Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Solo Flyer
Enviado por
Munnar KeralaDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Solo Flyer
Enviado por
Munnar KeralaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
What is SOLO Taxonomy? What does SOLO do?
SOLO is a model or taxonomy of learning. The SOLO model describes the structure of the learning
outcome. In this way, it makes clear to students and teachers
The SOLO model classifies students learning outcomes from
alike what the learning outcomes of an activity, unit or classroom
any activity, unit or classroom programme. Teachers and students
programme are.
can use it to easily sort learning outcomes into three levels
of knowledge: In the SOLO model, a students learning outcome may be
surface knowledge understanding at any one of five levels of complexity: no idea,
deep knowledge one idea, loose ideas, connected ideas, extended ideas.
conceptual (or constructed) knowledge.
This model works well with both descriptive (declarative
What does SOLO stand for? knowledge) and performance (functioning knowledge)
SOLO is an acronym for the Structure of the Observed learning outcomes.
Learning Outcome. Teachers can use SOLO to design differentiated learning tasks
Who developed this model of learning? and to create differentiated success criteria. They can use it with
University academics, Biggs and Collis, developed SOLO after any topic to:
researching samples of students thinking in many different plan the level of learning required for that topic
subjects (and across many different levels). assess the extent to which each student has reached that level
make decisions on next steps for learning.
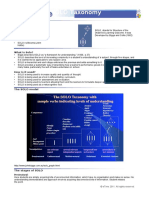
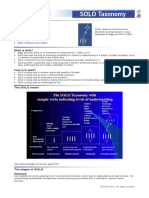
What are the five SOLO levels of understanding?
SOLO shows students learning outcomes at these five levels:
Prestructural level
The student has not yet grasped the idea and/or needs help to start.
Surface knowledge (loose ideas)
Unistructural level
The student has one relevant idea.
Multistructural level
The student has several relevant ideas.
Deep knowledge (connected ideas)
Relational level
The student has related (or linked or integrated) the ideas.
Conceptual or constructed knowledge (extended ideas)
Extended abstract level
The student has taken the related ideas and extended them.
What do people say about SOLO? How can schools, teachers and student use
In 2013 Professor John Hattie described SOLO as the most SOLO Taxonomy?
powerful model for understanding these levels and integrating Schools use SOLO as a school-wide common language of and
them into learning intentions and success criteria. for learning.
How will SOLO benefit my students? Schools, teachers and students can use SOLO anywhere learning
Teachers have found that using SOLO in the classroom is a is happening. For example, they might use it to:
powerful approach because it helps students see that their inform planning and student inquiry
learning outcomes are due to their efforts and strategies rather work out what students prior knowledge is
than luck or fixed ability. write SOLO-coded learning objectives or learning intentions
(We are learning to statements that clearly show the
My learning outcome is due to my efforts to bring in ideas,
cognitive complexity of the task)
relate ideas and or extend ideas.
co-construct success criteria for each of the SOLO levels
I used the following effective strategies to help me bring in assess and self-assess learning outcomes for declarative and
ideas, relate ideas and/or extend ideas. (SOLO Higher Order functioning knowledge
Thinking (HOT) Maps and self-assessment rubrics, thinking determine next steps (feedback and feedforward)
skills or e-learning) make decisions about how to effectively use HOT SOLO
maps, thinking skills and e-learning strategies.
In this way SOLO supports students in developing metacognition,
self-regulation, self-efficacy, engagement and resilience when How do we get SOLO working in our school?
learning. With careful planning, SOLO can be integrated as a powerful and
Using SOLO, students and teachers can give and discuss popular school-wide model of learning:
feedback more effectively. These conversations may be between: Identify evidence-based strategies that make the biggest
students and students difference to students learning outcomes.
students and teachers Introduce the model.
teachers and teachers. Describe ways of using the model to make it easier to use
effective strategies for teaching and learning.
For example, the SOLO levels help teachers and students to Suggest ideas for introducing the model to students (and for
talk about: students to introduce the model to others).
what they are doing (level of the task) Provide resources to support teachers and students as they
how well it is going (level of students achievement of the task) use the model for example, SOLO symbols, maps, self-
what students should do next (next steps for learning). assessment rubrics, learning logs, hexagons, learning intention
Why is SOLO an excellent model to use in generator, posters, stamps and stickers.
Offer professional training on how to use the model in
the classroom? teacher planning, student learning and assessment using HOT
SOLO helps students learn to learn.
SOLO maps and self-assessment rubrics.
SOLO is a blissfully simple model, moving from idea to ideas Model classroom practice using SOLO-coded learning
to relate to extend. By making the learning outcome clear, it intentions, success criteria, HOT maps, self-assessment rubrics
improves students understanding of the purpose of everything and other SOLO tools.
they do. In the classroom it is an enabler, not another add Ask for (and act on) feedback from teachers and students who
on. It enables teachers to look at what they do and measure its have explored the use of SOLO in teaching and learning.
effect on students learning outcomes. Assess progress in how teachers and students are using
SOLO as a mental model for learning and give feed-forward
SOLO is academically robust, evidence based and well
on next steps.
established. It is also highly reliable in that teachers and students
Share successes and failures that you experience when you
tend to agree on what SOLO level the students have achieved.
implement the model. (Draw on descriptions from students,
SOLO challenges students to think more deeply by giving them teachers, administrators and communities about how they have
a framework for thinking about loose ideas, connected ideas and integrated SOLO into teaching and learning.)
extended ideas. Evaluate the effect of using SOLO in the classroom in terms of
improving students learning outcomes, raising their confidence
The task and the outcome can be at different levels of SOLO.
and increasing their engagement in learning.
This means that SOLO can easily differentiate learning tasks and
Encourage teachers and students to develop new ways to use
learning outcomes for every student.
the model to enhance learning and share these with others.
SOLO is used in constructive alignment (Biggs 2003) to design
learning intentions and success criteria for Outcomes-Based Do teachers need a lot of training to use SOLO?
Education (OBE). No. The model is simple.
SOLO provides a practical framework for looking at the learning
process and learning outcomes. It is aligned to evidence-based
practice and effective pedagogies that make common sense
to teachers.
So effective teachers do not need to throw out what they do
already and adopt something new. Instead, they look at what they
do in a new way through the lens of prestructural, unistructural,
multistructural, relational and extended abstract learning outcomes.
Você também pode gostar
- SOLO AssessmentforLearning 1Documento3 páginasSOLO AssessmentforLearning 1Munnar KeralaAinda não há avaliações
- Values Based Leadership - SyllabusDocumento14 páginasValues Based Leadership - SyllabusHallie Moberg BrauerAinda não há avaliações
- Differentiated Learning Theory and Practice April 2018Documento47 páginasDifferentiated Learning Theory and Practice April 2018JordanAinda não há avaliações
- Dictionary of Sociology 1994 Marshall OxfordDocumento596 páginasDictionary of Sociology 1994 Marshall OxfordLuis BastidasAinda não há avaliações
- Solo TaxonomyDocumento2 páginasSolo TaxonomyYhang KasanAinda não há avaliações
- SAP BudgetingDocumento25 páginasSAP BudgetingMohammadGhouse50% (2)
- Learner Agency Teacher Activity SheetDocumento4 páginasLearner Agency Teacher Activity SheetfriboAinda não há avaliações
- Quality Control Volume 1Documento182 páginasQuality Control Volume 1Saravnan Rajendran100% (3)
- Tesda Info SheetDocumento6 páginasTesda Info SheetJaizery Realubit OriñaAinda não há avaliações
- Hare RD Psychopathy JAP 1991Documento14 páginasHare RD Psychopathy JAP 1991Jovana Ognenovska Bakalovska0% (1)
- Solo TaxonomyDocumento16 páginasSolo TaxonomyNishaEvie100% (1)
- Applications of Social Learning Theory in EducationDocumento4 páginasApplications of Social Learning Theory in EducationHazwan Salleh0% (2)
- CDER's Quality Management Maturity Program: Fda/Cder/Opq/OqsDocumento26 páginasCDER's Quality Management Maturity Program: Fda/Cder/Opq/OqsAmbadas RautAinda não há avaliações
- Midrex 2018 DFM4QTR Final2 PDFDocumento20 páginasMidrex 2018 DFM4QTR Final2 PDFkalaiAinda não há avaliações
- Solo Taxonomy Handout2Documento3 páginasSolo Taxonomy Handout2Ketut KemahyasaAinda não há avaliações
- Solo Taxonomy ExplainedDocumento17 páginasSolo Taxonomy Explained3alliumcourtAinda não há avaliações
- Solo Taxonomy Part ADocumento32 páginasSolo Taxonomy Part Aapi-277363391100% (2)
- Being a 21st Century Educator: Five Trends You Really Want to KnowNo EverandBeing a 21st Century Educator: Five Trends You Really Want to KnowNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Intro of SOLO TaxonomyDocumento16 páginasIntro of SOLO TaxonomyVivekAinda não há avaliações
- Learning-Focused Relationships: Lorelie C. MissionDocumento39 páginasLearning-Focused Relationships: Lorelie C. MissionMichelle Labajo MaunesAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Strategic AnalysisDocumento4 páginasWhat Is Strategic AnalysisKeith Joshua Gabiason100% (1)
- CMMI DAR Effectively Apply The Decision Analysis and Resolution (DAR) ProcessDocumento26 páginasCMMI DAR Effectively Apply The Decision Analysis and Resolution (DAR) Processjgonzalezsanz8914100% (1)
- Understanding The Enhanced PypDocumento20 páginasUnderstanding The Enhanced PypRemmuel Santiago100% (2)
- Lesson Plan - CambridgeDocumento7 páginasLesson Plan - CambridgeMunnar KeralaAinda não há avaliações
- About Solo Taxonomy by Pam Hook PDFDocumento2 páginasAbout Solo Taxonomy by Pam Hook PDFYhang KasanAinda não há avaliações
- Solo Taxonomy Edu-511 Curriculum DevelopmentDocumento11 páginasSolo Taxonomy Edu-511 Curriculum DevelopmentMuhammad Shakir MalikAinda não há avaliações
- SOLO Taxonomy: PrestructuralDocumento3 páginasSOLO Taxonomy: PrestructuralDjelisa ArapaAinda não há avaliações
- Use of SOLO Taxonomy in The Delivery of Classroom Instruction v2Documento26 páginasUse of SOLO Taxonomy in The Delivery of Classroom Instruction v2Nanette M. SansanoAinda não há avaliações
- Teaching MethodsDocumento5 páginasTeaching Methodsmitchbitch69Ainda não há avaliações
- 02-1 ASSESSMENT IN BLENDED IN LEARNING (Part 1)Documento60 páginas02-1 ASSESSMENT IN BLENDED IN LEARNING (Part 1)Fabio Jr CapitoAinda não há avaliações
- Accounting For Teaching - Chapter 01 Understanding TeachingDocumento4 páginasAccounting For Teaching - Chapter 01 Understanding TeachingAcademic StuffAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Characteristics of Effective Instruction: Friday, May 22, 2009Documento2 páginas5 Characteristics of Effective Instruction: Friday, May 22, 2009aimigdragonAinda não há avaliações
- Module 6Documento13 páginasModule 6Mark Emmanuelle AsiloAinda não há avaliações
- Creatting SLMsDocumento30 páginasCreatting SLMsDino DizonAinda não há avaliações
- Solo 1smallDocumento55 páginasSolo 1smallAnn Louise De LeonAinda não há avaliações
- Curriculum DevelopmentDocumento4 páginasCurriculum DevelopmentMerlinda CarilloAinda não há avaliações
- The Instructional Model Based On The Constructivist ApproachDocumento20 páginasThe Instructional Model Based On The Constructivist Approachjuan.bacchialAinda não há avaliações
- Solo Taxonomy Hand Out 2Documento3 páginasSolo Taxonomy Hand Out 2HONGWEN CAIAinda não há avaliações
- Differentiated Instruction PD 10-18-13Documento31 páginasDifferentiated Instruction PD 10-18-13api-253863541Ainda não há avaliações
- Edu 262 Lesson Planning Assessment Project 1Documento17 páginasEdu 262 Lesson Planning Assessment Project 1api-318145494Ainda não há avaliações
- Kulanu Torah Academy: Differentiated Instruction Developed byDocumento61 páginasKulanu Torah Academy: Differentiated Instruction Developed byColleenMaimaiChimeeAinda não há avaliações
- Udl - Tips For Developing Learning GoalsDocumento5 páginasUdl - Tips For Developing Learning Goalsapi-675699033Ainda não há avaliações
- Bloom's Taxonomy and Lesson ObjectivesDocumento14 páginasBloom's Taxonomy and Lesson ObjectivesDeanne YsabelleAinda não há avaliações
- N BPT S Self AssessmentDocumento3 páginasN BPT S Self AssessmentLidia AzouzAinda não há avaliações
- Reflective Essay F.ADocumento4 páginasReflective Essay F.AAbdelghni IdrissiAinda não há avaliações
- Con PDFDocumento109 páginasCon PDFIskola PanninéniAinda não há avaliações
- Significant Learning Worksheet - 17042023Documento5 páginasSignificant Learning Worksheet - 17042023Theresiana Debora100% (1)
- Marzano Comparison ModelDocumento3 páginasMarzano Comparison Modelapi-279800731Ainda não há avaliações
- Step 1: Proactively DesignDocumento6 páginasStep 1: Proactively DesignJordan LagayanAinda não há avaliações
- 2.3-Solo TaxonomyDocumento9 páginas2.3-Solo TaxonomyKousar YasminAinda não há avaliações
- Group Presentation ICE TaskDocumento11 páginasGroup Presentation ICE TaskSlondile VundlaAinda não há avaliações
- NbptsselfassessmentDocumento3 páginasNbptsselfassessmentapi-636979609Ainda não há avaliações
- Ep 5-fs1Documento8 páginasEp 5-fs1Jeny MontillaAinda não há avaliações
- Stradegy Based Lesson PlanDocumento9 páginasStradegy Based Lesson Planapi-667913796Ainda não há avaliações
- N BPT S Self AssessmentDocumento2 páginasN BPT S Self AssessmentMark BricenoAinda não há avaliações
- Guideline For Portfolio PreparationDocumento3 páginasGuideline For Portfolio PreparationznyingwaAinda não há avaliações
- MIHAELA BIRESCU The Concept of Visible Learning and Its Applications in Hungarian Bilingual Education PDocumento19 páginasMIHAELA BIRESCU The Concept of Visible Learning and Its Applications in Hungarian Bilingual Education PARADENSIS aradAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation 3Documento57 páginasPresentation 3api-3751911Ainda não há avaliações
- Nbptsselfassessment Julia HiserDocumento2 páginasNbptsselfassessment Julia Hiserapi-439492422Ainda não há avaliações
- Learningwalks PDFDocumento10 páginasLearningwalks PDFZulaiha MohamedAinda não há avaliações
- Samson Ipdp Sy22-23Documento2 páginasSamson Ipdp Sy22-23api-540437387Ainda não há avaliações
- Great Virtues - SEL Reflection For EducatorsDocumento2 páginasGreat Virtues - SEL Reflection For EducatorsDivya SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- NbptsselfassessmentDocumento2 páginasNbptsselfassessmentapi-464335930Ainda não há avaliações
- Barizo - Midterm Teaching EnglishDocumento28 páginasBarizo - Midterm Teaching EnglishJullianne JO OcquianaAinda não há avaliações
- TTL Group 2 Beed 3DDocumento50 páginasTTL Group 2 Beed 3DÇhřiśtïán Đąvə Łaýuğ IIAinda não há avaliações
- RandallDocumento2 páginasRandallapi-618599970Ainda não há avaliações
- Social and Emotional Learning A Dive Into Sel in An Alternative Education School 4Documento6 páginasSocial and Emotional Learning A Dive Into Sel in An Alternative Education School 4api-622511939Ainda não há avaliações
- Toolkit 3 - Formative AssessmentDocumento45 páginasToolkit 3 - Formative AssessmentComaythang5Ainda não há avaliações
- Nbptsselfassessment JasonnakonechnyDocumento3 páginasNbptsselfassessment Jasonnakonechnyapi-572999899Ainda não há avaliações
- SR Elite, Aiims S60, Neet MPL& LTC - Ic Grand Test - 9 - 01-05-19Documento24 páginasSR Elite, Aiims S60, Neet MPL& LTC - Ic Grand Test - 9 - 01-05-19Munnar KeralaAinda não há avaliações
- NIFT M.ftech Sample QuestionsDocumento7 páginasNIFT M.ftech Sample QuestionsMunnar KeralaAinda não há avaliações
- SR Elite, Aiims S60, Neet MPL& LTC - Ic Grand Test - 9 - 01-05-19Documento24 páginasSR Elite, Aiims S60, Neet MPL& LTC - Ic Grand Test - 9 - 01-05-19Munnar KeralaAinda não há avaliações
- 4C MappingDocumento24 páginas4C MappingMunnar KeralaAinda não há avaliações
- Avpss Assess 13 14uparDocumento9 páginasAvpss Assess 13 14uparMunnar KeralaAinda não há avaliações
- Fill in The Blanks For X in SocialDocumento2 páginasFill in The Blanks For X in SocialMunnar KeralaAinda não há avaliações
- Passenger BusinessDocumento6 páginasPassenger BusinessMunnar KeralaAinda não há avaliações
- Statistical Summary-Indian Railways: As On March 31 As On March 31Documento2 páginasStatistical Summary-Indian Railways: As On March 31 As On March 31Munnar KeralaAinda não há avaliações
- Data Structure & Algorithm AnalysisDocumento4 páginasData Structure & Algorithm AnalysisBadrul AminAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 7 - WorkStudyDocumento29 páginasUnit 7 - WorkStudyHarsh ChachanAinda não há avaliações
- Nomophobia A Rising Trend in StudentsDocumento4 páginasNomophobia A Rising Trend in StudentsMax AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Emotional Inteligence ScaleDocumento16 páginasEmotional Inteligence ScaleKriti ShettyAinda não há avaliações
- Advertising Structures - CI-BusinessDocumento3 páginasAdvertising Structures - CI-BusinessTerry FlewAinda não há avaliações
- 3D Surface Mapping Using Ultrasonic SensorsDocumento3 páginas3D Surface Mapping Using Ultrasonic SensorsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyAinda não há avaliações
- Wesolowski 2012dDocumento9 páginasWesolowski 2012dMelissa DanoAinda não há avaliações
- Naturalistic and Islamic Approaches To Psychology, Psychotherapy, and Religion - JF Psy of ReligionDocumento16 páginasNaturalistic and Islamic Approaches To Psychology, Psychotherapy, and Religion - JF Psy of ReligionDimas WichaksonoAinda não há avaliações
- Siregar Et Al 2020Documento15 páginasSiregar Et Al 2020UtamiAinda não há avaliações
- Qlib: An AI-oriented Quantitative Investment PlatformDocumento8 páginasQlib: An AI-oriented Quantitative Investment Platformjayeshrane2107Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7 - SPPLR Eval SelecDocumento45 páginasChapter 7 - SPPLR Eval SelecAditya parmarAinda não há avaliações
- Learning Needs and Quality Care Among Family Caregivers and Elderly Patients of Guadalupe, Cebu City, Central PhilippinesDocumento22 páginasLearning Needs and Quality Care Among Family Caregivers and Elderly Patients of Guadalupe, Cebu City, Central PhilippinesLianne VergaraAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1Documento41 páginasModule 1Paul Jean MerinoAinda não há avaliações
- Neuroeconomics 1Documento3 páginasNeuroeconomics 1mihaela irofteAinda não há avaliações
- Focus Group InterviewDocumento18 páginasFocus Group Interviewpromotion sectionAinda não há avaliações
- W10 Anova Dua HalaDocumento50 páginasW10 Anova Dua HalaAnonymous hHT0iOyQAzAinda não há avaliações
- Soldiers Heart Thesis StatementDocumento6 páginasSoldiers Heart Thesis Statementkimberlyharrisbaltimore100% (2)
- Unit - Iii: Plant Location & Plant LayoutDocumento30 páginasUnit - Iii: Plant Location & Plant LayoutVikas SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Frequency DistributionDocumento19 páginasFrequency DistributionRhaine EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Britt Research ProposalDocumento4 páginasBritt Research Proposalapi-258119727Ainda não há avaliações
- Financial Health of The Construction Industry of Pakistan - A Perspective of Major StakeholdersDocumento15 páginasFinancial Health of The Construction Industry of Pakistan - A Perspective of Major StakeholdersomerumeromerAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Literature Review For Dissertation ProposalDocumento8 páginasSample Literature Review For Dissertation ProposalWebsiteThatWillWriteAPaperForYouCanadaAinda não há avaliações