Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Dermatology Revision
Enviado por
Abdelrahman Mohamed0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
158 visualizações7 páginas55
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documento55
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
158 visualizações7 páginasDermatology Revision
Enviado por
Abdelrahman Mohamed55
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 7
Bacterial infections
Impetigo Folliculitis Sycosis Furncle Carbuncle Erythiplas Cellulitis erythrasma
contagiosa barbae
Etiology Cocci + poor Stap aureus ( Staph aureus ( Infection of Diabetes Inflammation INF of lower Corynebactrium
hygiene & infection of folliculitis of lower part of of upper dermis ( staph minutissimum (
moisture or upper part of the beard area the hair dermis ( B aureus strpt DM )
scabies & hair follicle ) follicle hemolytic stept pyogenes
pediculosis )
C/P 1- Ordinary Follicular Follicular Red papules Multiple deep Erythrematous As erythiplas Reddish brown
2- Bullous : new pustules pustules & boils open on tender swollen but illdefined patches in
born staph papules surface by area with border interriginous
infection fistulae sharp border areas /
may be fatal + Give red
3- Circinate : constitutional S fluorescence
extension of with woods
ordinary light
4- Ulcerative :
crust & scars
Complications Post streptococcal Lymphedema
glomerulonephritis
Treatment Topical antiseptics Same Same Same Incision & Erythromycin Aggressive Topical AB and
+ topical drainage + AB antifungal ?
antibiotics and systemic AB systemic AB
systemic if sever
Viral infections
Herpes simplex Herpes zoster Warts Mollascum contagiosum
Aetioligy HSV I : herpes libialis Varicella Zoster virus Human papilloma virus Pox virus
HSV II : herpes progenitalis
C/P 1- HSV I : Vesilces along distribution of a 1- Common warts : Dome shaped papule with
a. superficial vesicles sensory nerve + local LNs verroucus papules central umblication and
perioroficail ulcers enlargement leave scar give 2- Plane warts : flat topped white chessy material if
swollen gums & permenant immunity papules squeezed can be sexual
lymphadenopathy + 3- Filiform warts :
constitutional manifestations DANGEROUS in : peduculated
b. recurrent attacks in lips & face Bilateral 4- Digitiform warts : finger
less sever Old age like
c. ocular type Gangrenous 5- Planter warts : foot =
d. herpitic witlow : in fingers Recurrent tender grow inward
very painful 6- Genital warts : moist
2- HSV II : vesicles on genitals foul smelling in MM &
and ulcers / if pregnant CS skin
Complications 2ry infections / eye cimolications / Eye complication ? post herpitic Oncogenicity ( cervical cancer )
CNS : encephalitis / erythema neuralgia
multiforme / cancer cervix
Treatment Antiseptic lotions 1- Topical : drying AS lotion 1- Cautery : electro- cryo Cauterization
Acyclovir cream 5 times / Acyclovir cream laser chemical
daily 5 days 2- Systemic : Acyclovir 800 2- Podophyllon resin in
IDU for eye lesions mg 5 X 7 - Analgesics alcohol : for veneral
Acyclovir tab 200 mg 5 X 5 3- Radiotherapy
4- Autosuggestion
Fungal infections
Dermatophytes Yeasts
Tinea capitis Tinea circinata Tinea pedis Other types Pityriasis versicolor Candidiasis
Cause Trichophyta & Trichophyta & Trichophyta & 1- Tinea cruris : Malassezia furfur Candida albicans
microspore microspore epidermophyta scrotum not the pathogenic form
involed of pityrrosporum
2- Tinea axillaris orbiculare
C/P 1- Scaly type :child Annular patches Sodden white 3- Tinea barbae Macule hypo or 1- Cutaneous
bal patch with with active edge and macerated skin with 4- Tinea mannum : hyper pigmented candidiasis :
scales healing centre bad dour between in palm with fine scales in a. Intertrigo :
2- Black dot : hair itching is common toes 5- Tinea uguium : upper chest arms i. Axilla & groin
breaks leave dots on exposed surfaces onchomycosis In summer ii. Eriosio
3- Kerion : also adult thickened interdigitalis
with boggy greenish nails mastocytica
swelling & iii. Angular
pustules chelitis
cicatricial alopecia iv. Napkin
4- Favus : diffuse dermatitis
loss of hair with b. Paronychia : nail
mousy odour fold tender nail
yellow crusts corrugated
cicatricail alopecia 2- Mucosalcandidiasis :
oral thrush vulvo
vaginitis - balanitis
Diagnosis 1- Woods : DD : herald patch Woods light gives
green yellow
2- LM Parker ink stain :
3- Culture on spagitti & meatballs
saburoud appearance
Treatment Topical alone is Topical antifungal 2 1- Tincture iodine 1-Systemic : 1- Topical : castellani
useless daily + systemic 1% ketoconazole paint nystatin
( ketoconazole grisofulvin for 3 W 2- Systemic 200X10 oint
shampoo + antifunal in 2-Topical : Na 2- Systemic :
griseofulvin tab for 2 sever cases hyposulphide mycostatin oral
months imidazole zinc drops Azoles
pyrithione white amphotericin B in
field tincture sever
iodine
Scaly erythematous lesions
Psoriasis Lichen planus Discoid Lupus erythematousus Pityriasis rosea
Etiology Lack of UV rays - Psychological Chronic scaly erythematous Considered exanthematous
- Hemolytic infection - Liver disease eruption in skin reaction for upper respiratory
- Hypocalcemia - Sunrays viral infection ( HHV 6-7 )
- Pregnancy - Antimalairial gold
- Trauma / psychogenic
C/P Erythematous papule with Flat topped polyangular Erythematous plaques + adherent Herald patch ( outer
shiny scales lossely adherent violaceous itchy papules with scales + dilated pilosebaceous erythematous zone
bleed on removal ( Auspiz ) adherent scales in flexor areas orifices ( stippling ) + intermediate scaly one
with sever pruritis telangectesia + thin atrophic scar healing center ) parallel to rib
cicatricial alopecia in sun / 2ry eruption give
exposed areas chrismats tree appearance &
jacket with short sleeves
Clinical types 1- Psoriasis vulgaris 1- Ordinary LP 1- Ordinary type
a. Skin : in extensors back 2- Actinic LP : in sun exposed 2- Inverted type : occur
b. Scalp psoriasis area in summer distal
c. Nail psoriasis : bi;aterla 3- Mucosal : reticulate network 3- Abortive type : only
pitting hyperkeratotic nail ulcerative laesion herald
d. Flexural type : scaling is precancerous 4- Papular type : more
absent 4- LP of the scalp : cicatricai elevated
2- Erythrodermic alopecia 5- Flexural type
3- Arthropathic
4- Pustular : sterile pustules
Treatment 1- Local : coal tar Anthralin 1- Antihistaminics 1- Sun screens 1- PT reassurance
0.5% - corticosteroids 2- Steroids & aalcylic loacally 2- Systemic photoprotectives ( 2- Avoid hot baths
salicylic acid 5% - 3- Steroids retinoids and chloroquine ) 3- Calamine lotion
calcipotriol PUVA laser cyclosporine systemically 3- Corticosteroids ( local 4- Oral antihistaminics ,
2- Systemic : for extensive 4- Actinic : sunscreens 0 systemic intralesional ) topical corticosteroids and
psoriasis : Methotrexate chloroquine 200mg /day UVB
retinoids cyclosporine 5- Mucosal : steroids acitrtin
corticosteroids PUVA oral chloroquine
Allergic Dermatoses
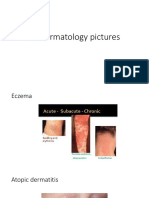
Eczema urticaria Erythema multiforms Drug eruptions
May be genetic in types as atopic & 1- Exogenous : foods as fish- 1- Genetic factors Allergy to the drug
allergic contact dermatitis chocolate / drugs as penicillin 2- Infections : HSV
injected or ingested / pollens
3- DRUGS : NSAIDs
2- Endogenous : infection
parasites SLE lymphoma 4- Autoimmune : SLE
pregnancy 5- Malignancy : lymph
1- Contact dermatitis : 1- Ordinary urticaria 1- EM minor : only 1- Urticarial &
a. 1ry irritant dermatitis : any individual 2- Facticious : very mild limmted to skin no angioedema
b. Allergic contact dermatitis : type IV
in genetic susceptile
follow trauma or mild mucosal 2- Erythroderma (
2- Discoid eczema : well defined 3- Cholinergic : itchy involvement no exfoliative dermatitis )
3- Atopic eczema : genetic with FH sensation after sweating systemic involvement 3- Photosensitive drug
a. Infantile : on cheeks & hands with wheals on scalp neck 2- EM major : extensive reaction
b. Childhood : on flexures upper chest mucosal and systemic 4- Acneform eruptions
c. Adult : hyperpigmentation &
lichenification
4- Physical : either solar involvement death ( steroids )
4- Stasis eczema : venous insufficiency pressure cold heat 5- Fixed drug eruption
edema oozing vesiculation itching 5- Popular : due to insect bite : with sulfonamides &
5- Seborrheic eczema : by malassezia in infants & children / NSAIDs / fixed to the
furfur wheal then papule over it drug & site /
a. Infantile type : scales on scalp &
diaper area
permengnate colored
b. Aadult : from androgens on macule vesicles &
sebaceous glands eruption
-acute eczema : erythema swelling Sudden appearance of elevated Primary lesion : iris ( target ) Acute atypical inflammatory
vesicles edematous lesion varies in size lesion erythematous annukar eruptions suside after
-chronic eczema : lichenification & transient for few hours ring with central vesicle / in stoppage of drug
excoriations mucosa : may form painful
HGE bullae & erosions
1- Acute : drying antiseptic lotion & 1- local : cold 3- Local : compresses
corticosteroid cream witth compresses calamine calamine lotion
hydrous base systemic lotion steroids steroids antiseptics
antihistaminics & corticosteroids 2- Systemic : oral 4- Systemic :
2- Chronic : local corticosteroids antihistaminic antihistaminics
cream parentral AH oral steroids antibiotics
3- Atopic : + topical steroids parentral 5- Major needs
immunomodulators & UVB steroids adrenaline hospitalization and
4- Seborrheic : antidandruff SC or IM TTT of complications
shampoo
Vitiligo ALopecia Acne
Etiology Melanocytes are destroyed and disappear 1- Cicatricial : mechanical trauma Block of follicular opening by KCs
from epidermis due to : fungal inection DLE lichen planus dilatation of the lower part disruption
1- Autoimmune : antimelanocyte AB 2- Non cicatricial : of the epithelium discharge into the
precipitated by psycho or a. Telogen : postpartum dermis inflammation especially with
mechanical trauma nutritional deficiency propionobacterium acnes lead to papule
2- Neurogenic L melanocytotoxic b. Anagen : cytotoxic pastule nodulocystic lesions
substances from nerve endings retinoids mercury
3- Chemical : melanocytotoxic c. Familial baldness :
substances from rubber gloves etc overactivity 5alfa reductase
4- UV rays d. Areata : genetic factors
immunological actors
Types 1- Focal vitilgo 1- Cicatricial 1- Mild ; comedones no papules
2- Unilateral vitilgo 2- Non cicatricail : telogen effulfium 2- Moderate : comedones paules
3- Generalized vitilgo anagen effluvium androgenitic pustules
4- Universal vitiligo alopecia alopecia areata ( patchy 3- Sever : nodules & cysts
marginaalis ophiasis totalis
universalis )
DD DD : tinea versicolor pityriasis alba-
postinflammatory hypopigmentation
Tratment 1- Phoyototherapy : PUVA 1- topical ; local irritants 1- topical : erythromycin lotion
2- Steroids & immunomodulators corticosteroids cream PUVA retinoids benzyl peroxide
3- Surgical : punch gafting & tissue minoxidil azelic acid
culture 2- systemic : antidepressant 2- systemic : antibiotics (tetracycline)
4- camouflage corticosteroids + retinoids dapsone & steroids (
sever )
The following topics has to be studied from the department book : leprosy & protozoal infections
Prepared by
Mahmoud abdel Ghany Behairy
Você também pode gostar
- Dermatology RevisionDocumento7 páginasDermatology RevisionmksharmaaAinda não há avaliações
- Dermatology MemoryDocumento7 páginasDermatology MemoryBenny PojerAinda não há avaliações
- Nail Changes: III-A '07 - Derma MegatableDocumento21 páginasNail Changes: III-A '07 - Derma MegatableAileen Peña100% (2)
- Dermatology Slides - Introduction To Clinical DermatologyDocumento34 páginasDermatology Slides - Introduction To Clinical DermatologyAzry Mustapa100% (1)
- CLINICAL DERMATOLOGY (NXPowerLite)Documento119 páginasCLINICAL DERMATOLOGY (NXPowerLite)api-3710926Ainda não há avaliações
- DermatologyDocumento6 páginasDermatologygnuzzo100% (3)
- Dermatology NotesDocumento59 páginasDermatology NotesAbdullah Matar Badran50% (2)
- Dermatology QuestionsDocumento19 páginasDermatology QuestionsBenjamin Nelson50% (2)
- Dermatology PDFDocumento37 páginasDermatology PDFanabananan100% (2)
- Viva Questions DermatologyDocumento5 páginasViva Questions DermatologyRavva0% (1)
- Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical DermatologyDocumento1.146 páginasAtlas and Synopsis of Clinical DermatologyAnda Madalina Zaharia100% (6)
- Wood Lamp DermatologyDocumento6 páginasWood Lamp Dermatologyindriyanti natasya ayu utami kotten100% (1)
- Dermatology GuideDocumento89 páginasDermatology GuideZeljnaznanja100% (3)
- Derma MegatableDocumento21 páginasDerma MegatableNicole ChanAinda não há avaliações
- Dermatology Venereology LeprosyDocumento86 páginasDermatology Venereology LeprosyDolamani RohidasAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Dermatology: Differential DiagnosisDocumento73 páginasClinical Dermatology: Differential DiagnosisHalim MaherAinda não há avaliações
- Handbook of DermatologyDocumento235 páginasHandbook of DermatologyNicholas MiteiAinda não há avaliações
- Complete Dermatology NotesDocumento41 páginasComplete Dermatology NotesSetlhare MotsamaiAinda não há avaliações
- Dermatology Class NotesDocumento48 páginasDermatology Class Notesapi-26938624100% (6)
- Differential Diagnosis in Dermatology Fourth Edition: Richard Ashton, Barbara Leppard and Hywel CooperDocumento30 páginasDifferential Diagnosis in Dermatology Fourth Edition: Richard Ashton, Barbara Leppard and Hywel CooperAussie Aulia100% (1)
- Dermatology MnemonicDocumento16 páginasDermatology MnemonicAhmed RamiAinda não há avaliações
- Dermatology - Papulosquamous DisordersDocumento34 páginasDermatology - Papulosquamous DisordersskAinda não há avaliações
- Dermatology FinalDocumento16 páginasDermatology FinalMelinda100% (2)
- Derm - Monitoring Systemic MedicationsDocumento3 páginasDerm - Monitoring Systemic MedicationsriskhakovAinda não há avaliações
- 5 - Differential Diagnosis of DermatologyDocumento6 páginas5 - Differential Diagnosis of DermatologyAyaa YousefAinda não há avaliações
- Hair Growth Disorders N Pigmentary DisordersDocumento7 páginasHair Growth Disorders N Pigmentary Disordersmrosaregina michelleAinda não há avaliações
- ACS (I) Textbook of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery (2 Volume Set)Documento51 páginasACS (I) Textbook of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery (2 Volume Set)Huyền Thanh0% (3)
- Srinadh Neonatal Skin Conditions FinalDocumento110 páginasSrinadh Neonatal Skin Conditions FinalSrinadh Pragada100% (1)
- Dermatology Review NotesDocumento8 páginasDermatology Review Notesnmb1986Ainda não há avaliações
- Clinical Cases in Dermatology Modern Management of Acne Actinic Keratosis and Atopic DermatitisDocumento7 páginasClinical Cases in Dermatology Modern Management of Acne Actinic Keratosis and Atopic DermatitisJpratoAinda não há avaliações
- An Approach To The Patient With ErythrodermaDocumento42 páginasAn Approach To The Patient With ErythrodermaShakilAinda não há avaliações
- Topical Steroids DermatologyDocumento23 páginasTopical Steroids DermatologyRitika Agarwal100% (1)
- DermatologyStudent Atlas 2009Documento310 páginasDermatologyStudent Atlas 2009Andaru Kusuma Praja100% (4)
- Study Guide-Dermatology 2021Documento14 páginasStudy Guide-Dermatology 2021Nasir RafieAinda não há avaliações
- 0 Basic Principles of DermatologyDocumento42 páginas0 Basic Principles of Dermatologymusatii100% (1)
- All Dermatology PicturesDocumento140 páginasAll Dermatology PicturesAshty RzgarAinda não há avaliações
- Dermatology QuestionsDocumento8 páginasDermatology QuestionsDrMubashir ShaikhAinda não há avaliações
- PATHOPHYS - DermatologyDocumento19 páginasPATHOPHYS - Dermatologyaagioaa100% (1)
- DermatologyDocumento44 páginasDermatologyakufahaba100% (2)
- Dermatology DDXDocumento29 páginasDermatology DDXM.Dalani100% (2)
- General Considerations For Topical PreparationsDocumento6 páginasGeneral Considerations For Topical PreparationsOccamsRazorAinda não há avaliações
- Dermatology HandbookDocumento70 páginasDermatology Handbookrobchris1975100% (12)
- Dermatology Questions and AnsDocumento147 páginasDermatology Questions and AnsEl FaroukAinda não há avaliações
- Dermatology BookDocumento479 páginasDermatology BookBharath Magesh100% (2)
- ABC of DermatologyDocumento149 páginasABC of DermatologyAndreea Alexandru100% (15)
- Cases Surgery For Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers: bcc, scc, mcc.No EverandCases Surgery For Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers: bcc, scc, mcc.Ainda não há avaliações
- Fast Facts: Dermatological Nursing: A practical guide on career pathwaysNo EverandFast Facts: Dermatological Nursing: A practical guide on career pathwaysAinda não há avaliações
- Manual of Skin Surgery: A Practical Guide to Dermatologic ProceduresNo EverandManual of Skin Surgery: A Practical Guide to Dermatologic ProceduresNota: 1 de 5 estrelas1/5 (1)
- Case Studies in Advanced Skin Cancer Management: An Osce Viva ResourceNo EverandCase Studies in Advanced Skin Cancer Management: An Osce Viva ResourceAinda não há avaliações
- Dermatology Essentials for Medical AssistantsNo EverandDermatology Essentials for Medical AssistantsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Epigenetics and DermatologyNo EverandEpigenetics and DermatologyQianjin LuNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (1)
- Nursing the NeonateNo EverandNursing the NeonateMaggie MeeksAinda não há avaliações
- Derma Transcribed Table FormDocumento9 páginasDerma Transcribed Table FormGerlyn MarcelinoAinda não há avaliações
- Derma Tweets by DR Ahmed GodaDocumento7 páginasDerma Tweets by DR Ahmed GodaAbdelrahman MohamedAinda não há avaliações
- Behavior and Ethics QuestionsDocumento26 páginasBehavior and Ethics QuestionsRahul VadlapatlaAinda não há avaliações
- Def MechDocumento1 páginaDef MechAbdelrahman MohamedAinda não há avaliações
- Childhood Development TheoriesDocumento1 páginaChildhood Development TheoriesAbdelrahman MohamedAinda não há avaliações
- Physiology High YieldDocumento13 páginasPhysiology High YieldAshamdeep AntaalAinda não há avaliações
- Medical MnemonicsDocumento256 páginasMedical MnemonicssitalcoolkAinda não há avaliações
- Crunch Time ReviewDocumento14 páginasCrunch Time ReviewAbdelrahman MohamedAinda não há avaliações
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Care of Older Adult (NCM 114)Documento2 páginasIn Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Care of Older Adult (NCM 114)Karen TangAinda não há avaliações
- 4.3.6. Changing The Parameters of A Volume GroupDocumento2 páginas4.3.6. Changing The Parameters of A Volume GroupNitesh KohliAinda não há avaliações
- Organigation DeveDocumento3 páginasOrganigation Devemerin sunilAinda não há avaliações
- Geriatric AnaesthesiaDocumento24 páginasGeriatric Anaesthesiakarl abiaad100% (2)
- Second Grading EappDocumento2 páginasSecond Grading EappConnieRoseRamos100% (2)
- Amtek Auto Analysis AnuragDocumento4 páginasAmtek Auto Analysis AnuraganuragAinda não há avaliações
- Impact of Micro FinanceDocumento61 páginasImpact of Micro FinancePerry Arcilla SerapioAinda não há avaliações
- 50 p7 Kids AvikdeDocumento2 páginas50 p7 Kids AvikdebankansAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment Submission Form: Pgid Name of The MemberDocumento9 páginasAssignment Submission Form: Pgid Name of The MemberNamit GaurAinda não há avaliações
- Elementary SurveyingDocumento19 páginasElementary SurveyingJefferson EscobidoAinda não há avaliações
- Hard Soft Acid Base TheoryDocumento41 páginasHard Soft Acid Base TheorythinhbuAinda não há avaliações
- Asset Management PlanDocumento160 páginasAsset Management Planbkalatus1100% (1)
- Week9 Phylum NemathelminthesDocumento26 páginasWeek9 Phylum NemathelminthesCzerinne Angela Justinne AlarillaAinda não há avaliações
- Parwati DeviDocumento25 páginasParwati DevikvntpcsktprAinda não há avaliações
- Gigold PDFDocumento61 páginasGigold PDFSurender SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Tugas, MO - REVIEW JURNAL JIT - Ikomang Aditya Prawira Nugraha (1902612010304)Documento12 páginasTugas, MO - REVIEW JURNAL JIT - Ikomang Aditya Prawira Nugraha (1902612010304)MamanxAinda não há avaliações
- ResultofCFAPMSAExaminations Winter2022Documento62 páginasResultofCFAPMSAExaminations Winter2022Nauman NafeesAinda não há avaliações
- LET Facilitating Learning EDITED3Documento12 páginasLET Facilitating Learning EDITED3Likhaan PerformingArts HomeStudio100% (5)
- REVISION For END COURSE TEST - Criticial ThinkingDocumento14 páginasREVISION For END COURSE TEST - Criticial Thinkingmai đặngAinda não há avaliações
- What Are RussiaDocumento3 páginasWhat Are RussiaMuhammad SufyanAinda não há avaliações
- Midterm Decision Analysis ExercisesDocumento5 páginasMidterm Decision Analysis ExercisesAYLEN INJAYAAinda não há avaliações
- Life in The Past - Year 6 WorksheetsDocumento11 páginasLife in The Past - Year 6 WorksheetstinaAinda não há avaliações
- Congental Abdominal Wall DefectsDocumento38 páginasCongental Abdominal Wall DefectsAhmad Abu KushAinda não há avaliações
- TOEIC® Practice OnlineDocumento8 páginasTOEIC® Practice OnlineCarlos Luis GonzalezAinda não há avaliações
- Su Jok, Twist Therapy AND Smile MeditationDocumento7 páginasSu Jok, Twist Therapy AND Smile MeditationprateekAinda não há avaliações
- Fortune 2010Documento14 páginasFortune 2010Stefan JenkinsAinda não há avaliações
- RA 9344 As Amended by RA 10630 - HandoutsDocumento9 páginasRA 9344 As Amended by RA 10630 - HandoutsJan Re Espina CadeleñaAinda não há avaliações
- Direct Filter Synthesis Rhea PreviewDocumento25 páginasDirect Filter Synthesis Rhea Previewoprakash9291Ainda não há avaliações
- Debus Medical RenaissanceDocumento3 páginasDebus Medical RenaissanceMarijaAinda não há avaliações
- Man Is Made by His BeliefDocumento2 páginasMan Is Made by His BeliefLisa KireechevaAinda não há avaliações