Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Bachelor of Sciences Hons in Bioscience With Chemistry
Enviado por
Anusia Thevendaran0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
15 visualizações4 páginasThis document summarizes an experiment comparing the reactions of ethanal and propanone. It finds that ethanal and propanone both form white precipitates with sodium hydrogensulphite, demonstrating an addition reaction. Ethanal forms an orange precipitate with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine, showing a condensation reaction, while propanone forms a yellow precipitate. Ethanal, but not propanone, undergoes color changes from orange to green when reacted with acidified potassium dichromate(VI), demonstrating that aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids while ketones are not easily oxidized.
Descrição original:
o
Título original
org exp 8
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThis document summarizes an experiment comparing the reactions of ethanal and propanone. It finds that ethanal and propanone both form white precipitates with sodium hydrogensulphite, demonstrating an addition reaction. Ethanal forms an orange precipitate with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine, showing a condensation reaction, while propanone forms a yellow precipitate. Ethanal, but not propanone, undergoes color changes from orange to green when reacted with acidified potassium dichromate(VI), demonstrating that aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids while ketones are not easily oxidized.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
15 visualizações4 páginasBachelor of Sciences Hons in Bioscience With Chemistry
Enviado por
Anusia ThevendaranThis document summarizes an experiment comparing the reactions of ethanal and propanone. It finds that ethanal and propanone both form white precipitates with sodium hydrogensulphite, demonstrating an addition reaction. Ethanal forms an orange precipitate with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine, showing a condensation reaction, while propanone forms a yellow precipitate. Ethanal, but not propanone, undergoes color changes from orange to green when reacted with acidified potassium dichromate(VI), demonstrating that aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids while ketones are not easily oxidized.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 4
BACHELOR OF SCIENCES HONS IN BIOSCIENCE WITH
CHEMISTRY
NAMES: ANUSIA A/P THEVENDARAN
ID:17WLR00332
COURSE TITLE: BACH1623 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
EXPERIMENT: 8 ( Reactions of aldehydes and ketones)
Objective: To differentiate some reactions of ethanal and propanone.
Introduction:
A carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double bonded to an oxygen
atom, C=O such as aldehydes and ketones are belonged to this group. This a carbonyl group,
have differ in location of atom is bonded to the carbonyl carbon. The carbonyl carbon of an
aldehyde is bonded to a hydrogen atom and one carbon atom. The carbonyl carbon of a ketone is
bonded to two carbon atoms. Aldehydes and ketones are found in sugars ,flavor and intermediate
of biological chemical production.
One of the properties of aldehydes and ketones is intermolecular forces. The double connection
makes the CO double bond even larger dipole than a CO single bond. This make it a more
attractive force than ethers. Another one of the physical properties of aldehydes and ketones is
solubility. Aldehydes and ketones cannot give a H-bond but they can receive two H-bonds from
water since the carbonyl has two lone pairs. Since they have a larger dipole than alcohols, water
will form a stronger H-bond to them. Aldehydes and ketones are neutral (neither acidic nor
alkaline).
All aldehydes and ketones are flammable. The lower molecular weight ones which have a lower
boiling point will be more volatile (evaporate more) and therefore have the potential for flashing
or explosion (rapid oxidation) because of premixed with oxygen in the air. Aldehydes can be
oxidized to carboxylic acids. Ketones are not easily oxidized. This is one way to distinguish
between the aldehydes and the ketones. The aldehydes and ketones can undergo addition
reactions. An addition reaction is where a whole molecule is added across the double bond and it
becomes a single bond. In addition, both aldehydes and ketones can be reduced. This type of
addition reaction is where H2 is added to the carbonyl to give the corresponding alcohol.
Aldehydes can be reduced, [H], back to primary alcohols and ketones can be reduced to
secondary alcohols by the addition of H2 and a catalyst. Aldehydes and ketones can both react
with alcohols (usually under acid conditions) to form an addition product. Any alcohol should
react but usually the alcohols chosen are small like methanol or ethanol.
Apparatus: Safety spectacles, Protective gloves, test-tube , test-tube holder and rack, boiling
test-tube and Bunsen Burner.
Chemicals:Saturated sodium hydrogensulphite, Ethanal, Propanone, 2, 4 –
dinitrophenylhydrazine ( 5 g in 100 ml methanol), 3.16*10-5 M of sulfuric acid solution, sodium
hydroxide solution, Potassium dichromate (VI) solution, Diluted sulphuric acid, Fehling’s
solution 1, Fehling’s solution 2, silver nitrate( 0.05M), Ammonia solution and iodine solution.
Procedure:
A. Addition reaction with sodium hydrogensulphite
1. 1.8 g of sodium hydrogensulphite solid was weight and transfer into a test tube.
Distilled water was added until 1 cm above the solid level. The solution was shake
and dip into 90 Celsius water bath until all sodium hydrogensulphite solid dissolves.
2. 1cm3 of ethanal was added slowly drop by drop into the dissolved sodium
hydrogensulphite solution.
3. The tube was gently shake and the solution was poured on a watch glass and
evaporated the water on the moderately heated hot plate. The observation was noted.
4. Steps 1 to 3 was repeated using propane instead of ethanal.
B. Condensation reaction with 2, 4 – dinitrophenylhydrazine
1. 1cm3 of 2, 4 – dinitrophenylhydrazine solution was poured into a test tube and then
was added 5-6drops of ethanal .
2. 1cm3 of 3.16*10-5 M of sulfuric acid solution was slowly added into the mixture
prepared in step 1 and was shake gently. The observation was noted.
3. Steps 1 to 2 was repeated for propane .
C. Reaction with alkali
1. 3cm3 of sodium hydroxide solution was poured into a test tube and 10 drops of ethanl
was added.
2. The test tube was shake gently and warm in a water bath at 90 Celsius for 5-10
minutes.The observation was noted.
3. Steps 1 to 2 was repeated for propane.
D. Oxidation reactions
(a) With acidified potassium dichromate (VI)
1. 5 drops of ethanal was added into a test tube,2 drops of potassium dichromate (VI)
solution and 10 drops of diluted sulphuric acid followed by 4-5 drops of ethanal.
2. The test tube was shake gently and warm in a water bath at 90 Celsius for 5-10
minutes.The observation was noted.
3. Steps 1 to 2 was repeated for propane.
(b) With Fehling ‘s solution
1. 1cm3 of fehling’s solution 1 was added into a boiling test tube and then added
fehling’s solution 2 dropwise until the precipitate just dissolves.
2. Seven drops of ethanl was added.The test tube was shake gently and the mixture was
boiled on top of the Bunsen burner flame until no further colour change occurs. The
observation was noted.
3. Steps 1 to 2 was repeated for propane.
(c) With Tollen’s reagent
1.5cm3 of silver nitrate( 0.05M) was added into boiling test tube and was added one drop
of sodium hydroxide solution.
2. Concentrated ammonia solution was added drop by drop until the precipitate of silver
oxide nearly dissolves.
3. 1 to 2 drops of ethanal was added, the test tube was shake gently and the mixture was
boiled on top of the Bunsen burner flame. The observation was noted.
4.Steps 1 to 3 was repeated for propane.
E. Triiodomethane reaction
1. 5 drops of ethanal was added into a test tube and followed by 1cm3 of iodine solution was
cork and shake.
2. Sodium hydroxide was added drop by drop until the colour of iodine disappears and straw-
coloured solutions remains. The observation was noted.
3.Steps 1 to 2 was repeated for propane.
Results:
Test Ethanal Propanone
A.Addition reaction with Crystal white precipitated Crystal white precipitated
sodium hydrogensulphite
B.Condensation reaction with orange yellow
2, 4 – dinitrophenylhydrazine
C.Reaction with alkali colorless
D.Oxidation reactions
(a)With acidified potassium Orange to green No reaction
dichromate (VI)
(b)With Fehling ‘s solution Blue to green No reaction
(c)With Tollen’s reagent Colorless to mirror image No reaction
E. Triiodomethane reaction Orange dark precipitated Yellow precipitated
Discussions:
The aldehyde or ketone is shaken with a saturated solution of sodium hydrogensulphite in water
and it produce as white crystals. This react well for aldehydes but for ketones, one of the
hydrocarbon groups attached to the carbonyl group needs to be a methyl group.
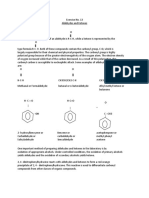
The equation for ethanal is:
The equation for propane is:
http://1chemistry.blogspot.my/2011/09/reactions-of-aldehydes-ketones-and.html
https://www.chemguide.co.uk/organicprops/carbonylmenu.html#top
Você também pode gostar
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisNo EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (2)
- Experiment: Title: ObjectiveDocumento23 páginasExperiment: Title: Objectiveapi-3734333Ainda não há avaliações
- Lab Report Organic Chemistry (Experiment 7) Lim Wey LoonDocumento24 páginasLab Report Organic Chemistry (Experiment 7) Lim Wey LoonWEY LOON LIMAinda não há avaliações
- Reactions of Aldehydes and KetonesDocumento7 páginasReactions of Aldehydes and Ketones门门Ainda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Report 4Documento7 páginasChemistry Report 4Lih XuanAinda não há avaliações
- CHM301 - Lab ManualDocumento11 páginasCHM301 - Lab Manualsiti khadijahAinda não há avaliações
- Chem (Ii) 5Documento12 páginasChem (Ii) 5Nurul Hasanah100% (1)
- Labreport 8 OrganicDocumento12 páginasLabreport 8 OrganicHajarul AjiehahAinda não há avaliações
- Aldehydes and Ketones ExperimentDocumento2 páginasAldehydes and Ketones Experimentapi-218511741Ainda não há avaliações
- Chem-No.-13 2Documento5 páginasChem-No.-13 2ho laAinda não há avaliações
- CHM1024 Report 5: Reactions of Aldehydes and KetonesDocumento14 páginasCHM1024 Report 5: Reactions of Aldehydes and KetonesAkmal Adib Fadzil96% (98)
- Experiment 9 Organic Chemistry LabDocumento7 páginasExperiment 9 Organic Chemistry LabRhodelyn TolentinoAinda não há avaliações
- Laboratory Report 7Documento5 páginasLaboratory Report 7Azizul Ridhuan Wahid17% (6)
- Laporan Resmi Praktikum Aldehid Dan KetonDocumento36 páginasLaporan Resmi Praktikum Aldehid Dan KetonAhlan RiwahyuAinda não há avaliações
- Test For CARBOHYDRATESDocumento7 páginasTest For CARBOHYDRATESSoham N100% (2)
- Determining Aldehydic and Ketonic Group P2 Group 4Documento5 páginasDetermining Aldehydic and Ketonic Group P2 Group 4Arvy Wynard EleazarAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report HydrocarbonsDocumento16 páginasLab Report HydrocarbonsKent Marcvonne C. CarugdaAinda não há avaliações
- Preparation of IodoformDocumento18 páginasPreparation of IodoformHerminHardyantiUtami80% (5)
- Classification Tests For Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Containing CompoundsDocumento7 páginasClassification Tests For Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Containing CompoundsSamantha Louise MondonedoAinda não há avaliações
- Classification Tests For Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Containing CompoundsDocumento5 páginasClassification Tests For Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Containing CompoundsAcener Padua100% (1)
- An Experiment To Prepare Ethene Gas From Ethanol and Examine Its PropertiesDocumento6 páginasAn Experiment To Prepare Ethene Gas From Ethanol and Examine Its PropertiesanockAinda não há avaliações
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehydes and KetonesDocumento7 páginasCarbonyl Compounds Aldehydes and KetonesLynde Claire Dilag100% (1)
- Biochem KudigoDocumento30 páginasBiochem KudigoEyvette GoAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 4 & 5Documento10 páginasExperiment 4 & 5Mhi Ismail0% (1)
- Classification Test Expt 9Documento9 páginasClassification Test Expt 9Francia PalinesAinda não há avaliações
- Procedure Act 1Documento15 páginasProcedure Act 1Rhealyn LegaspiAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 6Documento4 páginasExperiment 6rcarianeAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report Kimia 1Documento11 páginasLab Report Kimia 1nur anith aqilahAinda não há avaliações
- 12Documento6 páginas12NathaLie Sta ElenaAinda não há avaliações
- The Properties of Alcohols I.: C H OH H R C R' OH H R C R' OH R'' RDocumento10 páginasThe Properties of Alcohols I.: C H OH H R C R' OH H R C R' OH R'' RWimbo TrionoAinda não há avaliações
- 8.1 CompleteDocumento16 páginas8.1 CompleteBflygraydudeAinda não há avaliações
- Systematic Identification of Organic CompoundsDocumento17 páginasSystematic Identification of Organic Compoundsyouni_2005100% (1)
- Lab Manual FGS0074Documento8 páginasLab Manual FGS0074hash117Ainda não há avaliações
- Experiment 5: Alcohols and Phenols: Eden Cabana, Niña Dominguez, Philip Gabriel Gimotea Locker No. 21Documento7 páginasExperiment 5: Alcohols and Phenols: Eden Cabana, Niña Dominguez, Philip Gabriel Gimotea Locker No. 21Anonymous 75TDy2yAinda não há avaliações
- FM7 Labreport 2Documento12 páginasFM7 Labreport 2Jei y’allAinda não há avaliações
- Activity No.5: Notre Dame of Dadiangas UniversityDocumento10 páginasActivity No.5: Notre Dame of Dadiangas Universitydenshang 10Ainda não há avaliações
- Biochem Laboratory MidtermDocumento15 páginasBiochem Laboratory MidtermNica DonioAinda não há avaliações
- CHM207 Experiment 5Documento14 páginasCHM207 Experiment 5NUR SABRINA MOHD SHAHAinda não há avaliações
- 2 5352688982180245339Documento11 páginas2 5352688982180245339حسين محمد مطرود كاظمAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry PracticalDocumento38 páginasChemistry PracticalMukhtar MalikAinda não há avaliações
- Qualitative Organic Analysis - Sem 3Documento37 páginasQualitative Organic Analysis - Sem 3Reshma SomanAinda não há avaliações
- Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids: Presented by GROUP 4 Psych 1-A Pacto Maribao Miranda Nalaunan NiqueDocumento28 páginasAldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids: Presented by GROUP 4 Psych 1-A Pacto Maribao Miranda Nalaunan NiqueMissy NalaunanAinda não há avaliações
- Lab ReportDocumento8 páginasLab ReportAlysson Vany ClochetteAinda não há avaliações
- Exercise 7 (Organic Derivatives of Water)Documento6 páginasExercise 7 (Organic Derivatives of Water)Wendell Kim Llaneta0% (1)
- Lab Report HydrocarbonsDocumento7 páginasLab Report HydrocarbonsAnnrisa Layong Abain25% (4)
- Lab 4 Alcohol - 2011-2Documento8 páginasLab 4 Alcohol - 2011-2Miisty Raiyen HallAinda não há avaliações
- Magic of ChemistryDocumento8 páginasMagic of ChemistryFadya Syahnariza Nan BarenoAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 32Documento14 páginasExperiment 32Morgan Elizabeth Lepley100% (6)
- CHM207 Exp6 LabreportDocumento7 páginasCHM207 Exp6 Labreportcikk ngah nanaAinda não há avaliações
- C C C C C C CCC: CCC C C CCCCCCCC C C CCCC CCCCC CC CCC CC C CCC CCC CC CCCCC C CCC C CCCC CCC C CCCCCC CDocumento5 páginasC C C C C C CCC: CCC C C CCCCCCCC C C CCCC CCCCC CC CCC CC C CCC CCC CC CCCCC C CCC C CCCC CCC C CCCCCC CShan TiAinda não há avaliações
- Group 1 - chm132 - Lab Report1 - An'nur Najwa Binti Abd Bayan - 2021463836Documento10 páginasGroup 1 - chm132 - Lab Report1 - An'nur Najwa Binti Abd Bayan - 2021463836AN'NUR NAJWA ABD BAYANAinda não há avaliações
- InChO1999 PracDocumento2 páginasInChO1999 PracCorneliaAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 2Documento4 páginasLab 2Jason Robert VictorAinda não há avaliações
- Expt 1 To 4 Lab ReportDocumento4 páginasExpt 1 To 4 Lab ReportEyvette GoAinda não há avaliações
- Demo Flinn Co2 SolubilitydemoDocumento3 páginasDemo Flinn Co2 Solubilitydemoapi-321107093Ainda não há avaliações
- Qualitative TestDocumento4 páginasQualitative TestSwati KaushalAinda não há avaliações
- Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes: Laboratory Work 1Documento4 páginasAlkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes: Laboratory Work 1Rheza AndikaAinda não há avaliações
- Chem213 Formal Final Report 2Documento14 páginasChem213 Formal Final Report 2Amanda Long100% (2)
- Acidic Reactions of Ethanoic AcidDocumento5 páginasAcidic Reactions of Ethanoic AcidKevin DevastianAinda não há avaliações
- Water: Determination of Spatial and Temporal Variability of Soil Hydraulic Conductivity For Urban RunoDocumento15 páginasWater: Determination of Spatial and Temporal Variability of Soil Hydraulic Conductivity For Urban RunoAnusia ThevendaranAinda não há avaliações
- Resources 06 00064 v2 PDFDocumento16 páginasResources 06 00064 v2 PDFAnusia ThevendaranAinda não há avaliações
- Polymer SampleDocumento14 páginasPolymer SampleAnusia ThevendaranAinda não há avaliações
- BABS2213 TutorialDocumento12 páginasBABS2213 TutorialAnusia ThevendaranAinda não há avaliações
- BABS2213 TutorialDocumento12 páginasBABS2213 TutorialAnusia ThevendaranAinda não há avaliações
- Scan QR Code at Autogate or Checkpoint Counter: Payment Type Public EbankDocumento1 páginaScan QR Code at Autogate or Checkpoint Counter: Payment Type Public EbankAnusia ThevendaranAinda não há avaliações
- 8 Statistical EstimationDocumento12 páginas8 Statistical EstimationAnusia ThevendaranAinda não há avaliações
- PRT 140 Physical Chemistry Programme Industrial Chemical Process SEM 1 2013/2014Documento72 páginasPRT 140 Physical Chemistry Programme Industrial Chemical Process SEM 1 2013/2014Anusia ThevendaranAinda não há avaliações
- Karyotyping LabDocumento16 páginasKaryotyping LabAnusia ThevendaranAinda não há avaliações
- BACH2113 Kinetics, Mechanisms and Stereochemistry Tutorial 3 - Stereochemistry (Part 1)Documento3 páginasBACH2113 Kinetics, Mechanisms and Stereochemistry Tutorial 3 - Stereochemistry (Part 1)Anusia ThevendaranAinda não há avaliações
- Soft Skill Cert RD 201709Documento5 páginasSoft Skill Cert RD 201709Anusia ThevendaranAinda não há avaliações
- Linkage Map Worksheet Genetics 2017Documento2 páginasLinkage Map Worksheet Genetics 2017Anusia ThevendaranAinda não há avaliações
- Diamond Science & TechnologyDocumento54 páginasDiamond Science & TechnologyAnusia ThevendaranAinda não há avaliações
- 6th Year Chemistry The Gas LawsDocumento31 páginas6th Year Chemistry The Gas LawsAnusia ThevendaranAinda não há avaliações
- Org Exp7Documento5 páginasOrg Exp7Anusia ThevendaranAinda não há avaliações
- Formal Report CarbohydratesDocumento4 páginasFormal Report CarbohydratesAnusia ThevendaranAinda não há avaliações
- T6 ProbDocumento3 páginasT6 ProbAnusia ThevendaranAinda não há avaliações
- Quo p1384 Posco-MkpcDocumento1 páginaQuo p1384 Posco-MkpcAnusia ThevendaranAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Fundamentals of Organic ChemistryDocumento5 páginasChapter 1 Fundamentals of Organic ChemistryOchem90Ainda não há avaliações
- Solved Rail Chapter 1Documento7 páginasSolved Rail Chapter 1spectrum_48Ainda não há avaliações
- Protein 3dDocumento86 páginasProtein 3dSitiHamidatulAliyahAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Large Biological MoleculesDocumento20 páginasChapter 5 The Structure and Function of Large Biological Moleculesjosue868Ainda não há avaliações
- Solid Stat1Documento54 páginasSolid Stat1Ashok PradhanAinda não há avaliações
- Actg 470-HW #1Documento3 páginasActg 470-HW #1Brittany Neilson0% (1)
- Chapter 16Documento6 páginasChapter 16YasirAinda não há avaliações
- 9701 w15 Ms 41Documento13 páginas9701 w15 Ms 41MCH100% (1)
- 807 Catananes and RotaxanesDocumento22 páginas807 Catananes and RotaxanessAinda não há avaliações
- Fin 221: Sample MCQ - Chapter 5Documento2 páginasFin 221: Sample MCQ - Chapter 5amalia izzatiAinda não há avaliações
- Guaranty and SuretyshipDocumento4 páginasGuaranty and SuretyshipLhiezle Balangatan100% (1)
- Gmewue: International Edition in EnglishDocumento14 páginasGmewue: International Edition in English560712Ainda não há avaliações
- Intro To Organic Chemistry PDFDocumento64 páginasIntro To Organic Chemistry PDFYuen Kim100% (1)
- Martinez Vs HSBCDocumento13 páginasMartinez Vs HSBCSophiaAinda não há avaliações
- 1st Year Chemistry All MCQS/Short Questions For Federal Board, Punjab Board.Documento10 páginas1st Year Chemistry All MCQS/Short Questions For Federal Board, Punjab Board.Mahnain Khattak73% (33)
- On Bootstrapping Hazard Rates From Cds Spreads: Typeset in L TEX 2εDocumento21 páginasOn Bootstrapping Hazard Rates From Cds Spreads: Typeset in L TEX 2εyiboAinda não há avaliações
- CHM143L - Expt. 1 Final ReportDocumento6 páginasCHM143L - Expt. 1 Final ReportJohn Paul TañedaAinda não há avaliações
- Metallic Bonding: What Is A Metallic Bond?Documento3 páginasMetallic Bonding: What Is A Metallic Bond?Najam Us SamadAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7. Solution To End-of-Chapter Comprehensive/Spreadsheet ProblemDocumento5 páginasChapter 7. Solution To End-of-Chapter Comprehensive/Spreadsheet ProblemBen HarrisAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter Four, Cycloalkanes (Part One - Monocyclic Alkane)Documento8 páginasChapter Four, Cycloalkanes (Part One - Monocyclic Alkane)Amin JamjahAinda não há avaliações
- Tata Steel Limited: Convertible Alternate Reference Securities (A)Documento3 páginasTata Steel Limited: Convertible Alternate Reference Securities (A)Shreyo Chakraborty0% (1)
- Annuity DueDocumento2 páginasAnnuity DueJsbebe jskdbsj50% (2)
- FCCBDocumento20 páginasFCCBHitesh MulaniAinda não há avaliações
- Philguarantee Vs V.P. Eisebio Cons. G.R. No. 140047 July 13 2004Documento2 páginasPhilguarantee Vs V.P. Eisebio Cons. G.R. No. 140047 July 13 2004Milcah MagpantayAinda não há avaliações
- Org ChemDocumento20 páginasOrg Chemirisyyy27Ainda não há avaliações
- Burghardt Hoskins The Convexity Bias in Eurodollar FutureDocumento16 páginasBurghardt Hoskins The Convexity Bias in Eurodollar FutureMohamad KarakiAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture2 MartinDocumento46 páginasLecture2 MartinLambert StrongAinda não há avaliações
- Hull OFOD10e MultipleChoice Questions Only Ch06Documento4 páginasHull OFOD10e MultipleChoice Questions Only Ch06Kevin Molly KamrathAinda não há avaliações
- Texas Instruments BA II Plus (TI BA II+)Documento14 páginasTexas Instruments BA II Plus (TI BA II+)Hasan Tariqul IslamAinda não há avaliações
- 160000MT White Sugar Cane Tender On Edition 2Documento31 páginas160000MT White Sugar Cane Tender On Edition 2KoMoLoKo100% (1)