Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Final Exam 2012 PDF
Enviado por
ashaTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Final Exam 2012 PDF
Enviado por
ashaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
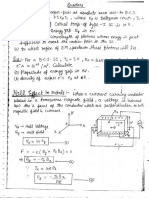
Final Exam 2012
Class XI
1. Write the following units, used for measuring large distances, in descending order- Light year, parsec and
astronomical unit. (1)
2. Area of parallelogram drawn with vectors and as its adjacent sides is 1/2 AB. What is the angle between
and ? (1)
3. What is the force acting on a body if distance travelled by it is proportional to time? (1)
4. What physical quantity is represented by area under force-displacement curve? (1)
5. Two solid spheres of same mass are made of metals of different densities. Which of then has larger moment of
inertia about its diameter? (1)
6. How will the ration stress/strain change if the deforming force is very large? (1)
0
7. Why a beaker filled with water at 4 C overflows whether the temperature is increased or decreased? (1)
8. Show graphically the variation of velocity of a small sphere dropped from rest into a viscous liquid with time. (1)
9. Find the dimensions of aXb in the equation F = a2x + b3t2, where F is force, x is distance and it t is time. (2)
10. Show that the area under velocity-time graph of an object moving with constant acceleration in a straight line
in a certain time interval is equal to the distance covered by the object in that interval. (2)
OR
Define the term relative velocity. Draw position-time graph of two objects moving with some relative with
respect to each other. (2)
11. A ball is thrown upward with an initial velocity of 100 m/sec. Draw velocity time graph for the ball and from the
graph find (i) maximum height attained by the ball
(ii) height of the ball after 15 sec. g = 10 m/sec2 (2)
12. A car of mass 1000 kg accelerates uniformly from rest to a velocity of 60 km/hr in 10 sec. Calculate
(i) gain in K.E (ii) average power of the engine. (2)
13. Derive an expression for moment of inertia of a circular disc about its diameter if moment of inertia about an
axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane is MR2 where M is the mass and R is radius
of the disc. State the theorem used. (2)
14. At what height above the earths surface, the value of g is same as in a mine 80km deep? (2)
15. Derive an expression for work done in an isothermal process. What do you mean by ve work in
such a process? (2)
16. A Carnot engine takes 3 X 10 cal of heat from a reservoir at 6270C and gives it to a sink at 270C. Find the
6
mechanical work obtained from the engine in Joule. (2)
17. Show that the pressure exerted by a gas is two-thirds the average K.E. per unit volume of the gas
molecules. (2)
18. An incident wave is represented by y (x, t) = 20 sin (2x 4t)
Write the expression for reflected wave (i) from the rigid boundary (ii) from an open boundary (2)
19. State Newtons second law of motion. Derive a mathematical relation for force if mass remains constant. Hence
deduce and state First law of motion. (3)
20. A light string passing over a smooth pulley connects two blocks of masses m1 and m2 vertically. If acceleration
of the system is g/8, find the ratio of the masses. (3)
21. Distinguish between static and kinetic friction. Why static friction is called a self-adjusting force?
Explain using graphical variation of friction with applied force. What is the maximum value of static friction
called? (3)
22. What is the nature of forces involved in an elastic collision? Calculate the velocities of two bodies after an
elastic collision in one-dimension. (3)
23. Define the term angular momentum, Give its units and dimensions. Derive a relation between torque and angular
momentum. (3) OR
A ring of diameter 0.4 m and mass 10 kg is rotating about its axis to the rate of 2100 rpm. Find
(i) moment of inertia (ii) angular momentum and (iii) rotational K.E. of the ring. (3)
24. Define orbital velocity of a satellite. Derive an expression for it. Show that all low satellites have same orbital
velocity. (3)
25. State Stokes law. Deduce this law by the method of dimensions stating the conditions under which it is
valid. (3)
26. Calculate the temperature at which root mean square velocity of gas molecules of a gas is double its value at
270C, pressure of the gas reaming constant. (3)
27. Show that in simple Harmonic Motion, acceleration lags behind the displacement by . Show the phase
relationship graphically also. (3)
28. (a) A projectile is thrown with velocity u at an angle with the horizontal. Derive an expression for the
horizontal range covered by it. (2)
0
(b) A ball is kicked at an angle of 30 with the vertical. If the horizontal component of its velocity is 19.6
m/sec, find the maximum height and horizontal range covered by the ball. (3)
OR
(a) State Triangle Law of Addition of vectors. Two vectors A and B are at an angle to each other. Show
mathematically that their resultant will make an angle with each vector if A = B. (3)
(b) Two forces are of equal magnitude F. How can the forces be combined to have a resultant of magnitude
(i) F (b) 2F (2)
29. State Bernoullis theorem. What type of liquid flow obeys this theorem? A cylindrical vessel of uniform cross-
section contains liquid upto a height H. At a depth h = (H/2) below the free surface of the liquid there is an
orifice. Using Bernoullis Theorem, find the velocity of efflux of the liquid. (5)
OR
What is the phenomenon of capillarity? Derive an expression for the rise of liquid in a capillary tube. What
will happen if the length of the capillary tube is smaller than the height to which liquid rises? Explain
briefly. (5)
30. A progressive wave is given by y (x, t) = 8 Cos (300 t 0.15 X), where x is in metre, y in cm and t is in
second, what is the: (i) direction of propagation (ii) wavelength (iii) frequency
(iv) wave speed (v) phase difference between two points 0.2 m apart? (5)
OR
Write expressions for potential energy an kinetic energy of a harmonic oscillator. Hence show that total
energy is conserved in SHM. Draw graphical variation of
(i) Potential Energy (ii) Kinetic Energy (iii) Total Energy with time. (5)
Você também pode gostar
- ICSE Class 11 Annual Exam Model Question Paper 2 - PHYSICSDocumento3 páginasICSE Class 11 Annual Exam Model Question Paper 2 - PHYSICSArindam SardarAinda não há avaliações
- Half Yearly Exam 2018-19 Class XI PhysicsDocumento3 páginasHalf Yearly Exam 2018-19 Class XI PhysicsKavya RajpootAinda não há avaliações
- Chanakya Vidyalaya STD 11: Physics Unit TestDocumento51 páginasChanakya Vidyalaya STD 11: Physics Unit TestANUBHAV ThakurAinda não há avaliações
- Class Xi Physics Annual Exam 2017 18Documento3 páginasClass Xi Physics Annual Exam 2017 18Anupam TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- Physics (Theory) Class - Xi Course Code-042Documento10 páginasPhysics (Theory) Class - Xi Course Code-042Puneet KumarAinda não há avaliações
- List of DerivationsDocumento7 páginasList of DerivationsJaruAinda não há avaliações
- XI (2018-19) Physics Quarterly Exam QPDocumento7 páginasXI (2018-19) Physics Quarterly Exam QPD SamyAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Set 4Documento4 páginasCBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Set 4yatinchaudhary0571Ainda não há avaliações
- 11 PHY Set 2Documento5 páginas11 PHY Set 2dikshachoud44Ainda não há avaliações
- CAPE Physics Unit I MarathonDocumento26 páginasCAPE Physics Unit I MarathonLeighton ThompsonAinda não há avaliações
- Worksheet XI AE Physics 202324Documento3 páginasWorksheet XI AE Physics 202324cutuAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Models-I PU PhysicsDocumento40 páginas7 Models-I PU PhysicsMir RayyanAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper-09 (Solved)Documento23 páginasCBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper-09 (Solved)cbsesamplepaper0% (1)
- SEO-OPTIMIZED PHYSICS ASSIGNMENT TITLEDocumento6 páginasSEO-OPTIMIZED PHYSICS ASSIGNMENT TITLEAmogh VaishnavAinda não há avaliações
- A2 RevisionDocumento10 páginasA2 Revisiongaya8404Ainda não há avaliações
- Physics 5Documento7 páginasPhysics 5Sam ManochaAinda não há avaliações
- 11 - TH - Final - Phy Exam Sample PaperDocumento3 páginas11 - TH - Final - Phy Exam Sample PaperPrakhar SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Worksheet - RevisionDocumento7 páginasWorksheet - RevisionAliza IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE-Sample-Papers-for-Class-11-Physics-SET-A-11......-1Documento4 páginasCBSE-Sample-Papers-for-Class-11-Physics-SET-A-11......-1Neerada NasAinda não há avaliações
- Annual Examination Physics (Theory) Code - B: Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70Documento4 páginasAnnual Examination Physics (Theory) Code - B: Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70Sumathi SrinivasAinda não há avaliações
- Physics exam questions on energy, momentum, waves and heatDocumento4 páginasPhysics exam questions on energy, momentum, waves and heatAlexis Ameen CruzerAinda não há avaliações
- 11 Phy - Set B Ut-2Documento4 páginas11 Phy - Set B Ut-2dikshachoud44Ainda não há avaliações
- 2010 h2 Prelims Revsion BDocumento26 páginas2010 h2 Prelims Revsion BBenjamin Teo0% (1)
- TestDocumento10 páginasTestSIMPIAinda não há avaliações
- SQP Hy 11 2022 23Documento13 páginasSQP Hy 11 2022 23It's all About fitnessAinda não há avaliações
- PHYSICSDocumento21 páginasPHYSICSdishugirdhar08100% (1)
- Physics 2Documento7 páginasPhysics 2iitiansrd2025Ainda não há avaliações
- Lc021alp000ev 3Documento12 páginasLc021alp000ev 3SnivySerpentAinda não há avaliações
- GEMS International School, Karnal LC 1 Assessment Physics ExamDocumento4 páginasGEMS International School, Karnal LC 1 Assessment Physics ExamrachnaAinda não há avaliações
- Shack Pre-Mock Examinations 2016 P510/1 Physics Paper 1Documento9 páginasShack Pre-Mock Examinations 2016 P510/1 Physics Paper 1EfrataAinda não há avaliações
- AssignmentDocumento6 páginasAssignmentAishley MatharooAinda não há avaliações
- 11 Physics Sample Papers Solved 05Documento24 páginas11 Physics Sample Papers Solved 05Shivam GargAinda não há avaliações
- Trialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionDocumento6 páginasTrialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionMathew Cheng Yu HaoAinda não há avaliações
- Revision Test (Waves, Mechanical Properties of Solid)Documento3 páginasRevision Test (Waves, Mechanical Properties of Solid)ShioAinda não há avaliações
- Class Xi Practice Paper 1Documento2 páginasClass Xi Practice Paper 1Anonymous vRpzQ2BLAinda não há avaliações
- KCT MODEL EXAM ENGINEERING MECHANICSDocumento4 páginasKCT MODEL EXAM ENGINEERING MECHANICSArunGopal PonnusamyAinda não há avaliações
- Edexcel A-LEVEL PHY4 January 2003 QPDocumento2 páginasEdexcel A-LEVEL PHY4 January 2003 QPapi-3726022Ainda não há avaliações
- Physics exam with 30 questionsDocumento7 páginasPhysics exam with 30 questionsHarsh ChoudharyAinda não há avaliações
- 1 DaDocumento17 páginas1 DaTrishnee MunusamiAinda não há avaliações
- Physics - 2012Documento4 páginasPhysics - 2012ammaarafzalAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper-08 (Solved)Documento22 páginasCBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper-08 (Solved)cbsesamplepaperAinda não há avaliações
- Re-Test (2020-2021) Physics: (Managed by The Trust of Society of St. Basil)Documento3 páginasRe-Test (2020-2021) Physics: (Managed by The Trust of Society of St. Basil)Youthful BoyAinda não há avaliações
- Y11 Physics 2022 Model Paper Answer KeyDocumento71 páginasY11 Physics 2022 Model Paper Answer KeyMadhan chakravarthyAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Set 5Documento3 páginasCBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Set 5Prajin MuruganAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Questions Vol-Ii Bernard PDF PDFDocumento2 páginasPhysics Questions Vol-Ii Bernard PDF PDFSilva scary svAinda não há avaliações
- PHYSICS CorrectionDocumento2 páginasPHYSICS CorrectionAdewumi AdinoyAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Model QP Class XIDocumento4 páginasCBSE Model QP Class XIroythomascAinda não há avaliações
- Part - I (MCQ) (Compulsory) : M A A ADocumento2 páginasPart - I (MCQ) (Compulsory) : M A A AMansoor Ali KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Model Paper Physics Objective and SubjectiveDocumento4 páginasModel Paper Physics Objective and SubjectiveAsifa AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- Physics 1/F1002 dimensional analysis and vectorsDocumento19 páginasPhysics 1/F1002 dimensional analysis and vectorsIan Gerardo Memije NuñezAinda não há avaliações
- PHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 3 Questions PDFDocumento9 páginasPHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 3 Questions PDFAlbertAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Paper Physics Class XiDocumento6 páginasSample Paper Physics Class XiBhaskar JhaAinda não há avaliações
- Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Eaving Ertificate XaminationDocumento12 páginasCoimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Eaving Ertificate Xaminationfrank mutaleAinda não há avaliações
- Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Eaving Ertificate XaminationDocumento12 páginasCoimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Eaving Ertificate Xaminationfrank mutaleAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Sets Model Questions of PhysicsDocumento27 páginas5 Sets Model Questions of Physicsdast DonAinda não há avaliações
- PHYSICS - Model – I, II, IIIDocumento12 páginasPHYSICS - Model – I, II, IIIVenkata SatyasubrahmanyamAinda não há avaliações
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2No EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- White GrapheneDocumento4 páginasWhite GrapheneashaAinda não há avaliações
- 159 PDF PDFDocumento7 páginas159 PDF PDFashaAinda não há avaliações
- Nanoparticles: Preparation, Characterization, Applications: Wet-Chemical MethodsDocumento2 páginasNanoparticles: Preparation, Characterization, Applications: Wet-Chemical MethodsashaAinda não há avaliações
- Grating Normal DeviationDocumento2 páginasGrating Normal DeviationashaAinda não há avaliações
- Determining the Reduction Factor of a Helmoltz Tangent GalvanometerDocumento3 páginasDetermining the Reduction Factor of a Helmoltz Tangent GalvanometerashaAinda não há avaliações
- Special RelativityDocumento17 páginasSpecial RelativityDiego M GranziolAinda não há avaliações
- 34556-11820-JEST Sample Question PhysicsDocumento1 página34556-11820-JEST Sample Question PhysicsTrisha BanerjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Magnetic Field On The Axis of A CoilDocumento1 páginaMagnetic Field On The Axis of A CoilashaAinda não há avaliações
- III-B.Sc Practical: I Set-Experiments ListDocumento1 páginaIII-B.Sc Practical: I Set-Experiments ListashaAinda não há avaliações
- Measuring High Resistance Using a Ballistic GalvanometerDocumento1 páginaMeasuring High Resistance Using a Ballistic GalvanometerRavi Kanth M NAinda não há avaliações
- Self Inductance of A Given Coil by Anderson's BridgeDocumento2 páginasSelf Inductance of A Given Coil by Anderson's BridgeashaAinda não há avaliações
- Determine Coil Induction with Parallel ResonanceDocumento2 páginasDetermine Coil Induction with Parallel ResonanceashaAinda não há avaliações
- Measuring High Resistance Using a Ballistic GalvanometerDocumento1 páginaMeasuring High Resistance Using a Ballistic GalvanometerRavi Kanth M NAinda não há avaliações
- Self Inductance of A Given Coil by Anderson's BridgeDocumento2 páginasSelf Inductance of A Given Coil by Anderson's BridgeashaAinda não há avaliações
- Sushmitha Iind BSCDocumento1 páginaSushmitha Iind BSCashaAinda não há avaliações
- CSIR-UGC NET/JEF Exam Unit Wise Analysis Previous Question PapersDocumento1 páginaCSIR-UGC NET/JEF Exam Unit Wise Analysis Previous Question PapersashaAinda não há avaliações
- Physicsmanual 5Documento2 páginasPhysicsmanual 5ashaAinda não há avaliações
- Sushmitha Iind BSCDocumento1 páginaSushmitha Iind BSCashaAinda não há avaliações
- Unit Wise Analysis of Previous Question Papers of Csir-Ugc (Net/Jef) Exam (New Pattern)Documento1 páginaUnit Wise Analysis of Previous Question Papers of Csir-Ugc (Net/Jef) Exam (New Pattern)ashaAinda não há avaliações
- Mode ConstantsDocumento25 páginasMode ConstantsashaAinda não há avaliações
- Torsional PendulumDocumento1 páginaTorsional PendulumashaAinda não há avaliações
- Low Pass and High PassDocumento1 páginaLow Pass and High PassashaAinda não há avaliações
- 3.e by M by Thomson MethodDocumento4 páginas3.e by M by Thomson MethodashaAinda não há avaliações
- 0 05 Syllabus For NET With Tips FinalDocumento14 páginas0 05 Syllabus For NET With Tips FinalashaAinda não há avaliações
- State Eligibility Test Physical Sciences Previous Question PapersDocumento1 páginaState Eligibility Test Physical Sciences Previous Question PapersashaAinda não há avaliações
- Cover Page - IIT JAM Chemistry - MPDocumento2 páginasCover Page - IIT JAM Chemistry - MPashaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapterwise Analysis PDFDocumento1 páginaChapterwise Analysis PDFashaAinda não há avaliações
- Solid State Physics Full - 3Documento7 páginasSolid State Physics Full - 3ashaAinda não há avaliações
- IIT-JAM Chemistry Test Series Answer KeysDocumento4 páginasIIT-JAM Chemistry Test Series Answer KeysashaAinda não há avaliações
- Solid State Physics Full - 250Documento5 páginasSolid State Physics Full - 250ashaAinda não há avaliações
- F3-Flow Through A NozzleDocumento21 páginasF3-Flow Through A NozzleTAN PANG ZORAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment ME401 For GATE PreparationDocumento26 páginasAssignment ME401 For GATE Preparationhameem mohdAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Mechanics Lab Manual Calibration of Venturimeter ExperimentDocumento55 páginasFluid Mechanics Lab Manual Calibration of Venturimeter ExperimentpkvssraoAinda não há avaliações
- Vibracion Diesel Engines PDFDocumento6 páginasVibracion Diesel Engines PDFacere18Ainda não há avaliações
- CCEA Physics Past PaperDocumento24 páginasCCEA Physics Past PaperLabibAinda não há avaliações
- Walter Bagehot, The Postulates of English Political EconomyDocumento134 páginasWalter Bagehot, The Postulates of English Political Economymaivin2Ainda não há avaliações
- 19.1 Attitude Determination and Control SystemsDocumento30 páginas19.1 Attitude Determination and Control SystemsAnkit MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Worksheet For STD 9Documento8 páginasPhysics Worksheet For STD 9Amit GulatiAinda não há avaliações
- 12U Diagnostic Quiz Multiple Choice PhysicsDocumento13 páginas12U Diagnostic Quiz Multiple Choice PhysicsTariq ZaitounAinda não há avaliações
- Phase OTDR Coherent DetectionDocumento6 páginasPhase OTDR Coherent DetectiongeorgeAinda não há avaliações
- Science7 Q3 M4 v4Documento16 páginasScience7 Q3 M4 v4John Maricc RemediosAinda não há avaliações
- Automobile Vibration AnalysisDocumento18 páginasAutomobile Vibration AnalysisDavid PomaAinda não há avaliações
- 02b Kinematics (Two Dimension) PDFDocumento12 páginas02b Kinematics (Two Dimension) PDFJennie EmataAinda não há avaliações
- CH-7 Rotational Motion Worksheet-1Documento2 páginasCH-7 Rotational Motion Worksheet-1negishreshth1985Ainda não há avaliações
- Vibration BasicsDocumento120 páginasVibration Basicspradeep.selvarajan100% (1)
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 páginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenAinda não há avaliações
- Gravitation MCQs Module 2 AnswersDocumento5 páginasGravitation MCQs Module 2 AnswersHemanth Raj DevarajAinda não há avaliações
- Phy - Sample Paper - Xi-2023-24 - S - 01Documento18 páginasPhy - Sample Paper - Xi-2023-24 - S - 01ANSUMAN SUVANKARAinda não há avaliações
- IGCSE Physics Paper 1 ClassifiedDocumento235 páginasIGCSE Physics Paper 1 Classifiedlozzzzz79% (58)
- School science inertia force grade 8Documento1 páginaSchool science inertia force grade 8Gerlie VelascoAinda não há avaliações
- VECTOR AND PHYSICS QUESTIONSDocumento7 páginasVECTOR AND PHYSICS QUESTIONSJulieneAinda não há avaliações
- Doppler Effect Explained in 40 CharactersDocumento22 páginasDoppler Effect Explained in 40 CharactersFrooti DubeyAinda não há avaliações
- Openvsp Tutorial For Monash Uas: June 2018Documento61 páginasOpenvsp Tutorial For Monash Uas: June 2018Dwayne JohnsonAinda não há avaliações
- Science 10 - Q2 - M4Documento15 páginasScience 10 - Q2 - M4MERCADER, ERICKA JAinda não há avaliações
- ME422 Fluid Mechanics II Course OutlineDocumento3 páginasME422 Fluid Mechanics II Course OutlineMuhammad Abdur RehmanAinda não há avaliações
- Disha Publication New Pattern JEE Advanced Questions Physics. CB1198675309Documento5 páginasDisha Publication New Pattern JEE Advanced Questions Physics. CB1198675309Nilabha DasAinda não há avaliações
- External FlowsDocumento90 páginasExternal FlowsSüleyman BirgiAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz 003 100%Documento4 páginasQuiz 003 100%jrenceAinda não há avaliações
- Aerodynamics in Cars and Brief HistoryDocumento22 páginasAerodynamics in Cars and Brief HistoryDinku Seyoum ZelekeAinda não há avaliações
- SAT Physics Subject Test 2 Practice QuestionsDocumento20 páginasSAT Physics Subject Test 2 Practice QuestionsYash GuptaAinda não há avaliações