Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Sorafenib Chu
Enviado por
TowhidulIslamDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Sorafenib Chu
Enviado por
TowhidulIslamDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Sorafenib
Trade Names
Nexavar, BAY 43-9006
Classification
Signal transduction inhibitor
Category
Chemotherapy drug
Drug Manufacturer
Bayer and Onyx
Mechanism of Action
Inhibits multiple receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), some of which
are involved in tumor growth, tumor angiogenesis, and metastasis.
Potent inhibitor of intracellular kinases, including c-Raf and wild-
type and mutant B-Raf.
Targets vascular endothelial growth factor receptors, VEGF-R2 and
VEGF-R3, and platelet-derived growth factor receptor- (PDGFR-),
and in so doing, inhibits angiogenesis.
Mechanism of Resistance
None well characterized to date.
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed after an oral dose with peak plasma levels achieved
within 2 to 7 hours. Oral administration should be without food at least
1 hour before or 2 hours after eating, as food with a high fat content reduces
oral bioavailability by up to 29%.
Chemotherapeutic and Biologic Drugs 387
S
Distribution
Extensive binding (99%) to plasma proteins. Steady-state drug concentra-
tions are reached in 7 days.
Metabolism
Metabolized in the liver primarily by CYP3A4 microsomal enzymes and
by glucuronidation mediated by UGT1A9. Parent drug accounts for
70%85% at steady state, while the pyridine-N-oxide metabolite, which has
similar biological activity to sorafenib, accounts for 9%16%. Elimination is
hepatic with excretion in feces (,77%), with renal elimination of the gluc-
uronidated metabolites accounting for 19% of the administered dose. The
terminal half-life of sorafenib is approximately 25 to 48 hours.
Indications
1. FDA-approved for the treatment of advanced renal cell cancer.
2. FDA-approved for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular
cancer (HCC).
Dosage Range
Recommended dose is 400 mg PO bid. Dose may need to be reduced in
Asian patients, as they appear to experience increased toxicity to sorafenib.
Drug Interaction 1
Drugs such as ketoconazole, and other CYP3A4 inhibitors, may decrease
the rate of metabolism of sorafenib. However, one study with ketoconazole
administered at a dose of 400 mg once daily for 7 days did not alter the mean
AUC of a single oral dose of sorafenib 50 mg in healthy volunteers.
Drug Interaction 2
Drugs such as rifampin, phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, and
St. Johns Wort increase the rate of metabolism of sorafenib, resulting in its
inactivation.
Special Considerations
1. Sorafenib should be taken without food at least 1 hour before
or 2 hours after a meal.
2. No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with Child-Pugh A and B
liver dysfunction. However, sorafenib has not been studied in
patients with Child-Pugh C liver disease, and caution should be used
in this setting.
3. No dose adjustments are necessary in patients with mild-to-moderate
renal dysfunction. Sorafenib has not been studied in patients under-
going dialysis.
388 Physicians Cancer Chemotherapy Drug Manual
4. Use with caution when administering sorafenib with agents that are
metabolized and/or eliminated by the UGT1A1 pathway, such as iri-
notecan, as sorafenib is an inhibitor of UGT1A1.
5. Patients receiving sorafenib along with oral warfarin anticoagulant
S
therapy should have their coagulation parameters (PT and INR)
monitored frequently as elevations in INR and bleeding events have
been observed.
6. Closely monitor blood pressure while on therapy, especially during
the first 6 weeks of therapy, and treat as needed with standard
oral antihypertensive medication.
7. Skin toxicities, including rash and hand-foot reaction, should be
managed early in the course of therapy with topical treatments for
symptomatic relief, temporary interruption, dose reduction, and/or
discontinuation. Sun exposure should be avoided, and periodic der-
matologic evaluation is recommended.
8. Sorafenib therapy should be interrupted in patients undergoing
major surgical procedures.
9. Avoid Seville oranges, starfruit, pomelos, grapefruit, and grapefruit
juice while on sorafenib therapy.
10. Pregnancy category D. Breastfeeding should be avoided.
Toxicity 1
Hypertension usually occurs within 6 weeks of starting therapy and
well-controlled with oral antihypertensive medication.
Toxicity 2
Skin rash. Hand-foot skin reaction occurs in up to 30%. Rare cases of
actinic keratoses and cutaneous squamous cell cancer have been reported.
Toxicity 3
Bleeding complications with epistaxis most commonly observed.
Toxicity 4
Wound healing complications.
Toxicity 5
Constitutional side effects with fatigue and asthenia.
Toxicity 6
Diarrhea and nausea are the most common GI side effects.
Toxicity 7
Hypophosphatemia occurs in up to 45% of patients, but usually clinically
asymptomatic.
Chemotherapeutic and Biologic Drugs 389
Você também pode gostar
- Lung Carcinoma: Radiotherapy PlanningDocumento9 páginasLung Carcinoma: Radiotherapy PlanningTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- Gastric Carcinoma: Radiation Planning: Ebrt Assessment of Disease 1. Examinations: 2. Investigations: A. Non-InvasiveDocumento33 páginasGastric Carcinoma: Radiation Planning: Ebrt Assessment of Disease 1. Examinations: 2. Investigations: A. Non-InvasiveTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- WedgeDocumento9 páginasWedgeTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- 0529 Protocol Update 6.2.09 PDFDocumento57 páginas0529 Protocol Update 6.2.09 PDFTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- Read MeDocumento1 páginaRead MeTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- Youtube by ClickDocumento1 páginaYoutube by ClickTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- Carcinoma Rectum - Janak - NEWDocumento74 páginasCarcinoma Rectum - Janak - NEWTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- COVID Guideline V4.30.3.2020Documento29 páginasCOVID Guideline V4.30.3.2020gourabAinda não há avaliações
- Radiation Therapy For Breast Cancer 2016Documento162 páginasRadiation Therapy For Breast Cancer 2016Alexandra Nicoleta Teisi100% (1)
- Sindrome Mielo DisplásicoDocumento28 páginasSindrome Mielo Displásicolisina293Ainda não há avaliações
- Dhaka North City CorporatationDocumento9 páginasDhaka North City Corporatationathiqul100% (4)
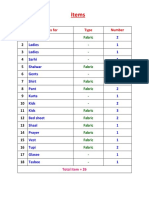
- Items: No Items For Type NumberDocumento1 páginaItems: No Items For Type NumberTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- Adult Body Mass Index (BMI) Chart: WeightDocumento2 páginasAdult Body Mass Index (BMI) Chart: WeightTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- How To Detect Bad RAM With The Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool - TechRepublic PDFDocumento1 páginaHow To Detect Bad RAM With The Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool - TechRepublic PDFTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- Carcinoma Rectum - Janak - NEWDocumento74 páginasCarcinoma Rectum - Janak - NEWTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Towhidul Islam: MBBS, BCS (Health) CCD Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University Cell Phone: 01725271380Documento1 páginaDr. Towhidul Islam: MBBS, BCS (Health) CCD Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University Cell Phone: 01725271380TowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- Horton 2018Documento15 páginasHorton 2018TowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- The Blockade of Immune Checkpoints Pardoll2012 PDFDocumento13 páginasThe Blockade of Immune Checkpoints Pardoll2012 PDFTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- Horton 2018Documento5 páginasHorton 2018TowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- Febrile NeutropeniaDocumento7 páginasFebrile NeutropeniaTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- WHO and RECIST CriteriaDocumento2 páginasWHO and RECIST CriteriaTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- Pregnancy Fact SheetDocumento3 páginasPregnancy Fact SheetTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- Horton 2018Documento15 páginasHorton 2018TowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- Bronchiolitis Peds.2014 2742.fullDocumento32 páginasBronchiolitis Peds.2014 2742.fullTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- 2008 RA Recommendations PDFDocumento23 páginas2008 RA Recommendations PDFTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnstico Diferencial de Vmitos PDFDocumento9 páginasDiagnstico Diferencial de Vmitos PDFLeoberto Batista Pereira SobrinhoAinda não há avaliações
- Analcancer 0617 7908Documento1 páginaAnalcancer 0617 7908TowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- Normal Tissue Responses To RadiationDocumento56 páginasNormal Tissue Responses To RadiationTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- Abvd Hem HLDocumento6 páginasAbvd Hem HLTowhidulIslamAinda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Clinics in Sports Medicine PDFDocumento173 páginasClinics in Sports Medicine PDFmostafa143941366Ainda não há avaliações
- PRF Applications in Dentistry ReviewDocumento9 páginasPRF Applications in Dentistry ReviewKarina Guerrero RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- 2021 Oral OncolDocumento9 páginas2021 Oral OncolAlanis BuenrostroAinda não há avaliações
- Increased Blood Flow and Vasculature in Solar LentigoDocumento5 páginasIncreased Blood Flow and Vasculature in Solar LentigoOzheanAMAinda não há avaliações
- Nanoparticle-Based Therapeutic Approaches For Wound Healing - A Review of The State-Of-The-ArtDocumento34 páginasNanoparticle-Based Therapeutic Approaches For Wound Healing - A Review of The State-Of-The-ArtMilan JovicAinda não há avaliações
- A New Approach To Cerebral Palsy Treatment DiscussDocumento13 páginasA New Approach To Cerebral Palsy Treatment DiscussArun KumarAinda não há avaliações
- The Lower Limb Tendinopathies Etiology, Biology and Treatment-Springer International (2016)Documento202 páginasThe Lower Limb Tendinopathies Etiology, Biology and Treatment-Springer International (2016)Tony Miguel Saba Saba100% (1)
- Differences in blood vessel growth using chitosan-aloe vera gel combinationsDocumento7 páginasDifferences in blood vessel growth using chitosan-aloe vera gel combinationsDita YuaritaAinda não há avaliações
- Seminars in Cell & Developmental BiologyDocumento10 páginasSeminars in Cell & Developmental BiologyagathapradanaAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment of Antiangiogenic Properties of Mallotus SPDocumento6 páginasAssessment of Antiangiogenic Properties of Mallotus SPSheila GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture-4 The Molecular Basis of Cancer Part-3Documento19 páginasLecture-4 The Molecular Basis of Cancer Part-3samyAinda não há avaliações
- CAM Assay: STC 12 4M PDFDocumento32 páginasCAM Assay: STC 12 4M PDFJensen AdrianoAinda não há avaliações
- Angiosuppressive Activity of Winged BeanDocumento14 páginasAngiosuppressive Activity of Winged BeanGlenn SiachuaAinda não há avaliações
- VEGF and AngiogénesisDocumento7 páginasVEGF and AngiogénesisMiranda YareliAinda não há avaliações
- Gac fruit's potential for eye disease preventionDocumento9 páginasGac fruit's potential for eye disease preventionEdgar BeltranAinda não há avaliações
- Ago-Rip Sequencing Identifies New Microrna-449A-5P Target Genes Increasing Sorafenib Efficacy in Hepatocellular CarcinomaDocumento14 páginasAgo-Rip Sequencing Identifies New Microrna-449A-5P Target Genes Increasing Sorafenib Efficacy in Hepatocellular Carcinomahasna muhadzibAinda não há avaliações
- Composition Based On Fi Ndings of Modern Bone BiologyDocumento4 páginasComposition Based On Fi Ndings of Modern Bone BiologyBernythefly axcAinda não há avaliações
- Anti VEGFDocumento43 páginasAnti VEGFanantkumar85Ainda não há avaliações
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Effects On Sports InjuriesDocumento11 páginasHyperbaric Oxygen Effects On Sports InjuriesNaydú Rey ArriagaAinda não há avaliações
- Sousa 2017Documento15 páginasSousa 2017PrashantAinda não há avaliações
- Umbilical Cord Blood BankingDocumento290 páginasUmbilical Cord Blood BankingcmAinda não há avaliações
- International Journal of Biological & Medical Research: Albin Jay C. Tabamo, LPT, Mscied-BioDocumento4 páginasInternational Journal of Biological & Medical Research: Albin Jay C. Tabamo, LPT, Mscied-BioBIOMEDSCIDIRECT PUBLICATIONSAinda não há avaliações
- Angiogénesis Terapéutica PDFDocumento262 páginasAngiogénesis Terapéutica PDFCarlos Sopán BenauteAinda não há avaliações
- Titanium Alloys Advances in Properties Control - 2013Documento153 páginasTitanium Alloys Advances in Properties Control - 2013Ahmadreza Aminian100% (2)
- Color Atlas of Vascular Tumors and Vascular Malformations (Enjolras)Documento310 páginasColor Atlas of Vascular Tumors and Vascular Malformations (Enjolras)Ciprian-Nicolae Muntean100% (1)
- Mechanisms of Vascular Disease: Robert FitridgeDocumento739 páginasMechanisms of Vascular Disease: Robert FitridgeasaAinda não há avaliações
- Lingual Nerve TreatmentDocumento9 páginasLingual Nerve TreatmentAlin OdorAinda não há avaliações
- Major Catalogue Complet PDFDocumento237 páginasMajor Catalogue Complet PDFHervis FantiniAinda não há avaliações
- HIV-Associated Kaposi's SarcomaDocumento5 páginasHIV-Associated Kaposi's SarcomaAnca LunguAinda não há avaliações
- Medicinal Properties and Uses of Orchids: A Concise ReviewDocumento8 páginasMedicinal Properties and Uses of Orchids: A Concise ReviewKrishnendu PramanikAinda não há avaliações