Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
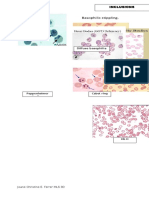
Gram Staining
Enviado por
Dixie DumagpiTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Gram Staining
Enviado por
Dixie DumagpiDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
LAVALLE, Jestin B.
BMLS Intern Microbiology
Gram Staining
1. Describe the peptidoglycan layer of the bacterial cell wall.
Peptidoglycan is a complex of polymer consisting of backbone, which is composed of alternating N-acetylglycosamine and
N-acetylmuramic acid connected by B-1,4 linkages; Set of identical tetrapeptide sidechains attached to N-acetyl muramic
acid and set of identical peptide cross bridge
Gram Pos (+) cell wall Gram Neg (-) cell wall
Peptidoglycan (20-40 layers) > Plasma membrane Outer membrane (Periplasmic space) > Peptidoglycan (2-4
laters) > Plasma membrane
Techoic Acid – antigenic/serologic determinant
2. Principles behind the difference in stain uptake of the Gram positive bacteria and Gram negative bacteria.
Gram Pos (+) Gram Neg (-)
Retains primary stain which is crystal violet iodine complex Do not retain crystal violet-iodine complex. Removed with
even it undergo decolorization with alcohol or acetone alcohol or acetone
Gram negative cell wall opens when the decolorizer is
added, so it will washes out the stains
Dark Blue or Violet Red due to safranin
Position Gram Pos (+) Gram Neg (-)
1 L - alanine L - alanine
2 D - glutamate D - glutamate
3 L - lysine Diaminepimelic acid
4 D - alanine D - alanine
DAP – immediate precursor of lysine biosynthesis
3. Discuss the procedure in Gram staining.
4. Explain briefly the general rule in Gram staining in relation to bacterial morphology.
All COCCI are gram POS (+) except: Neisseria spp, veilionella spp and Bramhamella spp, Acidaminococcus,
Megasphera
All BACILLI are gram NEG (-) except: Mycobacterium, Corynebacterium, Clostridia, Bacillus, Listeria,
Erysipelothrix, Lactobacillus, Actinomyces, Eubacterium, Propiobacterium, Mobiluncus, Bifido-bacterium
All SPIROCHETES are gram NEG (-)
LAVALLE, Jestin B. BMLS Intern Microbiology
5. What are gram variable bacteria?
Gram (+) bacteria becomes Gram (-) bacteria (vice versa)
o Ex. Gardnerella Vaginallis
o Mix of pink or purple cells: Actinomyces, Corynebacterium (+) (-)
Long period of hours leaks/damages cell wall leading to change in color (Neg)
6. Discuss the factors that contribute to the Gram variability of a bacteria.
Autolysis
Aging – decreased peptideglycan layer
Temperature of incubation results to loss of gram (+)
pH – change
Technical errors
Incomplete decolorization
Thick smear
Removal of MgRNA with bile salts
Você também pode gostar
- InclusionsDocumento2 páginasInclusionsDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- Ovalocyte 11. Acanthocyte: 1. SpherocyteDocumento1 páginaOvalocyte 11. Acanthocyte: 1. SpherocyteDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- A4 Curriculum VitaeDocumento2 páginasA4 Curriculum VitaeDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- Bacteriological Analysis of WaterDocumento1 páginaBacteriological Analysis of WaterDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 2: Fresh Tissue Preparation: LAVALLE, Jestin B. BMLS Intern HistopathologyDocumento2 páginasTopic 2: Fresh Tissue Preparation: LAVALLE, Jestin B. BMLS Intern HistopathologyDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- Bacteriological Analysis of WaterDocumento1 páginaBacteriological Analysis of WaterDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- Kato-Katz Method: LAVALLE, Jestin BDocumento2 páginasKato-Katz Method: LAVALLE, Jestin BDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- Joseph Marcelo "Erap" Ejercito EstradaDocumento1 páginaJoseph Marcelo "Erap" Ejercito EstradaDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- Primary Immunodeficiency Disease FinalDocumento35 páginasPrimary Immunodeficiency Disease FinalDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 1: Risk Management and Safety: LAVALLE, Jestin B. BMLS Intern HistopathologyDocumento2 páginasTopic 1: Risk Management and Safety: LAVALLE, Jestin B. BMLS Intern HistopathologyDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- CH 6 The ABO Blood Group SystemDocumento3 páginasCH 6 The ABO Blood Group SystemDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- Acid Fast StainingDocumento2 páginasAcid Fast StainingDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- Cedullo Malignant Non MalignantDocumento16 páginasCedullo Malignant Non MalignantDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- Debate Speech of First SpeakerDocumento3 páginasDebate Speech of First SpeakerDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- CH 5 The Antiglobulin TestDocumento2 páginasCH 5 The Antiglobulin TestDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment in Hema LecDocumento2 páginasAssignment in Hema LecDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- HistopathDocumento7 páginasHistopathDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- Kevin U. Dauila Mls3G Non-Malignant and Malignant Disorders of Wbcs Non-Malignant Disorders of WbcsDocumento17 páginasKevin U. Dauila Mls3G Non-Malignant and Malignant Disorders of Wbcs Non-Malignant Disorders of WbcsDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- HEMA AssignmentDocumento3 páginasHEMA AssignmentDixie DumagpiAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Sindroamele HemoragiceDocumento5 páginasSindroamele HemoragiceIoana GalAinda não há avaliações
- Prseptal and Orbital Cellulitis Associated With Temporal Abcess: A Rare PresentationDocumento6 páginasPrseptal and Orbital Cellulitis Associated With Temporal Abcess: A Rare PresentationTheresa JulietAinda não há avaliações
- Utilización de Streptomyces Sp. Rl8 Como Agente Probiótico en Pollos de La Raza LeghornDocumento10 páginasUtilización de Streptomyces Sp. Rl8 Como Agente Probiótico en Pollos de La Raza LeghornAndrea Urgilés GuerreroAinda não há avaliações
- MrsaDocumento63 páginasMrsaRAHULAinda não há avaliações
- Characteristics of Bacteria Worksheet: Archaebacteria - The Extreme BacteriaDocumento4 páginasCharacteristics of Bacteria Worksheet: Archaebacteria - The Extreme BacteriaElla NajahAinda não há avaliações
- MCB Question and Ans. Complied by AychrisDocumento8 páginasMCB Question and Ans. Complied by AychrisKelly KayodeAinda não há avaliações
- 39389-Article Text-160745-1-10-20220106 PDFDocumento8 páginas39389-Article Text-160745-1-10-20220106 PDFA'la Farodisil JinanAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal A Kel 1Documento7 páginasJurnal A Kel 1Pratiwi IshakAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Manual On Medical MicrobiologyDocumento159 páginasLab Manual On Medical MicrobiologyVrinda KharbandaAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiologist: 3.1.5 Isolation & Gram StainingDocumento8 páginasMicrobiologist: 3.1.5 Isolation & Gram Stainingapi-527824241Ainda não há avaliações
- BIOFOSUN®Operating Procedure of Susceptibility Test PanelDocumento19 páginasBIOFOSUN®Operating Procedure of Susceptibility Test PanelquankddAinda não há avaliações
- Recent Advances in Bacteriophage Therapy: How Delivery Routes, Formulation, Concentration and Timing Influence The Success of Phage TherapyDocumento12 páginasRecent Advances in Bacteriophage Therapy: How Delivery Routes, Formulation, Concentration and Timing Influence The Success of Phage TherapyHammerly LinoAinda não há avaliações
- What Microorganisms Are Deactivated by UltravioletDocumento2 páginasWhat Microorganisms Are Deactivated by UltravioletBurak UçkaçAinda não há avaliações
- Lactobacillus: Microbiology & ParasitologyDocumento2 páginasLactobacillus: Microbiology & ParasitologyHazel Vera BinguanAinda não há avaliações
- MacConkey AgarDocumento14 páginasMacConkey AgarAbdulaziz AbdullahiAinda não há avaliações
- LifeStraw Go-Universal - Filtration Performance SheetDocumento1 páginaLifeStraw Go-Universal - Filtration Performance SheettorgeAinda não há avaliações
- FT 56 - Lesson 1Documento51 páginasFT 56 - Lesson 1MA. NECOLE JEREMIAH GONZALESAinda não há avaliações
- The Bacteriocin Antimicrobial Test Activity of Probiotic Bacteria Isolated From Giant Prawns (Macrobrachium Rosenbergii)Documento10 páginasThe Bacteriocin Antimicrobial Test Activity of Probiotic Bacteria Isolated From Giant Prawns (Macrobrachium Rosenbergii)Reffy AdhaAinda não há avaliações
- Gram PosetiveDocumento82 páginasGram Posetiveabrham sharewAinda não há avaliações
- Stafilococcus (Coccus Gram Positif)Documento39 páginasStafilococcus (Coccus Gram Positif)arisita firmanAinda não há avaliações
- Log Book Dk2 - Kelompok 11 - Blok6Documento27 páginasLog Book Dk2 - Kelompok 11 - Blok6Doni SaragihAinda não há avaliações
- Biolog A Celular y Organism Os ModeloDocumento75 páginasBiolog A Celular y Organism Os Modeloalanis fernanda haro benitesAinda não há avaliações
- Mls 044: Clinical Bacteriology Session 9: Antimicrobial Agents - Mechanisms of Action and ResistanceDocumento5 páginasMls 044: Clinical Bacteriology Session 9: Antimicrobial Agents - Mechanisms of Action and ResistanceJJ AngAinda não há avaliações
- LegionellaDocumento13 páginasLegionellaBam ManAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology MnemonicsDocumento5 páginasMicrobiology MnemonicsFritzel SusbillaAinda não há avaliações
- BIOL 3150 Lab Manual Labs 5-7Documento10 páginasBIOL 3150 Lab Manual Labs 5-7arshiafathiAinda não há avaliações
- Disetrai Rasa Pahit Pada TempeDocumento99 páginasDisetrai Rasa Pahit Pada TempewisnuAinda não há avaliações
- RickettsiaDocumento22 páginasRickettsiavaidyamAinda não há avaliações
- Gram StainDocumento7 páginasGram StainYani ManuelAinda não há avaliações