Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
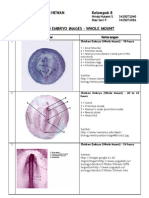
10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology Lab
Enviado por
Ivy CruzDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology Lab
Enviado por
Ivy CruzDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
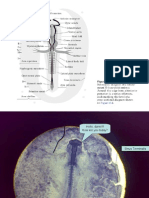
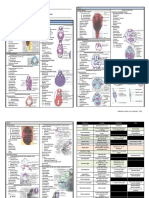
10mm Frog Embryo Jacobsons organ
- Saccular structure fromed by the evagination of the nasal
Whole Mount organ
Same as the 7mm frog. - Function in picking up the smell of food from the buccal
region
Transverse section Syn: vomeronasal organ
Level of the Telencephalon and Olfactory Organs Buccal cavity
- Region where the nasal cavity and mouth opens
Telencephalon - Lined with epithelium and is derived from stomodeum
- Anterior division of the prosencephalon - Jaws are tipped with many horny material and tooth germs
- Paired and each unit is roughly hemispherical but flattened at this region
at the midline - External to the jaws are lobose structures called the oral
- Each contains a cavity, known as the lateral ventricle papillae
formed by the evagination of the side of the neural tube at
the anterior end of the neurocoel Prechordal cartilage
- Hyaline cartilages beneath the telencephalon which will
Layers of brain under HPO: form the cartilaginous cranium called the chondocranium
- Ependymal layer Syn: trabecular cartilage
One cell thick, ciliated layer immediately
Melanocytes
surrounding the neurocoel
- Stellate cells scattered over the dorsolateral region of the
Cilia aid in the movement of the cerebrospinal
brain and lateral to the nasal organs
fluid in the ventricles of the brain and in the
- Fine granules of melanin (light brown individually; black in
central canal of the spinal cord
aggregate)
- Mantle layer
Broad layer adjacent to the ependymal layer Mesenchyme
Form: gray matter of the central nervous system - Stellate , mesodermal cells filling up the space between the
- Marginal layer organs and the epidermis
Outermost layer - Form a loose reticulum with the outermost cells forming
Contains neuroblast from the inner layers and the dermis of the integument
nerve fibers
Form: white matter of the central nervous Epidermis
system - Outer layer of the skin composed of two strata of
ectodermal cells
Nasal Organ Free melanin granules and melanocytes can be seen here
- Found at the region of the telencephalon and lying ventral under the HPO
to it
- Formed by the invagination of the ectoderm
The olfactory nerve connecting the olfactory lobes to the brain
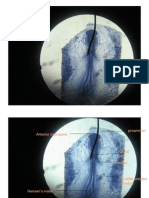
Level of the Diencephalon and the eye
arises from the olfactory epithelium.
Syn: olfactory organ Diencephalon
- Posterior subdivision of the prosencephalon that is
External naris
ventrally elongated and possesses a cavity called the III
- Opening of the nasal cavity to the outside
ventricle
- Marks the point of the original ectodermal invagination
Ifundibulum
Internal naris
- Funnel-like evagination of the diencephalic floor
- Opening of the nasal cavity into the buccal region
- Subsequently evaginatates the posterior or neural tube of
Syn: choana
the pituitary together with the stomodeum
Frontal organ In the more posterior sections of the diencephalons, this is
seen as a smaller, ventral component of the diencephalon
- Structure arises as an evagination of the diencephalic roof with thin roof and thick sides.
together with the epiphysis
- Beneath the epidermis, it migrates forward from the region Mesencephalon
of the diencephalon to the region of the telencephalon. - Middle region of the brain dorsal to the diencephalons
- Contains photoreceptors and may function as a third eye - Bears the 3rd and 4th cranial nerves
- Possesses a cavity known as the cerebral aqueduct
Pituitary body Hypobranchial cartilages
- Long masses of cartilages under the floor of the foregut
- Oval mass beneath the thin floor of the infundibulum that make up parts of the visceral skeleton and support
- Endocrine gland derived from the infundibulum and a solid the pharynx
ingrowth from the stomodeum Thyroid
If tracing is continued posteriorly, the hypophysis - A pair of small endocrine bodies associated with the
disappears and the tip of the notochord, flanked by pharynx located beneath the hypobranchial cartilages
parachordal cartilages will be seen.
Syn: hypophysis Skeletal muscle
- Mesodermal masses lying on the lateral and ventral side of
Eye the pharynx
Optic cup
Layers of the optic cup: Oral suckers
- Retina - A pair of glandular structures
Thick inner layer of the optic cup - Composed of elongated columnar cells
Differentiated into the following layers: - Ventral surface of the tadpole that produce a sticky slime
o Layer of ganglian cells (innermost for attachment to floating objects
sublayer of the retina) Syn: cementglands, mucous glands, adhesive glands
The axons of the nerve cells in this
sublayer form the optic nerve. The
region where the optic nerves cross in Level of the Myelencephalon and Auditory vesicle
the floor of the diencephalon is known
as the optic chiasma. Myelencephalon
o Layer of the bipolar neurons - Most posterior region of the brain with a thick floor (basal
Middle layer of cells that will synapse plates)
the receptor and the ganglian cells. - In later development, its thin roof becomes vascularized to
o Rods and cones Form: posterior choroids plexus
Outermost sublayer of the retina - Cavity is the IV ventricle
where the photoreceptoral process is
Auditory vesicle
formed.
- A completely closed hallow organ on each side of the
Pigmented epithelium medulla
- outer wall of the optic cup formed from the medial half of - Endolymmphatic duct
the optic vesicle Thick-walled tube between the medulla and the
Forms: iris of the eye ear vesicle
Marks the course of the invagination of the
Lens auditory vesicle from the ectoderm
- spherical body, partly enclosed by the optic cup - Utriculus
- formed by the thickenings of the inner wall of the lens
Large dorsal chamber of the ear vesicle
vesicle
- Semicircular canals
- Lens epithelium
The three mutually perpendicular folds of the
One-cell thick outer layer
auditory vesicle that is observed in older
- Lens fibers
specimens
Columnar cells at the core of the lens that will
The sensory epithelium is represented here by
later become long fibers arranged in layers
the thickened horizontal canal
Cornea - Sacculus
- Superficial covering of the eye formed by an assembly of Ill-defined ventral chamber of the auditory
ectodermal and mesodermal cells between the ectoderm vesicle
and the lens Forms: lagena in lower vertebrates
Forms: cochlea in higher vertebrates
Choroid and sclera
- Outer investments of the optic cup Auditory capsule
- At this stage of development, they are represented by the - Mesenchymal cells surrounding the auditory vesicle that
mesodermal cells aggregating outside the pigmented will form the cartilaginous ear capsule that surrounds and
epithelium. protects the inner ear
Pharynx Auditory ganglion
- Broad gut at this level which is lined by endodermal cells - Mass of nerve cells on the medial side of the auditory
vesicle
Syn: acoustic ganglion
Notochord - Trigeminal ganglion (V)
A larger mass of nerve cells bodies anterior and
- Round structure originating from mesoderm dorsal to the acoustico-facialis ganglion
- Lying dorsal to the gut and ventral to the hindbrain Syn: semilunar ganglion
- Defines the anterior/posterior axis in the developing - Glossopharyngeal ganglion
embryo
External wall of the opercular cavity formed by a
- Provides skeletal support during early development
body fold
Mesenchymal cells of the notochord
Metencephalon
Form: notochordal sheath
- Anterior subdivision of the rhombencephalon
Parachordals - Lies behind the optic lobes and medial to the V ganglion
- Cartilages flanking the notochord on each side
Heart Level of the Pronephros and first spinal ganglion
- a lightly coiled tube twisted to the right
Spinal cord
Pericardial cavity - Derived from the posterior region of the neural tube
- chamber enclosing the hear
Neural Canal
Conus arteriosus - The cavity that is laterally compressed by the thick lateral
- most anterior region of the heart walls of the spinal cord
- connects the ventricle with the ventral aorta - Ependymal cells that line the central canal possess cilia
Syn: bulbus cordis and pigment granules
Syn: central canal
Ventricle
- heart chamber that receives blood from the sinus venosus Gray matter
and delivers it to the ventricle - Inner layer of the spinal cord close to the ependymal
- Composed of a compact mass of neuroblast and neuroglia
Atrium
- dorsal, thin-walled chamber that receives blood from the White matter
sinus venosus and delivers it to the ventricle - Peripheral layer of the spinal cord containing the axons of
the neurons in the gray matter
Sinus venosus
- most posterior chamber lying on the right, anterior to the Meninges
liver - Membranous covering of the central nervous system
- receives the venous blood and delivers it to the atrium which begins to form at this developmental stage
Opercular cavity First spinal ganglia
- paired chamber continuous with the gut and lying on each - Masses of nerve cell bodies ventrolateral to the spinal cord
side of the heart
Myotomes
- contains the internal gills with branchial blood vessels
- Thickened primordia of skeletal muscles on each side of
Syn: gill chamber
the notochord
Dorsal aorta - Skeletal muscle fibers are arranged longitudinally
- blood vessel located above each gill chamber
Pleroperitineal cavity
Aortic arches - Coelomic cavity containing the viscera except the heart
- blood vessels lying within the branchial arches and - The pleural cavity that contains the lungs and the
encircling the pharynx peritoneal cavity that contains the digestive organs,
- connect the dorsal aorta with the ventral aorta associated glands, kidney, and reproductive organs are still
The aortic arches that are involved are 3-6 because they continuous.
are gill bearing.
Esophagus
Ganglia - Tubular organ with folded mucosal lining located below
- Facial ganglion (VII) the notochord
Large mass of nerve cell bodies Dorsal aorta
Anterior to the auditory ganglion - Paired blood vessel between the notochord and the
Acoustico-facialis ganglion body arising from esophagus
the fusion of the facial and auditory ganglia - Fuse into a single blood vessel posteriorly
Syn: geniculate ganglion
Pronephros
- Paired excretory organs that arise from the nephrotome
- Located at the ventrolateral region of the body cavity
Pronephric tubules
- Ducts of the pronephros lined by cuboidal epithelium
Posterior cardinal veins
- Blood vessels within the pronephros and supplies the
latter with blood
Nephrostome
- Opening of the pronephric tubules into the coelom
Nephric duct
- Lone duct that can be observed at the most caudal section
of the pronephros
- Moves medially and eventually joins the cloaca where it
empties its contents
Glomus
- Two triangular shaped strucutres
- Seen ventrally to the dorsal aorta that hang down into the
coelomic cavity
- Tufts of small blood vessels surrounded on their lateral
and ventral surfaces by the thin wall of coelom
- Glomi are functional components of the pronephric kidney
- Waste products from the blood diffuse from the glomi into
the coelomic fluid
Stomach
- Posterior continuation of the esophagus with folded lining
and thick muscular walls
- Evaginations of the endodermal lining form the rudiments
of the gastric glands
Duodenum
- Region of the gut between the pyloric end of the stomach
and the intestine
- Represented here in the upper right corner of the body
cavity
Intestine
- Located posterior to the duodenum and is filled with the
abundant yolk platelets
Liver
- Highly vascularized and enlarged organ to the right of the
midline
- Spaces in it are called sinusoids
Gall bladder
- Once-cell thick, large vesicle associated with the liver
Bile duct
- Thick-walled tube that appears in place of the gallbladder
Pancreas
- Large organ within the curvature of the stomach
- Located to the right of the liver and bile duct
- Identified by the presence of the nest of cells (alveoli)
surrounding small ducts
Você também pode gostar
- Porges-2003-The Polyvagal Theory-Phylogenetic Contributions To Social BehaviorDocumento11 páginasPorges-2003-The Polyvagal Theory-Phylogenetic Contributions To Social BehaviorJohn Bakalis100% (1)
- Chick Embryo 72 HoursDocumento48 páginasChick Embryo 72 HoursogheeluvAinda não há avaliações
- The 4x4 Matrix Guide to Addressing Stability/Motor Control DysfunctionDocumento23 páginasThe 4x4 Matrix Guide to Addressing Stability/Motor Control Dysfunctionpfi_jenAinda não há avaliações
- Chick Embryo (Embryology Lab)Documento9 páginasChick Embryo (Embryology Lab)humanupgrade100% (1)
- Vascular Complication of Injectable FillerDocumento17 páginasVascular Complication of Injectable Fillerahmed100% (1)
- 33 Hour Embryo Sections and Labeled DiagramsDocumento24 páginas33 Hour Embryo Sections and Labeled Diagramsnabilalk100% (1)
- 10 MM Transverse Section Level of Telencephalon and Olfactory OrgansDocumento9 páginas10 MM Transverse Section Level of Telencephalon and Olfactory OrgansMarina of The SeaAinda não há avaliações
- Dumaguit (2021)Documento12 páginasDumaguit (2021)Dimple May Gianne DumaguitAinda não há avaliações
- 33-Hour Chick ReviewerDocumento5 páginas33-Hour Chick ReviewerBeatriceAinda não há avaliações
- 7 MM Frog DevelopmentDocumento28 páginas7 MM Frog DevelopmentaemilianneAinda não há avaliações
- 48hr and 72hr Chick EmbryoDocumento28 páginas48hr and 72hr Chick EmbryoRichelle IgnacioAinda não há avaliações
- How Do Organisms Reproduce PDFDocumento25 páginasHow Do Organisms Reproduce PDFBala VisaAinda não há avaliações
- 48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFDocumento5 páginas48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFSheanna May FuriaAinda não há avaliações
- 7 MM FrogDocumento28 páginas7 MM FrogNiki Reroll04Ainda não há avaliações
- Embryo Lab: 72 HR Chick ReviwerDocumento7 páginasEmbryo Lab: 72 HR Chick ReviwerGail AmuraoAinda não há avaliações
- Frog EmbryosDocumento43 páginasFrog EmbryosNics Martinez100% (7)
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsAinda não há avaliações
- 10mm Frog TadpoleDocumento30 páginas10mm Frog TadpoleSarah Margaret Chong33% (3)
- 48 96 Hour Chick Embryo Wholoe Mount and Serial Sections EmbryologyDocumento34 páginas48 96 Hour Chick Embryo Wholoe Mount and Serial Sections EmbryologyChristalie Bea Fernandez100% (2)
- 72-HR ChickDocumento16 páginas72-HR Chick411452123100% (1)
- 4Mm Frog Embryo: Lab Exercise 4 OrganogenesisDocumento16 páginas4Mm Frog Embryo: Lab Exercise 4 OrganogenesisDimple May Gianne DumaguitAinda não há avaliações
- Chick 48 HRDocumento50 páginasChick 48 HRaa628Ainda não há avaliações
- Activity No. 7 The Frog EmbryoDocumento13 páginasActivity No. 7 The Frog EmbryoFerhaeeza KalayakanAinda não há avaliações
- Chick Embryo ImagesDocumento19 páginasChick Embryo ImagesnesyaAinda não há avaliações
- Exercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmDocumento23 páginasExercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmrexartooz95% (19)
- 72 HR ReviewerDocumento8 páginas72 HR ReviewerAstrid AmadorAinda não há avaliações
- Chick Serial SectionsDocumento74 páginasChick Serial SectionsKazuki FuchoinAinda não há avaliações
- EmbryoLab 10mm FrogDocumento13 páginasEmbryoLab 10mm FrogpauAinda não há avaliações
- 48-Hour Chick ReviewerDocumento5 páginas48-Hour Chick ReviewerBeatrice100% (1)
- 24-Hr Chick: Structure Description FateDocumento18 páginas24-Hr Chick: Structure Description FateDimple May Gianne DumaguitAinda não há avaliações
- 48 Hour Chick Embryo Serial SectionsDocumento22 páginas48 Hour Chick Embryo Serial SectionsNathan Bantayan100% (1)
- 4 MM FrogDocumento5 páginas4 MM FrogMarina of The SeaAinda não há avaliações
- Embryo Lab Org 2Documento14 páginasEmbryo Lab Org 2pauAinda não há avaliações
- Serial Sections of a 10 mm Pig EmbryoDocumento16 páginasSerial Sections of a 10 mm Pig EmbryoMichaela Faye100% (1)
- Chick 33 HRDocumento14 páginasChick 33 HRaa628Ainda não há avaliações
- 24 Hour Chick EmbryoDocumento27 páginas24 Hour Chick Embryoaa6280% (1)
- Exercise 8 Pig Embryo (Posterior Sections)Documento16 páginasExercise 8 Pig Embryo (Posterior Sections)Gail AmuraoAinda não há avaliações
- Early Chick Embryo Development StagesDocumento74 páginasEarly Chick Embryo Development StagesMinette EmmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- Development of Frog EmbryoDocumento13 páginasDevelopment of Frog EmbryoNexieAinda não há avaliações
- 48 Hour Chick LabelledDocumento89 páginas48 Hour Chick LabelledSasha Gutierrez100% (1)
- Mitochondria and Golgi in Adipose CellsDocumento3 páginasMitochondria and Golgi in Adipose CellsIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Chick 72 HR DDocumento35 páginasChick 72 HR Daa628Ainda não há avaliações
- Atlas of Complex OrthodonticsDocumento564 páginasAtlas of Complex OrthodonticsHanh Pham90% (10)
- Blood Transfusion GuideDocumento92 páginasBlood Transfusion GuideCaroline TupanAinda não há avaliações
- 24-Hr Chick EmbryoDocumento8 páginas24-Hr Chick EmbryopauAinda não há avaliações
- BennGottfried - 1912 Morgue - Exverse Gedichte PDFDocumento15 páginasBennGottfried - 1912 Morgue - Exverse Gedichte PDFMario José Cervantes MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- DEVELOPMENT OF PIG EMBRYODocumento4 páginasDEVELOPMENT OF PIG EMBRYOAstrid AmadorAinda não há avaliações
- The Catholic Social Teachings is reputed as the ChurchÕs Best Kept SecretDocumento3 páginasThe Catholic Social Teachings is reputed as the ChurchÕs Best Kept SecretIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Pig Embryo Development StagesDocumento12 páginasPig Embryo Development StagesKarmina SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Ronica Black - DeeperDocumento149 páginasRonica Black - DeeperV100% (1)
- 4mm Frog EmbryoDocumento3 páginas4mm Frog EmbryoIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Embryo Lab Exercise 4Documento17 páginasEmbryo Lab Exercise 4Karmina SantosAinda não há avaliações
- 24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabDocumento3 páginas24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabIvy Cruz50% (2)
- 7mm Frog Embryo - EMBLabDocumento3 páginas7mm Frog Embryo - EMBLabIvy Cruz100% (1)
- ANIMAL GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT: The Tadpole (External Gill Stage)Documento6 páginasANIMAL GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT: The Tadpole (External Gill Stage)Junko TsukudaAinda não há avaliações
- 33 hour Chick Embryo Development StagesDocumento36 páginas33 hour Chick Embryo Development StagesSasha GutierrezAinda não há avaliações
- Ex4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoDocumento14 páginasEx4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoNexie100% (1)
- 7 MM Frog EmbryoDocumento20 páginas7 MM Frog EmbryoCourtneyAinda não há avaliações
- Chick Embryo WMDocumento6 páginasChick Embryo WMdhyan_ajjah67% (3)
- Exercise 17 Serial Transverse Section of A 33 Hour Chick Embryo PDFDocumento4 páginasExercise 17 Serial Transverse Section of A 33 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela FayeAinda não há avaliações
- 24hr Chick Cross SectionsDocumento16 páginas24hr Chick Cross Sectionsaa628100% (9)
- Biology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 2: Embryology of Frog & ChickDocumento9 páginasBiology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 2: Embryology of Frog & ChickPunk Midget-FairyAinda não há avaliações
- Exp 2 4.1 1Documento11 páginasExp 2 4.1 1Carlo MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- 18 Hour Chick EmbryoDocumento7 páginas18 Hour Chick Embryoaa628100% (2)
- Exercise 21 Serial Transverse Section of A 72 Hour Chick Embryo PDFDocumento8 páginasExercise 21 Serial Transverse Section of A 72 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela FayeAinda não há avaliações
- 33.48,72 From 2011Documento63 páginas33.48,72 From 2011aa628Ainda não há avaliações
- 72 HrsDocumento35 páginas72 HrsChristalie Bea FernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Development of the pig embryo anterior regionsDocumento11 páginasDevelopment of the pig embryo anterior regionsvada_soAinda não há avaliações
- 33-Hour Chick Development StagesDocumento5 páginas33-Hour Chick Development StagesJedd VirgoAinda não há avaliações
- Nervous + Animal DiversityDocumento7 páginasNervous + Animal DiversityMaisonette MichAinda não há avaliações
- CH 10 MusclesDocumento5 páginasCH 10 MusclesIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Botany ReviewerDocumento23 páginasBotany ReviewerIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Evolution and Diversity of Woody and Seed Plants: Chapter 5 on LignophytesDocumento1 páginaEvolution and Diversity of Woody and Seed Plants: Chapter 5 on LignophytesIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- 7mm Frog Embryo - EMBLabDocumento3 páginas7mm Frog Embryo - EMBLabIvy Cruz100% (1)
- Evolution and Diversity of Woody and Seed Plants: Chapter 5 on LignophytesDocumento1 páginaEvolution and Diversity of Woody and Seed Plants: Chapter 5 on LignophytesIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Exercise 1 - Embryology LabDocumento7 páginasExercise 1 - Embryology LabIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Chordates TaxaDocumento1 páginaChordates TaxaIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Love, Loss and Life's Deepest QuestionsDocumento3 páginasLove, Loss and Life's Deepest QuestionsIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- 24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabDocumento3 páginas24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabIvy Cruz50% (2)
- Muscular System Comparative Anatomy LabDocumento2 páginasMuscular System Comparative Anatomy LabIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- 4mm Frog EmbryoDocumento3 páginas4mm Frog EmbryoIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Abdominis Contract To Actively Aid ExhalationDocumento4 páginasAbdominis Contract To Actively Aid ExhalationIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- 4mm Frog EmbryoDocumento3 páginas4mm Frog EmbryoIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Exercise 3 - Embryology LabDocumento3 páginasExercise 3 - Embryology LabIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Exercise 2 - Embryology LabDocumento2 páginasExercise 2 - Embryology LabIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Histo 1st ShiftDocumento25 páginasHisto 1st ShiftIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Acd 4 Arm and Cubital FossaDocumento32 páginasAcd 4 Arm and Cubital FossaIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Abdominis Contract To Actively Aid ExhalationDocumento4 páginasAbdominis Contract To Actively Aid ExhalationIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory Sytem of The CatDocumento3 páginasCirculatory Sytem of The CatIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- 2017 Year at A Glance PDFDocumento1 página2017 Year at A Glance PDFtoanomisAinda não há avaliações
- Gymnosperm TaxaDocumento1 páginaGymnosperm TaxaIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Kingdom ProtozoaDocumento3 páginasKingdom ProtozoaIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- CPPI Presentation Borres Et Al.Documento19 páginasCPPI Presentation Borres Et Al.Ivy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Phylum Chordata TaxonomyDocumento1 páginaPhylum Chordata TaxonomyIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Bryophytes Taxonomy ReviewerDocumento1 páginaBryophytes Taxonomy ReviewerIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Ana Chem Lab NotesDocumento2 páginasAna Chem Lab NotesIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Legend: Phylum - Violet Class - Blue Subclass - Green Order - Red Family - Orange Genus - Yellow Species - PinkDocumento1 páginaLegend: Phylum - Violet Class - Blue Subclass - Green Order - Red Family - Orange Genus - Yellow Species - PinkIvy CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Vegeta To Overcome ConstipationDocumento11 páginasVegeta To Overcome ConstipationLucia Ida Ayu KristianaAinda não há avaliações
- Https Examinationservices - Nic.in Examsys22part2 Downloadadmitcard AdmitCardKVS - AspxDocumento1 páginaHttps Examinationservices - Nic.in Examsys22part2 Downloadadmitcard AdmitCardKVS - AspxReema SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Hypoxic Encephalopathy Secondary To Status Epilepticus Secondary To Central Nervous System InfectionDocumento158 páginasHypoxic Encephalopathy Secondary To Status Epilepticus Secondary To Central Nervous System Infectionallexiscampaner100% (1)
- Science 6Documento13 páginasScience 6Aris VillancioAinda não há avaliações
- Australia & New Zealand Collector's Guide AnimalsDocumento16 páginasAustralia & New Zealand Collector's Guide AnimalscastropereiraAinda não há avaliações
- Annual Plan Bio f5.2.0Documento3 páginasAnnual Plan Bio f5.2.0Khairul Anwar ZakariaAinda não há avaliações
- Protists: By: Harrison DempseyDocumento8 páginasProtists: By: Harrison DempseyharrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Dengue Fever Nursing Care PlansDocumento6 páginasDengue Fever Nursing Care PlansHikaru TakishimaAinda não há avaliações
- A Laboratory based study on the Larvicidal effects of Aquatain, a Monomolecular Film and Mousticide™ [Trypsin Modulating Oostatic Factor [TMOF-Bti] formulation for the control of Aedes albopictus (Skuse) and Culex quinquefasciatus Say in PakistanDocumento6 páginasA Laboratory based study on the Larvicidal effects of Aquatain, a Monomolecular Film and Mousticide™ [Trypsin Modulating Oostatic Factor [TMOF-Bti] formulation for the control of Aedes albopictus (Skuse) and Culex quinquefasciatus Say in PakistanRizwan AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Benefits and risks of genetically engineered animals for researchDocumento7 páginasBenefits and risks of genetically engineered animals for researchUthaya Kumar RajendranAinda não há avaliações
- Standard Edgewise Technique: First Order BendsDocumento45 páginasStandard Edgewise Technique: First Order BendsAgia Tessa AndrianiAinda não há avaliações
- List of Latin Words With English Derivatives - WikipediaDocumento128 páginasList of Latin Words With English Derivatives - WikipediaKokAinda não há avaliações
- B.L.I.S.T.T Health Declaration Form: Baguio - La Trinidad - Itogon - Sablan - Tuba - TublayDocumento1 páginaB.L.I.S.T.T Health Declaration Form: Baguio - La Trinidad - Itogon - Sablan - Tuba - TublayIsaias IsaiasAinda não há avaliações
- Global Market For Astaxanthin - Natural and Synthetic 2017 To 2024Documento5 páginasGlobal Market For Astaxanthin - Natural and Synthetic 2017 To 2024Industry Experts, Inc.Ainda não há avaliações
- Fluids Electrolytes BalanceDocumento21 páginasFluids Electrolytes BalancemonmonAinda não há avaliações
- Case Report on Right Knee FuruncleDocumento47 páginasCase Report on Right Knee Furuncle馮宥忻Ainda não há avaliações
- 3b. Connective Tissue 228Documento15 páginas3b. Connective Tissue 228Musharaf RehmanAinda não há avaliações
- SAFE520bP - Injury ReportDocumento1 páginaSAFE520bP - Injury ReportMiracle DavidAinda não há avaliações
- Hoagland - Courage of TurtlesDocumento6 páginasHoagland - Courage of TurtlesAlexander JorgensenAinda não há avaliações
- Artificial InseminationDocumento19 páginasArtificial InseminationDonna Lei G. RosarioAinda não há avaliações
- Human reproduction self-assessment questionsDocumento2 páginasHuman reproduction self-assessment questionsEdyWidjajaAinda não há avaliações
- World Issues - Vaccine Preventable Diseases - EssayDocumento3 páginasWorld Issues - Vaccine Preventable Diseases - EssaymikaylaAinda não há avaliações



























































































![A Laboratory based study on the Larvicidal effects of Aquatain, a Monomolecular Film and Mousticide™ [Trypsin Modulating Oostatic Factor [TMOF-Bti] formulation for the control of Aedes albopictus (Skuse) and Culex quinquefasciatus Say in Pakistan](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/362668767/149x198/6b2579b410/1509011381?v=1)












