Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
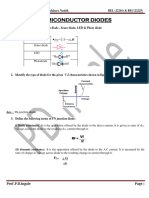
Zener Diodes
Enviado por
Charles PettersonDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Zener Diodes
Enviado por
Charles PettersonDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
analogangle By Ron Mancini
The ultimate zener-diode reference
y recent columns discussed the physics and
M
age, you can use R3 to increase the
zener voltage. (Usually, R2, R1=0.)
applications of discrete-zener-diode references, These circuits use thin-film, laser-
trimmed resistors to obtain initial
and the conclusion they reached is that discrete errors as low as 0.01%, and the
trimming can include temperature
zener diodes make poor references because of tolerance compensation, which can yield
temperature coefficients as low as
buildup (references 1 and 2). ICs surface. The buried-junction 0.6%.
Early-IC designers achieved zener zener diode has an extremely sta- One common reference circuit,
characteristics using reverse-bi- ble subsurface-breakdown mecha- which several semiconductor
ased, npn-transistor base-emitter nism that yields almost-perfect manufacturers supply and which
junctions. This zener-breakdown noise performance. Furthermore, uses a buried-zener diode, is the
effect occurs at the die surface, so it surface contamination and oxide REF02; you can couple a REF02
is subject to contamination and
oxide-charge problems. Surface
zener diodes have several prob- THE BURIED-ZENER DIODE STILL REQUIRES A RATHER
lems: They require breakdown
voltages of greater than 5V, they HIGH 8V, BUT IT IS SUPERIOR IN ALL OTHER RESPECTS.
are noisy, and they have poor
short- and long-term voltage drift. effects do not affect the buried with an external op amp to obtain
Later-IC designers learned that junction, so the resulting zener dual voltage references (Figure 2).
they could bury the transistor diode makes an outstanding volt- The REF02 is the 5V reference, and
base-emitter junction under the age reference. Using a 6.3V zener the differential amplifier inverts
V
diode is common because it is the the 5V to generate a 5V refer-
most stable zener diode over time ence. The matched resistors in the
and temperature (Reference 3). differential amplifier ensure that
I The buried-zener diode still the negative reference voltage
1R
+ requires a rather high 8V, but it is tracks the positive reference volt-
V
V2 _
OUT
superior in all other respects. age and is accurate. Substituting an
2R R 4
Zener diodes still have several op amp with discrete resistors for
problems, such as line regulation, the differential amplifier allows
R3 load regulations, and a fixed volt- different negative reference volt-
age output. IC designers solve ages, but the discrete resistors sac-
these problems using an op amp rifice the precision of the differen-
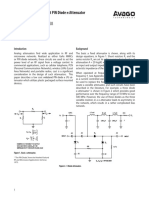
The buried-zener- and a current source (Figure 1). A tial amplifier. These references are
Figure 1
diode reference often current source biases the zener flexible as well as accurate, and a
includes a current source and an op amp diode, which keeps the zener cur- wealth of application information
to reduce line- and load-regulation toler- rent constant in spite of line-volt- about them exists on the Web.
ances. age fluctuations. The op amp
buffers the zener References
15V
diode, thus mini- 1. Mancini, Ron, Anatomy of a
2 mizing the effect of precision-voltage reference, EDN,
V
0.1 F
IN
V 6
0 5V
load-current fluctu- June 24, 2004, pg 24.
REF02
3 5 ations. An added 2. Mancini, Ron, Designing a
TEMP TRIM
GND
advantage of the op- zener-diode regulator, EDN, Aug
25k
4 25k amp buffer is that 5, 2004, pg 24.
15V
you can adjust the 3. Miller, Perry and Doug
_
ratio of R2 to R1 to Moore, Precision Voltage Refer-
INA
5V
obtain output volt- ences, Analog Applications Journal,
25k 105
+ ages smaller than the November 1999, pg 1.
15V
zener voltage. (Usu-
25k
ally, R3=0.) When Ron Mancini is staff scientist
the required output at Texas Instruments. You can
Figure 2
Adding a differential amplifier to a voltage is greater reach him at 1-352-569-9401,
REF02 yields tracking dual-polarity references. than the zener volt- rmancini@ti.com.
26 edn | September 30, 2004 www.edn.com
Você também pode gostar
- Special-Purpose Diodes: Dr. Amnach KhawneDocumento39 páginasSpecial-Purpose Diodes: Dr. Amnach KhawneCarlos IbaAinda não há avaliações
- 1207ch03 All DidoesDocumento43 páginas1207ch03 All DidoesKartik PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Special Purpose DiodeDocumento39 páginasChapter 3 Special Purpose DiodeSyed MuneebAinda não há avaliações
- CH4 Special-Purpose DiodesDocumento28 páginasCH4 Special-Purpose DiodesAyesha TahirAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 03completeDocumento56 páginasChapter 03completeMohammad SubhanAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Manual Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering-B.tech-Eee-2ndDocumento31 páginasLab Manual Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering-B.tech-Eee-2ndDeepanshu GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Bel Bec Ch01 Print OutDocumento38 páginasBel Bec Ch01 Print Outkenemep346Ainda não há avaliações
- Trask Mixer MusingsDocumento15 páginasTrask Mixer MusingsFraesenfresseAinda não há avaliações
- EE 211 CHAPTER 2 Part2Documento22 páginasEE 211 CHAPTER 2 Part2RickAinda não há avaliações
- (L4) - (JLD 3.0) - Semiconductors - 30th DecDocumento66 páginas(L4) - (JLD 3.0) - Semiconductors - 30th DecAshfaq khanAinda não há avaliações
- Laboratory Report Cover Sheet: 21Ecc211L - Devices and Digital Ic Lab Third Semester, 2023-24 (Odd Semester)Documento12 páginasLaboratory Report Cover Sheet: 21Ecc211L - Devices and Digital Ic Lab Third Semester, 2023-24 (Odd Semester)nikunj sharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Special Purpose DiodesDocumento43 páginasSpecial Purpose DiodesllovresAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 3-Special Purpose DiodesDocumento45 páginasCHAPTER 3-Special Purpose DiodesAbdullahAinda não há avaliações
- Zener DiodeDocumento14 páginasZener Diodes211053176Ainda não há avaliações
- EC8261-Circuits and Devices LaboratoryDocumento60 páginasEC8261-Circuits and Devices LaboratoryNandha KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Zenner DiodeDocumento23 páginasZenner DiodeKrishanu NaskarAinda não há avaliações
- Zener Diode and Diode ApplicationDocumento62 páginasZener Diode and Diode Applicationnibar dyllanAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Analog ElectronicsDocumento59 páginasBasic Analog ElectronicsPritesh Bhoumick100% (3)
- 02 Zenerdiodes PPT PRPDocumento29 páginas02 Zenerdiodes PPT PRPVarsha PrajapatiAinda não há avaliações
- Modified Electron Device Lab ManualDocumento73 páginasModified Electron Device Lab ManualVIVEK BHOGAR (RA2011030010136)Ainda não há avaliações
- Edc - 2 Marks With AnswerDocumento0 páginaEdc - 2 Marks With AnswerJoshua DuffyAinda não há avaliações
- Special Purpose DiodesDocumento10 páginasSpecial Purpose Diodeskmsriram92Ainda não há avaliações
- MMODULE4Documento6 páginasMMODULE4Jericho MejiaAinda não há avaliações
- Prelab ZinerDocumento6 páginasPrelab Zinerمحمود القويريAinda não há avaliações
- EDC 2 Marks All Five UnitsDocumento31 páginasEDC 2 Marks All Five UnitsSundar GaneshAinda não há avaliações
- Diodes Character PDFDocumento8 páginasDiodes Character PDFgraceAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Special Purpose DiodesDocumento40 páginasChapter 3 Special Purpose DiodesZain AliAinda não há avaliações
- Zener Diode Introduction To Zener DiodesDocumento6 páginasZener Diode Introduction To Zener DiodesSahil BhagatAinda não há avaliações
- Electron DeviceDocumento112 páginasElectron DevicekrishnaAinda não há avaliações
- PN-junction Diodes and Its ApplicationsDocumento37 páginasPN-junction Diodes and Its ApplicationsRahul sandireddyAinda não há avaliações
- A Low-Cost Surface Mount PIN Diode π Attenuator PDFDocumento8 páginasA Low-Cost Surface Mount PIN Diode π Attenuator PDFerdemsecenAinda não há avaliações
- Zenerdiodes 150209070235 Conversion Gate02Documento29 páginasZenerdiodes 150209070235 Conversion Gate02Pushkin RathoreAinda não há avaliações
- ZDDocumento29 páginasZDVikram TomerAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Devices: Tauqeer Aslam 07010810-045Documento4 páginasElectronic Devices: Tauqeer Aslam 07010810-045naina_samimaAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Zener DiodeDocumento28 páginas5 Zener Diodechandan.cj99Ainda não há avaliações
- Diseñor RVDDocumento2 páginasDiseñor RVDEdgar JimenezAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3Documento32 páginasChapter 3api-394738731Ainda não há avaliações
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesNo EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (7)
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2No EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2Ainda não há avaliações
- ECE132: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Lab: Experiment 10Documento8 páginasECE132: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Lab: Experiment 10Madhur YadavAinda não há avaliações
- 19EEE181 ReportDocumento14 páginas19EEE181 ReportabcdAinda não há avaliações
- Versatile Zener Diode TesterDocumento2 páginasVersatile Zener Diode TesterDarko ZeravicaAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment No. 5 Diode Approximation: Abstract - Bridges Are Unarguably One Key Components of TheDocumento3 páginasExperiment No. 5 Diode Approximation: Abstract - Bridges Are Unarguably One Key Components of TheJohn Kenneth BulabosAinda não há avaliações
- EI2203 EDC 2marksDocumento14 páginasEI2203 EDC 2marksBhanu KodaliAinda não há avaliações
- Zener Diode As Voltage Regulator and Its V-I CharacteristicsDocumento13 páginasZener Diode As Voltage Regulator and Its V-I CharacteristicsRUPAM GHOSHAinda não há avaliações
- Zenor DiodeDocumento5 páginasZenor Diodesonu kumarAinda não há avaliações
- CH 3 Special-Purpose DiodesDocumento2 páginasCH 3 Special-Purpose DiodesMohamed AmgadAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1 - 1v2Documento43 páginasModule 1 - 1v2Prakash L SAinda não há avaliações
- All MOS Transistors Bandgap Reference Using Chopper Stabilization TechniqueDocumento5 páginasAll MOS Transistors Bandgap Reference Using Chopper Stabilization Techniquecvkxwnxrh8Ainda não há avaliações
- Parul Institute of Engineering & TechnologyDocumento10 páginasParul Institute of Engineering & TechnologyDhrumit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Electronics For InventorsDocumento1 páginaPractical Electronics For InventorsDERYA KANDAZAinda não há avaliações
- ECE 201: Electronics I Semiconductors, PN Junction and DiodesDocumento65 páginasECE 201: Electronics I Semiconductors, PN Junction and DiodesSameh AtallahAinda não há avaliações
- Zener DiodeDocumento4 páginasZener DiodeMUZAMMIL YOUSAF L1S15BSCS0097Ainda não há avaliações
- Phantom Power CheckerDocumento3 páginasPhantom Power CheckerWandersonRicardoJesusFrançosaAinda não há avaliações
- EE105 5 Special Purpose DiodesDocumento28 páginasEE105 5 Special Purpose DiodesKahMun LimAinda não há avaliações
- Zener Diode - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento4 páginasZener Diode - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaManitAinda não há avaliações
- Ec0221 Ed Lab ManualDocumento68 páginasEc0221 Ed Lab ManualGoutham ShanAinda não há avaliações
- Radio Frequency Transistors: Principles and Practical ApplicationsNo EverandRadio Frequency Transistors: Principles and Practical ApplicationsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2)
- 1993 Book ElectricalCircuitAnalysisAndDeDocumento421 páginas1993 Book ElectricalCircuitAnalysisAndDeDavi Darriaux100% (1)
- 8 Pin Mosfet Data PDFDocumento18 páginas8 Pin Mosfet Data PDFazrilAinda não há avaliações
- Stm32Cubef3: Stm32Cube Mcu Package For Stm32F3 Series With Hal, Low-Layer Drivers and Dedicated MiddlewareDocumento4 páginasStm32Cubef3: Stm32Cube Mcu Package For Stm32F3 Series With Hal, Low-Layer Drivers and Dedicated MiddlewarePablo SalazarAinda não há avaliações
- Ev 5000Documento14 páginasEv 5000SeeniAinda não há avaliações
- EMC VNX Parts Location GuideDocumento44 páginasEMC VNX Parts Location GuideAcalPD100% (1)
- IC - MC3417 - MC3418 - DatasheetsDocumento20 páginasIC - MC3417 - MC3418 - Datasheetsmnolasco2009Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction To FieldbusDocumento11 páginasIntroduction To FieldbusMatthewAinda não há avaliações
- Voltage Doubler ADocumento2 páginasVoltage Doubler AErole Technologies Pvt ltd Homemade EngineerAinda não há avaliações
- Cummins: Fault Code: 768 PID: S009 SPN: 923 FMI: 11Documento3 páginasCummins: Fault Code: 768 PID: S009 SPN: 923 FMI: 11Enrrique LaraAinda não há avaliações
- Oracle Solaris 10 Zones Step-by-Step Guide - TechSupportDocumento13 páginasOracle Solaris 10 Zones Step-by-Step Guide - TechSupportrasimAinda não há avaliações
- 450.50-N1 (222) - SC-EQ Communication CardDocumento60 páginas450.50-N1 (222) - SC-EQ Communication CardUlisses AlbuquerqueAinda não há avaliações
- Products 84154634 10Documento11 páginasProducts 84154634 10JoshAinda não há avaliações
- Python OOPS ExercisesDocumento7 páginasPython OOPS Exercisesaadham gureisonAinda não há avaliações
- CICS DB2 Debugging TechniquesDocumento36 páginasCICS DB2 Debugging TechniquesJose Luis FloresAinda não há avaliações
- UX - UI DESIGN (MOOC Course) Mid Term ExaminationDocumento11 páginasUX - UI DESIGN (MOOC Course) Mid Term Examinationruff ianAinda não há avaliações
- Info 02-2022 - ENDocumento3 páginasInfo 02-2022 - ENjorge.88Ainda não há avaliações
- Tetris Game Report - SUN - LIDocumento11 páginasTetris Game Report - SUN - LIjianfeng sunAinda não há avaliações
- AFF A400 Systems: Installation and Setup InstructionsDocumento5 páginasAFF A400 Systems: Installation and Setup InstructionsAnton KobrinskyAinda não há avaliações
- Lifetime Support Hardware 301321Documento52 páginasLifetime Support Hardware 301321PrashantAinda não há avaliações
- Price List Special HD DVR & KitDocumento1 páginaPrice List Special HD DVR & Kitbiar berkahAinda não há avaliações
- Ees Power MibDocumento19 páginasEes Power MibRevan Faredha ApparitionAinda não há avaliações
- MPC Tutorial Odd Sem 2012Documento14 páginasMPC Tutorial Odd Sem 2012Siddharth NawaniAinda não há avaliações
- Ax2012 Enus Retail AllDocumento152 páginasAx2012 Enus Retail AlljdbcodbcAinda não há avaliações
- LA4525Documento8 páginasLA4525Antonieta Cano CruzAinda não há avaliações
- DCX 8510 4 HardwareManualDocumento156 páginasDCX 8510 4 HardwareManualSandeep ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- C9800 Module 3 Verify The Config Troubleshooting Basics and ToolsDocumento34 páginasC9800 Module 3 Verify The Config Troubleshooting Basics and ToolsGilles DellaccioAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 1: Computer: Systems DesignDocumento16 páginasLesson 1: Computer: Systems DesignChanchan LebumfacilAinda não há avaliações
- SAS - Statistical Analysis SystemDocumento34 páginasSAS - Statistical Analysis SystemureachsolutionsAinda não há avaliações
- How To Compile Porting Layer C Code For Android ClientDocumento2 páginasHow To Compile Porting Layer C Code For Android ClientAmruth AAinda não há avaliações
- How To Update Xperia M4 Aqua To Marshmallow ManuallyDocumento3 páginasHow To Update Xperia M4 Aqua To Marshmallow Manuallysiege@telkom.netAinda não há avaliações