Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
98-366 Networking Fundamentals - Skills Measured
Enviado por
Alex PascuDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
98-366 Networking Fundamentals - Skills Measured
Enviado por
Alex PascuDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
98-366 Networking Fundamentals
Skills Being Measured
This exam measures your ability to accomplish the technical tasks listed below.
The percentages indicate the relative weight of each major topic area on the exam. The higher the percentage,
the more questions you are likely to see on that content area on the exam.
The information after This objective may include but is not limited to is intended to further define or scope the
objective by describing the types of skills and topics that may be tested for the objective. However, it is not an
exhaustive list of skills and topics that could be included on the exam for a given skill area. You may be tested on
other skills and topics related to the objective that are not explicitly listed here.
Understanding Network Infrastructures
Understand the concepts of Internet, intranet, and extranet.
o This objective may include but is not limited to: VPN, security zones, firewalls.
Understand local area networks (LANs).
o This objective may include but is not limited to: perimeter networks; addressing; reserved address
ranges for local use (including local loopback ip), VLANs; wired LAN and wireless LAN
Understand wide area networks (WANs).
o This objective may include but is not limited to: leased lines, dial-up, ISDN, VPN, T1, T3, E1, E3, DSL,
Cable, , etc. and their characteristics (speed, availability). Item idea: Map T1, etc to a LAN or WAN
Understand wireless networking.
o This objective may include but is not limited to: Types of wireless networking standards and their
characteristics (802.11A,B,G,N including different Ghz ranges), types of network security
(WPA/WEP/802.1X etc.), point-to-point (P2P) wireless, wireless bridging
Understand network topologies and access methods.
Understanding Network Hardware
Understand switches.
o This objective may include but is not limited to: transmission speed; number and type of ports;
number of uplinks; speed of uplinks; managed or unmanaged switches; VLAN capabilities; Layer 2 and
Layer 3 switches,, security options; hardware redundancy; support; backplane speed; switching types,
mac table;understanding capabilities of hubs vs. switches
Understand routers.
o This objective may include but is not limited to: transmission speed considerations, directly connected
routes, static routing, dynamic routing (routing protocols), default routes; routing table and how it
selects best route(s); routing table memory, NAT, software routing in Windows Server
Understand media types.
o This objective may include but is not limited to: cable types and their characteristics, including media
segment length and speed; fibre optic; twisted pair shielded or nonshielded; catxx cabling, wireless; ;
susceptibility to external interference (machinery, power cables, etc); susceptibility to electricity
(lightning), susceptibility to interception,.
Understanding Protocols and Services
Understand the OSI model.
o This objective may include but is not limited to: OSI model; TCP model; examples of devices,
protocols, applications and which OSI/TCP layer they belong to; TCP and UDP; well-known ports for
most used purposes (not necessarily Internet); packets and frames
Understand IPv4.
o This objective may include but is not limited to: subnetting; IPconfig; why use IPv6; addressing;
ipv4toipv6 tunneling protocols to ensure backwards compatibility; dual ip stack; subnetmask; gateway;
ports; packets; reserved address ranges for local use (including local loopback ip)
Understand IPv6.
o This objective may include but is not limited to: subnetting; IPconfig; why use IPv6; addressing;
ipv4toipv6 tunneling protocols to ensure backwards compatibility; dual ip stack; subnetmask; gateway;
ports; packets; reserved address ranges for local use (including local loopback ip)
Understand names resolution.
o This objective may include but is not limited to: DNS, WINS, steps in the name resolution process
Understand networking services.
o This objective may include but is not limited to: DHCP, remote access
Understand TCP/IP.
o This objective may include but is not limited to: tools, such as ping; tracert; pathping; Telnet;
IPconfig; netstat, reserved address ranges for local use (including local loopback ip); protocols
Você também pode gostar
- MTA OD 366 ExternalDocumento2 páginasMTA OD 366 ExternalSlime ManAinda não há avaliações
- MTA OD 366 ExternalDocumento2 páginasMTA OD 366 ExternalSlime ManAinda não há avaliações
- MTA OD 366 ExternalDocumento2 páginasMTA OD 366 ExternalSlime ManAinda não há avaliações
- MTA: Networking Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredDocumento3 páginasMTA: Networking Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredLuis Jesús Onsihuay AlbertoAinda não há avaliações
- Audience Description: 98-366: Networking FundamentalsDocumento3 páginasAudience Description: 98-366: Networking Fundamentalsraj kumarAinda não há avaliações
- CCST+Networking+Objective+Domain Cisco Final wCiscoLogoDocumento3 páginasCCST+Networking+Objective+Domain Cisco Final wCiscoLogoYomeroGteitoAinda não há avaliações
- Network and Data Communication Web BasisDocumento9 páginasNetwork and Data Communication Web BasisJearvi EvidorAinda não há avaliações
- DataComms Group 7 Assignment2020Documento7 páginasDataComms Group 7 Assignment2020Prince MavhuraAinda não há avaliações
- n10 005 PDFDocumento704 páginasn10 005 PDFPazAinda não há avaliações
- CompTIA Network Plus Training Kit Exam N10-005Documento704 páginasCompTIA Network Plus Training Kit Exam N10-005bibivee50% (2)
- VacancyDocumento52 páginasVacancySantosh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Networking Fundamentals: Course DescriptionDocumento4 páginasNetworking Fundamentals: Course DescriptionWahyu OhAinda não há avaliações
- 1-Introduction To Networks: The Open Systems Interconnection SpecificationsDocumento12 páginas1-Introduction To Networks: The Open Systems Interconnection Specificationsfatemeh sameniAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Networking Bootcamp: Routing, Switching And TroubleshootingNo EverandComputer Networking Bootcamp: Routing, Switching And TroubleshootingAinda não há avaliações
- Exploring The Network: Principles of NetworkingDocumento70 páginasExploring The Network: Principles of NetworkingMutmainnah ZailanAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Network Viva QuestionDocumento57 páginasComputer Network Viva QuestionNahim's kitchenAinda não há avaliações
- CHRMLDocumento17 páginasCHRMLjeffaidanterante346Ainda não há avaliações
- Lab Document Cse 312Documento74 páginasLab Document Cse 312RAKIB UDDIN CHOWDHURY 1804107Ainda não há avaliações
- Cisco Packet Tracer Implementation: Building and Configuring Networks: 1, #1No EverandCisco Packet Tracer Implementation: Building and Configuring Networks: 1, #1Ainda não há avaliações
- 5G+Essentials+1 2021Documento8 páginas5G+Essentials+1 2021sunil kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 4 - Wireless and Mobile Computing - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocumento10 páginasUnit 4 - Wireless and Mobile Computing - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inSana SheikhAinda não há avaliações
- CcnaDocumento8 páginasCcnaMd.Shahadot HossainAinda não há avaliações
- Top Network Engineer Interview Questions and Answers PDFDocumento8 páginasTop Network Engineer Interview Questions and Answers PDFAthul Bhagianath100% (1)
- Ccna Interview Questions AnswersDocumento30 páginasCcna Interview Questions AnswersMistah RoflcopterAinda não há avaliações
- SW 3/22/2010 CCNA3 Chap 7 Study Answers 1Documento6 páginasSW 3/22/2010 CCNA3 Chap 7 Study Answers 1Hien TauAinda não há avaliações
- The Secure Zone Routing Protocol (SZRP) 1Documento24 páginasThe Secure Zone Routing Protocol (SZRP) 1Kamalakar ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Local Area Networks: Essay 16Documento21 páginasLocal Area Networks: Essay 16Vishnu SatheeshAinda não há avaliações
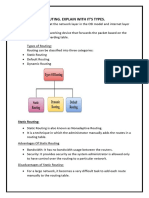
- What Is Routing. Explain With It'S TypesDocumento9 páginasWhat Is Routing. Explain With It'S TypesChaitra kharviAinda não há avaliações
- Task 9Documento17 páginasTask 9Krista Joy PetalioAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 4 - Characterizing The Existing InternetworkDocumento38 páginasLesson 4 - Characterizing The Existing Internetworkjackstone saitotiAinda não há avaliações
- TDC 562:computer Network Design & Analysis (Internet Engineering)Documento10 páginasTDC 562:computer Network Design & Analysis (Internet Engineering)serenus_hawkAinda não há avaliações
- Comet Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA)Documento6 páginasComet Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA)Sharan SakthiAinda não há avaliações
- Term Paper On Routers and SwitchesDocumento5 páginasTerm Paper On Routers and Switchesaflspfdov100% (1)
- Networking AssignmentDocumento80 páginasNetworking AssignmentSimon NdongaAinda não há avaliações
- Packet Tracer HelpDocumento938 páginasPacket Tracer Helpgolge_manAinda não há avaliações
- IoT Communication TechnologiesDocumento42 páginasIoT Communication TechnologiesdofilsenterpriseltdAinda não há avaliações
- List of ExperimentsDocumento83 páginasList of ExperimentsRocky SamuelAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment Hoang Van HiepDocumento22 páginasAssignment Hoang Van Hiephai hoangAinda não há avaliações
- 6lowpan: Overview, Assumptions, Problem Statement & GoalsDocumento17 páginas6lowpan: Overview, Assumptions, Problem Statement & GoalsnotessystemAinda não há avaliações
- 6lowpan: Overview, Assumptions, Problem Statement & GoalsDocumento17 páginas6lowpan: Overview, Assumptions, Problem Statement & GoalsNgocThanhDinhAinda não há avaliações
- 6lowpan 4Documento17 páginas6lowpan 4Yassine MalehAinda não há avaliações
- QoS Issues and Evolved 3G and Next Generation Network - v.1.010 TOCDocumento7 páginasQoS Issues and Evolved 3G and Next Generation Network - v.1.010 TOCArun DubeyAinda não há avaliações
- Cisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewNo EverandCisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (6)
- Network DesignDocumento9 páginasNetwork Designrumi noorAinda não há avaliações
- Nithish Network Consultant CVDocumento3 páginasNithish Network Consultant CVameasy findAinda não há avaliações
- Advance Networking: Outline of The CourseDocumento3 páginasAdvance Networking: Outline of The Courseअमित सिंह100% (1)
- Deploying IP and MPLS QoS for Multiservice Networks: Theory and PracticeNo EverandDeploying IP and MPLS QoS for Multiservice Networks: Theory and PracticeAinda não há avaliações
- LabSIM Network+ Guide To Networks 5th - 6thDocumento2 páginasLabSIM Network+ Guide To Networks 5th - 6thCynthia Indah FebriyantiAinda não há avaliações
- Awsn Question Bank - 2017 RegulationDocumento27 páginasAwsn Question Bank - 2017 Regulation19021Dhanush raj.NAinda não há avaliações
- Session - 2 NetworkDocumento20 páginasSession - 2 Networkmahdiyanjoo8Ainda não há avaliações
- Sample Interview Questions For Network EngineersDocumento5 páginasSample Interview Questions For Network EngineersJuma PaimanAinda não há avaliações
- IT7 - Networking 2 Module 3Documento143 páginasIT7 - Networking 2 Module 3Christian Jay CusayAinda não há avaliações
- Course Name: Internet Protocol Who Should AttendDocumento5 páginasCourse Name: Internet Protocol Who Should AttendArun KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Interview Questions and Answers For IP and PSCoreDocumento4 páginasInterview Questions and Answers For IP and PSCoreMervin MaulidiAinda não há avaliações
- Must Have IP NextGen Network ReferenceDocumento57 páginasMust Have IP NextGen Network ReferenceTower_Doc0% (1)
- Research Paper On Network Address TranslationDocumento8 páginasResearch Paper On Network Address Translationpabup1hebyl2100% (1)
- Smart City QB (Unit 4,5,6) (Atharva Garud)Documento31 páginasSmart City QB (Unit 4,5,6) (Atharva Garud)Dhruv MulaniAinda não há avaliações
- CMP2205 Computer NetworksDocumento5 páginasCMP2205 Computer NetworksNawroz ZhmanAinda não há avaliações
- 98-363 Web Development Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredDocumento3 páginas98-363 Web Development Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredAlex PascuAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 01Documento13 páginasChap 01Alex PascuAinda não há avaliações
- 98-349 Windows OS Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredDocumento3 páginas98-349 Windows OS Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredSilvia MariaAinda não há avaliações
- 98-365 Windows Server Admin Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredDocumento3 páginas98-365 Windows Server Admin Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredAlex PascuAinda não há avaliações
- 98-349 Windows OS Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredDocumento3 páginas98-349 Windows OS Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredSilvia MariaAinda não há avaliações
- 98-365 Windows Server Admin Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredDocumento3 páginas98-365 Windows Server Admin Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredAlex PascuAinda não há avaliações
- 98-363 Web Development Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredDocumento3 páginas98-363 Web Development Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredAlex PascuAinda não há avaliações
- 98-375 HTML5 Application Development Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredDocumento2 páginas98-375 HTML5 Application Development Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredAlex PascuAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Electromagnetics With Matlab - Lonngren & SavovDocumento699 páginasFundamentals of Electromagnetics With Matlab - Lonngren & SavovFirass Mckey100% (1)
- 98-361 Software Development Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredDocumento2 páginas98-361 Software Development Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredAlex PascuAinda não há avaliações
- 98-372 Microsoft .NET Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredDocumento3 páginas98-372 Microsoft .NET Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredAlex PascuAinda não há avaliações
- 98-367 Security Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredDocumento2 páginas98-367 Security Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredAlex PascuAinda não há avaliações
- 98 365 Study GuideDocumento65 páginas98 365 Study Guideumkamal10Ainda não há avaliações
- 98-374 Gaming Development Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredDocumento2 páginas98-374 Gaming Development Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredAlex PascuAinda não há avaliações
- Student Study Guide: Networking FundamentalsDocumento59 páginasStudent Study Guide: Networking FundamentalsDanielaMuhajAinda não há avaliações
- Curs 03Documento59 páginasCurs 03Alex PascuAinda não há avaliações
- Allan Carr - in Sfarsit NefumatorDocumento183 páginasAllan Carr - in Sfarsit NefumatorDragosAinda não há avaliações
- DP LAN Realtek 14036 DriversDocumento5.119 páginasDP LAN Realtek 14036 Driverss npAinda não há avaliações
- AFL QRG Fiber ManagementDocumento16 páginasAFL QRG Fiber ManagementLasanthaAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Data Sheet Nokia 7368 ISAM ONT G-240G-C For POLDocumento3 páginas1 Data Sheet Nokia 7368 ISAM ONT G-240G-C For POLMatthewtongAinda não há avaliações
- Reference Guide To Fiber Optics: The Fiber Optic Association, IncDocumento2 páginasReference Guide To Fiber Optics: The Fiber Optic Association, IncShantanu BiswasAinda não há avaliações
- DATACOM Multiple Choice Question 6Documento1 páginaDATACOM Multiple Choice Question 6girijamohapatraAinda não há avaliações
- Manual 1662Documento123 páginasManual 1662Matt BubaAinda não há avaliações
- Cross Over CablingDocumento26 páginasCross Over CablingRea TevesAinda não há avaliações
- Key Specs For Paloalto Interface TransceiversDocumento6 páginasKey Specs For Paloalto Interface TransceiversEloi Sabach SinagaAinda não há avaliações
- 1-Introduction To CiTRANS R800 Series - OTN DevicesDocumento26 páginas1-Introduction To CiTRANS R800 Series - OTN DevicesMel-jr ValenciaAinda não há avaliações
- Odu & OtuDocumento5 páginasOdu & OtuAjay BarwalAinda não há avaliações
- SEE Factory: Item Part No. Description QtyDocumento3 páginasSEE Factory: Item Part No. Description Qtykhuram183Ainda não há avaliações
- Jdsu Bert & RFC 2544 TestingDocumento13 páginasJdsu Bert & RFC 2544 TestingRaviAinda não há avaliações
- CIS 81 Fundamentals of Networking Chapter 5: Ethernet Part 2 of 2Documento88 páginasCIS 81 Fundamentals of Networking Chapter 5: Ethernet Part 2 of 2amgstiAinda não há avaliações
- Configuring VPC Virtual Port Channel With Cisco Nexus: Lab TopologyDocumento8 páginasConfiguring VPC Virtual Port Channel With Cisco Nexus: Lab TopologyKevin SAinda não há avaliações
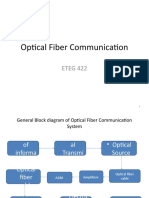
- Optical Fiber Communication: ETEG 422Documento38 páginasOptical Fiber Communication: ETEG 422subashAinda não há avaliações
- CRR 718 BenDocumento66 páginasCRR 718 BenOsama OkokAinda não há avaliações
- Tac03001-Ho04-i1.6-7302 7330 Isam Product Overview FDDocumento79 páginasTac03001-Ho04-i1.6-7302 7330 Isam Product Overview FDNathaly100% (1)
- Ds t8604 56284 en 1402 Hi PDFDocumento2 páginasDs t8604 56284 en 1402 Hi PDFMohamed Abou El hassanAinda não há avaliações
- OptiX OSN 550 Hardware Description (V100R006)Documento321 páginasOptiX OSN 550 Hardware Description (V100R006)Thunder-Link.com100% (4)
- Client ListDocumento32 páginasClient Listtariq96103Ainda não há avaliações
- Basic Private VLAN ConfigurationDocumento5 páginasBasic Private VLAN ConfigurationbbraganzaAinda não há avaliações
- ADSL PresentationDocumento18 páginasADSL PresentationskanshahAinda não há avaliações
- GSM Network ArchitectureDocumento11 páginasGSM Network ArchitectureYe YintAinda não há avaliações
- SDH Pocket GuideDocumento90 páginasSDH Pocket GuidekmnavinAinda não há avaliações
- 336 Data Entry Tma 12th PaperDocumento5 páginas336 Data Entry Tma 12th PaperFaran AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Underlying TechnologiesDocumento49 páginas3 Underlying TechnologiesTutun JuhanaAinda não há avaliações
- ALC+2 Training SlideDocumento128 páginasALC+2 Training SlideMariappan Letchumanan50% (2)
- Exampdf: Higher Quality, Better Service!Documento8 páginasExampdf: Higher Quality, Better Service!Marcio KatanAinda não há avaliações
- 6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs InstructionsDocumento3 páginas6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs InstructionsKietumetse Tsimane100% (1)
- G709otntutor WP Tfs TM Ae PDFDocumento12 páginasG709otntutor WP Tfs TM Ae PDFAjay BarwalAinda não há avaliações