Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Ch. 4 - Keltner - Psych/Nursing/Psychobiological Bases of Behavior
Enviado por
isapatrick8126Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Ch. 4 - Keltner - Psych/Nursing/Psychobiological Bases of Behavior
Enviado por
isapatrick8126Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
UVU - NURS 2430 - Unit I - Ch.
4: Psychobiological Bases of
Behavior
Study online at quizlet.com/_1hjl94
1. Ataxia Awkward posture and gait. Cerebeller 8. Nystagmus
dysfunction.
2. Asthensia Muscles tire easily. Cerebeller
dysfunction.
Involuntary rapid eye movement. Basal
3. Adiadochokinesia Inability to perform fin, rapidly repeated, ganglia dysfunction.
coordinated movements. Cerebeller
dysfunction. 9. Neuron
4. Parkinson's Rigidity, bradykinesia, resting tremor,
disease mask-like face, shuffling gait. Basal
ganglia dysfunction.
5. Chorea
The basic subunit of the nervous system.
10. Neuroplasticity Refers to the ability of the brain to change
neural pathways and synaptic connections
based on changes in behavior, environment,
neural processes, thinking, and emotions.
11. Homunculus
Sudden, jerky, and purposeless
movements (e.g. Huntington's disease,
Sydenham's disease). Basal ganglia
dysfunction.
6. Athetosis
Each human brain has two homunculi: the
sensory homunculus that feels and
processes sensations, and the motor
homunculus that controls physical
movement.
12. Movement Characterized by involuntary unexpected
Disorders of movements. Examples include Parkinson's
the Basal disease, Huntington's chorea, and
Ganglia nystagmus.
13. Movement Characterized by awkward voluntary
Disorders of movements. Examples include ataxia,
Slow, writhing, snakelike movement, the Cerebrum asthensia, and adiadochokinesia.
especially of the fingers and wrist. Basal
ganglia dysfunction.
7. Hemiballismus A sudden, wild flailing of one arm. Basal
ganglia dysfunction.
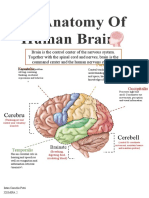
14. Lobes of 18. Temporal
the Brain Lobes
Frontal Lobe, Insular Lobe, Occipital Lobe, Parietal
Lobe, and Temporal Lobe
Associated with perception and recognition of
15. Frontal
auditory stimuli, memory, and speech.
Lobes
19. Insular
Lobes
Associated with higher level cognition, expressive
language, reasoning, planning, fine motor skills,
emotions, and problem solving.
Associated with consciousness, emotions,
16. Parietal
physical homeostasis, perception, motor control,
Lobes
self-awareness, cognitive functioning, and
interpersonal experience.
20. Limbic
System
Associated with movement, orientation,
recognition, and perception of stimuli.
17. Occipital
Lobes
Complex system in the brain involving instinct,
mood, emotions, and drives -
fight/flight/feed/f**k.
Prominent components: Hypothalamus,
Amygdala, Thalamus, Hippocampus.
Associated with visual processing.
21. Hypothalamus 24. Hippocampus
Section of the brain responsible for Elongated ridges on the floor of the lateral
hormone production influencing body ventricle of the brain. They are theorized to
temperature, thirst, hunger, sleep, circadian be the center of emotion, memory, and the
rhythm, moods, sex drive, and the release of autonomic nervous system.
other hormones in the body.
25. CNS
22. Amygdala
Small almond-shape set of neurons located
deep in the brain's medial temporal lobe.
Primary responsibility is in assessing threats. Central Nervous System. Composed of the
23. Thalamus brain and spinal cord.
26. PNS
Structure in the middle of the brain. It
correlates several important processes, Peripheral Nervous System. Composed of
including consciousness, sleep, and sensory sensory (or afferent) nerves and motor (or
interpretation. efferent) nerves.
27. S/S of Frontal Abrupt changes in personality, disinhibited
Lobe Injury behavior, loss of memory, impulsivity,
inattention
28. S/S of Visual and auditory aphasias
Temporal
Lobe Injury
29. Broca's Area 38. Seretonin Involved in mood, social behavior, appetite &
digestion, sleep, memory, and sexual desire.
Monoamine
Decreased levels in depression and anxiety.
39. GABA Most common inhibitory transmitter in the brain.
Amino acid
Decreased levels in anxiety.
40. Glutamate Most common excitatory transmitter in the brain.
Amino acid
Located in the posterior left prefrontal
lobe, associated with expressive or motor
language (talking).
30. Wernicke's Area
Located in the posterior left temporal
lobe, associated with receptive or sensory
language (listening and understanding).
31. S/S of Occipital Loss of vision
Lobe Injury
32. S/S of Left Problems in mathematics, long reading,
Parietal Lobe writing, and understanding symbols
Injury
33. S/S of Right Loss of imagery, visualization of spatial
Parietal Lobe relationships
Injury
34. Basal Ganglia Comprised of three major nuclei: the
caudate nucleus, the putamen, and the
globus pallidus. Structure is involved in
motor function.
35. Acetylcholine Involved in neuromodulation and activates
muscles.
Cholinergic
Decrease levels in Alzheimer's disease and
dementia.
36. Dopamine Involved in reward-motivated behavior,
motivation, attention/concentration, and
energy levels.
Monoamine
Increased levels in Schizophrenia.
37. Norepinephrine Involved in cognitive alertness, cardiac
functioning, stress management, and
mood.
Monoamine
Decreased levels in depression and
anxiety.
Você também pode gostar
- Cognitive NeuroscienceDocumento12 páginasCognitive NeuroscienceninamaedamilesAinda não há avaliações
- A Guide To Brain AnatomyDocumento7 páginasA Guide To Brain AnatomyPuppa AlexandraAinda não há avaliações
- Cognitive Neuroscience. Anatomy of The BrainDocumento11 páginasCognitive Neuroscience. Anatomy of The BrainKryzhel CuachonAinda não há avaliações
- The unconscious zone: The secret life of your brainNo EverandThe unconscious zone: The secret life of your brainAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocumento5 páginasChapter 1 - Introductionmanilyn dacoAinda não há avaliações
- Cerebrum With Spinal Cord: Speech and HearingDocumento2 páginasCerebrum With Spinal Cord: Speech and HearingJJ LimAinda não há avaliações
- CH 2 CnotesDocumento11 páginasCH 2 Cnotesvalcobacl.681.studAinda não há avaliações
- Psych IiDocumento8 páginasPsych IiNadia AbdurasidAinda não há avaliações
- (18-19) Brain Questions CVDocumento57 páginas(18-19) Brain Questions CVbartAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Neurosciences NotesDocumento41 páginasBasic Neurosciences NotesAbdul Mannan ChatthaAinda não há avaliações
- The Anatomy of BrainDocumento1 páginaThe Anatomy of BrainIntan CameliaAinda não há avaliações
- Physiological PsychologyDocumento16 páginasPhysiological PsychologyJanara Monique MarcialAinda não há avaliações
- Biological MindDocumento25 páginasBiological MindQuesiah González100% (1)
- Lobes of The BRAIN: Right Hemisphere Left HemisphereDocumento9 páginasLobes of The BRAIN: Right Hemisphere Left HemisphereAsniah Hadjiadatu AbdullahAinda não há avaliações
- Intro: PSY 106: Ch. 1 - IntroductionDocumento5 páginasIntro: PSY 106: Ch. 1 - IntroductionElla VelosoAinda não há avaliações
- Assessing Neurologic SystemDocumento7 páginasAssessing Neurologic Systemjanikkakristal100% (1)
- Frontal Syndromes Frontal Syndromes Pseudodepression PseudodepressionDocumento6 páginasFrontal Syndromes Frontal Syndromes Pseudodepression PseudodepressionilruialpAinda não há avaliações
- General Psychology ReviewerDocumento9 páginasGeneral Psychology ReviewerVhallerie joy CalpitoAinda não há avaliações
- Brain Part QUIZDocumento2 páginasBrain Part QUIZPerez, Hannah GraceAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 13 - Conditioned & Unconditioned ReflexesDocumento40 páginasLecture 13 - Conditioned & Unconditioned Reflexesסנאבל מוסאAinda não há avaliações
- Mirror NeuronsDocumento30 páginasMirror NeuronsAnushya PrasadAinda não há avaliações
- The Brain's Sense of Movement - Alan BerthozDocumento352 páginasThe Brain's Sense of Movement - Alan BerthozKaroline MarxAinda não há avaliações
- 8B Coordination in Animals and Plants 8B Checkpoint: 8B.1 The Central Nervous SystemDocumento8 páginas8B Coordination in Animals and Plants 8B Checkpoint: 8B.1 The Central Nervous SystemsalmaAinda não há avaliações
- General Psychology 4: THE Physiological Basis OF Behavior: Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R. Abejo RN, MANDocumento4 páginasGeneral Psychology 4: THE Physiological Basis OF Behavior: Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R. Abejo RN, MANMariel EfrenAinda não há avaliações
- Pdev Reviewer 1Documento8 páginasPdev Reviewer 1SCT. Jan GenesisAinda não há avaliações
- LECTURE 2 Biological Basis of BehaviorDocumento74 páginasLECTURE 2 Biological Basis of BehaviorColossal HeartAinda não há avaliações
- Intro To PsychDocumento5 páginasIntro To PsychJULIA IAN MARCOSAinda não há avaliações
- Cognitive Psychology-Ch2.Cognitive NeuroscienceDocumento9 páginasCognitive Psychology-Ch2.Cognitive NeuroscienceJm AlversadoAinda não há avaliações
- Cognitive Psychology TopicsDocumento11 páginasCognitive Psychology TopicsJulia AlforteAinda não há avaliações
- Perdev HW2Documento6 páginasPerdev HW2rianne margaretAinda não há avaliações
- PT Neuro Intro NotesDocumento13 páginasPT Neuro Intro NotesSusan K100% (1)
- AP PSYCH Major Structures of The Brain Review Chart MyersDocumento2 páginasAP PSYCH Major Structures of The Brain Review Chart MyersTiffany GallinaAinda não há avaliações
- Pedrajeta-Neurologic AssessmentDocumento11 páginasPedrajeta-Neurologic AssessmentAndrei PedrajetaAinda não há avaliações
- BIO 203 MTII Review Sheet: Central Nervous SystemDocumento4 páginasBIO 203 MTII Review Sheet: Central Nervous System孙绍钦Ainda não há avaliações
- On The Zombie WithinDocumento1 páginaOn The Zombie WithinhggfkpzfmsAinda não há avaliações
- Neurological AssessmentDocumento13 páginasNeurological AssessmentLorenz Jude CańeteAinda não há avaliações
- Cognitive PsychologyDocumento5 páginasCognitive Psychologymain.22001454Ainda não há avaliações
- Gen Psy Reviewer by The One and Only Gab Calma:D: Types of Psychological PerspectivesDocumento6 páginasGen Psy Reviewer by The One and Only Gab Calma:D: Types of Psychological PerspectivesMic VirreyAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2 CogpsyDocumento1 páginaLecture 2 CogpsyTracey GoldAinda não há avaliações
- NeuroDocumento174 páginasNeurofhey19100% (3)
- Cognitive Neuroscience Investigatory Project Nazila 11-D FinalisedDocumento35 páginasCognitive Neuroscience Investigatory Project Nazila 11-D Finalisedgaurimasaami2007Ainda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology Tetanus FinalDocumento17 páginasAnatomy and Physiology Tetanus Finalfelicisimo039690175% (4)
- Chapter 3Documento2 páginasChapter 3Mohammad MoosaAinda não há avaliações
- Capítulo 1: Introducción A Las Neurociencias Y PsicologíaDocumento71 páginasCapítulo 1: Introducción A Las Neurociencias Y PsicologíaJuanHerrera100% (1)
- L02 Cognitive NeuroscienceDocumento81 páginasL02 Cognitive NeuroscienceAmelliah Veatrize DatoAinda não há avaliações
- Abnormal PsychDocumento15 páginasAbnormal PsychkilluhmaylucianoAinda não há avaliações
- Approach To Pediatric Neurology - BasicDocumento16 páginasApproach To Pediatric Neurology - BasicAseel AyAinda não há avaliações
- Neurology 1.03 Approach To Cerebral Function - Dr. MartinezDocumento7 páginasNeurology 1.03 Approach To Cerebral Function - Dr. MartinezDeomicah SolanoAinda não há avaliações
- UCSP - Parts of The Brain Q1Documento15 páginasUCSP - Parts of The Brain Q1harperAinda não há avaliações
- Filbrich UE3050 Cours12 2023-2024Documento120 páginasFilbrich UE3050 Cours12 2023-2024lisa.daisneAinda não há avaliações
- CT Vs Mri: Structure General Function Specific Functions Spinal CordDocumento3 páginasCT Vs Mri: Structure General Function Specific Functions Spinal CordAnn ChenAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science VI-Nervous SystemDocumento4 páginasDetailed Lesson Plan in Science VI-Nervous SystemTrishia Mandapat75% (4)
- (Human Behavior and Community Health Education) : Biological ViewpointDocumento14 páginas(Human Behavior and Community Health Education) : Biological ViewpointKirstenAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 65 - Assessment of Neurologic FunctionDocumento3 páginasChapter 65 - Assessment of Neurologic FunctionJared MabulayAinda não há avaliações
- Assigment KBDocumento25 páginasAssigment KBZulfikar Mat GhaniAinda não há avaliações
- Nervous SystemDocumento4 páginasNervous SystemEllanny GloriaAinda não há avaliações
- Neuro Week 1Documento6 páginasNeuro Week 1Sheryhan BayleAinda não há avaliações
- Our Iceberg Is MeltingDocumento6 páginasOur Iceberg Is MeltingBindu Maurya100% (1)
- TurnoverDocumento1 páginaTurnoverisapatrick8126Ainda não há avaliações
- Advanced Pediatric AssessmentDocumento30 páginasAdvanced Pediatric Assessmentisapatrick8126100% (1)
- NQF: Patient SafetyDocumento3 páginasNQF: Patient Safetyisapatrick8126Ainda não há avaliações
- OB Version BDocumento6 páginasOB Version Bisapatrick8126100% (1)
- Craven & Hirnle's Nursing Procedures and Fundamentals OnlineDocumento4 páginasCraven & Hirnle's Nursing Procedures and Fundamentals Onlineisapatrick8126Ainda não há avaliações
- Maternity AssignmentDocumento2 páginasMaternity Assignmentisapatrick8126Ainda não há avaliações
- UVU - NURS 2430 - Unit III - Ch. 12: Introduction To Psychiatric DrugsDocumento2 páginasUVU - NURS 2430 - Unit III - Ch. 12: Introduction To Psychiatric Drugsisapatrick8126Ainda não há avaliações
- A Beautiful Mind Movie ReviewDocumento3 páginasA Beautiful Mind Movie Reviewjosedenniolim100% (1)
- Chapter 12 (Keltner) : Psychiatric Nursing, 7th Edition Introduction To Psychotropic Drugs Answer Key - Critical Thinking ExercisesDocumento2 páginasChapter 12 (Keltner) : Psychiatric Nursing, 7th Edition Introduction To Psychotropic Drugs Answer Key - Critical Thinking Exercisesisapatrick8126Ainda não há avaliações
- Adult Nursing 2 Math Review:Med. SurgDocumento11 páginasAdult Nursing 2 Math Review:Med. Surgisapatrick8126Ainda não há avaliações
- My Birth Plan: PreparationDocumento2 páginasMy Birth Plan: Preparationisapatrick8126Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 15 CARE Anxiety With AgoraphobiaDocumento4 páginasChapter 15 CARE Anxiety With Agoraphobiaisapatrick8126Ainda não há avaliações
- HESI Women's Health:Newborn DrugsDocumento8 páginasHESI Women's Health:Newborn Drugsisapatrick8126Ainda não há avaliações
- Varcolis FUNDAMENTAL OF PSY - NURSING - NCLEX RNDocumento20 páginasVarcolis FUNDAMENTAL OF PSY - NURSING - NCLEX RNisapatrick8126100% (1)
- Standardized Lab Values - Final - 031215Documento6 páginasStandardized Lab Values - Final - 031215isapatrick8126Ainda não há avaliações
- Nu DESCDocumento2 páginasNu DESCrezaAinda não há avaliações
- Application Letter Nurse AideDocumento2 páginasApplication Letter Nurse AideOliver Ian ReposoAinda não há avaliações
- Wiley - Design Details For Health - Making The Most of Design's Healing Potential, 2nd Edition - 978!0!470-52471-8Documento2 páginasWiley - Design Details For Health - Making The Most of Design's Healing Potential, 2nd Edition - 978!0!470-52471-8nasiru yusufAinda não há avaliações
- hsns370 Assessment 2 Submission To Royal Commission Bhima Devi Apodel Adhikari 220179000Documento13 páginashsns370 Assessment 2 Submission To Royal Commission Bhima Devi Apodel Adhikari 220179000api-525310113Ainda não há avaliações
- Care of The Elderly: "Roles of The Nurses To Resolve Geriatric Syndrome"Documento42 páginasCare of The Elderly: "Roles of The Nurses To Resolve Geriatric Syndrome"Tino PriyudhaAinda não há avaliações
- The Benefits of Interdisciplinary Practice in A Palliative Care Setting - A Music Therapy and Physiotherapy Pilot ProjectDocumento6 páginasThe Benefits of Interdisciplinary Practice in A Palliative Care Setting - A Music Therapy and Physiotherapy Pilot ProjectJuan Luis Köstner MartinoAinda não há avaliações
- ACB Scale - Legal Size PDFDocumento2 páginasACB Scale - Legal Size PDFMarina Swanson0% (1)
- The Right To Die Opinion Essay SampleDocumento1 páginaThe Right To Die Opinion Essay SampleIsmayil AgayevAinda não há avaliações
- Inappropriate Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors in Elderly Patients Discharged From Acute Care HospitalsDocumento6 páginasInappropriate Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors in Elderly Patients Discharged From Acute Care HospitalsFitriAinda não há avaliações
- Alignment of Prostheses and Orthoses: Written By: Markus Thonius OMM / CPO ICRC - Afghanistan Orthopaedic Workshop 1992Documento27 páginasAlignment of Prostheses and Orthoses: Written By: Markus Thonius OMM / CPO ICRC - Afghanistan Orthopaedic Workshop 1992Alfionita WikaAinda não há avaliações
- Denture Remounting Selective Grinding DR OsamaDocumento11 páginasDenture Remounting Selective Grinding DR OsamaReber ZebariAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study For Nursing FormatDocumento3 páginasCase Study For Nursing FormatjaoAinda não há avaliações
- Cancer Caregiving in The United States Research SUBRAYADO PDFDocumento330 páginasCancer Caregiving in The United States Research SUBRAYADO PDFRubí Corona TápiaAinda não há avaliações
- Pub105961487 PDFDocumento164 páginasPub105961487 PDFTriandini SanusiAinda não há avaliações
- Spices PDFDocumento2 páginasSpices PDFAnonymous S5UkdjJWAAinda não há avaliações
- Mini Mental State Examination Cognitive FIM Instrument and The Loewenstein Occupational Therapy Cognitive Assessment Relation To Functional Outco PDFDocumento4 páginasMini Mental State Examination Cognitive FIM Instrument and The Loewenstein Occupational Therapy Cognitive Assessment Relation To Functional Outco PDFDamira HalilovicAinda não há avaliações
- Taking CareDocumento333 páginasTaking Care4imAinda não há avaliações
- Samantha Bradley: Work ExperienceDocumento3 páginasSamantha Bradley: Work Experienceapi-399988983Ainda não há avaliações
- Clinical Frailty ScaleDocumento3 páginasClinical Frailty ScalengurahAinda não há avaliações
- Journal Medical WardDocumento5 páginasJournal Medical WardDarren FloresAinda não há avaliações
- CGNAStandardsOfPractice EnglishDocumento21 páginasCGNAStandardsOfPractice EnglishHandayani SitorusAinda não há avaliações
- Thumb Sucking Is A Behavior Found in HumansDocumento2 páginasThumb Sucking Is A Behavior Found in HumansashoorocksAinda não há avaliações
- Clinics & NursingDocumento39 páginasClinics & NursinggauravAinda não há avaliações
- Jessica Lightcap ResumeDocumento3 páginasJessica Lightcap Resumeapi-379934002Ainda não há avaliações
- Registry of Outcome Measures With MDC 2010Documento125 páginasRegistry of Outcome Measures With MDC 2010bdesai48100% (1)
- Geriatric Rehabilitation: Prepared By: Floriza P. de Leon, PTRPDocumento36 páginasGeriatric Rehabilitation: Prepared By: Floriza P. de Leon, PTRPFloriza de LeonAinda não há avaliações
- Geriatric EndocrinologyDocumento2 páginasGeriatric EndocrinologyAbditsion DhiisaniiAinda não há avaliações
- Dedham Transcript Jan. 26, 2012 My Fondest Memory IsDocumento2 páginasDedham Transcript Jan. 26, 2012 My Fondest Memory IsAndreaECalvinAinda não há avaliações
- Final OutputDocumento8 páginasFinal OutputMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigAinda não há avaliações
- The Best American Science Writing 2011 - Rebecca SklootDocumento195 páginasThe Best American Science Writing 2011 - Rebecca SklootProlagusAinda não há avaliações
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)No EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Nota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsAinda não há avaliações
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNo EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (32)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNo EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (404)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDNo EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (3)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNota: 2 de 5 estrelas2/5 (1)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeNo EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (254)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesNo EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (1412)
- Empath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainNo EverandEmpath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (95)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNo EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (82)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNo EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsNo EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (4)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessNo EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (328)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryNo EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (46)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNo EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsNo EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (170)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingNo EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1138)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.No EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (110)
- Summary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNo EverandSummary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (61)
- Critical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsNo EverandCritical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (39)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNo EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (6)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlNo EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (60)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisNo EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (8)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsAinda não há avaliações
- Hearts of Darkness: Serial Killers, The Behavioral Science Unit, and My Life as a Woman in the FBINo EverandHearts of Darkness: Serial Killers, The Behavioral Science Unit, and My Life as a Woman in the FBINota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (20)
- Make Him BEG for Your Attention: 75 Communication Secrets for Captivating Men to Get the Love and Commitment You DeserveNo EverandMake Him BEG for Your Attention: 75 Communication Secrets for Captivating Men to Get the Love and Commitment You DeserveNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (220)