Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Poster1 Arrhythmia Recognition e PDF
Enviado por
Sergio ChangTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Poster1 Arrhythmia Recognition e PDF
Enviado por
Sergio ChangDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
GE Healthcare
Arrhythmia Recognition
Cardiac Conduction System ECG Components Electrical and Mechanical Events
LEFT
ATRIUM
Sinoatrial
Node
HIS Bundle
RIGHT ATRI-
UM
Left Bundle
Branch
Right Bundle
Branch LEFT
VENTRICLE
1 Small Square = 1 mm (0.1 mV) 1 Small Square = .04 sec (40 msec)
RIGHT
VENTRICLE VERTICAL 1 Large Square = 5 mm (0.5 mV) HORIZONTAL 1 Large Square = .2 sec (200 msec) Mid Atrial Isovolumic Ventricular Isovolumic
AXIS
2 Large Squares = 1 mV
AXIS
5 Large Squares = 1 sec (1000 msec)
Diastole Contraction Ventricular Ejection Ventricular
Contraction Relaxation
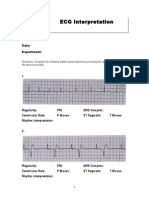
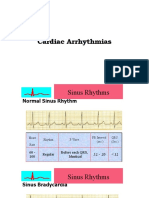
Sinus Rhythms Supraventricular Rhythms Conduction Defects
Normal Sinus Rhythm Premature Atrial Complexes PACs Atrial Tachycardia Right Bundle Branch Block
P Wave PR Interval QRS Characteristics
(in seconds) (in seconds)
Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS Before each QRS, 0.12 to 0.20 0.12 RSR in V1
(in seconds) (in seconds)
Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS identical
(in seconds) (in seconds)
60 100 bpm Regular Before each QRS, 0.12 to 0.20 < 0.12 140 250 bpm Regular Abnormal P before 0.12 to 0.20 < 0.12
identical Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS each QRS
(in seconds) (in seconds) (difcult to see) Left Bundle Branch Block
N/A Irregular Premature and 0.12 to 0.20 < 0.12
abnormal.
Sinus Arrhythmia May be hidden
Atrial Flutter
Premature Atrial Complex Isolated PAC
P Wave PR Interval QRS Characteristics
(in seconds) (in seconds)
Before each QRS, 0.12 to 0.20 0.12 QS or rS in V1 and V2
identical ST elevation
Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS Pre-excitation Syndrome
(in seconds) (in seconds) Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS (in seconds) (in seconds)
Usually Irregular Before each QRS, 0.12 to 0.20 < 0.12 (in seconds) (in seconds) A: 240 350 bpm A: Regular Flutter (F) waves usu- N/A < 0.12
60 100 bpm identical N/A Irregular Premature and 0.12 to 0.20 < 0.12 V: Varies with V: Regular, ally the negative com-
abnormal. conduction ratio group beating ponent of the utter
May be hidden or variable wave in II, III, aVF and
positive in V1
Sinus Tachycardia
Premature Atrial Complexes (Atrial Bigeminy) Atrial Fibrillation
Every other beat is a PAC
P Wave PR Interval QRS Characteristics
(in seconds) (in seconds)
Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS Before each QRS, < 0.12 Usually > 0.10 Delta wave
(in seconds) (in seconds)
identical distorts initial QRS
> 100 bpm Regular Before each QRS, 0.12 to 0.20 < 0.12 Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS
identical (in seconds) (in seconds)
A: 350 650 bpm Irregular Absent N/A < 0.12 First-Degree AV Block
Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS V: Slow to rapid Fibrillatory (f) waves
(in seconds) (in seconds)
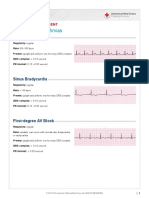
Sinus Bradycardia N/A Irregular Premature and 0.12 to 0.20 < 0.12
abnormal.
May be hidden Junctional Rhythm
Premature Atrial Complex with Aberrancy
P Wave PR Interval QRS Characteristics
(in seconds) (in seconds)
Before each QRS, > 0.20 < 0.12 Regular rhythm
Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS identical
(in seconds) (in seconds) Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS
< 60 bpm Regular Before each QRS, 0.12 to 0.20 < 0.12 (in seconds) (in seconds)
identical 40 60 bpm Regular Inverted in inferior < 0.12 < 0.12 Second-Degree AV Block Type I
leads; before, during
or after the QRS; (AV Wenckebach or Mobitz type I)
may be absent
Sinus Arrest or SA Block
P P P P P P
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm
Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS
(in seconds) (in seconds)
N/A Irregular Premature and 0.12 to 0.20 < 0.12
abnormal. Abnormal shape
May be hidden P Wave PR Interval QRS Characteristics
(in seconds) (in seconds)
Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS Conduction Increasingly < 0.12 QRS dropped in a
(in seconds) (in seconds) intermittent prolonged repeating pattern
40 100 bpm Irregular Identical before 0.12 to 0.20 < 0.12
each QRS.
P to P interval Nonconducted Premature Atrial Complex
may be xed before Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS Second-Degree AV Block Type II
and after the pause (in seconds) (in seconds) (Mobitz type II)
60 100 bpm Usually AV May be sinus P wave < 0.12 < 0.12
dissociation be- (AV dissociation)
cause of digitalis
toxicity
P Wave is buried in the T Wave.
NOTE: Notch is not present in other T Waves
Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS
Junctional Tachycardia
(in seconds) (in seconds) P Wave PR Interval QRS Characteristics
(in seconds) (in seconds)
N/A Irregular Premature and None Absent
abnormal. Sinus Usually normal Broad Some P waves
May be hidden and identical 0.12 are not conducted
(before and after a
blocked impulse)
Second-Degree AV Block 2:1 AV Block
Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS
(in seconds) (in seconds)
Usually Regular Inverted, absent or < 0.12 < 0.12
<140 bpm after QRS
P Wave PR Interval QRS Characteristics
(in seconds) (in seconds)
Sinus Normal or prolonged Narrow or broad 2:1 AV conduction
Third-Degree (Complete) AV Block
Arrhythmia Recognition (poster 1 of 2) Normal ECG Standards for Children by Age This poster includes Premature Ventricular Conduction, Pacemaker Lead
Placement, ST Segment Depression, Ventricular Rhythms, Pacemaker
This is part one of two posters to assist healthcare professionals in 01d 13d 37d 7 30 d 1 3 mo 3 6 mo 6 12 mo 13 y 35y 58y 8 12 y 12 16 y
Rhythms, Full Compensatory Pause and ECG Artifact. The ECG rhythm
recognizing basic arrhythmias. According to the Practice Standards Heart
Rate/Min
94 -155
(122)
91 - 158
(122)
90 - 166
(128)
106 - 182
(149)
120 - 179
(149)
105 - 185
(141)
108 - 169
(131)
89 - 152
(119)
73 - 137
(109)
65 - 133
(100)
62 - 130
(91)
60 - 120
(80) strips display lead II as the top waveform and lead V1 as the bottom
for Electrocardiographic Monitoring in Hospital Settings (Circulation. PR Interval 0.08 - 0.16 0.08 - 0.14 0.07 - 0.15 0.07 - 0.14 0.07 - 0.13 0.07 - 0.15 0.07 - 0.16 0.08 - 0.15 0.08 - 0.16 0.09 - 0.16 0.09 - 0.17 0.09 - 0.18 waveform. Classic examples are shown for each rhythm to provide basic
2004;110:2721-2746) in general, the mechanisms of arrhythmias are Lead II (0.107) (0.108) (0.102) (0.100) (0.098) (0.105) (0.106) (0.113) (0.119) (0.123) (0.128) (0.135) visualization and avoid complexities. The intended use of this poster is
the same in both adults and children. However, the ECG appearance of (Seconds) to compliment a text and/or course in addition to a reference guide for
the arrhythmias may differ due to developmental issues such as heart QRS Interval 0.02 - 0.07 0.02 - 0.07 0.02 - 0.07 0.02 - 0.08 0.02 - 0.08 0.02 - 0.08 0.03 - 0.08 0.03 - 0.08 0.03 - 0.07 0.03 - 0.08 0.04 - 0.09 0.04 - 0.09 arrhythmia recognition
size, baseline heart rate, sinus and AV node function, and automatic Lead V5 (0.05) (0.05) (0.05) (0.05) (0.05) (0.05) (0.05) (0.06) (0.06) (0.06) (0.06) (0.07)
The most common ECG rate, interval, and duration measurements are from the following publications: P Wave PR Interval QRS Characteristics
innervation. (Seconds)
Clinical Electrocardiography (Post Graduate Institute for Medicine). (in seconds) (in seconds)
All values 2nd 98th percentile; numbers in parentheses, means. Adapted from Pediatr Cardiol. 1979;1:123.
Understanding Electrocardiography (Mary Boudreau Conover). Normal but not related N/A Narrow or broad AV dissociation
ECG terminology and diagnostic criteria often vary from text to text and How to Quickly and Accurately Master Arrhythmia Interpretation (Dale Davis). to QRS
from one teacher to another. There are often several terms describing Principles of Clinical Electrocardiography (M. J. Goldman).
similar ndings (for example: Premature Atrial Contraction, Atrial Basic Dysrhythmias Interpretation and Management (Robert Huszar).
Premature Complex, Atrial Extrasystole, Supraventricular Ectopic Beat, An Introduction to Electrocardiography (Leo Shamroth).
etc.) It is important to correlate the ECG interpretation with the clinical Interpretation of Arrhythmias (Emanual Stein).
observation of the patient.
GE imagination at work
2027186-002 www.gehealthcare.com
Você também pode gostar
- Practice StripsDocumento9 páginasPractice StripsErica Yamamoto50% (4)
- DYSRHYTHMIAS (A.k.a. Arrhythmias) Disorders in TheDocumento3 páginasDYSRHYTHMIAS (A.k.a. Arrhythmias) Disorders in TheDarell M. Book100% (1)
- Normal Pediatric RR and HRDocumento1 páginaNormal Pediatric RR and HRRick FreaAinda não há avaliações
- Basic EKG Interpretation ExamDocumento13 páginasBasic EKG Interpretation Examtwdroppoint100% (1)
- Patho Exam 3 Study GuideDocumento5 páginasPatho Exam 3 Study GuideFarzanaAziziAinda não há avaliações
- Zero Based BudgetDocumento9 páginasZero Based Budgetapi-447860598Ainda não há avaliações
- Practice ECGStripsDocumento300 páginasPractice ECGStripsFarid RodríguezAinda não há avaliações
- CCU Clinical GuidelinesDocumento63 páginasCCU Clinical GuidelinesHAMMYER ALROKHAMIAinda não há avaliações
- LS Identifying ArrhythmiasDocumento5 páginasLS Identifying ArrhythmiasClaudia Park100% (1)
- Arterial Lines in PACU: Presented by Autum Jacobs RN, BSNDocumento34 páginasArterial Lines in PACU: Presented by Autum Jacobs RN, BSNinuko1212Ainda não há avaliações
- ECG Fast and Easy PPDocumento38 páginasECG Fast and Easy PPTara McNeillAinda não há avaliações
- Ekg Cheat SheetDocumento5 páginasEkg Cheat SheetAnonymous QBa0UurPAinda não há avaliações
- Poster1 Arrhythmia Recognition e PDFDocumento1 páginaPoster1 Arrhythmia Recognition e PDFMiko RamosoAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Surgical Nursing Critical Thinking in Patient Care Single Volume 4th Edition Lemone Test BankDocumento4 páginasMedical Surgical Nursing Critical Thinking in Patient Care Single Volume 4th Edition Lemone Test BankRebeccaGilliamAinda não há avaliações
- Ekg Panum or OsceDocumento69 páginasEkg Panum or OsceGladish RindraAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Ecg Interpretation and Arrhythmia Recognition By: Ma. Victoria E. Martinez Er - RNDocumento34 páginasBasic Ecg Interpretation and Arrhythmia Recognition By: Ma. Victoria E. Martinez Er - RNMavic Martinez BuntalesAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiac II Study GuideDocumento6 páginasCardiac II Study GuiderunnermnAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs and Defibrillation: Department of Anesthesiology & Reanimation General Hospital TasikmalayaDocumento20 páginasDrugs and Defibrillation: Department of Anesthesiology & Reanimation General Hospital TasikmalayaAfrida Sahestina100% (1)
- Chest Tube Explanation by AllnursesDocumento3 páginasChest Tube Explanation by AllnursesYemaya84Ainda não há avaliações
- Sample Acls For DummiesDocumento3 páginasSample Acls For DummiesTodd Cole100% (1)
- EKG Quick Reference ChartDocumento4 páginasEKG Quick Reference ChartMildaAinda não há avaliações
- Guide To Oxygen Delivery SystemDocumento3 páginasGuide To Oxygen Delivery SystemDarwin Villestas0% (1)
- 12 Lead EKG: Dr. Rita A. Dello StrittoDocumento18 páginas12 Lead EKG: Dr. Rita A. Dello Strittocuteralph1972Ainda não há avaliações
- ECG Dysrhthmias IIIDocumento31 páginasECG Dysrhthmias IIIAmani KayedAinda não há avaliações
- 11 Steps of ECG - Ali Alnahari PDFDocumento16 páginas11 Steps of ECG - Ali Alnahari PDFBìnhAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing School EKGDocumento43 páginasNursing School EKGRob Dickerson100% (1)
- IV PDFDocumento63 páginasIV PDFelbagouryAinda não há avaliações
- DR K Chan - Ecg For SVT Made EasyDocumento66 páginasDR K Chan - Ecg For SVT Made Easyapi-346486620Ainda não há avaliações
- ECG Master Class-2Documento138 páginasECG Master Class-2Shohag ID Center100% (1)
- HW InotropesDocumento3 páginasHW InotropesNatalie YeohAinda não há avaliações
- Dysrhytmia NotesDocumento11 páginasDysrhytmia NoteshannahhwolfAinda não há avaliações
- Poster1 Arrhythmia Recognition e PDFDocumento1 páginaPoster1 Arrhythmia Recognition e PDFPierf-17Ainda não há avaliações
- Sinus Rhythm DisturbancesDocumento3 páginasSinus Rhythm DisturbancesMarcus Philip GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- EkgDocumento67 páginasEkgFendi Rafif Dad'sAinda não há avaliações
- ECG at A GlanceDocumento53 páginasECG at A Glancenurliah armandAinda não há avaliações
- P Waves: Fast & Easy Ecgs - A Self-Paced Learning ProgramDocumento31 páginasP Waves: Fast & Easy Ecgs - A Self-Paced Learning Program.100% (1)
- ACLS Class Packet PDFDocumento9 páginasACLS Class Packet PDFImam GultomAinda não há avaliações
- ACLS Algorithms (2011)Documento6 páginasACLS Algorithms (2011)senbonsakuraAinda não há avaliações
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenDocumento23 páginasELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenItsMe AJAinda não há avaliações
- EKG - Assignment Without AnswersDocumento10 páginasEKG - Assignment Without AnswersJon Millhollon100% (1)
- Cardiac Disorders HandoutDocumento14 páginasCardiac Disorders HandoutRizielle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Selected Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions For Patients With DysrhythmiasDocumento19 páginasSelected Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions For Patients With Dysrhythmiaslanie_jecielAinda não há avaliações
- CPR ACLS Study GuideDocumento18 páginasCPR ACLS Study GuideJohn Phamacy100% (1)
- EKG InterpretationDocumento63 páginasEKG InterpretationMiriam Cindy MathullaAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology RevisedDocumento59 páginasPharmacology Revisedjohnstockton12100% (1)
- Critical Care Drugs 1Documento21 páginasCritical Care Drugs 1Asri ErnadiAinda não há avaliações
- Acls Seminar MeDocumento62 páginasAcls Seminar MeAbnet Wondimu100% (1)
- DrugDocumento3 páginasDrugkhangsiean89100% (1)
- Cardiac NotesDocumento24 páginasCardiac NotesYary MayorAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular & Hematologic SystemDocumento163 páginasCardiovascular & Hematologic SystemRellie CastroAinda não há avaliações
- Ecg Interpretation: Presented by:-ROHINI RAI M SC Nursing Part I, C.O.N, N.B.M.C.HDocumento69 páginasEcg Interpretation: Presented by:-ROHINI RAI M SC Nursing Part I, C.O.N, N.B.M.C.HRohini RaiAinda não há avaliações
- ICU Cheat SheetDocumento2 páginasICU Cheat SheetPrescilla Randazzo100% (1)
- Acid BaseDocumento89 páginasAcid BaseEdouinaAinda não há avaliações
- ArrhyDocumento26 páginasArrhyMouriyan AmanAinda não há avaliações
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideNo EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideAinda não há avaliações
- Hyper-coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo EverandHyper-coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsAinda não há avaliações
- Bhatti NotesDocumento100 páginasBhatti NotesSergio Chang100% (2)
- Acute Renal FailureDocumento14 páginasAcute Renal FailuredrtpkAinda não há avaliações
- New Evidence PyramidDocumento3 páginasNew Evidence PyramidSergio ChangAinda não há avaliações
- 李白 许渊冲 李白诗选汉英对照SELECTED POEMS OF LI BAI CHINESE-ENGLISH PDFDocumento272 páginas李白 许渊冲 李白诗选汉英对照SELECTED POEMS OF LI BAI CHINESE-ENGLISH PDFSergio ChangAinda não há avaliações
- Montana Polst FormDocumento2 páginasMontana Polst FormitargetingAinda não há avaliações
- Teratogenic ItyDocumento8 páginasTeratogenic ItyValentin IanaAinda não há avaliações
- Stem Cell Research ArticleDocumento4 páginasStem Cell Research Articleapi-248217035Ainda não há avaliações
- Siemens Mri Magnetom Mreadings Prostate PDFDocumento100 páginasSiemens Mri Magnetom Mreadings Prostate PDFnanaa02Ainda não há avaliações
- Concept Map 3 MM (Abdominal Pain)Documento2 páginasConcept Map 3 MM (Abdominal Pain)Matt McKinleyAinda não há avaliações
- TRAMADOLDocumento4 páginasTRAMADOLRudie Lee PascualAinda não há avaliações
- Rekap Umr 2019-4Documento52 páginasRekap Umr 2019-4Derri HafaAinda não há avaliações
- Latihan Soal Procedure TextDocumento2 páginasLatihan Soal Procedure TextSuwari RisnawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Case Studies 2007 Townend 443 53Documento12 páginasClinical Case Studies 2007 Townend 443 53cioaca12Ainda não há avaliações
- Virtual Long Bone DissectionDocumento2 páginasVirtual Long Bone Dissectionapi-438665079Ainda não há avaliações
- Fluids and Electrolytes Study GuideDocumento13 páginasFluids and Electrolytes Study GuideElizabeth McKeeAinda não há avaliações
- 1 BarashDP - Paradigms Lost AbridgedDocumento7 páginas1 BarashDP - Paradigms Lost AbridgedFABIOAinda não há avaliações
- Ocd Information Guide 2015 PDFDocumento48 páginasOcd Information Guide 2015 PDFAbdul ZenAinda não há avaliações
- Human Biology Laboratory 4: Body Tissues and Organization List The 4 Tissue Types and Give A General Function: Pg. 40Documento4 páginasHuman Biology Laboratory 4: Body Tissues and Organization List The 4 Tissue Types and Give A General Function: Pg. 40bugyourselfAinda não há avaliações
- Screenshot 2564-04-16 at 09.45.04Documento95 páginasScreenshot 2564-04-16 at 09.45.04Sarunpong ImampaiAinda não há avaliações
- Physical Capabilities of Instructors at The End of Hot Fire Training (0305) (158529)Documento42 páginasPhysical Capabilities of Instructors at The End of Hot Fire Training (0305) (158529)Onion PapaAinda não há avaliações
- Avascular Necrosis - Causes, Symptoms, Prevention & TreatmentDocumento26 páginasAvascular Necrosis - Causes, Symptoms, Prevention & TreatmentSatrio Bangun NegoroAinda não há avaliações
- Quick Guide To Understanding Narcissistic Personality DisorderDocumento2 páginasQuick Guide To Understanding Narcissistic Personality Disorderpsychdocs100% (1)
- Heart Attack & Drinking Warm WaterDocumento1 páginaHeart Attack & Drinking Warm Waterjoshua_sx180% (5)
- Overview He Most As IsDocumento20 páginasOverview He Most As IsManushi ChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- Navjaat Shishu Suraksha Karyakram: Training ManualDocumento99 páginasNavjaat Shishu Suraksha Karyakram: Training ManualBiswaranjan Padhy100% (1)
- Long-Term Prediction of Functional Outcome After Stroke Using Single Items of The Barthel Index at Discharge From Rehabilitation CentreDocumento7 páginasLong-Term Prediction of Functional Outcome After Stroke Using Single Items of The Barthel Index at Discharge From Rehabilitation CentretitinAinda não há avaliações
- Interns 2016 DistributionDocumento13 páginasInterns 2016 DistributionKashish ChawlaAinda não há avaliações
- Floyd Landis Letter of ConfessionDocumento3 páginasFloyd Landis Letter of ConfessionCycling FanAinda não há avaliações
- Animal Health Registered Technician in Los Angeles CA Resume Ivette NazarioDocumento2 páginasAnimal Health Registered Technician in Los Angeles CA Resume Ivette NazarioIvetteNazarioAinda não há avaliações
- Cardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation and AtrialDocumento13 páginasCardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation and AtrialLabontu IustinaAinda não há avaliações
- Biochemistry and Histocytochemistry Research DevelopmentsDocumento377 páginasBiochemistry and Histocytochemistry Research Developmentsfenrisulven2010100% (1)
- Oral Wound Healing Efficacy of 1% Myristica Fragrans (Nutmeg) Determined Using MTT Assay: An in Vitro StudyDocumento5 páginasOral Wound Healing Efficacy of 1% Myristica Fragrans (Nutmeg) Determined Using MTT Assay: An in Vitro StudyDeepthi ManjunathAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 15 - Autonomic Nervous System Course OutlineDocumento9 páginasChapter 15 - Autonomic Nervous System Course OutlineleoAinda não há avaliações
- XareltofinalDocumento2 páginasXareltofinalMuniba NasimAinda não há avaliações