Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Unit 5
Enviado por
SelvakumarTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Unit 5
Enviado por
SelvakumarDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
MAHALAKSHMI
ENGINEERING COLLEGE
TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621213
QUESTION BANK
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Sub. Code : GE6252 Semester : II
Subject : BEEE Unit : V
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PART-A
1.what is modulation ? (AU MAY 09)
The process by which the base band signal modifies the carrier signal is
called modulation and resultant signal is called modulated signal.
2.What is demodulation ? (AU MAY 09)
At the receiving end ,the baseband signal and carrier signal are separated from
modulated signal by the process of demodulation.
3.List the different types of modulation techniques ? (AU MAY 11)
There are two types of modulations:
Analog modulation
pulse modulation
4.Define modulation index for AM ? (AU DEC 09)
Modulation index is the ratio of amplitude of the modulating signal and amplitude of
the carrier signals. It is also called modulation factor ,modulation coefficient or thr
degree of modulation.
5.Define frequency modulation? (AU DEC 10)
When frequency of the carrier varies as per amplitude variations of modulating
signal is known as frequency modulation (FM)
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 1
6.State the merits of FM over AM ? (AU DEC 10)
Frequency modulation has the following advantages :
The amplitude of FM wave is constant and hence transmitted power is
constant,independent of modulation depth ;whereas in A.M modulation
depth controls the transmitted power.
This means that low level modulation can be employed in FM
transmitters.Since the power is constant ,the FM calculated signal ,after the
low level modulation ,can be amplified by more efficient class-C amplifiers.
In AM ,67% of transmitted power is in the carrier ,for maximum modulation
depth ,which is totall y wasted as carrier does not carry any intelligence .In
FM ,all the transmitted power is useful .
FM receivers use the amplitude limiter circuits to eliminate the amplitude
variations caused by noise .Due to this ,FM reception is more immune to
noise than AM reception.
7.What are the applications of microwave application ? (AU DEC 09)
Because the terrestrial microwave application does not use cables
,microwave links often connect separate buildings where cabling would be too
expensive ,difficult to install or prohibited.
For example ,if two buildings are separated by a public road ,you may not be able to
get permission to install cable over or under the road.Microwave links would be a good
choice in this type of situation.
8.Mention the two advantages of modulation when compared to transmission of
unmodulate signal ? (AU DEC 10)
Reduces the height of antenna
Avoids mixing of signals
increases the range of communication
Allows the multiplexing of signals
9.What is the basic function of communication satellite ? (AU DEC 08)
communication satellite receives the microwave signals from the transmitter
on the earth.It amplifies the received signals and sends them back to the earth.
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 2
OTHER QUESTIONS:
1. What is an antenna?
An antenna is a transducer which converts the electrical energy to electromagnetic
energy to ease transmission of message through free space. At the receiver, we
make use of a receiving antenna and convert the electromagnetic signal back to
electrical signal.
2. Define analog signal.
The amplitude of the signal is varies continuously with time. This signal is called
analog signal. Example, voltage or current varies continuously with time.
3. What is meant by modulation?
Modulation is basically a process of increasing the frequency of the signal to be
transmitted. In the process of modulation, we take a high frequency signal called as
carrier signal and vary some characteristics of the carrier signal like amplitude,
frequency or phase in accordance with the instantaneous amplitude variation of the
message signal.
4. What are the types of modulation?
Modulation can be broadly classified into two types based on the nature of carrier
signal.
1. Sinusoidal Modulation
2. Pulse Modulation
In sinusoidal modulation, the carrier signal used is a sine signal.
In pulse modulation, the carrier signal used in a pulse signal.
5. Define Amplitude Modulation.
In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the carrier is varied in accordance with the
instantaneous amplitude of the message signal. i.e. whenever the modulating
signal
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 3
reaches maximum amplitude, the amplitude of the carrier is also made higher and
whenever the message signal reaches minimum amplitude, the amplitude of the
carrier is also minimum.
6. Define Frequency Modulation.
In frequency modulation, the frequency of the carrier signal is varied in accordance
to the instantaneous amplitude of the message signal. i.e. whenever the amplitude
the message signal is high, FM wave has higher frequency and whenever the
amplitude of the message is low, frequency of FM wave is also less.
7. What is bandwidth for AM wave?
Bandwidth is the difference between highest and lowest frequencies in the
transmission of AM wave.
Bandwidth = Upper side band frequency lower side band frequency
= (fc + fm) (fc fm) = 2fm
i.e., bandwidth of AM is equal to twice the modulating signal frequency.
8. Define pulse Amplitude Modulation.
In pulse amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the pulse is varied in accordance to
message signal amplitude.
9. What is meant by sampling?
Sampling in the process of taking the samples (Splitting) of a continuous time
signal at regular interval of time (called the samples).
10. What is meant by Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK)?
Amplitude shift keying is a digital modulation technique, in which a sinusoidal
signal of particular amplitude and frequency to the ON state pulse and a sinusoidal
signal of different amplitude or even zeros amplitude for the OFF state pulse.
11. What is meant by Frequency Shift Keying (FSK)?
FSK is a digital modulation technique, in which, a logic 0 and logic 1 will be
differentiated with a sinusoidal signal of different frequencies.
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 4
12. Compare AN and FM.
Sl.No. Amplitude Modulation Frequency Modulation
1. The amplitude of AM signal The amplitude of FM signal is
varies depending on constant and independent of
modulating signal. depth of modulation.
Transmitters are simple and Transmitter are complex and
2. cheap. hence expensive.
Bandwidth (BW) is very small BW is very high.
3.
Area of reception is large Area of reception is small.
4.
Noise cannot be easily Noise can be easily minimized.
minimized.
5.
13. What is the radio transmitter?
The transmitter is the electronic unit that accepts the information signal to be
transmitted and converts it into an RF signal capable of being transmitted over
long distances.
14. What are the primary functions of a radio receiver?
A radio receiver is required to perform three main functions.
1. Selection of the desired frequency from a large number of modulated
carrier frequencies that strike the receiving antenna at the same time.
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 5
2. Separation of the modulating audio frequencies from the modulated
carrier frequency by the process of detection or demodulation.
3. Conversion of AF currents into sound waves that can be easily heard by
the human ear.
15. What are the main characteristics of a receiver?
There are three main characteristics by which the quality of a receiver can be
judged. These are, 1. Selectivity 2. Sensitivity 3. Fidelity.
16. List the advantages of a Superheterodyne receiver
Improved selectivity in terms of adjacent channels.
More uniform selectivity over the complete frequency range.
Improved receiver stability
Higher gain per stage because IF amplifiers are operated at a lower
frequency.
Uniform Bandwidth because of fixed intermediate frequency.
17. What is meant by progressive scanning?
The scanning process in which the scanning electron beam sweeps across each
horizontal line in regular succession from top to bottom of the picture is called
Progressive Scanning.
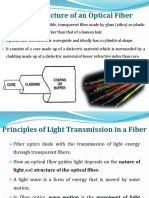
18. What are the modes of propagation in a optical fiber?
Apogee is the farthest point on the orbit of a satellite from the earth.
Perigee is the nearest point on the orbit of a satellite from the earth.
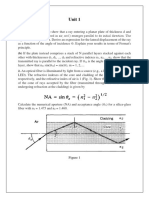
19. Define numerical aperture.
The numerical aperture (NA) is a measure of the light gathering ability of an
optical fiber. The fiber with a large numerical aperture accepts more light an compared
to fiber with small numerical aperture.
20. Write briefly on principle of total internal reflection used in fiber optics.
When light waves travel from one medium to another medium of different
refractive index, it undergoes refraction. When the angle of incidence is gradually
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 6
reduced, lesser than a critical angle, the light wave get reflected back into the
same medium without getting refracted. This phenomenon is called as total internal
reflection.
The principle of total internal reflection is employed in fiber optic
communication while transmitting information in the form of light waves.
PART-B
1.Explain the need of modulation .What are the difficulties will be faced if the
unmodulated signals are transmitted ?How the modulation overcomes them ?
(AU DEC 11)
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 7
2.With a neat diagram, explain the operation of amplitude modulation? (AU DEC
11)
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 8
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 9
3.Explain the power relations in AM Wave ? (AU DEC 09)
4.Sketch the circuit of simple resistor AM modulator and explain its working ?
(AU MAY 08)
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 10
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 11
5.Draw the circuit diagram of balanced modulator and explain its operation ? (AU
MAY 11)
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 12
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 13
6.With the help of suitable block diagram describe the working of TV transmitter
?(AU MAY 12)
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 14
7.Describe the satellite communication system ,with the help of block diagrams of
earth station transmitter and earth station receiver ?(AU MAY 12)
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 15
8.Write the detailed note on optical fiber communication ?(AU MAY 11)
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 16
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 17
9.With a neat diagram explain the operation of frequency modulation ?(APR 09)
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 18
10.Explain the microwave communication ?(AU APR 09)
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 19
11.Explain the fax machine with the block diagram ?(AU APR 12)
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 20
EEE DEPT/MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,TRICHY-621213 Page 21
Você também pode gostar
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Power Plant Engineering PK Nag1Documento994 páginasPower Plant Engineering PK Nag1Satti SihalohoAinda não há avaliações
- Fourier Optics and Hamiltonian Aberration TheoryDocumento43 páginasFourier Optics and Hamiltonian Aberration TheoryShiva MohammadzadehAinda não há avaliações
- Optical and Microwave Lab Manual PDFDocumento33 páginasOptical and Microwave Lab Manual PDFAravindhan SaravananAinda não há avaliações
- Power Plant Design HandbookDocumento135 páginasPower Plant Design HandbookRehman Zahid100% (1)
- Optical MicrosDocumento73 páginasOptical MicrosSaurabhBhardwajAinda não há avaliações
- Me Ped 3 PX7301 Dec 2014 PDFDocumento3 páginasMe Ped 3 PX7301 Dec 2014 PDFSelvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- PE 9272 Power Electronics For Renewable Energy SystemsDocumento3 páginasPE 9272 Power Electronics For Renewable Energy SystemskarthikapecAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1Documento33 páginasUnit 1SelvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Me Ped 3 PX7301 Dec 2016 PDFDocumento3 páginasMe Ped 3 PX7301 Dec 2016 PDFskrtamilAinda não há avaliações
- Me Ped 3 PX7301 May 2015Documento3 páginasMe Ped 3 PX7301 May 2015SelvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 4Documento29 páginasUnit 4SelvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Auc2008 & 2009Documento73 páginasAuc2008 & 2009SelvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Fiber Communication FundamentalsDocumento32 páginasOptical Fiber Communication FundamentalsyikamnnAinda não há avaliações
- Fiber Optics Trainer KitDocumento3 páginasFiber Optics Trainer KitPriyabrata BiswalAinda não há avaliações
- 01 Introduction Optical Comm PDFDocumento39 páginas01 Introduction Optical Comm PDFahmedAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Fiber Transmission MediaDocumento64 páginasOptical Fiber Transmission MediaMoneth Lozano100% (1)
- Lec - Ray Theory TransmissionDocumento27 páginasLec - Ray Theory TransmissionmathewAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Ball LensesDocumento3 páginasUnderstanding Ball Lensesbraulio.dantas-1Ainda não há avaliações
- Seminar Report On Optical Fiber Communication by Shradha PathakDocumento22 páginasSeminar Report On Optical Fiber Communication by Shradha Pathakkavya keerthiAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Fiber Structure & Light TransmissionDocumento83 páginasOptical Fiber Structure & Light Transmissionece Ms.G.Bhargavi100% (1)
- Merging Result (OCN)Documento52 páginasMerging Result (OCN)Atul SahAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Fiber Communication Historical DevelopmentDocumento36 páginasOptical Fiber Communication Historical DevelopmentSukhada Deshpande.Ainda não há avaliações
- POF ApplicationDocumento12 páginasPOF ApplicationParthAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Communication 2mark PDFDocumento20 páginasOptical Communication 2mark PDFAnant ShankarAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Fiber Communication System ComponentsDocumento96 páginasOptical Fiber Communication System ComponentsBerhane KifleAinda não há avaliações
- Snell's law and refraction through parallel planar layersDocumento7 páginasSnell's law and refraction through parallel planar layersVigneshwar DhavamaniAinda não há avaliações
- MCQDocumento6 páginasMCQengshimaa50% (2)
- BS en 60793-1-43-2015Documento24 páginasBS en 60793-1-43-2015Amer AmeryAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To StereomicrosDocumento22 páginasIntroduction To StereomicrosWina SuprianiAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 5 - Optical Fiber Waveguides Ray Theory Part - 2Documento8 páginasLecture 5 - Optical Fiber Waveguides Ray Theory Part - 2samarthAinda não há avaliações
- Numerical With AnswerDocumento19 páginasNumerical With AnswerRahul KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Tut Sheet 2016 EnggDocumento14 páginasTut Sheet 2016 EnggCharanjeet Bhatia0% (1)
- FOC MATERIAL INTRODUCTIONDocumento16 páginasFOC MATERIAL INTRODUCTIONDeepesh KushwahaAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Fiber Communication Model Test 2018Documento2 páginasOptical Fiber Communication Model Test 2018MEHEDI HASANAinda não há avaliações
- Optical FibresDocumento29 páginasOptical Fibresnikhil67% (3)
- Fiber Optic Ppt.1Documento112 páginasFiber Optic Ppt.1John Dareyrle G. Mapatac100% (1)
- Sample MCQ1Documento16 páginasSample MCQ1Punith ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- GE 6163 - Physics Lab Manual PDFDocumento21 páginasGE 6163 - Physics Lab Manual PDFsatya_vanapalli3422Ainda não há avaliações