Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Calculus Guide
Enviado por
Shahriar KDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Calculus Guide
Enviado por
Shahriar KDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
1
Calculus I Formulas
MAC 2311
1. Limits and Derivatives
2. Differentiation rules
3. Applications of Differentiation
4. Integrals
5. Applications of Integration
Professor: Dr. Mohammad Shakil
C0-Author: Jeongmin Correa
Mathematics Department
Miami Dade College -- Hialeah Campus
2
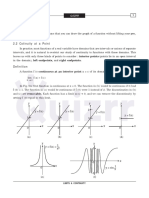
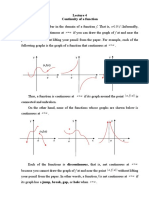
Any rational function is continuous where it is defined on its domain.
y y= f(x) Basic Limit Evaluations at
*
left right
x=a x
Relationship between the Limit and one-sided limits
(left & right ( )
Properties
(f(x) =a polynomial or rational func. in the domain of x)
f(x)
4. [f(x) f(x) (x) Limit at Infinity: Horizontal asymptotes
5. [f(x)g(x)] = f(x) g(x)
6. =
y y y
7. f(g(x)) = f ( (x)) H.P.
8. x x x
y y
9.
H.P.
Indeterminate Forms:
x x
(When a limit of rational func. has an indeterminate form, Find Vertical Asymptotes
Simplify the func. by common factors between numerator and denominator.)
1. Simplify the func. by common factors between numerator and
denominator.
2. Make the denominator =0 for x
Squeeze Theorem
3. x = a is the Vertical Asymptotes.
Limit of Trigonometric Functions
Absolute function
f(x) =
1. -(x-c) if x
2. 0 if x = c
3. x-c if x
Prove Continuous at x = a of f(x)
1. f(a) exists. f(a) is defined at x=a
Any polynomial is continuous everywhere all x.
Miami Dade College -- Hialeah Campus
3
Definition of the number e No Differentiable
(when )
corner discontinuous tangent line(m)=vertical f'(x) =
Slope; m y = p(x) = a polynomial degree n
1. m > 0 positive
2. m < 0 negative
3. m = 0 Horizontal
4. m = Vertical = no slope
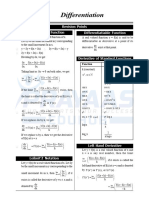
Derivatives and Rates of change
The Linear approximation = a tangent line approximation
a slope of secant line
The Linearization of at a y = f (x)
(x+h, f(x+h)) a slope of tangent line
(x , f(x))
The differentials dy by using L x x x-a) + f(a)
x h
x+h
The differentials dy by using L x x x-a) + f(a)
a tangent line
f(x+h) (x+h , f(x+h))
= average rate of change or different quotient
The slope of tangent line = m (of f(x) at x=a)
(dx,,dy) dy
(x, f(x))
= Velocity of f(x) as v x x+h
(limit of difference quotient or Derivative of f(x) at x=a)
An Equation of Tangent Line
but
Use the given f(x) p(
1. Find slope m
2. Find f'( =m
3. y - (x- ) --> to make y = ax + b form
Find Approximate the function
Differentiable at x
( x of L(x) is 0 because 0.04 is closest to 0)
Provided the limit exists.
We say that the func. y = f(x) is differentiable at x
Derivatives of y = f (x) L
y' = f'(x) = =
Differentiable at a = continuous at a ( x of L(x) is 0 because -0.015 is closest to 0)
No differentiable the f(x) could be continuous or not
No Limit, No differentiable
Miami Dade College -- Hialeah Campus
4
Differentiation Formulas Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Func.
3. Constant Multiple Rule c f(x) = c f '(x)
4. Sum & Difference Rule [ f(x) g(x)] = f '(x) g '(x)
5. Natural Exponential Func.
6. Power Rule = (n is any real number)
7. Product Rule [f(x) g(x)] = f ' (x) g(x) + f(x) g '(x)
8. Quotient Rule =
x x x Hyperbolic Functions
x x
1) = f '(x)
2) =
3)
4) sin (f(x)) = cos (f(x)) f '(x)
5) cos (f(x)) =
6) tan (f(x)) = (f(x)) f '(x)
7)
=[ (use form to solve)
Derivatives of Hyperbolic Functions
Derivatives of Trigonometric Func.
Inverse Hyperbolic functions
Miami Dade College -- Hialeah Campus
5
Derivatives of Inverse Hyperbolic functions Finding Absolute (Global) Max. & Min values (on a closed interval [a, b])
1. f '(x) = 0 Solve for x c , d... = the Critical Numbers (C.N.)= c, d, ...
2. 1) f(a) & f(b) from [a, b]
2) f(c) & f(d) from C.N.
3. Max.= the largest value
Min.= the smallest value
Finding Relative (Local) Max. & Min values on an opened interval
1. f '(x) = 0
a) Solve for x c , d... = the Critical Numbers (C.N.)
b) Critical Points: Find f(c), f(d),... --> (c, f(c)) (d, f(d))...
Hyperbolic Identities
1) 2. Use Arrow diagram
2) a) Draw an arrow line
3) b) Put C.N, on the line
4) c) Choose Testing Points (T.P.) on
5) 3. Increasing interval: f '(T.P.) 0
6) Decreasing interval: f' (T.P.) 0
7) =1 4. Find Relative (local) Values Max. ( ) at x= ( ),
8) Min. ( ) at x= ( )
9)
T.P. C.P. T.P. C.P. T.P.
f '(T.P.) 0 m=0 f' (T.P.) 0 m=0 f '(T.P.) 0
13)
14) Finding Inflection Points of Concavity Changes
1. Find
2.
Solve for x = Inflection Points I.P.
3. Use Arrow diagram
Intermediate Value Theorem
a) Draw an arrow line & Put I.P, on the line
Suppose that f(x) is continuous on [a, b]
c) Choose Testing Points (T.P.) on
Let f(a) N f(b) where f(a) f(b)
4.
Then it exists a number c is belong to (a, b) such that f(c)=N
5. Inflection Points: where the concavity changes (I.P., f(I.P.))
Extreme Values = Absolute (Global) Values
Max. f(c) f(x); (the largest) for all x in the domain of f
Min. f(d) f(x); (the smallest) for all x in the domain of f
continuous on a closed interval [a,b]
Relative (Local) Values
Max. f(c) f(x) when x is near c : x= a & c
T.P. I.P. T.P. I.P. T.P. .
Min. f(d) f(x) when x is near d : x= b & d
f '(T.P.) 0 m=0 f' (T.P.) 0 m=0 f '(T.P.) 0
continuous on a opened interval (
Some Optimization Problems
f(x)
1) Suppose that f(x) is continuous on an interval 'I'
f(c) f(d)
where and the x is the only one C.N.
2) If Absolute Min. at x=c
x =c x=d x =a x =b
If Absolute Max. at x=c
a, b, c,& d are critical numbers where f'(x) = 0 and solve for x
Miami Dade College -- Hialeah Campus
6
Simple Apply to Economics' Business L'Hospital's Rule
1. Demand Func. = D(x) = p(x) (=Price func. that price per unit)
where x = number of units demanding by consumer at that price 'p.'
It's good for forms
2. Revenue Func. 1. Derivative is continuous 'til it doesn't have the forms.
=(sold numbers selling price) 2. If doesn't have forms, make into the forms
Max. of Rev. = x
Indeterminate Powers ( forms)
3. The Profit Func. Using Derivatives of Logarithmic Func.
; C(x) = Cost Func. (P(x); a capital letter P)
Max. of Prof .= , solve for x (Make the same base)
The Intermediate Value Theorem
Marginal Analysis f(x) is continuous on [a, b] - a closed interval
1. Cost Func. = by Polynomial (=total cost) Let where
Then
such that
*
*
It's called 'Marginal Cost' of producing units.
3. Actual cost or Actual Revenue of Rolle's Theorem
If , then 1) f(x) is continuous on [a, b]
2) f(x) is differentiable in (a, b)
3) f(a) = f(b)
*Tip*
4) Then Then such that
1. Marginal ~ =
2. To find Max or Min. of Revenue
Mean Value Theorem
1) Find
1) f(x) is continuous on [a, b]
2)
2) f(x) is differentiable in (a, b)
3) , Q; When Revenue has Max. or Min? 3) f(a) f(b)
4) R(a)= ? (don't forget unit) Q; What is Max or Min. of Revenue?
(Finding Max or Min. of Profit is the same step)
3. To find Actual Revenue from sale of 4th Unit
1)
Newton's Method
2) (to find 4th value)
3)Find
unit
x
x
How to solve a Business Calculus' problem
1. Underline all numbers and functions
2. Find what is the main question (ex) Max. of Revenue ex) is given ,
3. Find all elements to solve the func. (ex)
4. Do the next step. (ex) solve for x
5. Don't forget unit of the answer. (ex) 40 thousand dollars
... (cont.)
*Keep repeating it 'til two numbers are very close each other & then stop.
Miami Dade College -- Hialeah Campus
7
Antiderivative Exponential & Logarithmic Forms
suppose
then f(x) called Antiderivative of g(x) w.r.t. , then Notation
Properties
x
Basic of Integral
Hyperbolic Forms
Trigonometric Forms
Miami Dade College -- Hialeah Campus
8
Differentiation Formulas Antiderivative(Integral) Formulas
Miami Dade College -- Hialeah Campus
9
Antiderivatives of = Indefinite Integral Definite Integral
is continuous. This represents the area x
F(x) is called Antiderivative of on an interval I under the curve y=f(x) bounded by x-axis a b
if . and the lines x=a and x=b.
1) Left and Right Endpoints
*Member of the family of Antiderivatives of y
so we use the idea that the slope of tangent line by slopes of secants lines
and the limit of these approximations.
0 0 x
Suppose we divides S into n th strips and the area A is between left and
3
right endpoints of the rectangles. (the width of all strips are same.)
-3 -3 L
(C is an arbitrary constant.)
The Substitution Rule
1. Let
Ex) is divided by four strips in [0, 1]
y (1, 1) y (1, 1) y (1, 1)
then
0 0 0
Area=A Using left end points Using right end points
The area using Left Endpoints=
1. Let
The area using Right Endpoints=
2) Sample Points
We also find the area with using sample points (any points in each strip).
y y=f(x)
Integral Substitution
The width
of all strips
are same.
a b
(n th strips)
The height if the th rectangle to be the value of at any number
in the th subinterval
3) Midpoint Rule
Miami Dade College -- Hialeah Campus
10
x Properties of Definite Integral
1- Using Right Endpoint
2- Using Midpoint
X The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
0 1 2 Suppose is continuous on [a, b]
The Substitution Rule of Definite Integral
*Norm of P *
Integrals of Symmetric functions suppose f(x) is continuous on [-a, a]
Miami Dade College -- Hialeah Campus
11
Areas between Curves
Suppose for all x in [a,b]
1. Find [a, b]
1. to find [a, b] ; when
2. which is ; test any No. between [a, b]
0 2. Find
then the bigger func. is and the other one is
1
Volumes by Cylindrical Shells
Find the area of the shaded region.
-4 0 3
1. Find [a, b] ; the radius y
(5, 4)
Find the area of the shaded region.
x 1. Find [c, d]= [-2, 4] 2. Find the Circumference
- test any No. in [-2, 4] It's about
3. Find the height x
y x=1
1. Find [a, b] ; the radius
2. Find the Circumference
It's about r=1
3. Find the height x
Let S be a solid that lies between x=a and x=b.
0 1
If the cross-sectional area of S in the plane , through x and perpendicular
to the x-axis, is A(x), where A is a continuous func.
Average Values of Func.
If is continuous on [a, b], then there exists a number c in [a, b] such that
y
y=8
x
x
Miami Dade College -- Hialeah Campus
12
Work Problems
*The Work done in moving the object from a to b
Hooke's Law
a positive constant (called the spring constant)
a natural length
a stretched length
a) Find the spring's force constant.
a) the spring's force constant =
1. Find it
2. Change the unit to m(Meter)
b) How much work is done ?
2. [a, b]=? [0.05, 0.08]
Miami Dade College -- Hialeah Campus
Você também pode gostar
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsNo EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (8)
- Calculus limits and continuityDocumento11 páginasCalculus limits and continuityAshwini MunirathnamAinda não há avaliações
- Concepts from Tensor Analysis and Differential GeometryNo EverandConcepts from Tensor Analysis and Differential GeometryAinda não há avaliações
- FIG. 1. (A) Slope of A Secant, (B) As X Approaches A, (C) Slope of A Tangent. Credit: Strang, G. & Herman, E. "Jed," 2021. Defining The DerivativeDocumento3 páginasFIG. 1. (A) Slope of A Secant, (B) As X Approaches A, (C) Slope of A Tangent. Credit: Strang, G. & Herman, E. "Jed," 2021. Defining The DerivativeLalbiakhluni ChhangteAinda não há avaliações
- Vertical Horizontal PDFDocumento8 páginasVertical Horizontal PDFRj LegoreAinda não há avaliações
- Limits and Continuity 2.9Documento3 páginasLimits and Continuity 2.9Johanna I. De Jesus MatosAinda não há avaliações
- Key concepts and theorems of functions and limitsDocumento33 páginasKey concepts and theorems of functions and limitsOutis WongAinda não há avaliações
- DiferentiabilityDocumento24 páginasDiferentiabilitypau miquelAinda não há avaliações
- Math1325 1 Sided LimitsDocumento9 páginasMath1325 1 Sided Limitsmyapplication dataAinda não há avaliações
- Diferent I AbilityDocumento24 páginasDiferent I AbilityLiliana AmpAinda não há avaliações
- Finding Derivatives and Tangent SlopesDocumento24 páginasFinding Derivatives and Tangent SlopesLiliana AmpAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture NotesDocumento3 páginasLecture NotesJustin Paul TumaliuanAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus I Formulas-Chapter-3-Dr. Wadii Hajji: 1 Steps To Graph A FunctionDocumento1 páginaCalculus I Formulas-Chapter-3-Dr. Wadii Hajji: 1 Steps To Graph A FunctionInesAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus FULLDocumento107 páginasCalculus FULLkanishkaAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Differentiation RulesDocumento4 páginasBasic Differentiation RulesFrank MarshallAinda não há avaliações
- 2 8Documento38 páginas2 8georgAinda não há avaliações
- Derivatives and Its ApplicationDocumento32 páginasDerivatives and Its ApplicationFitawrary Alene TeferaAinda não há avaliações
- CalTA-derivative (Drawn)Documento4 páginasCalTA-derivative (Drawn)HowardAinda não há avaliações
- WK 1 Introduction and Definition of DerivativesDocumento20 páginasWK 1 Introduction and Definition of DerivativesrenatoamarAinda não há avaliações
- Draw Graphs Limit FunctionsDocumento8 páginasDraw Graphs Limit FunctionsVanessa Au YongAinda não há avaliações
- Handout 4 - LimitsDocumento5 páginasHandout 4 - LimitsMarvin Yebes ArceAinda não há avaliações
- 17 Continuity Revision Notes QuizrrDocumento10 páginas17 Continuity Revision Notes QuizrrVarun ChandelAinda não há avaliações
- Math 1314 Rational Functions Rational Functions: Domains and RangesDocumento6 páginasMath 1314 Rational Functions Rational Functions: Domains and Rangesluluhbelle cruzAinda não há avaliações
- Outlines:: Continuity Derivative of A Functions DifferentiabilityDocumento17 páginasOutlines:: Continuity Derivative of A Functions DifferentiabilityAbidur Rahman ZidanAinda não há avaliações
- Limits and ContinuityDocumento32 páginasLimits and ContinuityAnik100% (2)
- Notes DifferentiabilityDocumento84 páginasNotes DifferentiabilitySrvAinda não há avaliações
- MOOC Introduction to Calculus Limits NotesDocumento5 páginasMOOC Introduction to Calculus Limits NotesDj OoAinda não há avaliações
- 2.6-Part 1 Limits at InfinityDocumento6 páginas2.6-Part 1 Limits at Infinityellipsepurplish532Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 LimitsDocumento19 páginasChapter 1 LimitsIrsyadAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus - LimitsDocumento2 páginasCalculus - LimitsAllel CensoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 Partial Derivatives - MATH1006 CalculusDocumento11 páginasChapter 4 Partial Derivatives - MATH1006 CalculusHerkhinwale OmoakinAinda não há avaliações
- 10 DifcalDocumento4 páginas10 DifcaljaysonrecortegAinda não há avaliações
- Graph Rational FunctionsDocumento8 páginasGraph Rational Functionsalayca cabatanaAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus1section1 3Documento10 páginasCalculus1section1 3api-358505269Ainda não há avaliações
- 1.3 Infinite Limits: Right X Approaches 1 From The LeftDocumento3 páginas1.3 Infinite Limits: Right X Approaches 1 From The LeftFrancis Rey Bactol PilapilAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Calculus - pdf5Documento6 páginas2 Calculus - pdf5novey_casioAinda não há avaliações
- Algebra1section3 3Documento11 páginasAlgebra1section3 3api-358505269Ainda não há avaliações
- 17 ContinuityDocumento11 páginas17 Continuitytusharfiitjee80Ainda não há avaliações
- Differentiation TargetDocumento113 páginasDifferentiation Targetipsita londheAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Notes - Week 2Documento13 páginasLecture Notes - Week 2Nathaniel LucasAinda não há avaliações
- Limits and DerivativesDocumento3 páginasLimits and DerivativeskennethAinda não há avaliações
- Lim Lim Lim: F (X) G (X) F (X) G (X)Documento2 páginasLim Lim Lim: F (X) G (X) F (X) G (X)Precious ViterboAinda não há avaliações
- UW Möbius - ContinuityDocumento10 páginasUW Möbius - ContinuityEmma ScottAinda não há avaliações
- A104 - Differential CalculusDocumento15 páginasA104 - Differential CalculusKrystel Monica ManaloAinda não há avaliações
- PC FUNCTIONS End Behavior of Polynomial and Rational FunctioDocumento16 páginasPC FUNCTIONS End Behavior of Polynomial and Rational FunctioHector R.Ainda não há avaliações
- Calculus Worksheet CH 3 - Derivatives Test ReviesDocumento2 páginasCalculus Worksheet CH 3 - Derivatives Test ReviesAdamAinda não há avaliações
- Limits, Continuity and DifferentiabilityDocumento12 páginasLimits, Continuity and DifferentiabilityA. SANDESHAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus 1 Topic 4Documento9 páginasCalculus 1 Topic 4muradAinda não há avaliações
- Notes Day 18-22Documento12 páginasNotes Day 18-22api-272815616Ainda não há avaliações
- Math 180 Derivative WorksheetDocumento8 páginasMath 180 Derivative WorksheetDeep PrajapatiAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Notes On Multivariable CalculusDocumento36 páginasLecture Notes On Multivariable CalculusAnwar ShahAinda não há avaliações
- 08 ContinuitytextbookDocumento19 páginas08 Continuitytextbookipsita londheAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus Overview: 0.1 Limits and ContinuityDocumento14 páginasCalculus Overview: 0.1 Limits and Continuitytanmoy bhattacharjeeAinda não há avaliações
- MA005 3.2 Definition of DerivativeDocumento15 páginasMA005 3.2 Definition of DerivativeDBCGAinda não há avaliações
- Rational FunctionsDocumento20 páginasRational FunctionsBretana joanAinda não há avaliações
- Nature of Roots of A PolynomialDocumento9 páginasNature of Roots of A Polynomialmeenu7823Ainda não há avaliações
- 3.6Documento5 páginas3.6goldsm65Ainda não há avaliações
- Lesson 6 - DifferentiationDocumento6 páginasLesson 6 - DifferentiationLewis PharmaceuticalsAinda não há avaliações
- Instantaneous Rate of Change - The DerivativeDocumento7 páginasInstantaneous Rate of Change - The DerivativeTrishul GyAinda não há avaliações
- Exactly One ElementDocumento20 páginasExactly One ElementhazimahAinda não há avaliações
- MoneyDocumento1 páginaMoneyShahriar KAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report 2Documento2 páginasLab Report 2Shahriar KAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4Documento39 páginasChapter 4Shoaib MughalAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report of SUSTDocumento1 páginaLab Report of SUSTShahriar KAinda não há avaliações
- Break On Through To The Single Side: Dilip B. Madan and Wim Schoutens July 26, 2007Documento20 páginasBreak On Through To The Single Side: Dilip B. Madan and Wim Schoutens July 26, 2007Bobby MilkAinda não há avaliações
- Coca-Cola Amatil's Interest Rate Risk Hedging StrategiesDocumento5 páginasCoca-Cola Amatil's Interest Rate Risk Hedging StrategiesLucas TingAinda não há avaliações
- Notes 5b - GradientDocumento10 páginasNotes 5b - GradientGlydle BautistaAinda não há avaliações
- Analyzing Risk and Return in Commodity FuturesDocumento5 páginasAnalyzing Risk and Return in Commodity FuturesSaggam RaviAinda não há avaliações
- RiskDocumento4 páginasRiskUtkarsh ChoudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Risk Management in BanksDocumento57 páginasRisk Management in BanksSunil RawatAinda não há avaliações
- 01 Aromatic Hydrocarbons BenzeneDocumento116 páginas01 Aromatic Hydrocarbons BenzeneHamid Hussain HamidAinda não há avaliações
- FIM DerivativesDocumento3 páginasFIM DerivativesS Ali MemonAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Modeling Course Outline - 16-17Documento3 páginasFinancial Modeling Course Outline - 16-17Stella KazanciAinda não há avaliações
- Replicating IndexDocumento12 páginasReplicating IndexzdfgbsfdzcgbvdfcAinda não há avaliações
- DerivativeDocumento47 páginasDerivativeMuhammad AshfaqAinda não há avaliações
- ForexDocumento7 páginasForexIrma Meow ChowdhuryAinda não há avaliações
- Homework Solutions for Linear Differential EquationsDocumento10 páginasHomework Solutions for Linear Differential EquationsDanayFerMarAinda não há avaliações
- CH 13 Hull OFOD8 TH EditionDocumento31 páginasCH 13 Hull OFOD8 TH EditionAlex WanowskiAinda não há avaliações
- BIS Primer PDFDocumento71 páginasBIS Primer PDFutah777Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 02Documento13 páginasChapter 02BonjamesNgAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-6.PDF Engg MathDocumento56 páginasUnit-6.PDF Engg MathSudersanaViswanathanAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2 ADocumento23 páginasLecture 2 AStanil StoevAinda não há avaliações
- Derivatives NotesDocumento4 páginasDerivatives NotesSoumyaNairAinda não há avaliações
- Risk ManagementDocumento4 páginasRisk ManagementAnonymous uxd1ydAinda não há avaliações
- And Structured Notes Functionality: IRS KEYDocumento1 páginaAnd Structured Notes Functionality: IRS KEYVikram SuranaAinda não há avaliações
- Profile-S S Kantilal Ishwarlal Securities Private LimitedDocumento1 páginaProfile-S S Kantilal Ishwarlal Securities Private LimitedmohsinAinda não há avaliações
- 1 PDFDocumento10 páginas1 PDFLuis SahuaAinda não há avaliações
- ALL MAths Formulas FromDocumento25 páginasALL MAths Formulas FromLovleen GargAinda não há avaliações
- CDS Market GuideDocumento26 páginasCDS Market GuideKumar Viswajeet Singh100% (1)
- Click To Get WAEC Syllabus For Other Subjects: SourceDocumento16 páginasClick To Get WAEC Syllabus For Other Subjects: SourceAhmad AbdurrazzaqAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 141Documento35 páginasLecture 141Krishan988Ainda não há avaliações
- Greek Letters of FinanceDocumento40 páginasGreek Letters of FinanceshahkrunaAinda não há avaliações
- International FinanceDocumento9 páginasInternational FinancelawrelatedAinda não há avaliações
- IUPAC Seniority Rules PDFDocumento10 páginasIUPAC Seniority Rules PDFAnonymous vRpzQ2BLAinda não há avaliações
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsNo EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (8)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormNo EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsNo EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeNo EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2)
- Making and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenNo EverandMaking and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingNo EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (21)
- Calculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusNo EverandCalculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (2)
- Psychology Behind Mathematics - The Comprehensive GuideNo EverandPsychology Behind Mathematics - The Comprehensive GuideAinda não há avaliações
- A Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathNo EverandA Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormNo EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (20)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)No EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Ainda não há avaliações
- How Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsNo EverandHow Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (9)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.No EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldNo EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (79)
- Math Magic: How To Master Everyday Math ProblemsNo EverandMath Magic: How To Master Everyday Math ProblemsNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (15)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorNo EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (3)
- Strategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceNo EverandStrategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceAinda não há avaliações
- Classroom-Ready Number Talks for Kindergarten, First and Second Grade Teachers: 1,000 Interactive Activities and Strategies that Teach Number Sense and Math FactsNo EverandClassroom-Ready Number Talks for Kindergarten, First and Second Grade Teachers: 1,000 Interactive Activities and Strategies that Teach Number Sense and Math FactsAinda não há avaliações
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersNo EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (6)