Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Solutions SPHS 12 3 M
Enviado por
arpitaDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Solutions SPHS 12 3 M
Enviado por
arpitaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CLASS XII SET A
MATHEMATICS
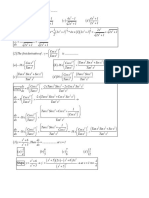
dx
61. ( x a) (b x)
=
1 xa 1 x a 1 x a
(A) 2sin c (B) sin c (C) 2sin c (D) t n +C
ba ba ba
Solution: Put x = acos2 + bsin2 the given integral becomes.
2(b a)sin cos d
I
(acos
1
2
bsin2 a) (acos2 bsin2 b 2
2b a sin cos d b a x a
2 d 2 sin1 c
= b a sin cos b a = 2 + c = ba
Hence (A) is the correct answer.
sin x
62. sin x cos x dx is equal to:
x 1 x 1
(A) log sin x cos x c (B) log sin x cos x c
2 2 2 2
x 1
(C) log sin x cos x c (D)
2 2
Solution: Let sin x = A( sin x cos x) + B. d.c of (sin x cos x)
or sin x = A ( sin x cos x) + B ( cos x + sin x)
or sin x= (A + B ) sin x + (B A) cos x
equating the coefficient of sin x and cos x, we get
A + B = 1 and B A = 0
A = 1/2, B = 1/2
1
sin x cos x 1 cos x sin x
I=
2
2
sin x cos x
1 1 cos x sin x x 1
= 2
dx
2 sin x cos x
dx + log (sin x - cos x ) + c
= 2 2 .
Hence (B) is the correct answer.
www.edudigm.in | 8961066637 / 8585070735
CLASS XII SET A
cos 5 x cos 4 x
63. 1 2cos 3x
dx is equal to:
sin2x sin2x sin 2 x sin 2 x
(A) sin x c (B) sin x c (C) sin x c (D) sin x c
2 2 2 2
9x x 3x 9x 3x x
2 cos cos cos 2 cos cos cos
2 2 3x 2 2 3x dx 2
3x
2 2 dx
3 3x
1 2 2 cos 1 cos 3 cos 4 cos
Solution: 2 2
= 2 2
9x 3x x
2 cos cos cos
2
9x
2 2 dx
=
cos
2 = cos 2x cos x dx
sin 2x
sin x c
= 2 .
Hence (C) is the correct answer.
dx
64. cos 6
x sin 6 x
is equal to
(A) loge (tan x cot x) + c (B) loge (cot x tan x) + c (C) tan-1 (tan x cot x) +c (D) tan-1 (2 cot 2 x) + c
dx sec 6 x (1 tan2 x )2 sec 2 xdx
dx
1 tan6 x
Let I = cos x sin x = 1 tan x
6 6 6
Solution: =
If tan x = p, then sec2 x dx = dp
1
p2 1 2
p dp
(1 p2 )2 dp (1 p2 ) 1
dp p2 p2 2 1
= 1 p = p p 1
6 4 2
= p
dk
I k2 1
tan1(k ) c
1 1
p k 1 dp dk
2
If p , then p
1
tan1 p c 1 1
= p = tan (tan x cotx) c = tan ( 2 cot 2 x) c
Hence (C) is the correct answers.
www.edudigm.in | 8961066637 / 8585070735
CLASS XII SET A
3 2cos x
65. (2 3cos x) 2
dx is equal to
sin x 2cos x 2 cos x 2sin x
(A) c (B) 3sin x 2 c (C) c (D) c
3cos x 2 3cos x 2 3sin x 2
3 2cos x
(2 3 cos x ) 2
dx
Solution: Let I =
Multiplying Nr. & Dr. by cosec2x
(3cos ec 2 x 2 cot x cos ec x )
(2 cos ecx 3 cot x )2
I= dx
3 cos ec 2 x 2 cot x cos ec x
(2cos ec x 3cot x )2
=- dx
1 sin x
c
2cos ec x 3cot x 2 3cosx
= = .
Hence (A) is the correct answer.
x sin x
66. 1 cos x dx is equal to
x x x x
(A) x tan c (B) tan c (C) x tan x c (D) tan c
2 2 2 2
x sin x 1 x
dx sec ( x sin x )dx
2
Solution: I = 1 cos x 2 2
1 x 2 x
I= 2
x sec 2
2 2
tan dx
2
1 tan x / 2 1 tan x / 2
=2
x
1/ 2
2 1/ 2 tan x / 2dx
= x tanx/2 +c
Hence (A) is the correct answer.
www.edudigm.in | 8961066637 / 8585070735
CLASS XII SET A
sin x cos x
67. 9 16sin 2 x dx is equal to:
1 5 4(sin x cos x) 1 5 4(sin x cos x)
(A) ln +c (B) ln +c
40 5 4(sin x cos x) 40 5 4(sin x cos x)
1 5 4(sin x cos x) 1 5 4(sin x cos x)
(C) ln +c (D) ln +c
40 5 4(sin x cos x) 40 5 4(sin x cos x)
sin x cos x
Solution:
Let I = 9 16 sin 2x
dx
Let t = sin x cos x t2 = 1 sin 2x
sin 2x = (1 t2)
dt dt
9
16 (1 t 2
)
25
16t 2
I=
5
1 dt t
1 1 4
2 ln
16 5 16 5 5
t2 2 t
= 4 = 4 4
+c
1 5 4t 1 5 4(sin x cos x )
ln ln
= 40 5 4 t +c= 40 5 4(sin x cos x ) + c.
Hence (A) is the correct answer.
68. tan x cot x dx is equal to :
1
(A) 2 sin1 (sin x + cos x) + c (B) sin1 (sin x cos x) + c
2
1
(C) ..sin1 (sin x cos x) + c (D) sin1 (sin x + cos x) + c
2
Let I =
tan x cot x
Solution: dx
sin x cos x
=
2 2 sin x cos x dx
(sin x cos x )
=
2 sin 2x dx
Let t = sin x cos x
t2 = 1 sin 2x
dt = (cos x + sin x) dx
dt
2
1 t 2 = 2 sin1 (t) + c
I=
I = 2 sin1 (sin x cos x) + c.
Hence (C) is the correct answer.
www.edudigm.in | 8961066637 / 8585070735
CLASS XII SET A
1
69. x x
2 4
1
3/4
dx is equal to :
1/ 4 1/ 4 1/ 4 1/ 4
1 1 1 1
(A) 1 4 +c (B) 1 4 + c (C) 1 4 +c (D) 1 4 +c
x x x x
1
x x 2 4
1 3/4
Solution: Let I = dx
dx
1
3/4
x 5 1 4
= x
dx
4 1 1
5 5
Let 1 + x4 = t x dx = dt x dx = 4 dt
1 dt 1 3 / 4 1
I=4 t
3/4
4
t dt 4t1 / 4
4 +c
1/ 4
1
1 4
I = x + c.
Hence (B) is the correct answer.
dx
70. 2x 3 4x 5
is equal to:
(A) tan1 4x - 5 + c (B) tan1 4x 5 + c (C) tan1 5x + 4 + c (D) tan1 5x - 4 + c
dx
2x 3 4x 5
Solution: Let I =
t5
Put 4x + 5 = t x = 4
dt
dx = 4
dt
1 2t 10 3 t 1 dt
(t 1)
I= 4 4 2 t
=
Let t =u
du
I = u 1
2
tan1 t c
I = tan1 4x 5 + c.
Hence (B) is the correct answer.
www.edudigm.in | 8961066637 / 8585070735
CLASS XII SET A
x 1
x x2
1
71. e tan dx is equal to
1 x 2
1 1 1 1 1
(A) xetan x
c (B) x 2 e tan x
c (C) 1
c (D) 2
e tan x
+c
tan x x
xe
e sec
p tan p dp
p 2
Solution: I= (If p = tan-1x x = tanp dx = sec2p dp)
1
tan x
= ep tanp = x e +c
Hence (A) is the correct answer.
1 7cos 2 x
sin
f (x)
72. dx C, then f(x) is equal to
7
x cos x 2
sin x 7
(A) sin x (B) cos x (C) tan x (D) cot x
Solution (C)
1 7cos 2 x sec2 x 7 sec2 x
sin 7 x cos 2 x
dx
sin 7 x sin 7 x
dx
sin 7
x
dx 7
7
dx
- sin x = I1 I2
sec2 x
tan x tan x.cos x tan x
7
dx 7
7 8
dx I2
Now I1 = sin x sin x sin x sin7 x
tan x
2
C
I1 I2 = sin x
f(x) = tan x
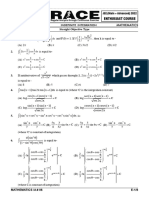
73. From the matrix equation AB = AC, we can conclude B = C provided
(A) A is singular (B) A is non-singular (C) A is symmetric (D) None of these
Solution If A is non-singular A-1 will exist and hence
2 4 2
74. tan 1 x tan 1 tan 1 x 0 has real roots
x x x
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4.
2 2 4
tan 1 x tan x tan 1
Solution The given equation can be written as x x x
2 2
x x
tan 1
x x 4
tan 1
2 2 x
1 x x
x x
4
x 4 4
1 1 x2 2
4
1 x2 2 x x
x
x 4 0 x2 2
4
x 2 x has two real values.
www.edudigm.in | 8961066637 / 8585070735
CLASS XII SET A
a 2 1 ab ac
75. If ab b 1 bc = 1, where a, b, c are real, then
2
ac bc c2 1
(A) a 2 b2 c2 1 (B) a + b + c = 1 (C) a2 + b2 + c2 = 0 (D) a+c=2b
Solution R,R ,R C ,C ,C
Multiply 1 2 3 respectively by a, b, c and take out a, b, c common from 1 2 3
respectively.
a2 1 a2 a2
D b2 b2 1 b2
c2 c2 c2 1
R1 R 2 R 3
and take 1 a common
2
Apply
1 1 1
D 1 a 2 b 2 b2 1 b2
c2 c2 c2 1
C2 C1, C3 C1
Make two zeros by
D a 2 b2 c2 1 1 given
a 2 b 2 c2 0 c
76. If A = { }, then the number of equivalence relation containing (1, 2) is
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 8
Solution The smallest equivalence relation R1 on A containing (1, 2) is {(1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (1, 2),
(2, 1)]. We are left with four pairs (1, 3), (3, 1), (2, 3) and (3, 2). Now to get another equivalence
relation R2 on A. if we add any one pair out of the above four pair say (1,3), then for
symmetry we have to add (3, 1). Also. to maintain transitivity we are forced to add (2, 3) and
(3, 2). Thus, the only equivalence relation on A bigger that R1 is the universal relation. Hence.
the total number of equivalence relations on A containing (1, 2) is two.
Paragraph for Questions Nos. 77 to 78
Consider the equation x + y [x] [y] = 0, where [] = Greatest integer function.
77. The number of integral solutions to the equation, is
(A) 0 (B) 1 (C) 2 (D) none of these
Solution (C)
For integral solution
(x 1) (y 1) = 1
Solutions are (0, 0) or (2, 2)
www.edudigm.in | 8961066637 / 8585070735
CLASS XII SET A
78. Equation of one of the lines on which the non-integral solution of given equation, lies is
(A) x + y = -1 (B) x + y = 0 (C) x + y = 1 (D) x + y = 5
(B)
Solution For non integral solution,
Let x = [x] + f1 and
Y = [y] + f2
[x] [y] = [x] + f1 + [y] + f2
[x] 1[y] 1 f1 f2 1
Now 0 f1 + f2 < 2
f1 + f2 = 1
x 1 y 1 2
Which is possible for
[x] = 3 and [y] = 2 or [x] = 2 and [y] = 3
or [x] = - 1 and [y] = 0 or [x] = 0 and [y] = - 1
The x + y = [x] [y] becomes x + y = 6 or x + y = 0
Non integral solution lies on x + y = 6 or x + y = 0.
Paragraph for Questions Nos. 79 to 80
Let In = x n a 2 x 2 dx, a 0 and n be a non-negative integer and
3/ 2
x n 1 a 2 x 2
1 2 3/ 2
In = a 2 BIn 1 . Where A and B are constant, and I1 = a x2
A 3
79. A must be equal to
(A) n (B) n + 1 (C) n + 2 (D) n + 3
80. B must be equal to
n n 1 n2 n 1
(A) (B) (C) (D)
n2 n2 n2 n2
3/ 2
x n 1. a 2 x 2 n 1
n 1 n 2 3/ 2
Solution In x .x a x dx
2 2
x a x
2 2
dx
3 3
3/ 2
x n 1 a 2 x 2
=
3
n 1
3
a 2 x n 2 x n a 2 x 2 dx
3/ 2
x n 1 a 2 x 2 n 1 2 n 2 2
a x 2 dx x n a 2 x 2 dx
3
= a x
3
3/ 2
x n 1 a 2 x 2 n 1 a 2 I n 1
= n 2 In
3 3 3
www.edudigm.in | 8961066637 / 8585070735
CLASS XII SET A
3/ 2
x n 1 a 2 x 2 n 1 a 2 I
In = n 2
n2 n2
Multiple Correct Type: Question No. (81-90):
This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D), out of which
ONE or MORE is correct.
81. If is equal to then
(A) x x x (B) x x (C) x x (D) x x x
( )
Soln:
82. If x p x q x where is onst nt o inte r tion then
(A) p q x x x n| |
(B) p q x x x n| |
(C) p q x x x n| |
(D) p q x x x n| |
Solution Convert all into tanx, you will get which can be easily integrated
83. x is equal to:
(A) ot ot x (B) ot t n x (C) t n t n x (B) t n os x
Solution Multiplying both numerator by se we get, , take t n
84. os x t n x then
(A) x ( ) (B) x ( )
(C) sin os x ( ) (D) t n os x ( )
Solution t n x os , use this to solve it
85. If the numerical value of tan os t n is a/b then
(A) a + b = 23 (B) a b = 11 (C) (D) 2a = 3b
( )
Solution os t n t n t n t n
86. For the function f(x) = n (sin o x),
(A) Domain is * + (B) Range is ( n + (C) Domain is (1, 2] (D) Range is R
Solution sin o x o x
www.edudigm.in | 8961066637 / 8585070735
CLASS XII SET A
87. A un tion rom the set o n tur l num ers to inte ers e ine y
when n is o
f(n) = { is
when n is even
(A) one-one (B) many-one (C) onto (D) into
Solution Range is all integers
88. If A [ ], then
(A) |A| (B) A is non-singular
(C) Adj. A= [ ] (D) A is skew symmetric matrix
Solution Based on the definition
89. Which of the following statement is always true?
(A) Adjoint of a symmetric matrix is a symmetric matrix
(B) Adjoint of a unit matrix is unit matrix
(C) A (adj A) = (adj A) A
(D) Adjoint of a diagonal matrix is diagonal matrix
Solution Based on definition
sin os sin sin os
90. Let | os os os sin sin |, then
sin sin sin os
(A) is independent of (B) is independent of
(C) is constant (D) +
Solution Expand it and check each options
www.edudigm.in | 8961066637 / 8585070735
Você também pode gostar
- Lecture 11of 12: Topic: 2.0 Trigonometric Functions SUBTOPIC: 2.7 Integration of Trigonometric FunctionDocumento25 páginasLecture 11of 12: Topic: 2.0 Trigonometric Functions SUBTOPIC: 2.7 Integration of Trigonometric FunctionMieerra JassminAinda não há avaliações
- Math - 9 SolveDocumento10 páginasMath - 9 SolveLittle WizardAinda não há avaliações
- CPP - Indefinite IntegrationDocumento13 páginasCPP - Indefinite Integrationcjoshi1710Ainda não há avaliações
- Assign-1 Integration by Use of Basic FormulaeDocumento3 páginasAssign-1 Integration by Use of Basic FormulaeDhruv KuchhalAinda não há avaliações
- Trigonometric Integrals-Solutions: ReviewDocumento3 páginasTrigonometric Integrals-Solutions: ReviewMarCheLinaAinda não há avaliações
- 2.4 Differentiation of Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento16 páginas2.4 Differentiation of Trigonometric FunctionsAhmad SolihuddinAinda não há avaliações
- 7.2-Trignometric IntegralsDocumento19 páginas7.2-Trignometric Integralsمصطفى احمدAinda não há avaliações
- 4 Determinants: Level-IIDocumento27 páginas4 Determinants: Level-IIBaljeet Singh100% (1)
- Maths QuestionsDocumento7 páginasMaths QuestionsJatinAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 4 Self Review SolutionsDocumento2 páginasLecture 4 Self Review SolutionsGareth WongAinda não há avaliações
- M14 - Indefinite IntegrationDocumento24 páginasM14 - Indefinite IntegrationBhawna SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- 2016 2 Sel Methodist ADocumento9 páginas2016 2 Sel Methodist ANur B TapriAinda não há avaliações
- K03052 - 20200424155345 - 7.3 Trigo SubsDocumento32 páginasK03052 - 20200424155345 - 7.3 Trigo Subshariz syazwanAinda não há avaliações
- NaturemathfDocumento3 páginasNaturemathfzdfbdfb12Ainda não há avaliações
- .11 Integration - Integration by Parts Method (Examples)Documento8 páginas.11 Integration - Integration by Parts Method (Examples)hariz syazwanAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz (1) Calculus - PDF - 1631305864Documento3 páginasQuiz (1) Calculus - PDF - 1631305864Omar HeshamAinda não há avaliações
- Integral Trigonometri Part 3Documento28 páginasIntegral Trigonometri Part 3ones29telaumbanuaAinda não há avaliações
- Trigonometric Diff and IntegrateDocumento1 páginaTrigonometric Diff and IntegrateKop FriendAinda não há avaliações
- Integrals Wo WatermarkDocumento12 páginasIntegrals Wo Watermarkmeghashyam.raju1210Ainda não há avaliações
- I Integration-04 - ExerciseDocumento13 páginasI Integration-04 - ExerciseRaju SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Test2 - 20182019 SchemeDocumento11 páginasTest2 - 20182019 SchemenorsyahirahafiqahAinda não há avaliações
- 5.4 Integration Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento12 páginas5.4 Integration Trigonometric Functionshariz syazwanAinda não há avaliações
- Ri 2023 Math TP SolnDocumento17 páginasRi 2023 Math TP SolnVenkateswaran Gayathri (Bbss)Ainda não há avaliações
- Trigonometric Equation-04 - Exercise-2Documento20 páginasTrigonometric Equation-04 - Exercise-2Raju SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Add Maths 2004 Suggested SolutionDocumento10 páginasAdd Maths 2004 Suggested Solutionapi-26423290Ainda não há avaliações
- MTH501 Assignment No.1Documento4 páginasMTH501 Assignment No.1Umar KhanAinda não há avaliações
- AMA1110 Tutorial - 2sDocumento3 páginasAMA1110 Tutorial - 2sBrian LiAinda não há avaliações
- Caps 16Documento4 páginasCaps 16Sai Venkata Krishna GAinda não há avaliações
- Zadatak 4.: Rje SenjeDocumento1 páginaZadatak 4.: Rje SenjeMayaAinda não há avaliações
- C.B.S.E. SAMPLE PAPER 2021-22 (TERM-II) : Mathematics Class-XIIDocumento57 páginasC.B.S.E. SAMPLE PAPER 2021-22 (TERM-II) : Mathematics Class-XIIjokes & comedies onlyAinda não há avaliações
- AOD Sheet 1 Mathongo SolutionsDocumento8 páginasAOD Sheet 1 Mathongo SolutionsPranav Singh RajputAinda não há avaliações
- Integration Using Trig Identities or A Trig SubstitutionDocumento7 páginasIntegration Using Trig Identities or A Trig SubstitutionJanry GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- FormulaSheet Lesson2Documento11 páginasFormulaSheet Lesson2thatokgosiyagae389Ainda não há avaliações
- Practice Pre-CalculusDocumento2 páginasPractice Pre-CalculusHector Dorian Alburquerque MoralesAinda não há avaliações
- MAA HL 3.5-3.9 TRIGONOMETRIC EQUATIONS AND FUNCTIONS - SolutionsDocumento16 páginasMAA HL 3.5-3.9 TRIGONOMETRIC EQUATIONS AND FUNCTIONS - SolutionsPradyot ChakrabortyAinda não há avaliações
- Maths Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-4) - PaperDocumento9 páginasMaths Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-4) - PaperAnanmay ChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- (Maa 5.20) Integration by Parts - SolutionsDocumento6 páginas(Maa 5.20) Integration by Parts - Solutionsdhruvkhera2Ainda não há avaliações
- Activity No. 3 TRIGONMETRIC POWERSDocumento10 páginasActivity No. 3 TRIGONMETRIC POWERSrymacAinda não há avaliações
- PrintedTutorial 2 PDFDocumento3 páginasPrintedTutorial 2 PDFsophixAinda não há avaliações
- RT-2 Set-C SolDocumento4 páginasRT-2 Set-C Solsachinplayer2006Ainda não há avaliações
- Indefinite Integration One Shot - Practice Sheet - JEE Challengers 2023Documento7 páginasIndefinite Integration One Shot - Practice Sheet - JEE Challengers 2023ttojo7105Ainda não há avaliações
- Differentiation: Dy DX Dy DX Dy DXDocumento3 páginasDifferentiation: Dy DX Dy DX Dy DXcharan dheepAinda não há avaliações
- STEP Support Programme STEP 2 Trigonometry Questions: SolutionsDocumento7 páginasSTEP Support Programme STEP 2 Trigonometry Questions: SolutionsMUHAMMAD ARSLANAinda não há avaliações
- MATH 259 - Review Sheet (Prerequisite Topics) : (This Is NOT A Comprehensive List!)Documento4 páginasMATH 259 - Review Sheet (Prerequisite Topics) : (This Is NOT A Comprehensive List!)Celal KermangilAinda não há avaliações
- Formula CompilationDocumento6 páginasFormula CompilationKirstie Alley San JoseAinda não há avaliações
- DPP No. 7: PhysicsDocumento3 páginasDPP No. 7: PhysicsUddhav SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematical Physics Useful Formulae PDFDocumento29 páginasMathematical Physics Useful Formulae PDFKunal RanaAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Digression: Differential Calculus On R: N N 1 X X DX X DX 1+x DX 2 XDocumento4 páginas2 Digression: Differential Calculus On R: N N 1 X X DX X DX 1+x DX 2 XGag PafAinda não há avaliações
- Cal1 TD2 (2023 24)Documento2 páginasCal1 TD2 (2023 24)Da VyAinda não há avaliações
- Cape Math Unit 2 Module 1 Exam 2016 - 17Documento11 páginasCape Math Unit 2 Module 1 Exam 2016 - 17Emily ZhengAinda não há avaliações
- Integration 11B: 1 A B C D OR Let Then 2 ADocumento4 páginasIntegration 11B: 1 A B C D OR Let Then 2 AgsfdewAinda não há avaliações
- Integration 11B: 1 A B C D OR Let Then 2 ADocumento4 páginasIntegration 11B: 1 A B C D OR Let Then 2 AgsfdewAinda não há avaliações
- MC Ty Intusingtrig 2009 1Documento7 páginasMC Ty Intusingtrig 2009 1Rozanne TingAinda não há avaliações
- (123dok - Com) Bab Xvi Integral 2Documento4 páginas(123dok - Com) Bab Xvi Integral 2Yahya IrfansyahAinda não há avaliações
- Kalkulus UNDIPDocumento31 páginasKalkulus UNDIPRosdian AriefAinda não há avaliações
- Integral Kalkulus Dan Integral TheoremsDocumento24 páginasIntegral Kalkulus Dan Integral TheoremsRifa NabillaAinda não há avaliações
- 12th DIFFERENTIATION: - Theory & ProblemsDocumento11 páginas12th DIFFERENTIATION: - Theory & Problemsarjun sabuAinda não há avaliações
- Indefinite IntDocumento8 páginasIndefinite Intdhruv1007bansalAinda não há avaliações
- MathsDocumento2 páginasMathssatyasravanthAinda não há avaliações
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsNo EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Engineering EntranceDocumento11 páginasEngineering EntrancearpitaAinda não há avaliações
- Binomial TheoremDocumento14 páginasBinomial TheoremarpitaAinda não há avaliações
- Test 3 Answer Key Sphs Cbse XiDocumento4 páginasTest 3 Answer Key Sphs Cbse XiarpitaAinda não há avaliações
- Scrib 1Documento1 páginaScrib 1arpitaAinda não há avaliações
- Test 3 Answer Key Sphs Cbse XiiDocumento4 páginasTest 3 Answer Key Sphs Cbse XiiarpitaAinda não há avaliações
- Asl Class11Documento6 páginasAsl Class11arpitaAinda não há avaliações
- CRMO-2015 Questions and SolutionsDocumento3 páginasCRMO-2015 Questions and SolutionsarpitaAinda não há avaliações
- Mstse 2015 16 Sample Paper 10xx ADocumento15 páginasMstse 2015 16 Sample Paper 10xx Aarpita0% (1)
- Challenges and Thrills of Pre College Maths For GeometryDocumento1 páginaChallenges and Thrills of Pre College Maths For GeometryarpitaAinda não há avaliações
- IITJEE Mains: 2 Year CRP/ 1 Year CRP/ Pinnacle - 2 Year Integrated School ProgramDocumento2 páginasIITJEE Mains: 2 Year CRP/ 1 Year CRP/ Pinnacle - 2 Year Integrated School ProgramarpitaAinda não há avaliações
- Drawbacks of The Existing SystemDocumento7 páginasDrawbacks of The Existing SystemSachin Mohite100% (1)
- CSSMasterclassBook PDFDocumento168 páginasCSSMasterclassBook PDFyankeeAinda não há avaliações
- History of AAMI BIT StoryDocumento11 páginasHistory of AAMI BIT StoryManojAinda não há avaliações
- Quantification of Organic Acids by HPLCDocumento5 páginasQuantification of Organic Acids by HPLCLee HaronAinda não há avaliações
- The Art of Fishing PDFDocumento27 páginasThe Art of Fishing PDFsilentkillersbh1729Ainda não há avaliações
- Public Relations vs. Propaganda: Alexandru BASTIANDocumento6 páginasPublic Relations vs. Propaganda: Alexandru BASTIANFatima AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- Dissolving Clouds With Your MindDocumento14 páginasDissolving Clouds With Your MindTamajong Tamajong PhilipAinda não há avaliações
- Astm G5Documento12 páginasAstm G5caop217100% (1)
- Online Web Chat Application DocumentDocumento8 páginasOnline Web Chat Application DocumentENGINEER HEREAinda não há avaliações
- Rubrica para La Evaluación Del Examen OralDocumento1 páginaRubrica para La Evaluación Del Examen Oralnoemi reyes jaimesAinda não há avaliações
- The Context Switch in FreeRTOS On A Cortex MDocumento13 páginasThe Context Switch in FreeRTOS On A Cortex MKristof MulierAinda não há avaliações
- Java Programming 9Th Edition Farrell Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocumento32 páginasJava Programming 9Th Edition Farrell Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFaletheasophroniahae100% (9)
- STAT1008 Cheat SheetDocumento1 páginaSTAT1008 Cheat SheetynottripAinda não há avaliações
- Ps1 GeneralDocumento2 páginasPs1 Generalkulin123456Ainda não há avaliações
- Morane 4 PFN FffsDocumento20 páginasMorane 4 PFN FffsFatmen FataAinda não há avaliações
- WebSphere Application Server AMI Cheatsheet For DemoDocumento2 páginasWebSphere Application Server AMI Cheatsheet For DemoYakura CoffeeAinda não há avaliações
- Wolves, Witches, and Werewolves - Lycanthropy and Witchcraft From 1423 To 1700 PDFDocumento28 páginasWolves, Witches, and Werewolves - Lycanthropy and Witchcraft From 1423 To 1700 PDFshotoshAinda não há avaliações
- Reaction Paper On Abaca IssueDocumento2 páginasReaction Paper On Abaca IssueAeron Afunggol RuazolAinda não há avaliações
- Nonverbal Communication in The WorkplaceDocumento7 páginasNonverbal Communication in The WorkplaceHenrissa Granado TalanAinda não há avaliações
- Genpact Leansixsigma Training OfferingDocumento4 páginasGenpact Leansixsigma Training OfferingSwamy NunnaAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless Power TransmissionDocumento16 páginasWireless Power TransmissionSamboju TejashwaniAinda não há avaliações
- Transverse ShearDocumento4 páginasTransverse ShearrajdrklAinda não há avaliações
- 3412 Timing CalibrationDocumento4 páginas3412 Timing CalibrationHrvoje Škarica100% (3)
- Simple Linear RegressionDocumento55 páginasSimple Linear RegressionPatrick HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Command ReferenceDocumento368 páginasCommand Referenceom007Ainda não há avaliações
- PIT Error Overview - ParetoDocumento208 páginasPIT Error Overview - ParetoHariharan Yelomalei50% (2)
- Kaizen MR - Final PDFDocumento65 páginasKaizen MR - Final PDFbhatiaharryjassiAinda não há avaliações
- MaseeiDocumento34 páginasMaseeivikrant100% (1)
- Course On Fracture Mechanics - IIT RoparDocumento248 páginasCourse On Fracture Mechanics - IIT RoparSumit BasuAinda não há avaliações
- Professional AdjustmentDocumento10 páginasProfessional AdjustmentJayson V Caranto RNAinda não há avaliações