Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
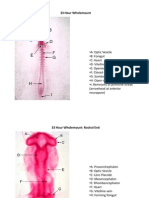
Exercise 8 Pig Embryo (Posterior Sections)
Enviado por
Gail AmuraoDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Exercise 8 Pig Embryo (Posterior Sections)
Enviado por
Gail AmuraoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
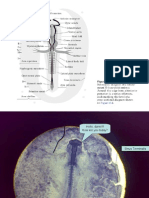
Comparative Vertebrate Embryology SY 2014-2015
PIG EMBRYO (POSTERIOR SECTIONS)
Levels of the Lung Buds (Stem Bronchi) and Foreleg Buds
1 Sacha Pajarillo 4Bio2
Comparative Vertebrate Embryology SY 2014-2015
paired posterior cardinal (postcardinal veins)
most dorsal vein
lying in place of the common cardinal veins in preceding level
foreleg buds
pair of bud-like tissue masses from the dorsolatersal sides of the body
made up of an outer layer ectoderm thickened at its apex as the apical ridge; core of mesoderm
at its core, interconnections of the ventral rami of the cervical and thoracic spinal nerves form the branchial
plexus; nerves of the forelimb branch out from this
esophagus
small middle hole beneath the pair of dorsal aorta
lung buds
pair of vesicles on both sides of the trachea
mediastinum
thick partition of mesenchyme
enclosing the trachea and the lung
pleural cavity
pair of coelomic cavities on each side of the mediastinum
where the lung buds developed
parietal pleura
lining of the lateral wall of the pleural cavity
visceral pleura
medial epithelial lining of th pleural cavity
will cover the lungs
septum transversum
mesenchymal partition extending across the body
2 Sacha Pajarillo 4Bio2
Comparative Vertebrate Embryology SY 2014-2015
posterior vena cava
blood vessel
embedded on the right side of the septum transversum
posteriorly, occupies a dorsal position in the substance of the liver
also known as inferior vena cava
ventricle
thick-walled mass below the septum transversum
Level of the Liver and the Stomach
3 Sacha Pajarillo 4Bio2
Comparative Vertebrate Embryology SY 2014-2015
4 Sacha Pajarillo 4Bio2
Comparative Vertebrate Embryology SY 2014-2015
spinal cord
segmental nature of the nerves arise on either side of the spinal cord, definite and clear, arise from the spinal
cord by the roots
dorsal root
contains the spinal ganglion and the sensory neurons
fibers from the dorsal root ganglion leading to the dorsolateral wall of the spinal cord
also known as afferent or sensory root
ventral root
made up of motor fibers from motor neurons of the basal plate of the spinal cord
fibers coming from the ventrolateral wall of the spinal cord
join the sensory root
also known as efferent or motor root
three branches of the spinal nerve trunk
dorsal ramus carries fibers associated with the dorsal parts of the body (skin, deep muscles of the back, spinal
column), close to the junction of the sensory and ventral root, small bundle of fibers which passes dorsolaterally,
also known as lateral ramus
ventral ramus carries fibers associated with the ventral and lateral body wall, large bundle of fibers which
passes ventrolaterally
ramus communicans branch from thr ventral ramus, carries fibers to the viscera via the prevertebral
sympathetic chain, passes medioventrally to the sympathetic ganglion located above the dorsal aorta and the
branchial plexus (innervates the limbs)
dorsal root ganglion
darkly nucleated body on both sides of the spinal cord
mammary ridges
pair of elevations on the dorsolateral part of the body
took the place of the foreleg buds in the series
present between the foreleg and hindleg buds
descending aorta
fused dorsal aorta, paired in branchial region
posterior to the pharynx, fuse to form the median dorsal aorta
sends branches to the different parts of the body of the embryo below the branchial region
sympathetic ganglion pair of ganglion immediately dorsal to the descending aorta
mesonephros
functional kidney at this stage
located on both sides of the descending aorta
retroperitoneal, lies posterior to the liver
mesonephric duct large oval canal found along its ventral margin
glomerulus
knots of blood capillaries
located at the lower medial side of each kidney
surrounded by very flat epithelium called Bowmans capsule
glomerulus and Bowmans capsule make up the Malpighian corpuscle or renal corpuscle
5 Sacha Pajarillo 4Bio2
Comparative Vertebrate Embryology SY 2014-2015
mesonephric tubules
coiled tubules located at the outer lateral portion of each mesonephros
found connected at the corpuscles
posterior cardinal veins
dorsolateral in the mesonephros
also known as postcardinal vein
stomach
horizontally enlarged segment of the foregut
replaces the esophagus
liver
large mass
has strands of cells (hepatic cord) and spaces between the strands (hepatic sinusoid)
divided into paired dorsal and ventral lobes
posterior vena cava
large blood vessels
embedded in the substance of the liver
drains blood from the subcardinal sinus to be sent to the sinus venosus
receives blood from the ductus venosus
preceeding level, embedded in the septum transversum
posteriorly, found at the right side of the stomach, partly embedded on the dorsal portion of the liver
supported by the caval mesentery
also known as inferior vena cava or postcava
ductus venosus
blood vessels ventral to the stomach
embedded between the dorsal and ventral lobes of the liver
formed by the invasion of the left and right umbilical veins by the liver cords
anteriorly, found emptying into the postcava
dorsal mesogaster
part of the dorsal mesentery
holds the stomach in place
enlarges greatly in the adult
becomes the dorsal omentum of the adult
becomes aggregated with mesenchymal cells to form the spleen
omental bursa
closed cavity to the right of the stomach
posteriorly, opens into the peritoneal cavity, opening is called epiploic foramen
hepatogastric ligament
mesentery connecting the liver and the stomach
with hepatoduodenal ligament, constitute the lesser omentum of the adult
falciform ligament
remnant of the ventral mesentery (lesser omentum)
attaches the liver to the ventral body wall
6 Sacha Pajarillo 4Bio2
Comparative Vertebrate Embryology SY 2014-2015
Level of the Common Bile Duct
7 Sacha Pajarillo 4Bio2
Comparative Vertebrate Embryology SY 2014-2015
somites
44 paired blocks from the posterior end of the myelencephalon to the tail
myocoel lumen
myotome dorsomedian part of the block, forms the skeletal muscles
dermatome ventrolateral portion, forms the connective tissue of the dermis
sclerotome ventromedian portion of the block, will migrate and surround the spinal cord and notochord, forms
the vertebral column
duodenum
small cavity
takes the place of stomach
common bile duct
large thick-walled cavity
embedded on the dorsal lobe of the liver, to the right of the duodenum
posteriorly, enters the duodenum
but before doing so, gives off a rounded tube, cystic duct, below the bile duct, embedded on the ventral lobe of
the liver
anteriorly, connected to a wider cavity, hepatic duct, that constricts to become the common bile duct
posterior vena cava
more dorsally located
stays close to th right side of the dorsal mesentery almost at the right side of the descending aorta
drains blood from the subcardinal veins and the hepatic portal veins
hepatic portal vein
blood vessel
embedded on the right lobe of the liver
earlier embryonic omphalomesenteric vein which drains blood from the intestine
gonad rudiment
ridge-like thickening or swelling of the coelomic epithelium on the medial side of each mesonephric kidney
big left and small right umbilical veins
blood vessels
embedded in the ventral lobe of the liver which lies on both sides of the cystic duct
anteriorly, join together in the lver as the ductus venosus
8 Sacha Pajarillo 4Bio2
Comparative Vertebrate Embryology SY 2014-2015
Level through the Gallbladder and Umbilical Cord
9 Sacha Pajarillo 4Bio2
Comparative Vertebrate Embryology SY 2014-2015
10 Sacha Pajarillo 4Bio2
Comparative Vertebrate Embryology SY 2014-2015
hepatic portal vein
mesentery between the dorsal and vnetral pancreatic rudiment, to the right of the duodenum
posteriorly, on the left side of the duodenum
continues as the superior mesenteric vein, to the intestinal loop which it drains
extends further into the umbilical cord as the common vitelline vein
drains further the yolk sac as the right and left vitelline veins
remains embedded on the dorsal mesentery
dorsal pancreas
large mass
embedded in the dorsal mesentery above the duodenum
outgrowth from the duodenum, connected by duct of Santorini
also known as dorsal pancreatic rudiment
ventral pancreas
mass embedded in the dorsal mesentery below the hepatic portal vein, to the right of the duodenum
develops as an outgrowth from the common bile duct, connected by duct of Wirsung degenerates at once
also known as ventral pancreatic rudiment
dorsal and ventral pancreatic rudiments will fuse to form the pancreas
gallbladder
cavity right below the dorsal mesentery bearing the duodenum
lies on a partially disappearing ventral lobe of the liver bounded by the pair of umbilical vein
continuation of the cystic duct
paired umbilical veins
pair of blood vessels
took the position of the ductus venosus
right umbilical vein smaller, degenerating
left umbilical vein retain, where blood flows from the placenta
also known as allantoic vein
cranial and caudal limb of the intestinal loop
protrusion of the intestinal loop into the extraembryonic coelom of the umbilical cord
cranial limb more dorsal, anteriorly continuous with the duodenum, will become the small intestine
caudal limb posteriorly continuous with the colon, will become the large intestine
superior mesenteric vein and artery
blood vessels between the cranial and caudal intestinal limb, embedded in the mesentery
superior mesenteric vein more dorsal
superior mesenteric artery posterior ventrolateral branch of the descending aorta
common vitelline vein
vein on top of the superior mesenteric vein
posterior section of the superior mesenteric vein
left and right umbilical arteries
pair of blood vessels below the intestinal limbs
more dorsal than the 2 pairs of blood vessels below the limbs
11 Sacha Pajarillo 4Bio2
Comparative Vertebrate Embryology SY 2014-2015
allantois
cavity between the left and right umbilical arteries
finds its way out of the umbilical cord to join the urogenital sinus
tail
lowermost portion
contains the spinal cord
Level through the Urogenital Sinus and Umbilical Cord
12 Sacha Pajarillo 4Bio2
Comparative Vertebrate Embryology SY 2014-2015
subcardinal veins
veins on the ventromedian border of the mesonephros, ventral to the descending aorta
converge with each other by forming a subcardinal anastomosis of the subcardinal sinus on the area where
mesonephros is in contact with each other
posterior or inferior vena cava where blood contained from the posterior region enters, new channel to the
heart
posterior portion of the postcardinal vein regress
mesocolon
prominent mesentery
holds the caudal limb of the intestinal loop (small cavity, lowermost portion of the mesentery)
mesonephric duct
pair of excretory duct of the mesonephros
found on each ventral limit of the mesonephros
posteriorly, continuous with the urogenital sinus
urogenital sinus
inverted U-shaped structure
constitute the tail
both ends lead to the mesonephric duct
rectum
cavity below the urogenital sinus, separated by the cloacal septum
cloacal septum not yet complete, urogenital sinus and rectum are still continuous towards the posterior section
umbilical veins
prominent blood vessels on both sides of the umbilical cord
a pair right below the mesonephric duct, a pair on both sides of the upper mesenchymal mass that contains the
tail
continuous with each other
umbilical arteries
medial blood vessels below the mesocolon, lying on both side of the middle cavity, allantois
posteriorly, continuous with descending aorta
allantois
flattened canal on the ventral wall of the urogenital sinus
emerges form the umbilical cord
joins the urogenital sinus
umbilical cord
lightly stained area
holds the allantois, vitelline blood vesels, umbilical blood vessels, and the cranial limb of the intestinal loop
Whartons jelly gelatinous connective tissue, matrix of the umbilical cord
13 Sacha Pajarillo 4Bio2
Comparative Vertebrate Embryology SY 2014-2015
Level of the Hindlimb Bud
14 Sacha Pajarillo 4Bio2
Comparative Vertebrate Embryology SY 2014-2015
hindleg bud
prominent thickenings on the lower portions of the sections
consist of an outer layer ectoderm and an inner core of somatic mesoderm
apical ectodermal ridge thickened ectoderm
pair of mesonephric duct
a pair close to the mesonephros, a pair at the lower level of the hindleg bud
mesocolon
mesentery that holds at its higher level the caudal limb of the intestinal loop and at it lower level the colon
ureter
small duct
emerges form the dorsal portion of the mesonephric duct
posteriorly, expands as the renal pelvis surrounded by a mass of cells called nephrotome
Level through the Spinal Nerve
15 Sacha Pajarillo 4Bio2
Comparative Vertebrate Embryology SY 2014-2015
spinal ganglia
separates masses of nerve cell body on both sides of the neural cavity
ventral roots of the spinal nerves
below the spinal ganglia
do not bear any spinal ganglion
sclerotome
undulated portions next to where the spinal ganglia or ventral roots of the spinal nerves are
made of dense caudal portion and less dense cranial portion
vertebra formed by fusion of the caudal half of the sclerotome with the cranial half of the next caudal
sclerotome
myotome
indented area left of the undulation of the sclerotome
less dense
dermatome
outermost dense area
covers the myotome
undulated but opposite to that of the sclerotome
epidermis
ouer covering of th body
intersegmental arteries
paired branches of the dorsal aorta on either side of the neural tube
16 Sacha Pajarillo 4Bio2
Você também pode gostar
- Posterior Development of Pig EmbryoDocumento4 páginasPosterior Development of Pig EmbryoAstrid AmadorAinda não há avaliações
- 48-Hour Chick ReviewerDocumento5 páginas48-Hour Chick ReviewerBeatrice100% (1)
- Development of The Pig EmbryoDocumento12 páginasDevelopment of The Pig EmbryoKarmina SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Chick 72 HR DDocumento35 páginasChick 72 HR Daa628Ainda não há avaliações
- 72 HR ReviewerDocumento8 páginas72 HR ReviewerAstrid AmadorAinda não há avaliações
- Early Chick EmbryoDocumento74 páginasEarly Chick EmbryoMinette EmmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- 72-HR ChickDocumento16 páginas72-HR Chick411452123100% (1)
- Serial Sections of 10 MM Pig EmbryoDocumento41 páginasSerial Sections of 10 MM Pig EmbryoChristalie Bea FernandezAinda não há avaliações
- 48 96 Hour Chick Embryo Wholoe Mount and Serial Sections EmbryologyDocumento34 páginas48 96 Hour Chick Embryo Wholoe Mount and Serial Sections EmbryologyChristalie Bea Fernandez100% (2)
- Biology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 2: Embryology of Frog & ChickDocumento9 páginasBiology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 2: Embryology of Frog & ChickPunk Midget-FairyAinda não há avaliações
- Chick EmbryoDocumento24 páginasChick Embryonabilalk100% (1)
- PigDocumento34 páginasPigaa62893% (14)
- Chick Embryo 72 HoursDocumento48 páginasChick Embryo 72 HoursogheeluvAinda não há avaliações
- 4 MM FrogDocumento5 páginas4 MM FrogMarina of The SeaAinda não há avaliações
- Chick Embryo (Embryology Lab)Documento9 páginasChick Embryo (Embryology Lab)humanupgrade100% (1)
- 33-Hour Chick ReviewerDocumento5 páginas33-Hour Chick ReviewerBeatriceAinda não há avaliações
- Chick 33 HRDocumento14 páginasChick 33 HRaa628Ainda não há avaliações
- Embryo Lab: 72 HR Chick ReviwerDocumento7 páginasEmbryo Lab: 72 HR Chick ReviwerGail AmuraoAinda não há avaliações
- 10 MM Transverse Section Level of Telencephalon and Olfactory OrgansDocumento9 páginas10 MM Transverse Section Level of Telencephalon and Olfactory OrgansMarina of The SeaAinda não há avaliações
- Chick Embryo WMDocumento6 páginasChick Embryo WMdhyan_ajjah67% (3)
- Ex4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoDocumento14 páginasEx4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoNexie100% (1)
- Embryo Lab Exercise 4Documento17 páginasEmbryo Lab Exercise 4Karmina SantosAinda não há avaliações
- 48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFDocumento5 páginas48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFSheanna May FuriaAinda não há avaliações
- 24 Hour Chick EmbryoDocumento27 páginas24 Hour Chick Embryoaa6280% (1)
- 24-Hr Chick EmbryoDocumento8 páginas24-Hr Chick EmbryopauAinda não há avaliações
- Frog EmbryosDocumento43 páginasFrog EmbryosNics Martinez100% (7)
- Chick 48 HRDocumento50 páginasChick 48 HRaa628Ainda não há avaliações
- 48 Hour Chick Embryo Serial SectionsDocumento22 páginas48 Hour Chick Embryo Serial SectionsNathan Bantayan100% (1)
- 7 MM FrogDocumento28 páginas7 MM FrogNiki Reroll04Ainda não há avaliações
- 33 Hour Chick Embryo Transverse SectionDocumento36 páginas33 Hour Chick Embryo Transverse SectionSasha GutierrezAinda não há avaliações
- 10mm Frog TadpoleDocumento30 páginas10mm Frog TadpoleSarah Margaret Chong33% (3)
- ANIMAL GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT: The Tadpole (External Gill Stage)Documento6 páginasANIMAL GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT: The Tadpole (External Gill Stage)Junko TsukudaAinda não há avaliações
- 48 Hour ChickDocumento13 páginas48 Hour ChickJowi SalAinda não há avaliações
- 24hr Chick Cross SectionsDocumento16 páginas24hr Chick Cross Sectionsaa628100% (9)
- EmbryoLab 10mm FrogDocumento13 páginasEmbryoLab 10mm FrogpauAinda não há avaliações
- 48hr and 72hr Chick EmbryoDocumento28 páginas48hr and 72hr Chick EmbryoRichelle IgnacioAinda não há avaliações
- 24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabDocumento3 páginas24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabIvy Cruz50% (2)
- 72 Hours Chick EmbryoDocumento18 páginas72 Hours Chick EmbryoZhairra Marie DionsonAinda não há avaliações
- Development of Frog EmbryoDocumento13 páginasDevelopment of Frog EmbryoNexieAinda não há avaliações
- Early DevelopmentDocumento5 páginasEarly DevelopmentMarina of The SeaAinda não há avaliações
- Stages of Development of Sea StarsDocumento5 páginasStages of Development of Sea StarsCamille100% (1)
- Chick Embryo ImagesDocumento19 páginasChick Embryo ImagesnesyaAinda não há avaliações
- 48 Hour Chick LabelledDocumento89 páginas48 Hour Chick LabelledSasha Gutierrez100% (1)
- Development of Embryo ChickDocumento14 páginasDevelopment of Embryo ChickSafira Dwi OktavianiAinda não há avaliações
- Exercise 21 Serial Transverse Section of A 72 Hour Chick Embryo PDFDocumento8 páginasExercise 21 Serial Transverse Section of A 72 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela FayeAinda não há avaliações
- 7 MM Frog EmbryoDocumento20 páginas7 MM Frog EmbryoCourtneyAinda não há avaliações
- 33.48,72 From 2011Documento63 páginas33.48,72 From 2011aa628Ainda não há avaliações
- 10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabDocumento4 páginas10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Exercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmDocumento23 páginasExercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmrexartooz95% (19)
- Parts of Frog HistologyDocumento6 páginasParts of Frog HistologyVanessa RebancosAinda não há avaliações
- Chick Embryo ReviewerDocumento9 páginasChick Embryo ReviewerKeana TapangAinda não há avaliações
- Activity No. 7 The Frog EmbryoDocumento13 páginasActivity No. 7 The Frog EmbryoFerhaeeza KalayakanAinda não há avaliações
- Embryo Lab Org 2Documento14 páginasEmbryo Lab Org 2pauAinda não há avaliações
- 72 HrsDocumento35 páginas72 HrsChristalie Bea FernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Gastrulation in MammalsDocumento16 páginasGastrulation in Mammalskashif manzoor75% (4)
- Histology of Glands: Dr. Zana TahseenDocumento28 páginasHistology of Glands: Dr. Zana TahseenAhmed JawdetAinda não há avaliações
- Anterior Posterior: o Posterior Renal Fascia Is Also Known As Zuckerkandl's Fascia)Documento4 páginasAnterior Posterior: o Posterior Renal Fascia Is Also Known As Zuckerkandl's Fascia)Lester AldridgeAinda não há avaliações
- The Urinary System: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityDocumento44 páginasThe Urinary System: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityRahmawati HamudiAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 5 Serous Sacs, Features and FunctionsDocumento7 páginasLecture 5 Serous Sacs, Features and Functionssomebody_maAinda não há avaliações
- Plant and Animal Organ System and Their FunctionDocumento21 páginasPlant and Animal Organ System and Their FunctionJovon GuyoAinda não há avaliações
- Syllab bscct1819-24102018Documento65 páginasSyllab bscct1819-24102018vasanthAinda não há avaliações
- Critical Care NursingDocumento17 páginasCritical Care Nursingsanish4u100% (1)
- Contraindications To Air TravelDocumento15 páginasContraindications To Air TravelsDamnAinda não há avaliações
- Set1 - Final FRCA Viva Qs - June 2009Documento35 páginasSet1 - Final FRCA Viva Qs - June 2009Adham Salem100% (1)
- Respiratory SystemDocumento9 páginasRespiratory SystemMary Eilleen CabralAinda não há avaliações
- (2013) Respiratory Diseases of The HorseDocumento238 páginas(2013) Respiratory Diseases of The Horsekaren montoyaAinda não há avaliações
- There Are Four Classic Stages of Anesthesia Disorientation, Excitement, AnesthesiaDocumento16 páginasThere Are Four Classic Stages of Anesthesia Disorientation, Excitement, Anesthesiadine4ya100% (2)
- NCP PTBDocumento9 páginasNCP PTBecbarticanAinda não há avaliações
- DLL For Respiratory SystemDocumento4 páginasDLL For Respiratory SystemJuvilla BatrinaAinda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento23 páginasUntitledMarceline GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of Chest PDFDocumento61 páginasAnatomy of Chest PDFRizwan QureshiAinda não há avaliações
- Computer-Controlled Mechanical Simulation of The Artificially Ventilated Human Respiratory SystemDocumento13 páginasComputer-Controlled Mechanical Simulation of The Artificially Ventilated Human Respiratory SystemOancea AdrianAinda não há avaliações
- Normal Fetal Development and GrowthDocumento42 páginasNormal Fetal Development and GrowthAbdullah EssaAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Documento86 páginasChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)physio43Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7Documento138 páginasChapter 7Bëar MëAinda não há avaliações
- англDocumento30 páginasанглaaccvAinda não há avaliações
- Alterations in OxygenationDocumento104 páginasAlterations in OxygenationMelchor Felipe Salvosa100% (1)
- HEALTH 8 Q4 WEEKGRADE-2nd-QUARTER 3 LAS 2Documento1 páginaHEALTH 8 Q4 WEEKGRADE-2nd-QUARTER 3 LAS 2Melieza Melody AmpanAinda não há avaliações
- Paediatric Clinical Chemistry: BY DR Okwor C.J Department of Chemical Pathology, UNECDocumento41 páginasPaediatric Clinical Chemistry: BY DR Okwor C.J Department of Chemical Pathology, UNECUdochukwu EnebeAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory SystemDocumento23 páginasRespiratory Systemjimboy baddiriAinda não há avaliações
- ĐỀ THI TUYỂN SINH VÀO LỚP 10 CHUYÊN ANH CÁC NĂM (SACHMOI24H.COM)Documento76 páginasĐỀ THI TUYỂN SINH VÀO LỚP 10 CHUYÊN ANH CÁC NĂM (SACHMOI24H.COM)Duy HảiAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology Finals Chapter Quiz Heart, Blood Vessela and Circulation, and Respiratory SystemDocumento13 páginasAnatomy and Physiology Finals Chapter Quiz Heart, Blood Vessela and Circulation, and Respiratory SystemMartin ManuelAinda não há avaliações
- Summer Assignment Scan PDFDocumento58 páginasSummer Assignment Scan PDFDavid CaseyAinda não há avaliações
- DR - Areej Magdi IGCSE Biology Edexcel-Oxford Quiz Name: Marks Obtained: TopicsDocumento8 páginasDR - Areej Magdi IGCSE Biology Edexcel-Oxford Quiz Name: Marks Obtained: TopicsMOHAMMED FURQAN BIN MUSTAFAAinda não há avaliações
- Hypo Ventilation SyndromesDocumento22 páginasHypo Ventilation SyndromesFer45Ainda não há avaliações
- ExamDocumento43 páginasExamFoxtrot NursingAinda não há avaliações
- QUARTER 1-WEEK 2 (OCTOBER 12-16, 2020) GRADE 9 (School Year: 2020-2021) DAY Learning Areas Learning Competencies Learning Tasks Mode of DeliveryDocumento3 páginasQUARTER 1-WEEK 2 (OCTOBER 12-16, 2020) GRADE 9 (School Year: 2020-2021) DAY Learning Areas Learning Competencies Learning Tasks Mode of DeliveryJomajFalcatanDelaCruzAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 2023 24 DPS DurgapurDocumento24 páginasAssignment 2023 24 DPS DurgapurSubham RoyAinda não há avaliações
- Lung Project - 2 Liter Bottle1Documento2 páginasLung Project - 2 Liter Bottle1Ulfa SariAinda não há avaliações