Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
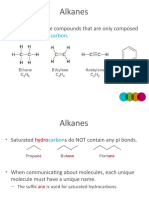
Alkane Nomenclature Rules
Enviado por
Tôn Ngọc Minh QuânDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Alkane Nomenclature Rules
Enviado por
Tôn Ngọc Minh QuânDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
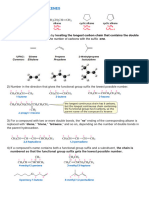
IUPAC Rules for Naming Alkanes
I. Unbranched (straight) chain alkanes
! Indicate the number of carbon atoms in the chain with a prefix followed by the ending -ane.
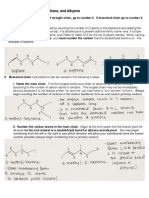
II. Branched chain alkanes
! Identify the longest chain of carbon atoms; this “parent chain” provides the root name.
When there are two or more parent chains of identical length, choose the parent chain with
the greater number of substituents.
! Identify and name the substituent(s).
! Number the parent chain.
! One substituent: number from the end that gives the substituent the lower number.
Use a hyphen to connect the number to the name.
! Two or more identical substituents: number from the end that gives the lower
number to the substituent encountered first.
The number of times the substituent occurs is indicated by a prefix di-, tri-, tetra-,
penta-, hexa-, and so on.
A comma is used to separate position numbers.
! Two or more different substituents: list the substituents in alphabetical order and
number from the end that gives the lower number to the substituent encountered
first. If there are different substituents in equivalent positions at opposite ends of
the parent chain, give the substituent of lower alphabetical order the lower number.
Prefixes such as di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, hexa-, and so on are not included in
alphabetizing.
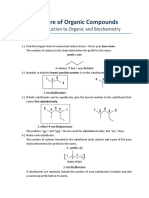
III. Cycloalkanes
! Prefix the name of the corresponding straight chain alkane with cyclo-.
! Identify and name the substituent(s) on the ring.
! Number the ring.
! One substituent: no number necessary (i.e., “1” is assumed).
! Two substituents: number so that substituent with lower alphabetical order given
lower number.
! Three or more substituents: number in order to give the substituents the lowest set
of numbers.
Você também pode gostar
- Play Guitar: Exploration and Analysis of Harmonic PossibilitiesNo EverandPlay Guitar: Exploration and Analysis of Harmonic PossibilitiesAinda não há avaliações
- IELTS Visuals Writing About Graphs, Tables and Diagrams PDFDocumento68 páginasIELTS Visuals Writing About Graphs, Tables and Diagrams PDFSaleh KhalidAinda não há avaliações
- Euclidean Geometry inDocumento1 páginaEuclidean Geometry inTôn Ngọc Minh Quân13% (8)
- 570 Academic Word List PDFDocumento5 páginas570 Academic Word List PDFĐức Anh Trương100% (1)
- Chem Assignment 1Documento4 páginasChem Assignment 1Protikal GamerAinda não há avaliações
- Alkanes - Saturated HydrocarbonsDocumento10 páginasAlkanes - Saturated HydrocarbonsJuan Carlos SihotangAinda não há avaliações
- Nomenclature Organic IUPAC RulesDocumento9 páginasNomenclature Organic IUPAC RulesSkyla DavisAinda não há avaliações
- KC-A2 CH1002-Nomenclature of AlkaneDocumento11 páginasKC-A2 CH1002-Nomenclature of Alkanefmukuka12Ainda não há avaliações
- Alkanes - Saturated Hydrocarbons: How To Name Organic Compounds Using The IUPAC RulesDocumento6 páginasAlkanes - Saturated Hydrocarbons: How To Name Organic Compounds Using The IUPAC RulesK S RayuduAinda não há avaliações
- IUPAC RulesDocumento14 páginasIUPAC RulesIce BoyAinda não há avaliações
- Alkenes NomenclatureDocumento3 páginasAlkenes NomenclatureJanna Ann JurialAinda não há avaliações
- If The Ring Has 2 Substituents, List in Alphabetical Order and Give Number 1 To First Named GroupDocumento12 páginasIf The Ring Has 2 Substituents, List in Alphabetical Order and Give Number 1 To First Named GroupAnonymous vRpzQ2BLAinda não há avaliações
- 14-04-20 - Nomenclature - Alkanes, AlkenesmamDocumento21 páginas14-04-20 - Nomenclature - Alkanes, AlkenesmamArthiAinda não há avaliações
- CS Art Integrated ProgectDocumento11 páginasCS Art Integrated ProgectSlim ShadyAinda não há avaliações
- Alkanes - Saturated HydrocarbonsDocumento9 páginasAlkanes - Saturated HydrocarbonsLâm Quách Trâm AnhAinda não há avaliações
- IUPAC NomenclatureDocumento4 páginasIUPAC NomenclatureNitesha MadhuAinda não há avaliações
- Nomenclature of Heterocyclic CompoundsDocumento43 páginasNomenclature of Heterocyclic CompoundsgfdgdghAinda não há avaliações
- 21 Iupac NomenclatureDocumento8 páginas21 Iupac NomenclatureAlliah Jasmine AlcalaAinda não há avaliações
- 8896ad74 1645604786190Documento81 páginas8896ad74 1645604786190Yash jangidAinda não há avaliações
- Algorithms QuestionsDocumento13 páginasAlgorithms QuestionsMuralidhar Nimmagadda0% (1)
- EGF2042 Chapter 2 (Naming Organic Compound) ORIGINALDocumento75 páginasEGF2042 Chapter 2 (Naming Organic Compound) ORIGINALhanis izzatiAinda não há avaliações
- Classifying and Naming of Functional GroupsDocumento30 páginasClassifying and Naming of Functional GroupsAlthea Buenavista TayobongAinda não há avaliações
- Meth-1 Hex-6 Undec-11 Eth-2 Hept-7 Dodec-12 Prop-3 Oct-8 But-4 Non-9 Pent-5 Dec-10Documento7 páginasMeth-1 Hex-6 Undec-11 Eth-2 Hept-7 Dodec-12 Prop-3 Oct-8 But-4 Non-9 Pent-5 Dec-10Twan MeyersAinda não há avaliações
- Naming Alkane and Cycloalkane: StartDocumento1 páginaNaming Alkane and Cycloalkane: Startrailey EderAinda não há avaliações
- The Steps For Naming An Organic Compound AreDocumento3 páginasThe Steps For Naming An Organic Compound AretasneemAinda não há avaliações
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: Basic PrinciplesDocumento11 páginasIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: Basic PrinciplesPablo KamgneAinda não há avaliações
- Alkane NomenclatureDocumento1 páginaAlkane Nomenclaturelakshay29960% (1)
- Alphabets and Strings Ordering of Strings RepresentationsDocumento4 páginasAlphabets and Strings Ordering of Strings RepresentationsRanbir SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Palindromic Permutation: InputDocumento1 páginaPalindromic Permutation: InputHello misterAinda não há avaliações
- SuffixtreesDocumento50 páginasSuffixtreesabhayanilarkAinda não há avaliações
- Permalex: InputDocumento1 páginaPermalex: InputHello misterAinda não há avaliações
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: Hybridized and Tetrahedral, With All Bond Angles of 109.5°Documento5 páginasAlkanes and Cycloalkanes: Hybridized and Tetrahedral, With All Bond Angles of 109.5°Alecs Elinor AmoguisAinda não há avaliações
- Asc Ascw: IntegerDocumento3 páginasAsc Ascw: IntegerIsrael CastroAinda não há avaliações
- Naming Aromatic CompoundsDocumento14 páginasNaming Aromatic Compoundssantosmaangelica16100% (1)
- Nomenclature HomeworkDocumento1 páginaNomenclature HomeworkPahal Kumari SinhaAinda não há avaliações
- Strings: Topics: String Class Associated Methods ExamplesDocumento8 páginasStrings: Topics: String Class Associated Methods ExampleskiyaraAinda não há avaliações
- Module05 StringsDocumento16 páginasModule05 Stringsefeerer582Ainda não há avaliações
- 220 Cipher TechniqueDocumento10 páginas220 Cipher Techniquecagedraptor100% (1)
- Book of Integer SequencesDocumento196 páginasBook of Integer SequencesJ GAinda não há avaliações
- Playfair Cipher The AlgorithmDocumento2 páginasPlayfair Cipher The AlgorithmRameez QureshiAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Notes On Nomenclature - Class 11Documento41 páginasChemistry Notes On Nomenclature - Class 11kaushikkartik536Ainda não há avaliações
- Orgo Naming RulesDocumento7 páginasOrgo Naming Ruleskirtmartinreyes14Ainda não há avaliações
- Classical Encryption TechniquesDocumento18 páginasClassical Encryption TechniquesBrian MattsAinda não há avaliações
- C Programs - All PrepDocumento7 páginasC Programs - All PrepsujeethAinda não há avaliações
- Common Names and Geneva SystemDocumento26 páginasCommon Names and Geneva SystemShivam GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Acid & Bases & Introduction To Organic ReactionsDocumento59 páginas2 Acid & Bases & Introduction To Organic ReactionsCesar CalderonAinda não há avaliações
- Strings PDFDocumento4 páginasStrings PDFtatigutla thulasammaAinda não há avaliações
- Python String MethodsDocumento4 páginasPython String Methodstatigutla thulasammaAinda não há avaliações
- Strings 1Documento25 páginasStrings 1ايادالعراقيAinda não há avaliações
- HFHFHFHFHFHFHFDocumento27 páginasHFHFHFHFHFHFHFAlicia GatesAinda não há avaliações
- Accessing Values in Strings: 'Hello World!' "Python Programming"Documento29 páginasAccessing Values in Strings: 'Hello World!' "Python Programming"Harshal JethwaAinda não há avaliações
- Akanes Alkenes Alkynes Aromatic Systematic Nomenclature (IUPAC) ofDocumento2 páginasAkanes Alkenes Alkynes Aromatic Systematic Nomenclature (IUPAC) ofJuaNn CarloSsAinda não há avaliações
- Acyclic HydrocarbonsDocumento14 páginasAcyclic Hydrocarbonsvishal_kalraAinda não há avaliações
- hwch21 Completed PDFDocumento8 páginashwch21 Completed PDFAlpha Benit NgongoAinda não há avaliações
- .Back Patching Is A Technique To Solve The Problem of Replacing Symbolic Names IntoDocumento8 páginas.Back Patching Is A Technique To Solve The Problem of Replacing Symbolic Names IntoDebashis ChakrabrtyAinda não há avaliações
- PresentionDocumento5 páginasPresentionمحمد حسوAinda não há avaliações
- Lecturenomenclature: Systematic Iupac Nomenclature of Unbranched AlkanesDocumento10 páginasLecturenomenclature: Systematic Iupac Nomenclature of Unbranched AlkanesSangram NalawadeAinda não há avaliações
- Coding NotesDocumento1 páginaCoding NoteswazzupnikhilAinda não há avaliações
- Alkane 1Documento15 páginasAlkane 1Dr Said HassanAinda não há avaliações
- Hammond Drawbar SettingsDocumento15 páginasHammond Drawbar SettingsJafet CervantesAinda não há avaliações
- 1402 Columnar TranspositionDocumento8 páginas1402 Columnar TranspositionKrish ParekhAinda não há avaliações
- C Fakepath Python Module2 StudyMaterial1Documento46 páginasC Fakepath Python Module2 StudyMaterial1suhaim shibiliAinda não há avaliações
- Newton MethodDocumento11 páginasNewton Methoddeba_jyoti_das100% (2)
- Newton-Raphson Method of Solving A Nonlinear EquationDocumento10 páginasNewton-Raphson Method of Solving A Nonlinear EquationGökçe DövenAinda não há avaliações
- Bài tập tuần 07 - Chuỗi ký tự: Yêu cầuDocumento2 páginasBài tập tuần 07 - Chuỗi ký tự: Yêu cầuTôn Ngọc Minh QuânAinda não há avaliações
- (Đề thi có 05 trang) Thời gian làm bài: 60 phút, không kể thời gian phát đềDocumento5 páginas(Đề thi có 05 trang) Thời gian làm bài: 60 phút, không kể thời gian phát đềTôn Ngọc Minh QuânAinda não há avaliações
- Alkane Nomenclature RulesDocumento1 páginaAlkane Nomenclature RulesTôn Ngọc Minh QuânAinda não há avaliações
- Test Unit 15 Mai Lan Huong Grade 11Documento4 páginasTest Unit 15 Mai Lan Huong Grade 11Tôn Ngọc Minh QuânAinda não há avaliações
- Reading ComprehensionDocumento24 páginasReading ComprehensionTôn Ngọc Minh QuânAinda não há avaliações
- A Solution To Score 8.0Documento53 páginasA Solution To Score 8.0Eric BuiAinda não há avaliações