Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
NCP BPH
Enviado por
yasira0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
196 visualizações1 páginaThe nursing care plan addresses a patient with impaired urinary elimination related to an enlarged prostate. The plan includes assessing the patient's voiding patterns, palpating the bladder, and monitoring for signs of urinary tract infection. Interventions include maintaining balanced fluid intake and output, perineal care, limiting irritants like caffeine, and obtaining urine tests. The goal is for the patient to demonstrate behaviors to prevent urinary retention and infection by the end of the shift.
Descrição original:
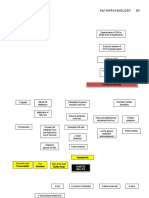
BENIGH PROSTATTIE HYPERTROPJY
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThe nursing care plan addresses a patient with impaired urinary elimination related to an enlarged prostate. The plan includes assessing the patient's voiding patterns, palpating the bladder, and monitoring for signs of urinary tract infection. Interventions include maintaining balanced fluid intake and output, perineal care, limiting irritants like caffeine, and obtaining urine tests. The goal is for the patient to demonstrate behaviors to prevent urinary retention and infection by the end of the shift.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
196 visualizações1 páginaNCP BPH
Enviado por
yasiraThe nursing care plan addresses a patient with impaired urinary elimination related to an enlarged prostate. The plan includes assessing the patient's voiding patterns, palpating the bladder, and monitoring for signs of urinary tract infection. Interventions include maintaining balanced fluid intake and output, perineal care, limiting irritants like caffeine, and obtaining urine tests. The goal is for the patient to demonstrate behaviors to prevent urinary retention and infection by the end of the shift.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
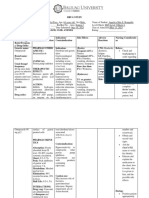
Davao Medical School Foundation. Inc.
Medical School Drive, Bajada, Davao City
College of Nursing
Nursing Care Plan
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation
Subjective: Impaired At the end of Independent: Goal met as
Patient urinary my shift the 1. Assess voiding pattern (frequency and amount). Compare urine output with fluid intake. Note evidenced by
verbalized i elimination patient will: specific gravity. patient :
wake up at R/T Rationale: An Identifies characteristics of bladder function (effectiveness of bladder
night around obstruction
demonstrate emptying, renal function, and fluid balance). demonstrating
2 to 3 times secondary behaviors 2. Palpate for bladder distension and observe for overflow. behaviors and
to urinate to enlarged
and Rationale: Bladder dysfunction is variable but may include loss of bladder contraction and techniques to
prostate techniques to inability to relax urinary sphincter, resulting in urine retention and reflux incontinence. prevent
prevent 3. Note reports of urinary frequency, urgency, burning, incontinence, nocturia, and size or force retention/
retention/ of urinary stream. urinary
urinary Rationale: This provides information about degree of interference with elimination or may infection.
infection. indicate bladder infection.
4. Assess the patients usual pattern of urination and occurrence of incontinence. Maintaining
maintain Rationale: Many patients are incontinent only in the early morning when the bladder has balanced I&O
balanced I&O stored a large urine volume during sleep. with clear, odor-
with clear, 5. Encourage adequate fluid intake (24 L per day) free urine, free
odor-free Rationale: Sufficient hydration promotes urinary output and aids in preventing infection. of bladder
urine, free of 6. Observe for cloudy or bloody urine, foul odor. distension/
bladder Rationale: Signs of urinary tract or kidney infection that can potentiate sepsis. urinary leakage
distension/ 7. Cleanse perineal area and keep dry. Provide catheter care as appropriate.
urinary Rationale: Proper perineal hygiene decreases risk of skin irritation or breakdown and
leakage. development of ascending infection.
8. Educate patient about the importance of limiting intake of alcohol and caffeine.
Rationale: These chemicals are known to be bladder irritants. They can increase detrusor
overactivity.
9. Obtain periodic urinalysis and urine culture and sensitivity as indicated.
Rationale: These tests monitor renal status.
Dependent:
1. Administer medications as indicated
Rationale: to promote urination and bladder relaxation
SUBMITTED TO: Mrs. Shirly May G. Dela Cerna RN, MN SUBMITTED BY: Yasierah K.Agalin , St.N DATE: November 17, 2017
Clinical Instructor BSN 4 student
Você também pode gostar
- Ineffective Airway Clearance NCPDocumento1 páginaIneffective Airway Clearance NCPBenz ParCoAinda não há avaliações
- Cu 4Documento3 páginasCu 4Paul SahagunAinda não há avaliações
- Ectopic Pregnancy NCP (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Documento10 páginasEctopic Pregnancy NCP (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Raiden VizcondeAinda não há avaliações
- Artillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaDocumento5 páginasArtillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaAl TheóAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objective S Nursing Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 páginasAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objective S Nursing Interventio N Rationale EvaluationJhun GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- Regañon - Rle Case # 1Documento22 páginasRegañon - Rle Case # 1Darla Janyll RegañonAinda não há avaliações
- St. Paul College of Ilocos Sur: Stages in The Natural History of Disease and The Levels of Prevention During Ncov-19Documento3 páginasSt. Paul College of Ilocos Sur: Stages in The Natural History of Disease and The Levels of Prevention During Ncov-19Marie Kelsey Acena Macaraig100% (1)
- Intussusception: PathophysiologyDocumento8 páginasIntussusception: PathophysiologyNaufal AndaluAinda não há avaliações
- RISK For INJURY Related To Regulatory Function (Sensory Difunction As Evidenced by Decrease Visual Acuity, Unable To Recognize Object 12-14 Inches Away, Not Wearing of Eyeglasses.Documento2 páginasRISK For INJURY Related To Regulatory Function (Sensory Difunction As Evidenced by Decrease Visual Acuity, Unable To Recognize Object 12-14 Inches Away, Not Wearing of Eyeglasses.Senyorita KHayeAinda não há avaliações
- Deficient Knowledge Related To Urinary Tract Infection: "Di Ako Aware About Sa UTI"as Verbalized by The ClientDocumento2 páginasDeficient Knowledge Related To Urinary Tract Infection: "Di Ako Aware About Sa UTI"as Verbalized by The ClientSeanmarie CabralesAinda não há avaliações
- German MeaslesDocumento8 páginasGerman MeaslesYdynn Parejas GavinaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care in MR.X With Urinary Retention: Disusun OlehDocumento4 páginasNursing Care in MR.X With Urinary Retention: Disusun OlehHafin WardanaAinda não há avaliações
- Nrg203: Care of Mother, Child, and Adolescent: (StudentDocumento6 páginasNrg203: Care of Mother, Child, and Adolescent: (Studentmikhaela sencilAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan On Platelet DisordersDocumento8 páginasNursing Care Plan On Platelet DisordersbhavanaAinda não há avaliações
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocumento6 páginasCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentKasandra Dawn Moquia Beriso100% (1)
- NCP Draft - Ectopic PregnancyDocumento7 páginasNCP Draft - Ectopic PregnancyD CAinda não há avaliações
- Cataract: Case Presentation - M.E.T.H.O.DDocumento7 páginasCataract: Case Presentation - M.E.T.H.O.DKismet SummonsAinda não há avaliações
- FNCP PoorsanitationmarwahDocumento3 páginasFNCP PoorsanitationmarwahAsniah Hadjiadatu AbdullahAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Intervention (Epiglottitis Disease)Documento2 páginasNursing Intervention (Epiglottitis Disease)Marianne Rose HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Deficient Knowledge: Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Care Plans (NCP)Documento3 páginasDeficient Knowledge: Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Care Plans (NCP)Vincent Paul SantosAinda não há avaliações
- NCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeDocumento2 páginasNCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeCindy MariscotesAinda não há avaliações
- Dela Rosa 2A MCN-Module 05Documento2 páginasDela Rosa 2A MCN-Module 05Atsu MiyaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Risk InfectionDocumento1 páginaNCP Risk InfectionEni RahmawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan About ANEMIA by Payongayong, Chielee Anne A.Documento2 páginasNursing Care Plan About ANEMIA by Payongayong, Chielee Anne A.Chielee Anne PayongayongAinda não há avaliações
- Orientation On Community Health - Doh Programs & ServicesDocumento11 páginasOrientation On Community Health - Doh Programs & ServicesAudrey Beatrice ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- Silliman University: Nursing Care Plan On Preeclampsia With Severe FeaturesDocumento8 páginasSilliman University: Nursing Care Plan On Preeclampsia With Severe FeaturesRyan Robert V. VentoleroAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDocumento8 páginasNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Knowledge Deficit FINALDocumento8 páginasNCP Knowledge Deficit FINALJOSHUA JOSE TERCEnOAinda não há avaliações
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration IndicationDocumento2 páginasName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration IndicationBrian BaggayanAinda não há avaliações
- Anxiety Disorders PDFDocumento29 páginasAnxiety Disorders PDFKhyle TolentinoAinda não há avaliações
- University of Northern PhilippinesDocumento6 páginasUniversity of Northern PhilippinesCatherine PradoAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoAinda não há avaliações
- Lapkas HegDocumento1 páginaLapkas HegkurniaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing of The Childbearing FamilyDocumento3 páginasNursing of The Childbearing Familyroby sorianoAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan of The NewbornDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan of The Newbornbowki namoAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology Cushing S SyndromeDocumento4 páginasPathophysiology Cushing S SyndromeMaria Luisa VillalunaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP, Ent, Risk For InfectionDocumento1 páginaNCP, Ent, Risk For InfectionGale DizonAinda não há avaliações
- Translational Research: Generating Evidence For PracticeDocumento24 páginasTranslational Research: Generating Evidence For Practicebeer_ettaaAinda não há avaliações
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento2 páginasNURSING CARE PLAN - Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDaniel Andre S. SomorayAinda não há avaliações
- Atun Maricris Jorre Ca2 Au Legarda Leadership Managemet Research DownloadableDocumento2 páginasAtun Maricris Jorre Ca2 Au Legarda Leadership Managemet Research DownloadableCharissa Magistrado De LeonAinda não há avaliações
- NCP DobDocumento2 páginasNCP DobPaulo GeneraloAinda não há avaliações
- Ncp-Drug Induced-PsychosisDocumento3 páginasNcp-Drug Induced-PsychosisMeryville Jacildo100% (1)
- NCP For COPDDocumento3 páginasNCP For COPDcy belAinda não há avaliações
- NCP of Endometrical CancerDocumento2 páginasNCP of Endometrical CancerFrando kennethAinda não há avaliações
- Neonatal Jaundice: Miriti M.D Master of Clinical Medicine:Accidents and Emerrgency MAY 2018Documento25 páginasNeonatal Jaundice: Miriti M.D Master of Clinical Medicine:Accidents and Emerrgency MAY 2018Dennis MiritiAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlansDocumento14 páginasNursing Care PlansTels Dela PeñaAinda não há avaliações
- JDM Care PlanDocumento5 páginasJDM Care PlangopscharanAinda não há avaliações
- N. Bacalso Ave., Cebu City Philippines: Page 1 of 32Documento32 páginasN. Bacalso Ave., Cebu City Philippines: Page 1 of 32Joule PeirreAinda não há avaliações
- Name: Oyardo Cherilyn BED NO.: 408 Attending Physician: DR - Baldovino Diet: Diet As Tolerated Diagnosis: Post-PartumDocumento7 páginasName: Oyardo Cherilyn BED NO.: 408 Attending Physician: DR - Baldovino Diet: Diet As Tolerated Diagnosis: Post-PartumshinloAinda não há avaliações
- Neonatal JaundiceDocumento12 páginasNeonatal JaundiceJustine NyangaresiAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Deficit Fluid VolumeDocumento4 páginasNCP Deficit Fluid VolumeKingJayson Pacman06Ainda não há avaliações
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocumento3 páginasCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- of ERYTHROBLASTOSIS FETALISDocumento12 páginasof ERYTHROBLASTOSIS FETALISMaricel Agcaoili GallatoAinda não há avaliações
- SIGNIFICANT SAQsDocumento407 páginasSIGNIFICANT SAQsFarid Iqbal100% (2)
- DRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquilloDocumento4 páginasDRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquillokarl eiron delos santosAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Identification Planning Nursing Intervention Evaluation IndependentDocumento7 páginasAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Identification Planning Nursing Intervention Evaluation IndependentQueenie Silva100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationSugar Capule - ManuelAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Diarrhea & VomitingDocumento4 páginasFluid Volume Deficit R/T Diarrhea & Vomitingjisoo100% (3)
- Nursing-Care-Plan - AgeDocumento7 páginasNursing-Care-Plan - AgePanda JocyAinda não há avaliações
- SGD Aa PDFDocumento11 páginasSGD Aa PDFyasiraAinda não há avaliações
- Neural Network - Your Text HereDocumento2 páginasNeural Network - Your Text HereyasiraAinda não há avaliações
- RRL InsertDocumento19 páginasRRL InsertyasiraAinda não há avaliações
- Tranzen1K BOIPEZADocumento51 páginasTranzen1K BOIPEZAyasiraAinda não há avaliações
- Check List: Your Title Text HereDocumento2 páginasCheck List: Your Title Text HereyasiraAinda não há avaliações
- Design - : Your Text HereDocumento2 páginasDesign - : Your Text HereyasiraAinda não há avaliações
- Communicatio N: Your Subtitle Text HereDocumento2 páginasCommunicatio N: Your Subtitle Text HereyasiraAinda não há avaliações
- CPAR MAS Preweek Quizzer May2004Documento23 páginasCPAR MAS Preweek Quizzer May2004kevinlim186100% (1)
- Location - Your Text Here: Lorem Ipsum Is Simply Dummy Text of The Printing and Typesetting IndustryDocumento2 páginasLocation - Your Text Here: Lorem Ipsum Is Simply Dummy Text of The Printing and Typesetting IndustryyasiraAinda não há avaliações
- 2 SlidesDocumento2 páginas2 SlidesyasiraAinda não há avaliações
- (-ENE) (-YNE) (-OL) (-OXY) (Benzene) : ChlorobenzeneDocumento2 páginas(-ENE) (-YNE) (-OL) (-OXY) (Benzene) : ChlorobenzeneyasiraAinda não há avaliações
- General Review AnswerDocumento8 páginasGeneral Review AnsweryasiraAinda não há avaliações
- DySAS General Review Acctg6 - AnsDocumento11 páginasDySAS General Review Acctg6 - Ansyasira0% (1)
- Electrical Safety in HealthcareDocumento2 páginasElectrical Safety in HealthcareNur Aqilah IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- Lumbar Interbody Fusions 1St Edition Edition Sunil Manjila Full ChapterDocumento67 páginasLumbar Interbody Fusions 1St Edition Edition Sunil Manjila Full Chapterlaurence.williams167100% (6)
- DM 2020-0187 - Must Know Covid IssuancesDocumento18 páginasDM 2020-0187 - Must Know Covid IssuancesFranchise AlienAinda não há avaliações
- Banner AT FM 10k PDFDocumento14 páginasBanner AT FM 10k PDFDamian RamosAinda não há avaliações
- Gagan ResumeDocumento6 páginasGagan Resumedrgaganwahi100% (2)
- Story of ChangeDocumento3 páginasStory of ChangeSend Sierra LeoneAinda não há avaliações
- Mosh RoomDocumento21 páginasMosh RoomBrandon DishmanAinda não há avaliações
- Format OpnameDocumento21 páginasFormat OpnamerestutiyanaAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Biology: Semester - Iii and Vii 2017-18Documento12 páginasChemical Biology: Semester - Iii and Vii 2017-18Yogesh ShekhawatAinda não há avaliações
- A Beauty 671-680Documento29 páginasA Beauty 671-680YollyAinda não há avaliações
- Top 10 Regulatory Challenges in The Healthcare EnvironmentDocumento3 páginasTop 10 Regulatory Challenges in The Healthcare EnvironmentNicki BombezaAinda não há avaliações
- Recall GuidelinesDocumento31 páginasRecall GuidelinesSandy PiccoloAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction and Analytical Report PDFDocumento111 páginasIntroduction and Analytical Report PDFJoão Pedro GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Abs & Core Workout Calendar - Mar 2020Documento1 páginaAbs & Core Workout Calendar - Mar 2020Claudia anahiAinda não há avaliações
- SUMMATIVE English8Documento4 páginasSUMMATIVE English8Therese LlobreraAinda não há avaliações
- ACCP-SCCM Critical Care Pharmacy Prep Course 2017 Vol.2 (PDF) WWW - Medicalbr.tkDocumento359 páginasACCP-SCCM Critical Care Pharmacy Prep Course 2017 Vol.2 (PDF) WWW - Medicalbr.tkRoman Lis50% (2)
- Antitrombotik, PPT 7Documento66 páginasAntitrombotik, PPT 7Rizky Saraswati IndraputriAinda não há avaliações
- Ewald Hecker's Description of Cyclothymia As A Cyclical Mood Disorder - Its Relevance To The Modern Concept of Bipolar IIDocumento7 páginasEwald Hecker's Description of Cyclothymia As A Cyclical Mood Disorder - Its Relevance To The Modern Concept of Bipolar IItyboyoAinda não há avaliações
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocumento10 páginasUrinary Tract Infectionjaah diazAinda não há avaliações
- Intro To EugenicsDocumento16 páginasIntro To EugenicsJesus LivesAinda não há avaliações
- June02.2016 Bbill Calls For Monitoring of Absences To Curb AbsenteeismDocumento2 páginasJune02.2016 Bbill Calls For Monitoring of Absences To Curb Absenteeismpribhor2Ainda não há avaliações
- Homeopathic Remedy Pictures Alexander Gothe Julia Drinnenberg.04000 1Documento6 páginasHomeopathic Remedy Pictures Alexander Gothe Julia Drinnenberg.04000 1BhargavaAinda não há avaliações
- Talent MappingDocumento18 páginasTalent MappingSoumya RanjanAinda não há avaliações
- TinnitusDocumento34 páginasTinnitusHnia UsmanAinda não há avaliações
- Summative Test Science Y5 SECTION ADocumento10 páginasSummative Test Science Y5 SECTION AEiLeen TayAinda não há avaliações
- PrelimDocumento10 páginasPrelimHeide Basing-aAinda não há avaliações
- Professional Teacher - Secondary (Social Studies) - 03-2024Documento45 páginasProfessional Teacher - Secondary (Social Studies) - 03-2024PRC BaguioAinda não há avaliações
- Bar Coding Near MissDocumento8 páginasBar Coding Near Missenorth1234Ainda não há avaliações
- Action PlanDocumento3 páginasAction PlanApollo Banaag-Dizon100% (1)
- The Girl With Green Eyes by John EscottDocumento10 páginasThe Girl With Green Eyes by John EscottAyman Charoui essamadiAinda não há avaliações