Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
3laser Machining Ass
Enviado por
xinfeng HEDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
3laser Machining Ass
Enviado por
xinfeng HEDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Laser Machining Assist Gas Flow Characterization and Optimization
Sponsor: LASERDYNE SYSTEMS Division, PRIMA North America, Inc.
Sponsors General Business Statement: LASERDYNE SYSTEMS designs, manufactures, and markets multi-
axis laser machines that incorporate C02 and Nd:YAG lasers on a worldwide basis for precision drilling, cutting,
and welding of 3D parts. The company is the worlds leading supplier of multi-axis laser systems for turbine engine
(jet engine) applications.
Sponsors Advisor, Title, and Phone Number: Terry L. VanderWert, Vice President, (763) 433-3684
Sponsors Address: 8600 109th Avenue North, Champlin, MN 55316
University of St. Thomas School of Engineering Academic Advisor: Professor Camille M. George, Ph.D.
Team Member Names: Brian M. Farnes (ME), Gerald W. Grabowski (ME), Ryan D. Lovik (ME), and Scott M.
Schnobrich (ME)
Senior Design Clinic I-II (ENGR 480-481) 2005-2006 Project Mission Statement: Characterize the flow through
the existing laser machining gas assist system and investigate means to reduce gas consumption, through changes to
the 7.5 focal length nozzle assembly, while maintaining or improving cut quality.
Major Design Requirements:
1. Characterize the flow through the existing laser machining gas assist system. This includes determining the
pressure losses throughout the system and determining the mass flow rates through the system for various
operating pressures and nozzle types and diameters.
2. Investigate means to reduce the gas consumption through changes to the 7.5 focal length nozzle assembly,
while maintaining or improving cut quality.
3. Locate, select, and purchase various commercially available nozzle designs that may be used to reduce gas
consumption, while maintaining or improving cut quality.
4. Analyze the performance of the new nozzle designs as well as LASERDYNEs existing designs through
cutting trials, Schlieren visualization, and CFD simulation.
Senior Design Project Summary: The project was begun by performing experiments to characterize the flow
through LASERDYNEs existing gas assist system. We successfully determined the mass flow rates through the
system at various operating pressures, nozzle designs, and nozzle diameters. Additionally, we were able to compute
an efficiency through comparing the mass flow rates of the actual system to that of an ideal system. Also, we
performed pressure testing which indicated a total pressure drop of 22.5%, with only 1.5% over our area of
influence, the nozzle assembly.
Given that we did not have to redesign the nozzle assembly to reduce pressure losses, our focus for improving the
system was placed on determining nozzle designs that may deliver the gas to the cut more efficiently. Cold drawn
and double nozzles were selected and purchased to compare their performance to LASERDYNEs existing standard
nozzle designs. Nozzle flows were compared using Schlieren visualization techniques, which allow one to see the
structure of the supersonic flow out of the nozzles. Additionally, we performed cutting trials, utilizing a full design
of experiments, to analyze the performance of the different nozzle designs.
Schlieren image of a 3mm exit diameter Laser cutting in action, using commercial
cold form nozzle flowing into free space. double nozzle tip and nozzle adapter of our
design.
University of St. Thomas School of Engineering -- 2006 Senior Design Show
Você também pode gostar
- Performance Exhaust Systems: How to Design, Fabricate, and Install: How to Design, Fabricate, and InstallNo EverandPerformance Exhaust Systems: How to Design, Fabricate, and Install: How to Design, Fabricate, and InstallNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (8)
- DESIGN_ANALYSIS_OF_EXHAUST_MANIFOLD_IN_DIFFERENT_METALS_ON_SOLIDWORKS_ijariie13097Documento9 páginasDESIGN_ANALYSIS_OF_EXHAUST_MANIFOLD_IN_DIFFERENT_METALS_ON_SOLIDWORKS_ijariie13097ds8123395Ainda não há avaliações
- Design and Optimization of Exhaust System For Internal Combustion EnginesDocumento3 páginasDesign and Optimization of Exhaust System For Internal Combustion EnginesAzhari GunawanAinda não há avaliações
- Research and Design of Snow Hydrology Sensors and Instrumentation: Selected Research PapersNo EverandResearch and Design of Snow Hydrology Sensors and Instrumentation: Selected Research PapersAinda não há avaliações
- Design and Analysis of Automobile Exhaust AssemblyDocumento7 páginasDesign and Analysis of Automobile Exhaust AssemblyIJRASETPublicationsAinda não há avaliações
- Optimization of fuel nozzles for maximum thrust using multi-disciplinary optimizationDocumento6 páginasOptimization of fuel nozzles for maximum thrust using multi-disciplinary optimizationGowtham Kumar DronamrajuAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Wellbore Hydraulics and Hole Cleaning: Unlock Faster, more Efficient, and Trouble-Free Drilling OperationsNo EverandPractical Wellbore Hydraulics and Hole Cleaning: Unlock Faster, more Efficient, and Trouble-Free Drilling OperationsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Modeling of Spray InfectionDocumento5 páginasModeling of Spray InfectionHarshdeep BrarAinda não há avaliações
- SimulationDocumento4 páginasSimulationbharatsharmamechAinda não há avaliações
- Analyzing The Effects of Splitter Blade On The Performance Characteristics For A High-Speed Centrifugal PumpDocumento11 páginasAnalyzing The Effects of Splitter Blade On The Performance Characteristics For A High-Speed Centrifugal PumpBRENDA VIVIANA ARANDA JURADOAinda não há avaliações
- Malik 2020 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1500 012036Documento8 páginasMalik 2020 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1500 012036Irawan MalikAinda não há avaliações
- Hyperxtrude 112912 WebDocumento4 páginasHyperxtrude 112912 WebGladson BernardoAinda não há avaliações
- Transonic Axial-Flow Blade Shape Optimization Using Evolutionary Algorithm and Three-Dimensional Navier-Stokes SolverDocumento11 páginasTransonic Axial-Flow Blade Shape Optimization Using Evolutionary Algorithm and Three-Dimensional Navier-Stokes SolverEslam NagyAinda não há avaliações
- Modelling of Supersonic Gas Flow of NozzlesDocumento8 páginasModelling of Supersonic Gas Flow of NozzlesAndrea IobAinda não há avaliações
- WP Flow Simulation Gas MixingDocumento5 páginasWP Flow Simulation Gas MixingpengkritikAinda não há avaliações
- Review - Investigation of Pressure Swirl Atomisation PDFDocumento5 páginasReview - Investigation of Pressure Swirl Atomisation PDFDr. Nandakumar K. Director Research - ADMINAinda não há avaliações
- CFD Optimization With Altair Hyperworks: in This Issue July 2006Documento6 páginasCFD Optimization With Altair Hyperworks: in This Issue July 2006slv_prasaadAinda não há avaliações
- High Performance Supersonic Missile Inlet Design UDocumento35 páginasHigh Performance Supersonic Missile Inlet Design UEmine YıldızAinda não há avaliações
- Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of A Resistance MufflerDocumento4 páginasComputational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of A Resistance Mufflermahesh_1402Ainda não há avaliações
- Chi Tte War 2018Documento11 páginasChi Tte War 2018RohitShingadeAinda não há avaliações
- Vvimpo PDFDocumento23 páginasVvimpo PDFJustin JosephAinda não há avaliações
- Design and Analysis of Air Intake System For Single Cylinder EngineDocumento23 páginasDesign and Analysis of Air Intake System For Single Cylinder EngineEditor IJTSRD100% (1)
- Seminar Casting OrginalDocumento8 páginasSeminar Casting OrginalSreekumar RajendrababuAinda não há avaliações
- Capabilities Brochure S J Smith CoDocumento24 páginasCapabilities Brochure S J Smith CoAmplified LocalAinda não há avaliações
- Moldflow Insight Detail Brochure1Documento8 páginasMoldflow Insight Detail Brochure1antonkoenrAinda não há avaliações
- Optimization of Vane Demister Based On Neural Netw PDFDocumento12 páginasOptimization of Vane Demister Based On Neural Netw PDFMarco Antono DomingosAinda não há avaliações
- Rocket Nozzle Design & Flow AnalysisDocumento9 páginasRocket Nozzle Design & Flow AnalysisNainan TrivediAinda não há avaliações
- Computers & Fluids: Mine YumusßakDocumento13 páginasComputers & Fluids: Mine YumusßakshamoonjamshedAinda não há avaliações
- Design and Analysis of Exhaust System For The Two Wheeler Using FEADocumento8 páginasDesign and Analysis of Exhaust System For The Two Wheeler Using FEASourabh ApteAinda não há avaliações
- 【CAE】Automotive Door Handle Manufacturer Uses Moldex3D to Solve Weld Line IssuesDocumento16 páginas【CAE】Automotive Door Handle Manufacturer Uses Moldex3D to Solve Weld Line IssueszaldsonAinda não há avaliações
- CFD Analysis & Optimization of Fuel Injector by Changing Its GeometryDocumento5 páginasCFD Analysis & Optimization of Fuel Injector by Changing Its GeometryIJIRSTAinda não há avaliações
- Ijmet 08 08 073Documento9 páginasIjmet 08 08 073aman potdarAinda não há avaliações
- Optimisation of Screw CompressorsDocumento29 páginasOptimisation of Screw CompressorsSaeedAkbarzadehAinda não há avaliações
- e3sconf_star2024_00027Documento11 páginase3sconf_star2024_00027seherr719Ainda não há avaliações
- 10 1 1 649 9843 PDFDocumento63 páginas10 1 1 649 9843 PDFSakthikumarAinda não há avaliações
- Optimization of Labyrinth Seal For Screw Compressor Ht2007 32275Documento8 páginasOptimization of Labyrinth Seal For Screw Compressor Ht2007 32275Van Ryzal PurbaAinda não há avaliações
- Six Sigma-Based Approach To Optimize Deep Drawing Operation VariablesDocumento22 páginasSix Sigma-Based Approach To Optimize Deep Drawing Operation Variableswhereischinatown100% (2)
- 12_Design of a Propeller Fan Using 3-D Inverse Design Method and CFD for High Efficiency and Low Aerodynamic NoiseDocumento7 páginas12_Design of a Propeller Fan Using 3-D Inverse Design Method and CFD for High Efficiency and Low Aerodynamic NoisekcpatnaikAinda não há avaliações
- Efficient Global Optimization of Analog Circuits Using Predictive Response Surface Models On Discretized Design SpaceDocumento23 páginasEfficient Global Optimization of Analog Circuits Using Predictive Response Surface Models On Discretized Design SpaceMa SeenivasanAinda não há avaliações
- Design Optimal Wind Tunnel Test ModelDocumento16 páginasDesign Optimal Wind Tunnel Test ModelgeorgekenjiputraAinda não há avaliações
- Simulation and Analysis of Applications of Pesticide Sprayer VehicleDocumento11 páginasSimulation and Analysis of Applications of Pesticide Sprayer VehicleShivraj ParleAinda não há avaliações
- A Study of The Impact of Multiple Drilling Parameters On Surface Roughness, Tool Wear and Material Removal Rate While Drilling Al6063 Applying Taguchi TechniqueDocumento10 páginasA Study of The Impact of Multiple Drilling Parameters On Surface Roughness, Tool Wear and Material Removal Rate While Drilling Al6063 Applying Taguchi TechniqueIJAERS JOURNALAinda não há avaliações
- Compresor ElliotDocumento12 páginasCompresor ElliotMARTINA FERRARIAinda não há avaliações
- Ad Ow: An Open-Source Computational Fluid Dynamics Solver For Aerodynamic and Multidisciplinary OptimizationDocumento46 páginasAd Ow: An Open-Source Computational Fluid Dynamics Solver For Aerodynamic and Multidisciplinary OptimizationRafael TavaresAinda não há avaliações
- Life Management and Extension StudiesDocumento6 páginasLife Management and Extension StudiesAhmed SalmanAinda não há avaliações
- Ijmerr 52e00b22d2840Documento9 páginasIjmerr 52e00b22d2840Natan Dos SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Structure Simulation and Blade Design of An Aircraft EngineDocumento12 páginasStructure Simulation and Blade Design of An Aircraft Enginesirajul_musthafaAinda não há avaliações
- Modelling The Influence of Fuel Injection Parameters On Diesel Engine EmissionsDocumento13 páginasModelling The Influence of Fuel Injection Parameters On Diesel Engine EmissionsSeyedAinda não há avaliações
- Research Paper On Pipe Bending MachineDocumento4 páginasResearch Paper On Pipe Bending Machineafnkdjwhaedkbq100% (1)
- Centrifugal PumpDocumento3 páginasCentrifugal PumpJournalNX - a Multidisciplinary Peer Reviewed JournalAinda não há avaliações
- 2019 - IJFTE - Mehul CD NozzleDocumento6 páginas2019 - IJFTE - Mehul CD NozzleMehul BambhaniaAinda não há avaliações
- Execution Plan PDFDocumento9 páginasExecution Plan PDFVatsal SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Brochure SimSci SIM4MEServicesForDynamicSimulation 08-10Documento12 páginasBrochure SimSci SIM4MEServicesForDynamicSimulation 08-10harry_chemAinda não há avaliações
- Welcome To International Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)Documento5 páginasWelcome To International Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)IJERDAinda não há avaliações
- Optimizing Impeller GeometryDocumento7 páginasOptimizing Impeller GeometryDanang JoyoeAinda não há avaliações
- The Design and Analysis of Gas Turbine BladeDocumento3 páginasThe Design and Analysis of Gas Turbine Bladeaerobrother100% (3)
- Research Papers On Air Bearing TechnologyDocumento5 páginasResearch Papers On Air Bearing Technologyh01fhqsh100% (1)
- IntroductionDocumento7 páginasIntroductionxyonieAinda não há avaliações
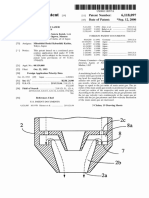
- Ulllted States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 6,118,097: Kaga Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2000Documento27 páginasUlllted States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 6,118,097: Kaga Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2000xinfeng HEAinda não há avaliações
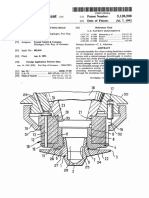
- Laser Nozzle AssemblyDocumento5 páginasLaser Nozzle Assemblyxinfeng HEAinda não há avaliações
- Characterization of The Melt Removal Rate in Laser Cutting of Thick-SectionDocumento9 páginasCharacterization of The Melt Removal Rate in Laser Cutting of Thick-Sectionxinfeng HEAinda não há avaliações
- 10.1007 - s00170 012 4402 yDocumento15 páginas10.1007 - s00170 012 4402 yxinfeng HEAinda não há avaliações
- Duan2001 1Documento9 páginasDuan2001 1xinfeng HEAinda não há avaliações
- 10.1007 - s00170 011 3209 6Documento14 páginas10.1007 - s00170 011 3209 6xinfeng HEAinda não há avaliações
- Computational Fluid Dynamics Study For Flow ofDocumento17 páginasComputational Fluid Dynamics Study For Flow ofxinfeng HEAinda não há avaliações
- 10.1007 - s00170 017 0107 6Documento10 páginas10.1007 - s00170 017 0107 6xinfeng HEAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of The DynamicDocumento10 páginasAnalysis of The Dynamicxinfeng HEAinda não há avaliações
- 10.1007 - 978 1 4020 9340 1Documento396 páginas10.1007 - 978 1 4020 9340 1xinfeng HE100% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S0143816608001747 MainDocumento8 páginas1 s2.0 S0143816608001747 Mainxinfeng HEAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S0735193313002078 MainDocumento6 páginas1 s2.0 S0735193313002078 Mainxinfeng HEAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S0141635917301599 MainDocumento28 páginas1 s2.0 S0141635917301599 Mainxinfeng HEAinda não há avaliações
- Khan 080220Documento29 páginasKhan 080220xinfeng HEAinda não há avaliações
- Wo 2016177596Documento39 páginasWo 2016177596xinfeng HEAinda não há avaliações
- ST RDDocumento2 páginasST RDBalteshwar SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Record results of toy soldier experiment times with different massesDocumento42 páginasRecord results of toy soldier experiment times with different massesTeoh Han Jie100% (1)
- Quarter3 Week4 ClimateDocumento11 páginasQuarter3 Week4 ClimateJohn EdselAinda não há avaliações
- Notes On Continuum MechanicsDocumento13 páginasNotes On Continuum Mechanicsdalves31503Ainda não há avaliações
- Microsoft Office Tips and TricksDocumento12 páginasMicrosoft Office Tips and TricksJayr BVAinda não há avaliações
- Glass Transition Temperature: IntroductionDocumento7 páginasGlass Transition Temperature: IntroductionBarkha RaniAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics T (954/1) Functions QuizDocumento1 páginaMathematics T (954/1) Functions QuizmasyatiAinda não há avaliações
- Control of Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output ProcessesDocumento27 páginasControl of Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output Processesmeseret sisayAinda não há avaliações
- Microelectronic Circuit Design 5th Edition Jaeger Blalock Solution ManualDocumento21 páginasMicroelectronic Circuit Design 5th Edition Jaeger Blalock Solution Manualruth100% (23)
- Noc18 cs48 Assignment3Documento4 páginasNoc18 cs48 Assignment3shweta100% (1)
- MBA (Travel & Tourism) 1st Year Sylabus 2020-21 - 28th SeptDocumento34 páginasMBA (Travel & Tourism) 1st Year Sylabus 2020-21 - 28th SeptHimanshuAinda não há avaliações
- Green Building Store MVHR Brochure-File032484Documento9 páginasGreen Building Store MVHR Brochure-File032484Anthi ValavaniAinda não há avaliações
- COSC 2307: Sub-QueriesDocumento23 páginasCOSC 2307: Sub-QueriesBhavikDaveAinda não há avaliações
- PAPER I MATHEMATICS PRACTICE SETDocumento6 páginasPAPER I MATHEMATICS PRACTICE SETRitesh Raj PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- RC Beam Deflection and Stress AnalysisDocumento4 páginasRC Beam Deflection and Stress AnalysisMaxAinda não há avaliações
- Monico Gen. 2 Gateway Datasheet PDFDocumento2 páginasMonico Gen. 2 Gateway Datasheet PDFRicardo OyarzunAinda não há avaliações
- Benzophenone/THF StillDocumento3 páginasBenzophenone/THF Stillbloggsjoe1970Ainda não há avaliações
- Roll Handling Data Form: Company DetailsDocumento1 páginaRoll Handling Data Form: Company DetailsAlfredo MinchezAinda não há avaliações
- BRINELL BH3000 - WilsonHardnessDocumento2 páginasBRINELL BH3000 - WilsonHardnessKhoa Bui AnhAinda não há avaliações
- PHYSICS O-LEVEL PAST PAPER QUESTIONS ON MOMENTSDocumento7 páginasPHYSICS O-LEVEL PAST PAPER QUESTIONS ON MOMENTSelty TanAinda não há avaliações
- Well CompletionDocumento26 páginasWell Completionnitesh kumarAinda não há avaliações
- A2 Biopharm MetalDocumento28 páginasA2 Biopharm MetalThanh Nghị BùiAinda não há avaliações
- Akvola Technologies MicroGas S Technical Specifications - Web PDFDocumento2 páginasAkvola Technologies MicroGas S Technical Specifications - Web PDFHardik VavdiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Software Test MetricsDocumento8 páginasSoftware Test MetricscmarrivadaAinda não há avaliações
- TVS Apache RTR 180 Service ManualDocumento25 páginasTVS Apache RTR 180 Service ManualSandino JoseAinda não há avaliações
- Solution of Problem Set 1 For Purity Hydrocarbon Data PDFDocumento4 páginasSolution of Problem Set 1 For Purity Hydrocarbon Data PDFDrumil TrivediAinda não há avaliações
- Quantum Garage Door OpenerDocumento32 páginasQuantum Garage Door OpenerNguiBDAinda não há avaliações
- Maa 2.8 ExponentsDocumento12 páginasMaa 2.8 ExponentsMuborakAinda não há avaliações
- This Study Resource Was: Titration Level 1Documento4 páginasThis Study Resource Was: Titration Level 1Camaya RumbleAinda não há avaliações
- Explorer - Help RESCODocumento18 páginasExplorer - Help RESCOTomás Oteros OrdóñezAinda não há avaliações
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesNo EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (14)
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisNo EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Asset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresNo EverandAsset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresAinda não há avaliações
- Inherently Safer Chemical Processes: A Life Cycle ApproachNo EverandInherently Safer Chemical Processes: A Life Cycle ApproachNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Flow Analysis for Hydrocarbon Pipeline EngineeringNo EverandFlow Analysis for Hydrocarbon Pipeline EngineeringAinda não há avaliações
- Guidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementNo EverandGuidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementAinda não há avaliações
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesNo EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationNo EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationAinda não há avaliações
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersNo EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (12)
- Incidents That Define Process SafetyNo EverandIncidents That Define Process SafetyAinda não há avaliações
- Safety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryNo EverandSafety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryAinda não há avaliações
- Industrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualNo EverandIndustrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (7)
- LNG Risk Based Safety: Modeling and Consequence AnalysisNo EverandLNG Risk Based Safety: Modeling and Consequence AnalysisAinda não há avaliações
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataNo EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (22)
- Machinery Lubrication Technician (MLT) I and II Certification Exam GuideNo EverandMachinery Lubrication Technician (MLT) I and II Certification Exam GuideNota: 2 de 5 estrelas2/5 (1)
- Oil and Gas Pipelines and Piping Systems: Design, Construction, Management, and InspectionNo EverandOil and Gas Pipelines and Piping Systems: Design, Construction, Management, and InspectionNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (16)
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsNo EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (10)
- Pipeline Integrity: Management and Risk EvaluationNo EverandPipeline Integrity: Management and Risk EvaluationNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (6)
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsNo EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (11)
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersNo EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Nutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeNo EverandNutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeAinda não há avaliações
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsNo EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Wellbore Hydraulics and Hole Cleaning: Unlock Faster, more Efficient, and Trouble-Free Drilling OperationsNo EverandPractical Wellbore Hydraulics and Hole Cleaning: Unlock Faster, more Efficient, and Trouble-Free Drilling OperationsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)