Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Workshop
Enviado por
nachigansDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Workshop
Enviado por
nachigansDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
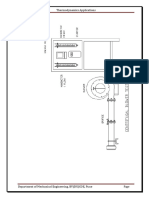
Workshop exercise – Fans and Blowers
FANS AND BLOWERS
QUESTION
An induced draft industrial fan is used to draw air through a bag filter. The following
information is given for this fan:
Flow rate is 90 m3/s at a static pressure of 80 mm water column (WC)
65 mm WC is the static pressure across the bag filter
Motor power drawn is 120 kW
Motor efficiency is 86%
Impeller diameter is 70 mm
RPM is 1000
The company decided to replace the bag filter with an electrostatic precipitator (ESP). After
installation of the ESP:
Static pressure across the ESP is 20 mm WC
Flow rate increased by 20%
The flow rate can be brought back to 90 m3/s by two options: (a) Impeller trimming and (b)
Reduced pulley diameter to reduce the RPM
Calculate the following:
1. Fan static efficiency before installation of the ESP
2. The new impeller diameter if the impeller is trimmed, that would result in a reduction in fan
efficiency of 5%
3. The new RPM that would result in a fan efficiency of 60%
4. Which of the two options is more energy efficient
Energy Efficiency Guide for Industry in Asia – www.energyefficiencyasia.org © UNEP 1
Workshop exercise – Fans and Blowers
SOLUTION
1. Calculate the fan static efficiency before installation of the ESP
Power input at fan shaft
= power drawn by motor x motor efficiency
= 120 x 0.86
= 103.2 kW
Fan static efficiency
= Flow x Pressure developed across fan
102 x Power required at fan shaft
= 90 x 80
102 x 103.2
= 0.68 = 68 %
2. Calculate the new impeller diameter if the impeller is trimmed, that would result in a
reduction in fan efficiency of 5%
New fan static efficiency = 68% - 5% = 63%
New static pressure across the fan
= total static pressure – static pressure across bag filter + static pressure across ESP
= 80 – 65 + 20
= 35 mm WC
New flow rate Q
= original flow rate x increase
= 90 m3/s x 1.2
= 108 m3/s
Static pressure at a flow rate of 90 m3/s with ESP installed (H2)
Q1 / Q2 = (H1/H2)2
Where
Q = flow rate
H = static pressure or head
108 / 90 = (35/H2)2
H2 = 32 mm
Power required at the fan shaft
Fan static efficiency = Flow x Pressure developed across fan
102 x Power required at fan shaft
0.63 = (90 x 32) / (102 x power developed at fan shaft)
Power developed at fan shaft = 44.8 kW
Energy Efficiency Guide for Industry in Asia – www.energyefficiencyasia.org © UNEP 2
Workshop exercise – Fans and Blowers
New impeller diameter (D2)
(D1 / D2) = (kW1 / kW2) 1/ 3
D2 = (kW2 / kW1) 1/ 3 x D1
= 44.8 / 103.2) 1/ 3 x 70
= 53 mm
3. Calculate the new RPM that would result in a fan efficiency of 60%
Power required at fan shaft
Fan static efficiency = Flow x Pressure developed across fan
102 x Power required at fan shaft
0.60 = 90 x 32 / 102 x Power required at fan shaft
Power required at fan shaft = (90 x 32) / (102 x 0.60) = 47 kW
New RPM (N2)
(N1 / N2) = (kW1 / kW2) 1/ 3
Where
N = RPM
KW = power
N2 = (kW2 / KW1) 1/ 3 x N1
= (47/ 103.2) 1/ 3 x 1000
= 769 RPM
4. Determine which of the two options is more energy efficient
Power required by impeller trimming = 44.8 kW
Power required by reducing RPM = 47 kW
Therefore impeller trimming is the more energy efficient option.
Energy Efficiency Guide for Industry in Asia – www.energyefficiencyasia.org © UNEP 3
Você também pode gostar
- Fan and BlowersDocumento11 páginasFan and Blowerstungau87Ainda não há avaliações
- γ γ × ∆ × × × × P 81 - 9 2 Cp A: Selected questionsDocumento6 páginasγ γ × ∆ × × × × P 81 - 9 2 Cp A: Selected questionsHhaabbde SybaritzAinda não há avaliações
- Aerodynamics 5Documento10 páginasAerodynamics 5Mohammed AbdoAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Mechanics II (Chapter 5)Documento10 páginasFluid Mechanics II (Chapter 5)Kaffel100% (1)
- Axial Fan Testing EquipmentsDocumento8 páginasAxial Fan Testing EquipmentsVijay ShetAinda não há avaliações
- Transportasi Fluida (Compressible Fluid-Fan Blower)Documento36 páginasTransportasi Fluida (Compressible Fluid-Fan Blower)Evia Salma ZauridaAinda não há avaliações
- Pressure Ake Int Absolute Stage Last of Pressure e Arg Disch AbsoluteDocumento8 páginasPressure Ake Int Absolute Stage Last of Pressure e Arg Disch Absolutemasih tadayonAinda não há avaliações
- Fan LawsDocumento8 páginasFan LawsKaijie LinAinda não há avaliações
- Air Compressor System Compressor Fundamentals: IntercoolingDocumento56 páginasAir Compressor System Compressor Fundamentals: IntercoolingAmarendra Mani TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- @S V All FansDocumento19 páginas@S V All Fanshasanadel88Ainda não há avaliações
- Ojeda, Khen Mehko C. - Me 417-Bsme 4aDocumento8 páginasOjeda, Khen Mehko C. - Me 417-Bsme 4akhinojidaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction المقدمةDocumento29 páginasIntroduction المقدمةziadAinda não há avaliações
- Fan & SystemDocumento31 páginasFan & SystemAlberto FranciscoAinda não há avaliações
- Back Pressure ExhaustDocumento12 páginasBack Pressure ExhaustmarjukiAinda não há avaliações
- 4 Performance of A Centrifugal FanDocumento7 páginas4 Performance of A Centrifugal Fanfinix33Ainda não há avaliações
- Blower Manual PDFDocumento6 páginasBlower Manual PDFDatta DoifodeAinda não há avaliações
- Centrifugal Blower Test Rig PDFDocumento7 páginasCentrifugal Blower Test Rig PDFGurmeet Mehma100% (2)
- Requirements of The Erp Directive On Hvac Systems. What You Need To KnowDocumento9 páginasRequirements of The Erp Directive On Hvac Systems. What You Need To KnowchristianxlaAinda não há avaliações
- Fans and Blowers Part I ModuleDocumento26 páginasFans and Blowers Part I ModuleCharlyn Flores67% (3)
- Calculate Leakage AmountDocumento2 páginasCalculate Leakage AmountThivanka Nirushan Withanage100% (1)
- Paper-4 SetA Key Final 8may2009Documento10 páginasPaper-4 SetA Key Final 8may2009SHAMSIK2002Ainda não há avaliações
- Ventialtion Calculation SampleDocumento21 páginasVentialtion Calculation SampleNico EchavarriaAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Notes 2.7.0Documento18 páginasLecture Notes 2.7.0krsdz1500Ainda não há avaliações
- 6 Centrifugal BlowerDocumento7 páginas6 Centrifugal BlowerdhundterahoAinda não há avaliações
- UtilityDocumento8 páginasUtilityAmit JainAinda não há avaliações
- 3.2 Design SystemDocumento48 páginas3.2 Design SystemMahmoud RababahAinda não há avaliações
- Industrial ElkonDocumento8 páginasIndustrial ElkonsherryAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial-1: Rel Rel HW Rel TWDocumento3 páginasTutorial-1: Rel Rel HW Rel TWsaurabhAinda não há avaliações
- PressorsDocumento8 páginasPressorsManoj MisraAinda não há avaliações
- How To Calculate A Id Fan Capacity and Sutable Motor in Kw'sDocumento5 páginasHow To Calculate A Id Fan Capacity and Sutable Motor in Kw'shariprasadr519957% (7)
- Mechanical Power Department 4 Year Turbo-Machinery II Centrifugal CompressorDocumento5 páginasMechanical Power Department 4 Year Turbo-Machinery II Centrifugal Compressorاحمد تاشهاويAinda não há avaliações
- Hydro TurbinesDocumento17 páginasHydro TurbinesSavesh Tripathi100% (1)
- Ventilation Calculation For Generators RoomDocumento3 páginasVentilation Calculation For Generators RoomRashid Ahmed Siddiqui100% (1)
- Fans BlowersDocumento23 páginasFans BlowersPhilip Anthony MasilangAinda não há avaliações
- B1. Fan Laws and Fan Control - RobinsonDocumento74 páginasB1. Fan Laws and Fan Control - RobinsonNelly Isabel Narvaez PachecoAinda não há avaliações
- Industrial Fans: Delivery ProgramDocumento42 páginasIndustrial Fans: Delivery ProgramKvvPrasadAinda não há avaliações
- Hydraulic Turbines QuestionsDocumento2 páginasHydraulic Turbines QuestionsMohamad MousaAinda não há avaliações
- Pelton TurbineDocumento13 páginasPelton TurbineHitarth ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Energy Audit Methodology: Fans, Pumps and CompressorDocumento39 páginasEnergy Audit Methodology: Fans, Pumps and CompressorRhen Jhing LopezAinda não há avaliações
- Air Compressor ProblemsDocumento9 páginasAir Compressor ProblemsChristian Diano100% (4)
- Assessment of CompresorsDocumento14 páginasAssessment of CompresorsranveerAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 11 PDFDocumento11 páginasLecture 11 PDFpsunmoorthyAinda não há avaliações
- 7ADC8292A41A4EB196A3FFDEE99589FDDocumento4 páginas7ADC8292A41A4EB196A3FFDEE99589FDyashvantAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical VentilationDocumento81 páginasMechanical VentilationYusuf MislamAinda não há avaliações
- Fans and Blowers ProblemsDocumento8 páginasFans and Blowers ProblemsJULIAN DOMINIC SOLEDADAinda não há avaliações
- Energy ConservationDocumento27 páginasEnergy ConservationJAY PARIKHAinda não há avaliações
- EXP 7 To Determine The Volumetric Efficiency of A Four Stroke Petrol Engine at Variable LoadDocumento2 páginasEXP 7 To Determine The Volumetric Efficiency of A Four Stroke Petrol Engine at Variable Load70130046Ainda não há avaliações
- BeeDocumento20 páginasBeeAnudeep ChittluriAinda não há avaliações
- GDJP QBDocumento40 páginasGDJP QBguna sekaranAinda não há avaliações
- Air CompressorDocumento31 páginasAir CompressorEr Bali Pandhare33% (3)
- CFM Calculation For Exhaust FanDocumento2 páginasCFM Calculation For Exhaust FanSAKDA MAPRADITKUL100% (8)
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IAinda não há avaliações
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGNo EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGAinda não há avaliações
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorNo Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlNo EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesAinda não há avaliações
- Hydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideNo EverandHydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (8)
- About Upgrad: Link HereDocumento1 páginaAbout Upgrad: Link HereShukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações
- Master File of School Emails Across USADocumento4.126 páginasMaster File of School Emails Across USAShukla Suyash75% (4)
- M1 DataDocumento306 páginasM1 DataShukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações
- Chowgule Group Strategy - Job DescriptionDocumento3 páginasChowgule Group Strategy - Job DescriptionShukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações
- BBL WBBL 2020 DataDocumento201 páginasBBL WBBL 2020 DataShukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações
- 4e1adcf3-0ec0-4c57-9d5e-0ca5c0a80121Documento117 páginas4e1adcf3-0ec0-4c57-9d5e-0ca5c0a80121Shukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações
- Survey Primary Teachers Attitudes Towards STEM EducationDocumento27 páginasSurvey Primary Teachers Attitudes Towards STEM EducationShukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações
- Low Heat Input SMAW Welding ElectrodesDocumento62 páginasLow Heat Input SMAW Welding ElectrodesShukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações
- Indus Valley Civilisation Major Sites PDFDocumento1 páginaIndus Valley Civilisation Major Sites PDFShukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações
- PUB AD (9 A) - Chapter - 9 - Importance of HRD, Recruitment, Training PDFDocumento8 páginasPUB AD (9 A) - Chapter - 9 - Importance of HRD, Recruitment, Training PDFShukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações
- Jindal Steel & Power Limited: P.B.No.86.Barbil-Joda Highway, Barbil-758035 (Orissa)Documento1 páginaJindal Steel & Power Limited: P.B.No.86.Barbil-Joda Highway, Barbil-758035 (Orissa)Shukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações
- 5837 LM PAD P01 M20 Behavioural Approach LMDocumento2 páginas5837 LM PAD P01 M20 Behavioural Approach LMShukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações
- Referencesandfurtherreading: WWW - Demnetgov.Ruc - DKDocumento2 páginasReferencesandfurtherreading: WWW - Demnetgov.Ruc - DKShukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Vibration ?: Imperfections in The Machine: Design Assembly Manufacture Operation Installation MaintenanceDocumento2 páginasWhat Is Vibration ?: Imperfections in The Machine: Design Assembly Manufacture Operation Installation MaintenanceShukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações
- OTE Outotec Pallet Cars For Sintering and PelletizDocumento4 páginasOTE Outotec Pallet Cars For Sintering and PelletizShukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações
- 2 ND Selection BedDocumento12 páginas2 ND Selection BedShukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações
- Agile Manufacturing: A Taxonomy of Strategic and Technological ImperativesDocumento30 páginasAgile Manufacturing: A Taxonomy of Strategic and Technological ImperativesShukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações
- Researchpaper Application of Lean in A Small and Medium Enterprise SME SegmentDocumento8 páginasResearchpaper Application of Lean in A Small and Medium Enterprise SME SegmentShukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações
- Circular Pelletizing enDocumento8 páginasCircular Pelletizing enShukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Innovations and Challenges in Msme SectorDocumento5 páginas10 Innovations and Challenges in Msme SectorShukla SuyashAinda não há avaliações