Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
2 Marks Questions Unit I AM Modulation
Enviado por
Anonymous 3yqNzCxtTz0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
493 visualizações3 páginasamplitude modulation 2mark questions
Título original
2 Marks Questions Unit I AM modulation
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoamplitude modulation 2mark questions
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
493 visualizações3 páginas2 Marks Questions Unit I AM Modulation
Enviado por
Anonymous 3yqNzCxtTzamplitude modulation 2mark questions
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 3
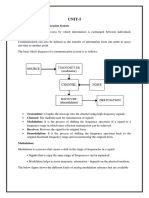
UNIT-I
AMPLITUDE MODULATION
(2 Marks Questions and Answers)
1. Define modulation?
Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier
Signal is varied in accordance with the instantaneous value of the modulating signal.
2. What are the types of analog modulation?
(i)Amplitude modulation. (ii)Angle Modulation
3. Define the term modulation index for AM.
Modulation index is the ratio of amplitude of modulating signal (Em) to
amplitude of carrier (Ec).
4. What are the degrees of modulation?
a) Under modulation (m < 1)
b) Critical modulation (m=1)
c) Over modulation (m>1)
5. What is the need for modulation?
Needs for modulation:
a) Ease of transmission
b) Multiplexing
c) Reduced noise
d) Narrow bandwidth
e) Frequency assignment
f) Reduce the equipments limitations.
6. What is the difference between high level and low level modulation?
In high level modulation, the modulator amplifier operates at high power levels
and delivers power directly to the antenna. In low level modulation, the modulator
amplifier performs modulation at relatively low power levels. The modulated signal is
then amplified to high power level by class B power amplifier. The amplifier feeds
power to antenna.
7. Define Detection.
Detection is the process of extracting modulating signal from the modulated
carrier. Different types of detectors are used for different types of modulations.
8. Define Amplitude Modulation.
In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of a carrier signal is varied according
to variations in amplitude of modulating signal.
The AM signal can be represented mathematically as, eAM = (Ec + Em sinmt
) sinct and the modulation index is given as,m = Em EC
9. What is Super Heterodyne Receiver?
The super heterodyne receiver converts all incoming RF frequencies to a fixed
lower frequency, called intermediate frequency (IF). This IF is then amplitude and
detected to get the original signal.
10. What is single tone and multi tone modulation?
If modulation is performed for a message signal with more than one frequency
component then the modulation is called multi tone modulation.
If modulation is performed for a message signal with one frequency
component then the modulation is called single tone modulation.
Analog Communication Systems 4 Dept. of ECE, SV Colleges, Tirupati
11. What are the advantages of VSB-AM?
1. It has bandwidth greater than SSB but less than DSB system.
2. Power transmission greater than DSB but less than SSB system.
3. No low frequency component lost. Hence it avoids phase
Distortion.
12. How will you generating DSBSC-AM?
There are two ways of generating DSBSC-AM such as
a).Balanced modulator
b).Ring modulators
13. Define Demodulation.
Demodulation or detection is the process by which modulating voltage is
recovered from the modulated signal. It is the reverse process of modulation. The
devices used for demodulation or detection are called demodulators or detectors. For
amplitude modulation, detectors or demodulators are categorized as,
a) Square-law detectors b) Envelope detectors
14. Define Multiplexing.
Multiplexing is defined as the process of transmitting several message signals
simultaneously over a single channel.
15. Define Frequency Division Multiplexing.
Frequency division multiplexing is defined as many signals are
transmitted simultaneously with each signal occupying a different frequency slot
within a common bandwidth.
16. Define Guard Band.
Guard Bands are introduced in the spectrum of FDM in order to avoid any
interference between the adjacent channels. Wider the guard bands, Smaller the
interference.
17. Define SSB-SC.
(i) SSB-SC stands for Single Side Band Suppressed Carrier
(ii) When only one sideband is transmitted, the modulation is referred to
as Single side band modulation. It is also called as SSB or SSB-SC.
18. Define DSB-SC.
After modulation, the process of transmitting the sidebands (USB, LSB) alone
and suppressing the carrier is called as Double Side Band-Suppressed Carrier.
19. Define Coherent Detection.
During Demodulation carrier is exactly coherent or synchronized in both the
frequency and phase, with the original carrier wave used to generate the DSB-SC
wave. This method of detection is called as coherent detection or synchronous
detection.
20. What is Vestigial Side Band Modulation?
Vestigial Sideband Modulation is defined as a modulation in which one of the
sideband is partially suppressed and the vestige of the other sideband is transmitted
to compensate for that suppression.
21. What are the advantages of signal sideband transmission?
a) Power consumption
b) Bandwidth conservation
c) Noise reduction
22. What are the disadvantages of single side band transmission?
Analog Communication Systems 4 Dept. of ECE, SV Colleges, Tirupati
a) Complex receivers: Single side band systems require more complex and
expensive receivers than conventional AM transmission.
b) Tuning difficulties: Single side band receivers require more complex
And precise tuning than conventional AM receivers.
23. What is frequency translation?
Suppose that a signal is band limited to the frequency range extending from a
frequency f1 to a frequency f2. The process of frequency translation is one in which
the original signal is replaced with a new signal whose spectral range extends from
f1 and f2 and which new signal bears, in recoverable form the same information as
was borne by the original signal.
24. What is BW for AM wave?
The difference between these two extreme frequencies is equal to the
bandwidth of the AM wave.
Therefore, Bandwidth, B = (c + m) - (c - m) B = 2m
25. What is the BW of DSB-SC signal?
Bandwidth, B = (c + m) - (c - m) B = 2
It is obvious that the bandwidth of DSB-SC modulation is same as that of general AM
waves.
26. What are the demodulation methods for DSB-SC signals?
The DSB-SC signal may be demodulated by following two methods:
(i) Synchronous detection method.
(ii)Using envelope detector after carrier reinsertion.
27. Write the applications of Hilbert transform?
(i) For generation of SSB signals, (ii)For designing of minimum phase type
filters, (iii) For representation of band pass signals.
28. What are the methods for generating SSB-SC signal?
SSB-SC signals may be generated by two methods as under:
(i)Frequency discrimination method or filter method.
(ii)Phase discrimination method or phase-shift method.
Analog Communication Systems 4 Dept. of ECE, SV Colleges, Tirupati
Você também pode gostar
- K. Ramakrishnan College of Technology:) Samayapuram, Trichy - 621 112Documento20 páginasK. Ramakrishnan College of Technology:) Samayapuram, Trichy - 621 112ManimegalaiAinda não há avaliações
- Ec 6402 Communication Theory: Unit-I Amplitude Modulation 1. Define Modulation?Documento16 páginasEc 6402 Communication Theory: Unit-I Amplitude Modulation 1. Define Modulation?Dinesh Kumar RAinda não há avaliações
- CS ShortQuestions&AnswersDocumento13 páginasCS ShortQuestions&AnswersPanga AnithaAinda não há avaliações
- Learn Amateur Radio Electronics on Your SmartphoneNo EverandLearn Amateur Radio Electronics on Your SmartphoneAinda não há avaliações
- CT 2 Marks - 2 UnitsDocumento14 páginasCT 2 Marks - 2 UnitsNEELAVATHI.G MEC-AP/ECEAinda não há avaliações
- Maria College of Engineering and Technology, Attoor: Unit-I Amplitude Modulation SystemsDocumento27 páginasMaria College of Engineering and Technology, Attoor: Unit-I Amplitude Modulation Systemsyohans shegawAinda não há avaliações
- The Technician's Radio Receiver Handbook: Wireless and Telecommunication TechnologyNo EverandThe Technician's Radio Receiver Handbook: Wireless and Telecommunication TechnologyAinda não há avaliações
- Ac Unit1Documento5 páginasAc Unit1sravanAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Marks-Unit-1Documento143 páginas2 Marks-Unit-1Thenappan SAinda não há avaliações
- Two Marks QuestionDocumento26 páginasTwo Marks QuestionsuryasitAinda não há avaliações
- Communication Theory Two MarksDocumento40 páginasCommunication Theory Two Markssenthilkumar100% (1)
- Communication Theory 2 MarksDocumento24 páginasCommunication Theory 2 MarksabvajaAinda não há avaliações
- Anna University Engineering Question Bank: Home About Us Downloads Answers Upload Contact USDocumento42 páginasAnna University Engineering Question Bank: Home About Us Downloads Answers Upload Contact USChenthil KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Experinment AM Short ReportDocumento14 páginasExperinment AM Short ReportMuhammad JibranAinda não há avaliações
- Ac Unit 1 2marksDocumento5 páginasAc Unit 1 2marksvictor kAinda não há avaliações
- Analog and DigitalDocumento26 páginasAnalog and DigitalMd Raton AliAinda não há avaliações
- IT 2202 PocDocumento41 páginasIT 2202 PocapecevsbAinda não há avaliações
- Analog and Digital CommunicationDocumento20 páginasAnalog and Digital CommunicationnofeelingrahulAinda não há avaliações
- CT QBDocumento23 páginasCT QBAli khan7Ainda não há avaliações
- Analog Communications: BY P.Swetha, Assistant Professor (Units 1, 2 & 5) K.D.K.Ajay, Assistant Professor (Units 3 & 4)Documento88 páginasAnalog Communications: BY P.Swetha, Assistant Professor (Units 1, 2 & 5) K.D.K.Ajay, Assistant Professor (Units 3 & 4)Sagar Babu NandigamaAinda não há avaliações
- Analog Communications-Notes PDFDocumento110 páginasAnalog Communications-Notes PDFjyothimunjam100% (1)
- CS File-1Documento19 páginasCS File-1Shruti NarangAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-Ii Angle Modulation 2marks Questions and AnswersDocumento4 páginasUnit-Ii Angle Modulation 2marks Questions and AnswersbnatarajAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter Two: Topics Discussed in This SectionDocumento35 páginasChapter Two: Topics Discussed in This SectionSolomon Tadesse AthlawAinda não há avaliações
- JA Meshal Alotaibi: Background of DSB-AMDocumento4 páginasJA Meshal Alotaibi: Background of DSB-AMMaharshiGohelAinda não há avaliações
- EC1311 Communication EngineeringDocumento23 páginasEC1311 Communication EngineeringVidya NeemuAinda não há avaliações
- Analog and Digital Communication Important Questions AnswersDocumento21 páginasAnalog and Digital Communication Important Questions AnswersMehboob Khokhar75% (4)
- Adc QB 2020Documento14 páginasAdc QB 2020priyaroopaAinda não há avaliações
- Mod C A C M 4 C MDocumento17 páginasMod C A C M 4 C MJKAinda não há avaliações
- Amplitude ModulationDocumento16 páginasAmplitude Modulationrov100Ainda não há avaliações
- Basic of Communication EngineeringDocumento66 páginasBasic of Communication EngineeringRohitUikeyAinda não há avaliações
- Afit Modulations - SentDocumento37 páginasAfit Modulations - SentadebanwoadelanaAinda não há avaliações
- Adc Two MarksDocumento22 páginasAdc Two MarksapecevsbAinda não há avaliações
- Communication TheoryDocumento156 páginasCommunication TheoryMuumini De Souza NezzaAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-I: Introduction To Communication SystemDocumento107 páginasUnit-I: Introduction To Communication SystemSivaKumarAinda não há avaliações
- 1 and 2 NotesDocumento65 páginas1 and 2 NotesMylavarapu SriprithamAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Communication System Chapter Two Analog Modulation TechniquesDocumento47 páginasIntroduction To Communication System Chapter Two Analog Modulation Techniqueshenok getachewAinda não há avaliações
- Question Bank (I and II)Documento4 páginasQuestion Bank (I and II)Anonymous 4u5XkWGOAinda não há avaliações
- Analog and Digital CommunicationDocumento11 páginasAnalog and Digital CommunicationKarthi KeyanAinda não há avaliações
- CSP Lab1Documento8 páginasCSP Lab1Jossan EleazarEDENAinda não há avaliações
- Amplitude Modulation1Documento44 páginasAmplitude Modulation1Dilbagh SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Analog Communication SystemsDocumento15 páginasAnalog Communication SystemsJuan Angel Cerda GuerraAinda não há avaliações
- U6 L2 Multichannel Transmission TechniquesRF Over Fiber1Documento4 páginasU6 L2 Multichannel Transmission TechniquesRF Over Fiber1Pratiwi Kusumawardani Ji-WeeAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2Documento31 páginasLecture 2taif.mossa88Ainda não há avaliações
- Analog Communication Lab Final Doc SRN PDFDocumento90 páginasAnalog Communication Lab Final Doc SRN PDFChaitanya ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- EC21B1001 JOssan LAb1Documento8 páginasEC21B1001 JOssan LAb1Jossan EleazarEDENAinda não há avaliações
- Ele 3203 - Lab6 - Am - SSB (1) - 1Documento5 páginasEle 3203 - Lab6 - Am - SSB (1) - 1Maitha SaeedAinda não há avaliações
- Agni College of Technology Agni College of Technology Agni College of TechnologyDocumento19 páginasAgni College of Technology Agni College of Technology Agni College of TechnologyparantnAinda não há avaliações
- It 1202 - Principles of CommunicationDocumento20 páginasIt 1202 - Principles of CommunicationainugiriAinda não há avaliações
- Communication Lecture PDFDocumento179 páginasCommunication Lecture PDFMasum BillahAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1 PDFDocumento31 páginasUnit 1 PDFvijayAinda não há avaliações
- ET-353, Lecture 13&14 (AM) (AM-DSB-LC, DSBSC)Documento66 páginasET-353, Lecture 13&14 (AM) (AM-DSB-LC, DSBSC)Jahanzaib MushtaqAinda não há avaliações
- Communication Engineering 2 MarksDocumento38 páginasCommunication Engineering 2 MarksNandhini100% (2)
- Modulation Systems Used in Satellite CommunicationsDocumento15 páginasModulation Systems Used in Satellite CommunicationsMuhammad Riaz Khan100% (1)
- ECOM - Expt 1Documento5 páginasECOM - Expt 1Joe MilsapAinda não há avaliações
- Kaizen CostingDocumento4 páginasKaizen CostingAnonymous 3yqNzCxtTzAinda não há avaliações
- DispersionDocumento8 páginasDispersionAnonymous 3yqNzCxtTzAinda não há avaliações
- Cost Control MeaningDocumento26 páginasCost Control MeaningAnonymous 3yqNzCxtTzAinda não há avaliações
- Measures of Central TendencyDocumento14 páginasMeasures of Central TendencyAnonymous 3yqNzCxtTzAinda não há avaliações
- Self Balancing LedgersDocumento10 páginasSelf Balancing LedgersAnonymous 3yqNzCxtTzAinda não há avaliações
- Wild, Shaw, and Chiappetta Fifth EditionDocumento41 páginasWild, Shaw, and Chiappetta Fifth EditionAnonymous 3yqNzCxtTzAinda não há avaliações
- DR Rachna Mahalwala - B.Com III Year Management AccountingDocumento5 páginasDR Rachna Mahalwala - B.Com III Year Management AccountingAnonymous 3yqNzCxtTzAinda não há avaliações
- Pricing Decisions PDFDocumento4 páginasPricing Decisions PDFAnonymous 3yqNzCxtTzAinda não há avaliações
- Tally MCQDocumento21 páginasTally MCQAnonymous 3yqNzCxtTzAinda não há avaliações
- Tally List of Ledger and GroupsDocumento7 páginasTally List of Ledger and GroupsAnonymous 3yqNzCxtTz100% (1)
- Faculty Profiles: Sri Venkateswara University: TirupatiDocumento2 páginasFaculty Profiles: Sri Venkateswara University: TirupatiAnonymous 3yqNzCxtTzAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Seminar ReportDocumento7 páginasSample Seminar ReportAnonymous 3yqNzCxtTzAinda não há avaliações
- Tally ERP 2017-18 - Basic LevelDocumento44 páginasTally ERP 2017-18 - Basic LevelAnonymous 3yqNzCxtTzAinda não há avaliações
- Drone Hacker 123Documento13 páginasDrone Hacker 123Anonymous 3yqNzCxtTzAinda não há avaliações
- Sri Venkateswara UniversityDocumento12 páginasSri Venkateswara UniversityAnonymous 3yqNzCxtTzAinda não há avaliações
- First Order Differential Microphone ArraysDocumento4 páginasFirst Order Differential Microphone ArraystatakillAinda não há avaliações
- HDDJ Turning An Old Hard Disk Drive Into A RotaryDocumento12 páginasHDDJ Turning An Old Hard Disk Drive Into A RotaryCarlos Baca SotoAinda não há avaliações
- EE Lab#08 Group#04Documento11 páginasEE Lab#08 Group#04Maida IrshadAinda não há avaliações
- Panasonic Gp2 Chassis Tx29f150m TV SMDocumento20 páginasPanasonic Gp2 Chassis Tx29f150m TV SMRider AlexandreAinda não há avaliações
- Abstraction: How Electronics Devices Begin?Documento11 páginasAbstraction: How Electronics Devices Begin?Shane Patrick PanilagAinda não há avaliações
- HW1 SolDocumento4 páginasHW1 SolRanga GuraniAinda não há avaliações
- 9A04501 Analog CommunicationsDocumento4 páginas9A04501 Analog CommunicationssivabharathamurthyAinda não há avaliações
- Surface Profile Measurment SOPDocumento2 páginasSurface Profile Measurment SOPMd Anamul HoqueAinda não há avaliações
- Operating Instructions 4427, 4428, 4429.: Always On The Safe SideDocumento14 páginasOperating Instructions 4427, 4428, 4429.: Always On The Safe SideMxScribdAinda não há avaliações
- DTMF Based Home Automation System Using MicrocontrollerDocumento19 páginasDTMF Based Home Automation System Using MicrocontrollersreevaathavaAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Logic Design Lab 213371Documento24 páginasComputer Logic Design Lab 213371Habib Ur rehmanAinda não há avaliações
- Cqm1 Cqm1h ManualDocumento75 páginasCqm1 Cqm1h ManualCicero MelloAinda não há avaliações
- APPENDIX I PRINCIPLES FOR LAYOUT PLANS AND SECTIONING DIAGRAMS FOR 25 KV Ac TRACTION PDFDocumento19 páginasAPPENDIX I PRINCIPLES FOR LAYOUT PLANS AND SECTIONING DIAGRAMS FOR 25 KV Ac TRACTION PDFankitAinda não há avaliações
- Ecore: ControllerDocumento2 páginasEcore: ControllerLeonardusAinda não há avaliações
- Infineon AIMDQ75R008M1H 1Documento16 páginasInfineon AIMDQ75R008M1H 1maxmoron600Ainda não há avaliações
- Some Useful Points and Comments To Be Considered by The BidderDocumento1 páginaSome Useful Points and Comments To Be Considered by The Bidderﺣﻤﻴﺪ ﻫﻤﺪﺍﻥ ﺍﻻﺷﻮﻝAinda não há avaliações
- Kocnice Za ElektromotoreDocumento73 páginasKocnice Za Elektromotorestefa981Ainda não há avaliações
- SDMO Brochure 700-3300 kVA MTU DBRDocumento16 páginasSDMO Brochure 700-3300 kVA MTU DBRAra AkramAinda não há avaliações
- Inside Your ComputerDocumento71 páginasInside Your Computernesher9100% (9)
- mate 8线路图Documento60 páginasmate 8线路图Bitler Flores TAinda não há avaliações
- DSP Lab 21-09-2021Documento78 páginasDSP Lab 21-09-2021POORNIMA PAinda não há avaliações
- Ca Si LV en Dry Type Transformers Brochure EM LP 1612 - OriginalDocumento6 páginasCa Si LV en Dry Type Transformers Brochure EM LP 1612 - OriginalJaime PaizAinda não há avaliações
- ZFB CalculationDocumento13 páginasZFB CalculationmaheshAinda não há avaliações
- 5.1 exercisesMSDocumento8 páginas5.1 exercisesMSEnano MailhosAinda não há avaliações
- Iec 60364 4 43 2008Documento15 páginasIec 60364 4 43 2008KristofAinda não há avaliações
- ENMED301055EN - Flite 210 - 042013Documento2 páginasENMED301055EN - Flite 210 - 042013Tirthankar DattaAinda não há avaliações
- CH3 - ModulationDocumento31 páginasCH3 - ModulationNorman OcoAinda não há avaliações
- Smart Blind StickDocumento4 páginasSmart Blind StickInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyAinda não há avaliações
- Epox KT133 ManualDocumento54 páginasEpox KT133 ManualChris BlackburnAinda não há avaliações
- Evertz 7746FS 1v6 - 3 ManualDocumento62 páginasEvertz 7746FS 1v6 - 3 ManualErik VahlandAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsNo EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Hacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxNo EverandHacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (67)
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsNo EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsAinda não há avaliações
- Microsoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900No EverandMicrosoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900Ainda não há avaliações
- Cybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringNo EverandCybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (40)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamNo EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamAinda não há avaliações
- Cybersecurity: The Beginner's Guide: A comprehensive guide to getting started in cybersecurityNo EverandCybersecurity: The Beginner's Guide: A comprehensive guide to getting started in cybersecurityNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNNo EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionNo EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (4)
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsNo EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsAinda não há avaliações
- Networking Fundamentals: Develop the networking skills required to pass the Microsoft MTA Networking Fundamentals Exam 98-366No EverandNetworking Fundamentals: Develop the networking skills required to pass the Microsoft MTA Networking Fundamentals Exam 98-366Ainda não há avaliações
- Azure Networking: Command Line Mastery From Beginner To ArchitectNo EverandAzure Networking: Command Line Mastery From Beginner To ArchitectAinda não há avaliações
- ITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationNo EverandITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksNo EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2)
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamNo EverandAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Computer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)No EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)Ainda não há avaliações
- Computer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityNo EverandComputer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (13)
- Internet of Things: Principles and ParadigmsNo EverandInternet of Things: Principles and ParadigmsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (6)
- Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignNo EverandOpen Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignAinda não há avaliações