Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
0620 w14 QP 61
Enviado por
Kevin DanyTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
0620 w14 QP 61
Enviado por
Kevin DanyDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
2
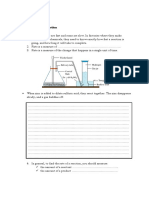
1 A student reacted dilute nitric acid with lead(II) oxide to prepare lead(II) nitrate. The diagram shows
the stages in the method used.
2 Lead(II) oxide
was added until
all the nitric acid
had reacted
1 50 cm3 of dilute nitric
acid was measured into
a beaker
DILUTE
NITRIC
ACID
heat
4 The solution was
allowed to cool
3 The mixture
was separated
solution of
lead(II) nitrate
(a) Complete the boxes to identify the pieces of apparatus. [2]
(b) Why is the dilute nitric acid heated?
.............................................................................................................................................. [1]
(c) The lead(II) oxide was weighed before and after the additions.
19 15
18 14
17 13
16 g 12 g
before after
Use the balance diagrams to work out the mass of lead(II) oxide added to the dilute nitric acid.
.............................................................................................................................................. [2]
UCLES 2014 0620/61/O/N/14
3
(d) (i) How would the student know when all of the dilute nitric acid had reacted in stage 2?
....................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) What method is used to separate the mixture in stage 3?
....................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) What term is used to describe the unreacted lead(II) oxide?
....................................................................................................................................... [1]
(e) Describe the effect of heating the solution of lead(II) nitrate until it boils and then heating for a
further ten minutes.
....................................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................. [2]
[Total: 10]
UCLES 2014 0620/61/O/N/14 [Turn over
4
2 Two experiments were carried out to show what factors affect the rate of decomposition of hydrogen
peroxide, H2O2.
In each experiment the volume of gas produced was measured every minute for ten minutes.
Experiment 1
The student used a mixture of 50 cm3 of hydrogen peroxide, 50 cm3 of water and
1 g of manganese(IV) oxide at a room temperature of 20 C.
The results were plotted to obtain the graph shown.
Experiment 2
The student repeated Experiment 1 but did not record how much of each substance was used. The
points were plotted on the grid.
80 Experiment 2
70
60
50
volume of
gas / cm3
40 Experiment 1
30
20
10
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
time / minutes
UCLES 2014 0620/61/O/N/14
5
(a) Complete the graph for Experiment 2. [1]
(b) Suggest the composition of the mixture used in Experiment 2. Explain your suggestion.
composition ...............................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................
explanation ................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................. [4]
(c) What is the function of the manganese(IV) oxide?
.............................................................................................................................................. [1]
(d) Sketch on the grid the curve that you would expect if Experiment 1 was repeated at 10 C. [2]
[Total: 8]
3 A student investigated the colours present in a fruit drink. The fruit drink was tested to check that
no artificial colours had been added. The apparatus below was used.
glass cover
beaker
paper
solvent
(a) (i) Name the method used.
....................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Why is there a glass cover on the beaker?
....................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b) When should the paper be removed from the beaker?
.............................................................................................................................................. [1]
UCLES 2014 0620/61/O/N/14 [Turn over
6
(c) The diagram shows the results of the experiment.
solvent front
colours from
artificial colours fruit drink
(i) How many different coloured compounds were present in the fruit drink?
....................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Are there any of the artificial colours present in the fruit drink? Explain your answer.
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................... [2]
[Total: 6]
UCLES 2014 0620/61/O/N/14
7
4 A student investigated the reaction between two different solutions of dilute hydrochloric acid, A
and B, and solution C which is alkaline.
Two experiments were carried out.
(a) Experiment 1
A burette was filled with solution A of dilute hydrochloric acid to the 0.0 cm3 mark. Using a
measuring cylinder, 20 cm3 of solution C was poured into a conical flask. A few drops of methyl
orange were added to the flask.
Solution A was added to the flask, with shaking, until the mixture just changed colour.
Use the burette diagram to record the burette reading in the table and complete the table.
24
25
26
initial reading
final burette reading / cm3
initial burette reading / cm3
difference / cm3
[2]
(b) Experiment 2
The burette was emptied and rinsed, first with distilled water, and then with a little of
solution B. The burette was filled with solution B of dilute hydrochloric acid to the 0.0 cm3 mark.
Experiment 1 was repeated using solution B.
Use the burette diagram to record the burette reading in the table and complete the table.
final reading
final burette reading / cm3
initial burette reading / cm3
difference / cm3
[2]
UCLES 2014 0620/61/O/N/14 [Turn over
8
(c) (i) What type of chemical reaction takes place when hydrochloric acid reacts with alkaline
solutions?
....................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Why is methyl orange added to the flask?
....................................................................................................................................... [1]
(d) Why was the burette rinsed, first with distilled water and then with solution B, before starting
Experiment 2?
....................................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................. [2]
(e) (i) In which experiment was the greater volume of dilute hydrochloric acid used?
....................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Compare the volumes of dilute hydrochloric acid used in Experiments 1 and 2.
....................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) Suggest, in terms of the concentration of solutions A and B, an explanation for the
difference in volumes used.
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................... [2]
(f) If Experiment 2 was repeated using 10 cm3 of solution C, what volume of dilute hydrochloric
acid would be used? Explain your answer.
....................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................. [2]
(g) Give one advantage and one disadvantage of using a measuring cylinder for solution C.
advantage ..................................................................................................................................
disadvantage ....................................................................................................................... [2]
UCLES 2014 0620/61/O/N/14
9
(h) Describe a method other than titration, using a different reactant, that could be used to
compare the concentrations of the two solutions of dilute hydrochloric acid, A and B.
....................................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................. [4]
[Total: 20]
UCLES 2014 0620/61/O/N/14 [Turn over
Você também pode gostar
- IGCSE Physics 2014 Assignment 04Documento16 páginasIGCSE Physics 2014 Assignment 04Kevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- It Is Sometimes Good To Have Feedback in An ICT SystemDocumento5 páginasIt Is Sometimes Good To Have Feedback in An ICT SystemKevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- Exam Grade08 2010 MatDocumento7 páginasExam Grade08 2010 MatKevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- C4 Vectors A - QuestionsDocumento2 páginasC4 Vectors A - QuestionsKevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- Rate (Speed) of ReactionDocumento2 páginasRate (Speed) of ReactionKevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Surds PDFDocumento8 páginas7 Surds PDFMomin FayzanAinda não há avaliações
- 1.2.2 Exercise 3 - Covalent and Dative Covalent BondingDocumento1 página1.2.2 Exercise 3 - Covalent and Dative Covalent BondingKevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- (Ebook) Introduction To Swing TradingDocumento76 páginas(Ebook) Introduction To Swing Tradingapi-3719573Ainda não há avaliações
- 8 7 IP Dilation WorksheetDocumento3 páginas8 7 IP Dilation WorksheetKevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- Physics: Form 4Documento37 páginasPhysics: Form 4RuddyMartiniAinda não há avaliações
- GCSE Chemistry Balancing Equations - Let's Balance! Student Task SheetDocumento3 páginasGCSE Chemistry Balancing Equations - Let's Balance! Student Task SheetKevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- Radioactivity or Radioactive DecayDocumento4 páginasRadioactivity or Radioactive DecayKevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- 03-Chemical Rxns N StoichiometryDocumento186 páginas03-Chemical Rxns N StoichiometryKevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- 58 Algebra Expand and FactoriseDocumento8 páginas58 Algebra Expand and FactoriseJoel GrayAinda não há avaliações
- 6663 01 Que 20150513 PDFDocumento32 páginas6663 01 Que 20150513 PDFkaruneshnAinda não há avaliações
- Questionpaper-Unitc1 6663 - June2007 PDFDocumento24 páginasQuestionpaper-Unitc1 6663 - June2007 PDFKevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- Combined 51Documento50 páginasCombined 51Kevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- Maths Specimen Paper 2 2014 2017Documento18 páginasMaths Specimen Paper 2 2014 2017Kevin AarasingheAinda não há avaliações
- 9709 2017 2018 SyllabusDocumento40 páginas9709 2017 2018 Syllabusmohsen123Ainda não há avaliações
- 0580 w10 QP 41Documento16 páginas0580 w10 QP 41Kevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- 1Documento11 páginas1Kevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- 9709 s17 QP 13 PDFDocumento20 páginas9709 s17 QP 13 PDFKevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- Versatile Innovative Simplicity: Annual Report 2017Documento103 páginasVersatile Innovative Simplicity: Annual Report 2017Kevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- IGCSE Maths Paper 2Documento12 páginasIGCSE Maths Paper 2Freddie Leo Dollaga RiveraAinda não há avaliações
- 0620 s14 QP 11Documento5 páginas0620 s14 QP 11Kevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- 0620 w10 QP 11Documento6 páginas0620 w10 QP 11Kevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- p4 Part 1Documento8 páginasp4 Part 1Kevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- Heart of AlgebraDocumento3 páginasHeart of AlgebraKevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- Table of Contents Template Word 03Documento3 páginasTable of Contents Template Word 03Kevin DanyAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Main Research PaperDocumento11 páginasMain Research PaperBharat DedhiaAinda não há avaliações
- DC Motor Dynamics Data Acquisition, Parameters Estimation and Implementation of Cascade ControlDocumento5 páginasDC Motor Dynamics Data Acquisition, Parameters Estimation and Implementation of Cascade ControlAlisson Magalhães Silva MagalhãesAinda não há avaliações
- Astera Data Integration BootcampDocumento4 páginasAstera Data Integration BootcampTalha MehtabAinda não há avaliações
- Non Circumvention Non Disclosure Agreement (TERENCE) SGDocumento7 páginasNon Circumvention Non Disclosure Agreement (TERENCE) SGLin ChrisAinda não há avaliações
- Mazda Fn4A-El 4 Speed Ford 4F27E 4 Speed Fnr5 5 SpeedDocumento5 páginasMazda Fn4A-El 4 Speed Ford 4F27E 4 Speed Fnr5 5 SpeedAnderson LodiAinda não há avaliações
- Planning A Real Estate ProjectDocumento81 páginasPlanning A Real Estate ProjectHaile SilasieAinda não há avaliações
- Water Jet CuttingDocumento15 páginasWater Jet CuttingDevendar YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Write UpDocumento5 páginasWrite Upmourad baAinda não há avaliações
- Mercedes BenzDocumento56 páginasMercedes BenzRoland Joldis100% (1)
- Neuropsychological Deficits in Disordered Screen Use Behaviours - A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocumento32 páginasNeuropsychological Deficits in Disordered Screen Use Behaviours - A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisBang Pedro HattrickmerchAinda não há avaliações
- Social Media Exposure and Its Perceived Impact On Students' Home-Based Tasks ProductivityDocumento9 páginasSocial Media Exposure and Its Perceived Impact On Students' Home-Based Tasks ProductivityJewel PascuaAinda não há avaliações
- Riddles For KidsDocumento15 páginasRiddles For KidsAmin Reza100% (8)
- GMWIN SoftwareDocumento1 páginaGMWIN SoftwareĐào Đình NamAinda não há avaliações
- CAS-GEC04 Module11 Food-SecurityDocumento6 páginasCAS-GEC04 Module11 Food-SecurityPermalino Borja Rose AnneAinda não há avaliações
- The European Journal of Applied Economics - Vol. 16 #2Documento180 páginasThe European Journal of Applied Economics - Vol. 16 #2Aleksandar MihajlovićAinda não há avaliações
- 50 Years of Teaching PianoDocumento122 páginas50 Years of Teaching PianoMyklan100% (35)
- Java development user guide eclipse tutorialDocumento322 páginasJava development user guide eclipse tutorialVivek ParmarAinda não há avaliações
- John Titor TIME MACHINEDocumento21 páginasJohn Titor TIME MACHINEKevin Carey100% (1)
- Wasserman Chest 1997Documento13 páginasWasserman Chest 1997Filip BreskvarAinda não há avaliações
- DELcraFT Works CleanEra ProjectDocumento31 páginasDELcraFT Works CleanEra Projectenrico_britaiAinda não há avaliações
- Log File Records Startup Sequence and Rendering CallsDocumento334 páginasLog File Records Startup Sequence and Rendering CallsKossay BelkhammarAinda não há avaliações
- WSP Global EnvironmentDocumento20 páginasWSP Global EnvironmentOrcunAinda não há avaliações
- JurnalDocumento9 páginasJurnalClarisa Noveria Erika PutriAinda não há avaliações
- Innovation Through Passion: Waterjet Cutting SystemsDocumento7 páginasInnovation Through Passion: Waterjet Cutting SystemsRomly MechAinda não há avaliações
- Polyol polyether+NCO Isupur PDFDocumento27 páginasPolyol polyether+NCO Isupur PDFswapon kumar shillAinda não há avaliações
- The Impact of School Facilities On The Learning EnvironmentDocumento174 páginasThe Impact of School Facilities On The Learning EnvironmentEnrry Sebastian71% (31)
- Orc & Goblins VII - 2000pts - New ABDocumento1 páginaOrc & Goblins VII - 2000pts - New ABDave KnattAinda não há avaliações
- DIN Flange Dimensions PDFDocumento1 páginaDIN Flange Dimensions PDFrasel.sheikh5000158Ainda não há avaliações
- Annamalai International Journal of Business Studies and Research AijbsrDocumento2 páginasAnnamalai International Journal of Business Studies and Research AijbsrNisha NishaAinda não há avaliações
- Memo Roll Out Workplace and Monitoring Apps Monitoring Apps 1Documento6 páginasMemo Roll Out Workplace and Monitoring Apps Monitoring Apps 1MigaeaAinda não há avaliações