Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Genetics 1
Enviado por
raphael0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
23 visualizações3 páginasreviewer
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoVocê está na página 1de 3
GENETICS = Heredity + Variation THOMAS hunt MORGAN (1910) CALVIN BRIDGES
Greek work “GEN” (1916)
To become or to grow Chromosome contained not one but many GENES.
Coined by William Bateson (1906) FREDRICK GRIFFITH (1928)
History Focused on the Molecular aspect.
HIPPOCRATES & ARISTOTLE (384-322 BC) Trying to prove the DNA.
Theory of Pangenesis Conjugation (Exchange of genetic material between
Gemmules or Semen bacteria or the transfer of plasmid)
JEAN BAPTISTE DE LAMARCK (1744-1829) OSWALD AVERY, COLIN MAC LEOD AND MACLYN MC
Theory of Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics CARTY (1944)
Giraffe experiment Identified the transforming agent as the genetic
AUGUST WEISMANN (1834-1914)
material of an organism.
Germplasm theory
Germplasm – Sex cells Used ‘restriction enzymes’ – capable of degrading
Contradicts the theory of pangenesis another compound or molecule.
GREGOR MENDEL (1822-1884) GEORGE BEADLE and EDWARD TATUM
Austrian Monk One gene one enzyme
Garden Peas experiment Neurospora, a mold that grows on bread in the tropics.
Father of Genetics ERWIN CHARGAFF (1950)
Mendelian factor Developed the ‘Chargaff rule’- The ration of purine
Mathematical basis of transmission of traits and pyrimidine.
1868 FRIEDRICH MIESCHER (1:1)
Isolated nuclein a compound that includes nucleic Purine = Adenine (A), Guanine (G)
acid, from pus cells obtained from discarded Pyrimidine = Cytosine (C), Thymine (T)
bandages. JAMES WATSON and FRANCIS CRICK (1953)
1870 WALTHER FLEMMING Molecular structure of the DNA
Discovered mitosis ROSALIND FRANKLIN
1900 CARL CORRENS in Germany, ERICK VON X-ray diffraction data of DNA
TSCHERMAK in Australia, HUGO DE VRIES in Holland FRANCIS CRICK and GEORGE GAMOV (1957)
Studies on Maize, Primrose, Poppies and other Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
flowering plants using mendel’s theory FRANCOIS JACOB and JACQUES MONOD
WILLIAM BATESON, Edith REBECCA SANDERS and Established the existence of genetic regulation
LUCIEN CUENOT 1902 mechanism of chromosomes / DNA in order to turn on
Same ratios obtained in Animals using mendel’s theory and off genes.
WALTER SUTTON and THEODOR BOVERI (1903) MARSHALL NIRENBERG, HEINRICH MATHAEI, and
Study about chromosomes and meiosis using fruit fly SEVERO OCHOA (1966)
EDMUND WILSON and NELLIE STEVENS (1905) Genetic code cracked – different combinations of
Proposed the idea that separate X and Y nitrogenous bases
One of the greatest discoveries in the field of genetics.
chromosomes determine sex. The ‘Triplet code’
WILLIAM BATESON and REGINALD crudell PUNNETT 1 codon = 3 nitrogenous bases = 1 amino acid
(1905-1908) PAUL BERG
Demonstrated that some genes modify the action of Isolated and employed a restriction enzyme to cut
other genes. Modifier gene DNA.
WILHELM JOHANNSEN Berg used ligase to paste two DNA strands together to
Coined the terms: ‘Gene' to describe the carrier of form a hybrid circular molecule.
heredity; ‘
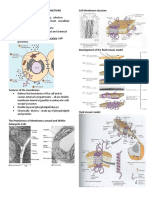
1972 – Recombinant Insulin CHROMOSOME
Genentech, Inc. and The City of Hope National Medical 1. Centromere/ Kinetochore/ Primary constriction
Center - For the attachment of spindle fibers in cell
A synthetic version of the human insulin gene was division
constructed and inserted into the bacterium Escheria 2. Secondary constriction/ satellite
coli. - Attachment of nucleolus, for protein synthesis
1985 3. Nucleolus organizing region
Genetically engineered plants resistant to insects, - Where you can found in nucleolus
viruses, and bacteria were field tested for the first time. - Region designated for the satellite
The NIH approved guidelines for performing
experiments in gene therapy on humans. 4. Chromomeres (smaller) & Knobs (larger)
1988 Types of chromosomes:
Harvard molecular geneticists PHILIP LEDER AND
TIMOTHY STEWART awarded the first patent for a
genetically altered animal, a mouse that is highly
susceptible to breast cancer.
1998
A rough draft of the human genome map is produced,
showing the locations of more than 30,000 genes.
Three Great Milestone in GENETICS Metacentric
1. GREGOR MENDEL Centromere is positioned at the center
Rules of Inheritance
2. JAMES WATSON and FRANCIS CRICK Arms are in equal length
Model for DNA structure Submetacentric
3. HUMAN GENOME PROJECT Centromere near at the center
Applications of Genetics Have short (p-arm) and long (q-arm) arms
. Plant and animal improvement Acrocentric
. Medicine
. Genetic Counseling Centromere near the terminal region
. Legal Applications Presence of satellite
. Genetic Engineering Telocentric
Genetics play a huge part in who we are. But we also Centromeres at the end/terminal region
have free will. Most of us hate GENETICS, because this CELL CYCLE:
will reveal the truth in us. 1. Interphase (non-dividing phase)
a. G1 = Growth of the cell due to inhibition
of water
Start of RNA synthesis and protein synthesis
Building of protoplasm and cytoplasmic organelles
b. Synthesis stage = most critical period
DNA duplication and synthesis
Centriole reproduction (animal cell)
RNA synthesis and protein synthesis continues.
Synthesis of histones.
c. G2 = Finalization stage
Intense protein synthesis
Completion of DNA synthesis and replication
Solenoid = layers of beads on a string Chromosomes starting to condense
Locus = position of genes in the chromosome Formation of microtubules
Eukaryotic = DNA + Histones Prepares the cell for division
Prokaryotic = DNA is naked (nucleoid region)
2. Mitotic phase (dividing phase) Anaphase I: The whole chromosome move on the
a.Mitosis – for somatic cells opposite pole.
(Equational division) (Note: The whole chromosome moves on the end pole,
Cytoplasmic division that occurs in somatic cells (body there is no splitting)
cells) Telophase I: cytokinesis occurs.
Produces two identical daughter cells. (Note: The no. Of paired chromosomes/II in this stage is
Important in repairing tissues 0) no homlogus pairs
b. Meiosis – for sex cells MEIOSIS II:
(Reductional equational division) Prophase II: Condensation of cell coming from
telophase I.
Involves two divisions = Meiosis I and II that
Metaphase II: Chromosomes aligned at the equatorial
produces 4 haploid daughter cells. plate.
Occurs in Sex cells (Egg and sperm cells) Anaphase II: Separation of chromosomes that move
Important in production of gametes. towards each pole.
Mitosis: (Note: Centromere becomes functionally doubled)
Prophase: Nucleolus disappear and condensation of Telophase II: Cytokinesis occurs.
chromosomes.
Metaphase: Chromosomes moved at the equatorial
plate.
Anaphase: Centromeres split and chromatids move on
opposite pole.
Cytokinesis = Prophase, Metaphase, and Anaphase
Telophase: Cytokinesis occurs
Animals: Furrowing – force cutting from out to inside
Plants: Cell plate formation – outward movement,
from inside to outside.
MEIOSIS:
MEIOSIS I:
Prophase I: composed of substages.
Leptonema – chromosomes are concentrated in one
area. This is called “synizesis” = clamping on one side.
Zygonema / zygotin – pairing of homologous
chromosomes or the formation of bivalence (II). This
is called “synapsis” – the paired chromosomes check
one another.
Pachynema – formation of “chiasmata” – also known
as the crossing over and exchange of genetic material
between the homologous chromosomes.
Diplonema – Separation of bivalence and becomes
“univalent”.
Diakinesis – condensed form of chromosomes.
Metaphase I: Alignment of chromosomes at the
equatorial plate.
Você também pode gostar
- Cell Membrane Structures Ad Functions Cellbio 1Documento5 páginasCell Membrane Structures Ad Functions Cellbio 1raphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Laboratory Report Activity 1 PhysicsDocumento2 páginasLaboratory Report Activity 1 PhysicsraphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Lab Report 5Documento3 páginasPhysics Lab Report 5raphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Histolab 3 and 4Documento7 páginasHistolab 3 and 4raphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Lab Report 4Documento5 páginasPhysics Lab Report 4raphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Histo Lab Ws 2 Our PicsDocumento6 páginasHisto Lab Ws 2 Our PicsraphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Specialized Connective Tissues CartilageDocumento5 páginasSpecialized Connective Tissues CartilageraphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Cellbio Num. 5 and 6Documento2 páginasCellbio Num. 5 and 6raphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Phil Consti HW 2 Article 3Documento1 páginaPhil Consti HW 2 Article 3raphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Histolec HW ToxinsDocumento2 páginasHistolec HW ToxinsraphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report 2 PhysicsDocumento4 páginasLab Report 2 PhysicsraphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Biostat PrelimsDocumento9 páginasBiostat PrelimsraphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Histolabws2 PicsDocumento12 páginasHistolabws2 PicsraphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Arthritis HWDocumento9 páginasArthritis HWraphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Connective TissuesDocumento5 páginasConnective Tissuesraphael100% (1)
- Macromolecules LQ 2 Cellbio LecDocumento3 páginasMacromolecules LQ 2 Cellbio LecraphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Histolec 1 EpitheliumDocumento8 páginasHistolec 1 EpitheliumraphaelAinda não há avaliações
- The Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsDocumento2 páginasThe Parts of The Cell and Their Functionsraphael100% (1)
- Connective Tissue TypesDocumento2 páginasConnective Tissue Typesraphael100% (2)
- Cell Bio Act 2Documento2 páginasCell Bio Act 2raphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Bio Prelims 2Documento5 páginasCell Bio Prelims 2raphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Phil Consti PrelimsDocumento6 páginasPhil Consti PrelimsraphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Hereditary Stomatocytosis CellbioDocumento4 páginasHereditary Stomatocytosis CellbioraphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Mitosis and Meiosis ExercisesDocumento2 páginasMitosis and Meiosis ExercisesraphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Gall Bladder HistoDocumento3 páginasGall Bladder HistoraphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Enzyme IntroDocumento5 páginasEnzyme IntroraphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Histo 2Documento6 páginasHisto 2raphael100% (1)
- Lab Report 1 PhysicsDocumento4 páginasLab Report 1 PhysicsraphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Phil ConstiDocumento5 páginasPhil ConstiraphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (120)
- Agriculture ProjectDocumento18 páginasAgriculture ProjectRita BekeredjianAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocumento1 páginaCell Parts and Their Functionsjoan marie PeliasAinda não há avaliações
- 2003-Anoectochilus NarasimhaniiDocumento3 páginas2003-Anoectochilus NarasimhaniiSumathi RamamurthyAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology The Human ExperienceDocumento5 páginasMicrobiology The Human ExperiencezemmiphobiaAinda não há avaliações
- MolecularCellBiologyhandbook 15-16-0Documento35 páginasMolecularCellBiologyhandbook 15-16-0Iván Cruz Dávalos0% (1)
- Autecology: By: Jan Dave E. DeocampoDocumento44 páginasAutecology: By: Jan Dave E. DeocampoJan Dave DeocampoAinda não há avaliações
- Terrestrial Paleoecology Global Change PDFDocumento481 páginasTerrestrial Paleoecology Global Change PDFAnvelegAinda não há avaliações
- 1animal PDFDocumento1 página1animal PDFCristina BariAinda não há avaliações
- Molecular Biology & R-DNA TechnologyDocumento12 páginasMolecular Biology & R-DNA TechnologyRajnesh ParasharAinda não há avaliações
- SL 102 Soil Biological Properties Lect 1&2Documento65 páginasSL 102 Soil Biological Properties Lect 1&2Neville TAinda não há avaliações
- Snake Enrichment SOPDocumento4 páginasSnake Enrichment SOPChoirul UmamAinda não há avaliações
- 001 v5 (Basic, BX)Documento42 páginas001 v5 (Basic, BX)Joseph Bontrager100% (1)
- Early DevelopmentDocumento5 páginasEarly DevelopmentMarina of The SeaAinda não há avaliações
- Tut 1 - Characteristics of Living Things NotesDocumento24 páginasTut 1 - Characteristics of Living Things NotesTakudzwa Stephene KambaAinda não há avaliações
- Methods of Cryopreservation in FungiDocumento9 páginasMethods of Cryopreservation in FungiPratikshaAinda não há avaliações
- Activepure Technology GraphsDocumento6 páginasActivepure Technology GraphsFuture InnovationsAinda não há avaliações
- Genomic Imprinting Is An Epigenetic Phenomenon That Causes Genes To Be Expressed in A Parent-OfDocumento3 páginasGenomic Imprinting Is An Epigenetic Phenomenon That Causes Genes To Be Expressed in A Parent-OfRamy El-HadadAinda não há avaliações
- I. Polypodiopsida (Licopsida) : A. Order: OsmundalesDocumento26 páginasI. Polypodiopsida (Licopsida) : A. Order: OsmundalesCDB 1st Semester 2077Ainda não há avaliações
- VARIASI MORFOLOGI LIMA POPULASI Meretrix Spp. (Bivalvia:Veneridae) Di IndonesiaDocumento12 páginasVARIASI MORFOLOGI LIMA POPULASI Meretrix Spp. (Bivalvia:Veneridae) Di Indonesiarzq rhmhAinda não há avaliações
- Carbohydrate Metabolism of PlantsDocumento40 páginasCarbohydrate Metabolism of PlantsCalvin HuangAinda não há avaliações
- MILLER, 1990. Plant Regeneration From ExcisedDocumento3 páginasMILLER, 1990. Plant Regeneration From ExcisedgabriellendiasAinda não há avaliações
- MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS, DISTRIBUTION, AND MYCOTOXIN PROFILES OF Fusarium SPECIES FROM SOILS IN PENINSULAR MALAYSIA PDFDocumento42 páginasMORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS, DISTRIBUTION, AND MYCOTOXIN PROFILES OF Fusarium SPECIES FROM SOILS IN PENINSULAR MALAYSIA PDFKhoirunnisa AlfitriAinda não há avaliações
- Christy Bidstrup ArticleDocumento6 páginasChristy Bidstrup ArticleAnna GajdácsiAinda não há avaliações
- Zoology Printables LAPBOOKDocumento244 páginasZoology Printables LAPBOOKvalentinabuAinda não há avaliações
- Biodiversity and EvolutionDocumento6 páginasBiodiversity and EvolutionMicah TormonAinda não há avaliações
- Historical Evolution and Current Status of The Taxonomy of Genus Pseudomonas 2009 Infection Genetics and EvolutionDocumento16 páginasHistorical Evolution and Current Status of The Taxonomy of Genus Pseudomonas 2009 Infection Genetics and EvolutionY lepay100% (1)
- Redei 1975 ARGen Arabidopsis As A Genetic Tool PDFDocumento18 páginasRedei 1975 ARGen Arabidopsis As A Genetic Tool PDFAJMRAinda não há avaliações
- 2211-5463 12453 PDFDocumento392 páginas2211-5463 12453 PDFAkash RajAinda não há avaliações
- Adaptation For SurvivalDocumento13 páginasAdaptation For SurvivalAJAYI PETERAinda não há avaliações
- (Massimo Pigliucci) Ecology and Evolutionary Biolo (BookFi) PDFDocumento20 páginas(Massimo Pigliucci) Ecology and Evolutionary Biolo (BookFi) PDFJulian ManongdoAinda não há avaliações