Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Fourier Family CheatSheet v2.0
Enviado por
Nikesh BajajDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Fourier Family CheatSheet v2.0
Enviado por
Nikesh BajajDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Fourier: Cheat Sheet
FOURIER FAMILY
Continues Signal Discrete Signal
Fourier series Discrete Fourier series
Periodic
N 1
1 1
ak
Ts x(t )e s dt
jk t
x ( n) ak e jkst
k
X ( k ) ak
N
x ( n)e
n 0
j 2nk / N
Ts
N 1
X (k ) x(n)e j 2nk / N DFT & FFT
n 0
Frequency: Discrete & Aperiodic Frequency: Discrete & Periodic
Aperiodic
Fourier Transform Discrete Time Fourier Transform
x(t )e dt x ( n)e
jt
X ( j ) X () jn
Frequency: Continues & Aperiodic Frequency: Continues & Periodic
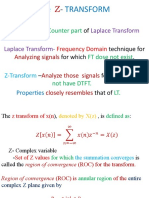
Laplace Transform Z-Transform
x(t )e dt x ( n) Z
st
X ( s) X ( z) n
ROC over Re(s) = n ROC over |Z| = r
By replacing j + j = s By replacing ej rej = Z
DFS & DFT: Discrete Fourier series is applicable for periodic discrete sequences, whereas DFT is
taken from DFS considering any aperiodic sequence as periodic with period equal to the length
of given sequence. Other way to drive DFT is by sampling DTFT of aperiodic sequence and taking
N samples from 0 to . DFT is one of the widest used transform among all Fouriers as practically
we have discrete signals (sequences) and it can be stored in memory. FFT Fast Fourier
Transform, is just fast way to compute DFT.
Laplace and Z- Transforms are extension (or generalization) of Fourier Transform and DTFT,
which is also applicable of signals which do not satisfy Dirichlet Criteria. Of course ROC for these
two transform are very essential part to know when signals analysis can be done.
NikB Nikesh Bajaj
Você também pode gostar
- DTFT DFT FS Ch8Documento103 páginasDTFT DFT FS Ch8Pindi Prince Pindi100% (1)
- Energy Density of Aperiodic SignalsDocumento9 páginasEnergy Density of Aperiodic SignalsaavdsAinda não há avaliações
- ElectrostaticsDocumento63 páginasElectrostaticsSarwar Hosen SimonAinda não há avaliações
- MP Lab ManualDocumento36 páginasMP Lab Manualapi-19951707Ainda não há avaliações
- Eee 152Documento35 páginasEee 152rushoeeeAinda não há avaliações
- Signals and Systems: CE/EE301Documento9 páginasSignals and Systems: CE/EE301Abdelrhman MahfouzAinda não há avaliações
- Unit Iii: Analysis of Discrete Time SignalsDocumento22 páginasUnit Iii: Analysis of Discrete Time SignalsAnbazhagan SelvanathanAinda não há avaliações
- HW Solutions MicroprocessorsDocumento35 páginasHW Solutions MicroprocessorsEllahe100% (1)
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocumento23 páginasDigital Signal ProcessingSanjay PalAinda não há avaliações
- Week 6 - Z-TransformDocumento15 páginasWeek 6 - Z-TransformRalph Ian CaingcoyAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1Documento12 páginasLecture 1Tanvir HussainAinda não há avaliações
- DSP Question Bank IV CSE - Cs - 2403docDocumento36 páginasDSP Question Bank IV CSE - Cs - 2403docSiva NandanAinda não há avaliações
- δ (n) = u (n) - u (n-3) = 1 ,n=0Documento37 páginasδ (n) = u (n) - u (n-3) = 1 ,n=0roberttheivadasAinda não há avaliações
- Z TansformDocumento65 páginasZ TansformThe Aviator00Ainda não há avaliações
- Department of Electrical Engineering EE365L: Communication SystemsDocumento20 páginasDepartment of Electrical Engineering EE365L: Communication SystemsAbrahan ShahzadAinda não há avaliações
- Exam 1Documento108 páginasExam 1ManikaushikAinda não há avaliações
- DSP Lab Report # 04Documento23 páginasDSP Lab Report # 04Abdul BasitAinda não há avaliações
- DFT/ FFT Using TMS320C5515 TM eZDSP USB Stick: Via CCS and MatlabDocumento12 páginasDFT/ FFT Using TMS320C5515 TM eZDSP USB Stick: Via CCS and MatlabTrung Hoang PhanAinda não há avaliações
- 4) MLR4: Zero Cond Mean E (U - x1,..xk) 0: 2) NO BIAS ConditionDocumento3 páginas4) MLR4: Zero Cond Mean E (U - x1,..xk) 0: 2) NO BIAS ConditionChristopher GianAinda não há avaliações
- Signals and Systems: CE/EE301Documento12 páginasSignals and Systems: CE/EE301Abdelrhman MahfouzAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Electrical Engineering EE365L: Communication SystemsDocumento16 páginasDepartment of Electrical Engineering EE365L: Communication SystemsAbrahan ShahzadAinda não há avaliações
- To Design An Adaptive Channel Equalizer Using MATLABDocumento43 páginasTo Design An Adaptive Channel Equalizer Using MATLABAngel Pushpa100% (1)
- Fortran Program: Motion of A Particle Under Central Force (Planetary Motion)Documento1 páginaFortran Program: Motion of A Particle Under Central Force (Planetary Motion)Abhijit Kar GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Impatt DiodeDocumento16 páginasImpatt DiodeTuhin Dutta100% (4)
- Signals and Networks Assignment 2Documento6 páginasSignals and Networks Assignment 2Avikalp SrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- SS PPT SrinDocumento300 páginasSS PPT Srinanjum samreen100% (1)
- Fourier Analysis of Signals and SystemsDocumento24 páginasFourier Analysis of Signals and SystemsBabul IslamAinda não há avaliações
- Z TransformDocumento1 páginaZ TransformmultisporkyAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1Documento5 páginasAssignment 1Saarthi SoodAinda não há avaliações
- DSP Lab Manual Final Presidency UniversityDocumento58 páginasDSP Lab Manual Final Presidency UniversitySUNIL KUMAR0% (1)
- MA6453-Probability and Queuing Theory PQT IMPORTANT QUESTIONSDocumento27 páginasMA6453-Probability and Queuing Theory PQT IMPORTANT QUESTIONSSiddhartha J0% (1)
- Formula PQTDocumento13 páginasFormula PQTசிவக்குமார் ஈஸ்வரன்Ainda não há avaliações
- Fourier AnalysisDocumento19 páginasFourier AnalysisPritam Pal100% (1)
- Junior Training SheetDocumento70 páginasJunior Training SheetJuan Sebastian Hoyos100% (1)
- ECE411 - 2 - DT Signals and SystemsDocumento12 páginasECE411 - 2 - DT Signals and SystemsMartine JimenezAinda não há avaliações
- Ph.D. Thesis of Farzana HussainDocumento360 páginasPh.D. Thesis of Farzana HussainFarzana HussainAinda não há avaliações
- ADC Chapter 1 NotesDocumento24 páginasADC Chapter 1 NotesatifAinda não há avaliações
- Filter Desing CompleteDocumento0 páginaFilter Desing Completewww.bhawesh.com.npAinda não há avaliações
- Signals and Systems: CE/EE301Documento21 páginasSignals and Systems: CE/EE301Abdelrhman MahfouzAinda não há avaliações
- EEE321 - Digital Signal Processing - LAB 5Documento6 páginasEEE321 - Digital Signal Processing - LAB 5Tâm NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- DSP Lab 05Documento12 páginasDSP Lab 05Mohsin AliAinda não há avaliações
- Instrumentation: ControlDocumento28 páginasInstrumentation: ControlMonowarul IslamAinda não há avaliações
- Transform: of Technique For For Which - For Which That ofDocumento119 páginasTransform: of Technique For For Which - For Which That ofsk abdullahAinda não há avaliações
- PQT Solved QB PDFDocumento62 páginasPQT Solved QB PDFDharumanAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Data TransmissionDocumento45 páginasDigital Data Transmissionneelima raniAinda não há avaliações
- Physical Chemistry Homework HelpDocumento14 páginasPhysical Chemistry Homework HelpEdu Assignment Help100% (1)
- Real-Time Clock Using 8253Documento11 páginasReal-Time Clock Using 8253Chandravadhana NarayananAinda não há avaliações
- ECE411 - 5 - Frequency Analysis of DT SystemsDocumento22 páginasECE411 - 5 - Frequency Analysis of DT SystemsMartine JimenezAinda não há avaliações
- Da AssignmentDocumento3 páginasDa AssignmentmadhurAinda não há avaliações
- PTSP Notes Unit 3 PDFDocumento11 páginasPTSP Notes Unit 3 PDFG S ArunAinda não há avaliações
- HW 6 SolDocumento2 páginasHW 6 Solricharai2312Ainda não há avaliações
- Maths Sampel Mini ProjectDocumento20 páginasMaths Sampel Mini ProjectAshish Kudu0% (1)
- DSP EC 2302 16 Mark QuestionsDocumento3 páginasDSP EC 2302 16 Mark QuestionsVenkat RamananAinda não há avaliações
- Lab # 04 Discrete Fourier Transform and Its PropertiesDocumento9 páginasLab # 04 Discrete Fourier Transform and Its PropertiesZohaib HaiderAinda não há avaliações
- ROC Z TransformDocumento15 páginasROC Z TransformMohammad Gulam Ahamad0% (1)
- Fourier SeriesDocumento2 páginasFourier Seriesshahroz12Ainda não há avaliações
- AdvDSP Lecture1Documento43 páginasAdvDSP Lecture1Alireza DabiryAinda não há avaliações
- Signals and Systems For Signals and Systems ForDocumento65 páginasSignals and Systems For Signals and Systems ForMenchaAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocumento39 páginasDigital Signal ProcessingAyesha TahirAinda não há avaliações
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Ainda não há avaliações
- Signals & Systems ECE220 Lec 1 Introduction and SignalsDocumento12 páginasSignals & Systems ECE220 Lec 1 Introduction and SignalsNikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Signals & Systems ECE220 Lec-4-Laplace-TransformDocumento4 páginasSignals & Systems ECE220 Lec-4-Laplace-TransformNikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Speech and Audio Signal Processing ECE554 - Lec - 5 STFT Analysis v2.1Documento17 páginasSpeech and Audio Signal Processing ECE554 - Lec - 5 STFT Analysis v2.1Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Signals & Systems ECE220 Lec-2-Systems And-ConvolutionDocumento4 páginasSignals & Systems ECE220 Lec-2-Systems And-ConvolutionNikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Speech and Audio Signal Processing ECE554 - Lec - 3 Waveform Coding v2.0Documento10 páginasSpeech and Audio Signal Processing ECE554 - Lec - 3 Waveform Coding v2.0Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Signals & Systems ECE220 Lec-3-FourierDocumento9 páginasSignals & Systems ECE220 Lec-3-FourierNikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Information Theory and Coding Test 1 v5.0Documento2 páginasInformation Theory and Coding Test 1 v5.0Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Speech and Audio Signal Processing ECE554 - Lec - 1 Speech Production v2.0Documento17 páginasSpeech and Audio Signal Processing ECE554 - Lec - 1 Speech Production v2.0Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Speech and Audio Signal Processing ECE554 - Lec - 0 Introduction v2.0Documento9 páginasSpeech and Audio Signal Processing ECE554 - Lec - 0 Introduction v2.0Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Information and Coding Theory ECE533 - Lec-2 Source Coding v4.0Documento10 páginasInformation and Coding Theory ECE533 - Lec-2 Source Coding v4.0Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Speech and Audio Signal Processing ECE554 - Lec - 5 STFT Analysis v2.0Documento10 páginasSpeech and Audio Signal Processing ECE554 - Lec - 5 STFT Analysis v2.0Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Speech and Audio Signal Processing ECE554 - Lec - 4 Time Domain Analysis v2.0Documento4 páginasSpeech and Audio Signal Processing ECE554 - Lec - 4 Time Domain Analysis v2.0Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Information and Coding Theory ECE533 - Lec-7 Number Theory v4.0Documento12 páginasInformation and Coding Theory ECE533 - Lec-7 Number Theory v4.0Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Information and Coding Theory ECE533 - Design Problem v4.1Documento4 páginasInformation and Coding Theory ECE533 - Design Problem v4.1Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Information and Coding Theory ECE533 - Lec-9 Convolutiona Turbo TCMDocumento6 páginasInformation and Coding Theory ECE533 - Lec-9 Convolutiona Turbo TCMNikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Advance Coding Theory V5.1-Lec-4 Linear Block CodesDocumento8 páginasAdvance Coding Theory V5.1-Lec-4 Linear Block CodesNikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Information and Coding Theory ECE533 - Lec-3 Foundation For ECC v4.0Documento6 páginasInformation and Coding Theory ECE533 - Lec-3 Foundation For ECC v4.0Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Radar Communication ECEP618 - Unit-3 MTI Pulse Doppler v1.0Documento7 páginasRadar Communication ECEP618 - Unit-3 MTI Pulse Doppler v1.0Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Information and Coding Theory ECE533 - Lec-6 Cyclic Codes v4.0Documento7 páginasInformation and Coding Theory ECE533 - Lec-6 Cyclic Codes v4.0Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Information and Coding Theory ECE533 - Lec-1 Introduction. Information Theory v4.0Documento9 páginasInformation and Coding Theory ECE533 - Lec-1 Introduction. Information Theory v4.0Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Information and Coding Theory ECE533 - HW2 DesignProblem ECE533 v4.1Documento2 páginasInformation and Coding Theory ECE533 - HW2 DesignProblem ECE533 v4.1Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Information and Coding Theory ECE533 - Lec-4 Group and Vector Space v4.0Documento3 páginasInformation and Coding Theory ECE533 - Lec-4 Group and Vector Space v4.0Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Radar Communication ECEP618 - Unit-4 Ambiguity and Pulse Compression v1.0Documento5 páginasRadar Communication ECEP618 - Unit-4 Ambiguity and Pulse Compression v1.0Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Statistics For Data Analysis Lec 1 Introduction and VisualizationDocumento8 páginasStatistics For Data Analysis Lec 1 Introduction and VisualizationNikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Statistics For Data Analysis Lec 4 Correlation and RegressionDocumento5 páginasStatistics For Data Analysis Lec 4 Correlation and RegressionNikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Radar Communication ECEP618 - Unit-2 Radar Equation v1.0Documento9 páginasRadar Communication ECEP618 - Unit-2 Radar Equation v1.0Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Radar Communication ECEP618 - Unit-1 Introduction v1.0Documento7 páginasRadar Communication ECEP618 - Unit-1 Introduction v1.0Nikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Statistics For Data Analysis - Lec-3-VariabilityDocumento6 páginasStatistics For Data Analysis - Lec-3-VariabilityNikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Statistics For Data Analysis Lec 2 Measure of Center TendancyDocumento6 páginasStatistics For Data Analysis Lec 2 Measure of Center TendancyNikesh BajajAinda não há avaliações
- Numerical Methods of Integration: Richa SharmaDocumento51 páginasNumerical Methods of Integration: Richa SharmafanusAinda não há avaliações
- Application Form For Incoming Grade 7Documento1 páginaApplication Form For Incoming Grade 7Gladylyn MirandaAinda não há avaliações
- Multicore Processor ReportDocumento19 páginasMulticore Processor ReportDilesh Kumar100% (1)
- VSoft Technologies Corporate BrochureDocumento12 páginasVSoft Technologies Corporate BrochureVSoft Technologies100% (1)
- BIT715 Handouts 1 45Documento419 páginasBIT715 Handouts 1 45jscansinoAinda não há avaliações
- ESD TutoDocumento5 páginasESD TutoSwaroop MohapatraAinda não há avaliações
- Quantifying The Impact of Learning Algorithm Parameter TuningDocumento6 páginasQuantifying The Impact of Learning Algorithm Parameter TuningdeAugAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Fuzzy Logic, Classical Sets and Fuzzy SetsDocumento20 páginasIntroduction To Fuzzy Logic, Classical Sets and Fuzzy SetstiuyiAinda não há avaliações
- Action Profiles in SAP CRM: Logout Getting Started Newsletters StoreDocumento7 páginasAction Profiles in SAP CRM: Logout Getting Started Newsletters StoreRanson PaulAinda não há avaliações
- SL1000 Programming Manual (Basic)Documento36 páginasSL1000 Programming Manual (Basic)KatsanaArunrat57% (7)
- Internal Order Settlement Through Individual ProcessingDocumento5 páginasInternal Order Settlement Through Individual Processingsaplearn80Ainda não há avaliações
- Waterfall To Agile GuideDocumento14 páginasWaterfall To Agile GuideabdulonnetAinda não há avaliações
- How Do I Prepare For A Software Engineering Job Interview?: 100+ AnswersDocumento1 páginaHow Do I Prepare For A Software Engineering Job Interview?: 100+ Answersp001Ainda não há avaliações
- Trading With RDocumento19 páginasTrading With Rcodereverser100% (1)
- PDK 203704 Parameter KW-R06 IX A5 KE enDocumento320 páginasPDK 203704 Parameter KW-R06 IX A5 KE enMalek KamelAinda não há avaliações
- Finite Element PrimerDocumento81 páginasFinite Element PrimerAnonymous ntE0hG2TPAinda não há avaliações
- CMSC 27100Documento3 páginasCMSC 27100Kaushik VasudevanAinda não há avaliações
- SerDia2010 - ManualDocumento127 páginasSerDia2010 - ManualAditi DasAinda não há avaliações
- Shaadicom CompressDocumento154 páginasShaadicom Compresspriyanshu sahuAinda não há avaliações
- The Re-Launch of Napster: Group 7Documento23 páginasThe Re-Launch of Napster: Group 7Avishek Nandy100% (1)
- Custom Macro Variable Peck Drilling Cycle MacroDocumento2 páginasCustom Macro Variable Peck Drilling Cycle MacroRelu ChiruAinda não há avaliações
- PDFPCDocumento27 páginasPDFPCmadsonengAinda não há avaliações
- Oracle Partitioning For DevelopersDocumento70 páginasOracle Partitioning For DevelopersLewis CunninghamAinda não há avaliações
- Siemens Tutorial and Experimental TaskDocumento10 páginasSiemens Tutorial and Experimental TaskMuktoAhmedAinda não há avaliações
- WML and Wmlscript Praticals List For Alfa ME BatchDocumento2 páginasWML and Wmlscript Praticals List For Alfa ME BatchDimple MaheshwariAinda não há avaliações
- Crystal Report 8.5 For Visual - 89028Documento8 páginasCrystal Report 8.5 For Visual - 89028dsadsadAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To SD AccessDocumento28 páginasIntroduction To SD Accessg100% (1)
- Hpe Arcsight Esm STDocumento47 páginasHpe Arcsight Esm STHitesh RahangdaleAinda não há avaliações
- 4th Quarter Tle 6Documento9 páginas4th Quarter Tle 6Jorry Pavo NepalAinda não há avaliações
- MS Word 2007Documento7 páginasMS Word 2007gel18Ainda não há avaliações