoryDocumento11 páginasFacebooks Historyapi-328029949Ainda não há avaliações