Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
New Microsoft Office Word Document
Enviado por
manoj kumarTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
New Microsoft Office Word Document
Enviado por
manoj kumarDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
EE6009 POWER ELECTRONICS FOR RENEWABLE ENERGY SYSTEMS LT P C
3003
OBJECTIVES:
To Provide knowledge about the stand alone and grid connected renewable energy systems.
To equip with required skills to derive the criteria for the design of power converters for
renewable energy applications.
To analyse and comprehend the various operating modes of wind electrical generators and
solar energy systems.
To design different power converters namely AC to DC, DC to DC and AC to AC converters for
renewable energy systems.
To develop maximum power point tracking algorithms.
UNIT I INTRODUCTION 9
Environmental aspects of electric energy conversion: impacts of renewable energy generation
onenvironment (cost-GHG Emission) - Qualitative study of different renewable energy
resources: Solar,wind, ocean, Biomass, Fuel cell, Hydrogen energy systems and hybrid
renewable energy systems.
UNIT II ELECTRICAL MACHINES FOR RENEWABLE ENERGY CONVERSION 9
Reference theory fundamentals-principle of operation and analysis: IG, PMSG, SCIG and DFIG.
99
UNIT III POWER CONVERTERS 9
Solar: Block diagram of solar photo voltaic system -Principle of operation: line commutated
converters (inversion-mode) - Boost and buck-boost converters- selection of inverter, battery
sizing, array sizing
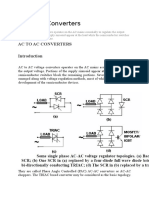
Wind: Three phase AC voltage controllers- AC-DC-AC converters: uncontrolled rectifiers, PWM
Inverters, Grid Interactive Inverters-matrix converters.
UNIT IV ANALYSIS OF WIND AND PV SYSTEMS 9
Stand alone operation of fixed and variable speed wind energy conversion systems and solar
system-Grid connection Issues -Grid integrated PMSG, SCIG Based WECS, grid Integrated
solar system
UNIT V HYBRID RENEWABLE ENERGY SYSTEMS 9
Need for Hybrid Systems- Range and type of Hybrid systems- Case studies of Wind-PV
Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT).
TOTAL :45 PERIODS
OUTCOMES:
Ability to understand and analyze power system operation, stability, control and protection.
Ability to handle the engineering aspects of electrical energy generation and utilization.
TEXT BOOK:
1. S. N. Bhadra, D.Kastha, S.Banerjee, Wind Electrical Systems, Oxford University Press,
2005.
2. B.H.Khan Non-conventional Energy sources Tata McGraw-hill Publishing Company,
New Delhi,2009.
REFERENCES:
1. Rashid .M. H power electronics Hand book, Academic press, 2001.
2. Ion Boldea, Variable speed generators, Taylor & Francis group, 2006.
3. Rai. G.D, Non conventional energy sources, Khanna publishes, 1993.
4. Gray, L. Johnson, Wind energy system, prentice hall linc, 1995.
5. Andrzej M. Trzynnadlowski, Introduction to Modern Pow
EE6601 SOLID STATE DRIVES LTPC
3003
OBJECTIVES:
To understand steady state operation and transient dynamics of a motor load system.
To study and analyze the operation of the converter/chopper fed dc drive, both qualitatively
and quantitatively.
To study and understand the operation and performance of AC motor drives.
To analyze and design the current and speed controllers for a closed loop solid state DC motor
drive.
UNIT I DRIVE CHARACTERISTICS 9
Electric drive Equations governing motor load dynamics steady state stability multi
quadrant Dynamics: acceleration, deceleration, starting & stopping typical load torque
characteristics Selection of motor.
UNIT II CONVERTER / CHOPPER FED DC MOTOR DRIVE 9
Steady state analysis of the single and three phase converter fed separately excited DC motor
drivecontinuous and discontinuous conduction Time ratio and current limit control 4
quadrant operation of converter / chopper fed drive.
UNIT III INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVES 9
Stator voltage controlenergy efficient drivev/f controlconstant airgap fluxfield weakening
mode voltage / current fed inverter closed loop control.
UNIT IV SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR DRIVES 9
V/f control and self control of synchronous motor: Margin angle control and power factor control
permanent magnet synchronous motor.
UNIT V DESIGN OF CONTROLLERS FOR DRIVES 9
Transfer function for DC motor / load and converter closed loop control with Current and
speed feedbackarmature voltage control and field weakening mode Design of controllers;
current controller and speed controller- converter selection and characteristics.
TOTAL: 45 PERIODS
OUTCOMES:
Ability to understand and apply basic science, circuit theory, Electro-magnetic field theory
control theory and apply them to electrical engineering problems.
TEXT BOOKS:
1. Gopal K.Dubey, Fundamentals of Electrical Drives, Narosa Publishing House, 1992.
2. Bimal K.Bose. Modern Power Electronics and AC Drives, Pearson Education, 2002.
3. R.Krishnan, Electric Motor & Drives: Modeling, Analysis and Control, Prentice Hall of
India, 2001.
REFERENCES:
1. John Hindmarsh and Alasdain Renfrew, Electrical Machines and Drives System, Elsevier
2012.
2. Shaahin Felizadeh, Electric Machines and Drives, CRC Press(Taylor and Francis Group),
2013.
3. S.K.Pillai, A First course on Electrical Drives, Wiley Eastern Limited, 1993.
4. S. Sivanagaraju, M. Balasubba Reddy, A. Mallikarjuna Prasad Power semiconductor drives
PHI, 5th printing, 2013.
5. N.K.De., P.K.SENElectric drives PHI, 2012.
6. Vedam Subramanyam, Thyristor Control of Electric Drives, Tata McGraw Hill, 2007.
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- 27 Points of Difference Between Personnel Management & HRDDocumento2 páginas27 Points of Difference Between Personnel Management & HRDMurtaza Ejaz33% (3)
- Benchmark Leadership Philosphy Ead 501Documento5 páginasBenchmark Leadership Philosphy Ead 501api-494301924Ainda não há avaliações
- Model Personal StatementDocumento2 páginasModel Personal StatementSwayam Tripathy100% (1)
- Simulation Model of Hydro Power Plant Using Matlab/SimulinkDocumento8 páginasSimulation Model of Hydro Power Plant Using Matlab/Simulinkmanoj kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Eee R13Documento33 páginasEee R13manoj kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Research Article: Improving The Efficiency of Photovoltaic Panels Using Machine Learning ApproachDocumento6 páginasResearch Article: Improving The Efficiency of Photovoltaic Panels Using Machine Learning Approachmanoj kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Diode Clamped Multilevel Inverter Fed BLDC Motor Using SEPIC ConverterDocumento5 páginasDiode Clamped Multilevel Inverter Fed BLDC Motor Using SEPIC Convertermanoj kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Power Electronics - QB - Final - PECDocumento52 páginasPower Electronics - QB - Final - PECmanoj kumarAinda não há avaliações
- EE8451, EE6303 Linear Integrated Circuits and Applications LICA - 2 Marks With Answers 2Documento47 páginasEE8451, EE6303 Linear Integrated Circuits and Applications LICA - 2 Marks With Answers 2manoj kumarAinda não há avaliações
- PDFDocumento9 páginasPDFmanoj kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Unit V Design of Controllers For Drives: 3.1transfer Function For DC MotorDocumento12 páginasUnit V Design of Controllers For Drives: 3.1transfer Function For DC Motormanoj kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Single Phase Dual Converter: Power Electronics by Prof. M. Madhusudhan Rao 1Documento3 páginasSingle Phase Dual Converter: Power Electronics by Prof. M. Madhusudhan Rao 1manoj kumarAinda não há avaliações
- There Are Few Types of Stepper MotorsDocumento41 páginasThere Are Few Types of Stepper Motorsmanoj kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Ac Volt Cont Cyclo ConvDocumento41 páginasAc Volt Cont Cyclo Convmanoj kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Unit Iii Induction Motor Drives: Dept. of EEEDocumento17 páginasUnit Iii Induction Motor Drives: Dept. of EEEmanoj kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Ee 2352 - Solidstate Drives: Unit - IIIDocumento16 páginasEe 2352 - Solidstate Drives: Unit - IIImanoj kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Resonant Converters: Problems With Switching DevicesDocumento18 páginasResonant Converters: Problems With Switching Devicesmanoj kumarAinda não há avaliações
- AC To AC Converters Unit 5Documento37 páginasAC To AC Converters Unit 5manoj kumar0% (1)
- Diagrama Hilux 1KD-2KD PDFDocumento11 páginasDiagrama Hilux 1KD-2KD PDFJeni100% (1)
- IOM - Rampa Hidráulica - Blue GiantDocumento32 páginasIOM - Rampa Hidráulica - Blue GiantPATRICIA HERNANDEZAinda não há avaliações
- Editorial WritingDocumento38 páginasEditorial WritingMelanie Antonio - Paino100% (1)
- Clevite Bearing Book EB-40-07Documento104 páginasClevite Bearing Book EB-40-07lowelowelAinda não há avaliações
- SPWM Vs SVMDocumento11 páginasSPWM Vs SVMpmbalajibtechAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1: Power and Responsibility: 1. Important Leadership QualitiesDocumento6 páginasUnit 1: Power and Responsibility: 1. Important Leadership QualitiesTrần Thanh MinhAinda não há avaliações
- Dashrath Nandan JAVA (Unit2) NotesDocumento18 páginasDashrath Nandan JAVA (Unit2) NotesAbhinandan Singh RanaAinda não há avaliações
- American J of Comm Psychol - 2023 - Palmer - Looted Artifacts and Museums Perpetuation of Imperialism and RacismDocumento9 páginasAmerican J of Comm Psychol - 2023 - Palmer - Looted Artifacts and Museums Perpetuation of Imperialism and RacismeyeohneeduhAinda não há avaliações
- EceDocumento75 páginasEcevignesh16vlsiAinda não há avaliações
- Asian Paints Final v1Documento20 páginasAsian Paints Final v1Mukul MundleAinda não há avaliações
- End Points SubrogadosDocumento3 páginasEnd Points SubrogadosAgustina AndradeAinda não há avaliações
- Beginning Cosmetic ChemistryDocumento1 páginaBeginning Cosmetic ChemistrySergio Rugerio0% (1)
- Oss Kpi SummaryDocumento7 páginasOss Kpi SummaryMohd FaizAinda não há avaliações
- BypassGoldManual PDFDocumento6 páginasBypassGoldManual PDFBrad FrancAinda não há avaliações
- Starex Is BTSDocumento24 páginasStarex Is BTSKLAinda não há avaliações
- Rubric For Audio Speech DeliveryDocumento2 páginasRubric For Audio Speech DeliveryMarie Sol PanganAinda não há avaliações
- BIM and Big Data For Construction Cost ManagementDocumento46 páginasBIM and Big Data For Construction Cost Managementlu09100% (1)
- Defenders of The Empire v1.4Documento13 páginasDefenders of The Empire v1.4Iker Antolín MedinaAinda não há avaliações
- RTD IncotestDocumento2 páginasRTD IncotestJabari KaneAinda não há avaliações
- B205A TMA Project Spring 2021 - UpdatedDocumento6 páginasB205A TMA Project Spring 2021 - UpdatedIoan 23Ainda não há avaliações
- Terasaki FDP 2013Documento40 páginasTerasaki FDP 2013MannyBaldonadoDeJesus100% (1)
- Experiment 2: Multimeter Laboratory ReportDocumento4 páginasExperiment 2: Multimeter Laboratory ReportNoir SalifoAinda não há avaliações
- Mass and Heat Balance of Steelmaking in Bof As Compared To Eaf ProcessesDocumento15 páginasMass and Heat Balance of Steelmaking in Bof As Compared To Eaf ProcessesAgil Setyawan100% (1)
- Asugal Albi 4540Documento2 páginasAsugal Albi 4540dyetex100% (1)
- Master Thesis On Smart GridDocumento6 páginasMaster Thesis On Smart Gridsandraandersondesmoines100% (2)
- Indian Pharmaceutical IndustryDocumento25 páginasIndian Pharmaceutical IndustryVijaya enterprisesAinda não há avaliações
- Angelina JolieDocumento14 páginasAngelina Joliemaria joannah guanteroAinda não há avaliações