Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Diagnostic Definitions Acute Otitis Media (AOM)
Enviado por
AngeLine BudimAn0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
14 visualizações2 páginas1) Acute otitis media (AOM) is defined as the presence of middle ear effusion, evidence of acute inflammation of the middle ear, and symptoms of otalgia, irritability, or fever occurring within 48 hours. Otitis media with effusion (OME) refers to middle ear effusion without acute symptoms.
2) For most children with AOM, antibiotics are not warranted as the condition spontaneously resolves in 80% of cases. Pain should be aggressively managed with analgesics. Antibiotics should only be used if a child remains significantly unwell after 48-72 hours of analgesics.
3) OME is often preceded by an episode of AOM and can cause transient hearing
Descrição original:
6
Título original
LO week 6 ICM 1
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documento1) Acute otitis media (AOM) is defined as the presence of middle ear effusion, evidence of acute inflammation of the middle ear, and symptoms of otalgia, irritability, or fever occurring within 48 hours. Otitis media with effusion (OME) refers to middle ear effusion without acute symptoms.
2) For most children with AOM, antibiotics are not warranted as the condition spontaneously resolves in 80% of cases. Pain should be aggressively managed with analgesics. Antibiotics should only be used if a child remains significantly unwell after 48-72 hours of analgesics.
3) OME is often preceded by an episode of AOM and can cause transient hearing
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
14 visualizações2 páginasDiagnostic Definitions Acute Otitis Media (AOM)
Enviado por
AngeLine BudimAn1) Acute otitis media (AOM) is defined as the presence of middle ear effusion, evidence of acute inflammation of the middle ear, and symptoms of otalgia, irritability, or fever occurring within 48 hours. Otitis media with effusion (OME) refers to middle ear effusion without acute symptoms.
2) For most children with AOM, antibiotics are not warranted as the condition spontaneously resolves in 80% of cases. Pain should be aggressively managed with analgesics. Antibiotics should only be used if a child remains significantly unwell after 48-72 hours of analgesics.
3) OME is often preceded by an episode of AOM and can cause transient hearing
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
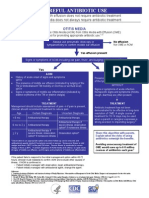
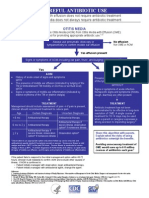
Diagnostic Definitions
Acute Otitis Media (AOM)
Middle Ear Effusion (MEE) - demonstrated by pneumatic otoscopy, tympanometry,
air fluid level, or a bulging tympanic membrane plus
Evidence of acute inflammation opaque, white, yellow, or erythematous tympanic
membrane or purulent effusion plus
Symptoms of otalgia, irritability, or fever
Otitis Media with Effusion (OME) MEE without symptoms of AOM with or without
evidence of inflammation
Distinguishing AOM and OME. The distinction between AOM and OME does not refer
to etiology or depend on whether pathogenic bacteria are present in the middle ear. No
gold standard exists for the diagnosis of AOM. The National AOM-guideline defines
AOM as a combination of :
1) middle ear effusion,
2) physical evidence of middle ear inflammation, and
3) the acute (< 48 hours) onset of signs and symptoms (i.e. ear pain, irritability, fever)
referable to the middle ear.
Otitis media with effusion (OME) is defined as middle ear effusion (MEE) in the absence
of acute symptoms.
Part I: Acute Otitis Media, Management of AOM
For most children, antibiotics are not warranted. Spontaneous resolution of AOM is to be
expected in approximately 80 per cent of children.
AOM does not always require antibiotics, providing that good follow up is
provided.
Aggressively manage pain with adequate systemic analgesics (not ASA).
If a child is significantly unwell after 48-72 hours of analgesics, treat with
antibiotics regardless of age.
Decongestants, antihistamines and steroids are not beneficial in the treatment of
AOM.
Part II: Otitis Media with Effusion (OME)
OME is associated with ear discomfort and recurrences of acute otitis media (AOM) and
often follows an episode of AOM. Transient hearing loss is frequently associated with
OME. Spontaneous resolution of OME occurs in 90 per cent of patients within three
months of infection.
On Going Care
When OME has been present for at least 12 weeks, observation is advised at 3 month
intervals until the resolution of effusion. If there are concerns of significant hearing loss
or structural abnormalities of the tympanic membrane, a formal hearing evaluation and
referral to an otolaryngologist is recommended.
Note: Decongestants, antihistamines, steroids, and antibiotics are NOT recommended in
the treatment of OME.
Você também pode gostar
- Ear Infection Essentials Understanding, Treating, and PreventingNo EverandEar Infection Essentials Understanding, Treating, and PreventingAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis MediaDocumento7 páginasOtitis MediaNorminaKiramAkmadAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis Media OtolaryngologyDocumento45 páginasOtitis Media OtolaryngologyDr.Sherif Bugnah100% (5)
- Otitis Media Clinical PresentationDocumento14 páginasOtitis Media Clinical PresentationIvan PathfinderAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis Media Diagnosis and TreatmentDocumento19 páginasOtitis Media Diagnosis and TreatmentreyhanrrAinda não há avaliações
- Update On Otitis MediaDocumento28 páginasUpdate On Otitis MediakarenafiafiAinda não há avaliações
- Child OtitismediaDocumento1 páginaChild OtitismediaDaniel Ramos GomezAinda não há avaliações
- ABTRACTDocumento1 páginaABTRACTPrajin SaranAinda não há avaliações
- Ears, Nose and Throat Diseases: Prepared By: Hannelli BelingonDocumento103 páginasEars, Nose and Throat Diseases: Prepared By: Hannelli BelingonPatricia Kamille I. PawidAinda não há avaliações
- OMA Case SlideshareDocumento34 páginasOMA Case SlideshareRizka Dany AfinaAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis MediaDocumento4 páginasOtitis MediaapocruAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis MediaDocumento9 páginasOtitis MediaMona Santi NainggolanAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Otitis Media (AOM) - 1Documento24 páginasAcute Otitis Media (AOM) - 1SabeerAinda não há avaliações
- Otalgia: By: Buenafe, Drexler Justine ADocumento13 páginasOtalgia: By: Buenafe, Drexler Justine AFaye Dianne Damian-BuenafeAinda não há avaliações
- 6.otitis MediaDocumento17 páginas6.otitis MediasavasAinda não há avaliações
- ENT PresentationDocumento79 páginasENT PresentationfelliciaAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis Media AkutDocumento17 páginasOtitis Media AkutSayid QawamuddinAinda não há avaliações
- Child OtitismediaDocumento1 páginaChild OtitismediaKrisna YudiAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis Media AkutDocumento30 páginasOtitis Media Akutindah sariAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis Media3Documento6 páginasOtitis Media3Anthony LopezAinda não há avaliações
- CPG On AomDocumento9 páginasCPG On AomEllese SayAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Otitis MediaDocumento8 páginasAcute Otitis MediaRose JosephAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Otitis MediaDocumento11 páginasAcute Otitis MediaFeliciaOctofinnaAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis Media With Effusion: Case ReportDocumento8 páginasOtitis Media With Effusion: Case ReportMas KaryonAinda não há avaliações
- Case Report OMEDocumento8 páginasCase Report OMEYosephine ninaAinda não há avaliações
- Penyebab Otalgia 2010Documento11 páginasPenyebab Otalgia 2010siska tiaraAinda não há avaliações
- Penyebab Otalgia 2010 PDFDocumento11 páginasPenyebab Otalgia 2010 PDFnotpentingAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis Media: Temidayo AbassDocumento23 páginasOtitis Media: Temidayo AbasstemidayoAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Otitis Media (AOM) : Revised 2004Documento5 páginasAcute Otitis Media (AOM) : Revised 2004dr.cintaAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Asti Widuri Sp. THTDocumento40 páginasDr. Asti Widuri Sp. THTMuhammad Faried FahdaAinda não há avaliações
- Otītis MediaDocumento12 páginasOtītis MediaABUBEKER BESHIRAinda não há avaliações
- Management of Otitis Media With Effusion in Children: Quick ReferenceDocumento8 páginasManagement of Otitis Media With Effusion in Children: Quick ReferenceNovy Sylvia WardanaAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis Media (Acute) : Symptoms and SignsDocumento3 páginasOtitis Media (Acute) : Symptoms and SignsAnthony LopezAinda não há avaliações
- 18mo With CongestionDocumento7 páginas18mo With CongestiondakewtwontonAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis MediaDocumento18 páginasOtitis MediaShesilia AgnestiAinda não há avaliações
- 4.otitis Media With EffusionDocumento33 páginas4.otitis Media With EffusionNur FauziahAinda não há avaliações
- The ENT History and ExaminationDocumento11 páginasThe ENT History and ExaminationSuresh MettaAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis Media: While The OMEDocumento2 páginasOtitis Media: While The OMEKim EurelleAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis MediaDocumento6 páginasOtitis Mediafrances1828Ainda não há avaliações
- Acute Otitis MediaDocumento3 páginasAcute Otitis MediaRiska PashaAinda não há avaliações
- Atelectasis 1Documento17 páginasAtelectasis 1Arief FakhrizalAinda não há avaliações
- Felyanto Puspa Haryani Wirda YunitaDocumento17 páginasFelyanto Puspa Haryani Wirda YunitaSilvia Hari PrastiwiAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis MediaDocumento55 páginasOtitis MediaJollyann SedaAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis Media AcuteDocumento30 páginasOtitis Media AcuteDede Gustina AyuAinda não há avaliações
- Test Questions and Answers Near The End: Direct Force Indirect Force Hearing Loss Ringing Bleed OtalgiaDocumento19 páginasTest Questions and Answers Near The End: Direct Force Indirect Force Hearing Loss Ringing Bleed OtalgialeeAinda não há avaliações
- Disease of The EarsDocumento20 páginasDisease of The EarsPrecy CoAinda não há avaliações
- Definition and AnatomyDocumento4 páginasDefinition and AnatomyRachelle Golimlim (Chelle)Ainda não há avaliações
- Acute Otitis MediaDocumento71 páginasAcute Otitis MediaMegawati Abubakar0% (1)
- Otitis MediaDocumento98 páginasOtitis MediaLody Lean CruzAinda não há avaliações
- PRACTICE TEACHING On Otitis Media FinalDocumento33 páginasPRACTICE TEACHING On Otitis Media FinalAjit ThangeAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis EksternaDocumento9 páginasOtitis EksternaKoas PatoAinda não há avaliações
- Ménière's Disease: An OverviewDocumento9 páginasMénière's Disease: An OverviewIkraam Abdul LatifAinda não há avaliações
- What Is OtolaryngologyDocumento37 páginasWhat Is OtolaryngologyPhạm Văn HiệpAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis ExternaDocumento27 páginasOtitis ExternaKesha Lemons-Price100% (1)
- Med 3, Chloe SaadeDocumento53 páginasMed 3, Chloe Saadeanon_767794134Ainda não há avaliações
- Anatomy & Physiology: Acute Otitis MediaDocumento7 páginasAnatomy & Physiology: Acute Otitis MediaAbigael Patricia GutierrezAinda não há avaliações
- CPG On OmeDocumento6 páginasCPG On OmeKita kitaAinda não há avaliações
- COM FinalDocumento10 páginasCOM FinalCeelin RoblesAinda não há avaliações
- Arteriovenous (Av) Fistula / CiminoDocumento9 páginasArteriovenous (Av) Fistula / CiminoAngeLine BudimAnAinda não há avaliações
- Who Icd Me and Cfs LongDocumento29 páginasWho Icd Me and Cfs LongAngeLine BudimAnAinda não há avaliações
- CD 10 CM Codes: Abdominal PainDocumento5 páginasCD 10 CM Codes: Abdominal PainAngeLine BudimAnAinda não há avaliações
- Transient Loss of ConsciousnessDocumento5 páginasTransient Loss of ConsciousnessAngeLine BudimAnAinda não há avaliações