Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Igc1 Element 3
Enviado por
rumanDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Igc1 Element 3
Enviado por
rumanDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
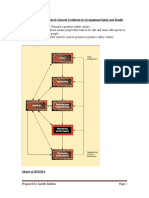
Materials:
1. Hazards of diferent 'types' of materials
2. Controls we will have to use
3. Handling of materials
4. Consideration of transport to and from site
A
5. building
Storage specificor site committeerequirements should be established. Consultation for development/
6. Disposal of waste materials
@source: Leads to:
http://www.cram.com/flashcards/igc-1-element-3-
1. Selection of the rightand contractor
1. Fire
Copy procedures
of their health safety policy
@title: Equipment
IGC
2. 1 Element
Security
Examples threat
of 3
risk response
assessments
Contractors: ArePremises
responsible 1.
2. Certification
for the work activityPlanning
and the
of spill
the
hazardswork present associated with that activity
Joint Occupiers @language-hint: 3.
2. Emergency
Sensory impairment
Qualifications
Inspection / Test andresponse
from:
training records of staf
All employees must co-operate and co-ordinate Environment
J.O.I
4.
1. Sitetheir
partial rules
Membership activities
sightedness proof to ensure
or good
organisation health
or and safety
certified bodystandards
Clients: Are responsible for hazards of the workplace 3.
1.
3. Maintenance
Air quality/from
Co-ordination procedures
of testing
work between client and the contractor
M.E.E.P = Materials, Equipment, Environment, 5.
2. Visitor/contractor
colour
Records
J.O.I
The
4. Shared
Hazards
People blindness
of maintenance
attitudes,
and controls control
values, and tests
beliefs for
and plant and
behaviours equipment.
relating to health and safety
Front
What (Term)
should Back
2.
Job (Definition)
Lighting
factors: (T.E.W.E.D)
are the be established?
factors to consider when selecting 6.
3.
5. Traffic
Deaf
Accident
a in management
one
contractor?
Transport/Storage ear
history records (excessive accidents, Subsequent corrective action take
M.E.E.P
What 4 key = Materials,
areas do Equipment,
clients manage Environment,3.
4.
7. Temperature
People
their contractors
4.
Verbal
Monitoring
P.P.E
Names Negatives:
Organisational in?previous
of the work
Factors: andto current
ensure contractors
(C.C.C.P.R) clients working to the agree'd health and sa
Materials - 6 Deterioration
6.
4. Training
Evacuation for factors:
authorised users
Leads
8 to common approach and subsequent 1.
5.
8. Language
TASK:
Additionally,
development
Illness
Proof of barrier
Characteristics
if there may
to managementof the
are exist.
work
specific ofitself
risks
jointassociated
issues of with
what? the workplace
advice then awarene
Environment - 7 7.
5.
2. Fit for
Access/egress
no written jobadequate
purpose
record as
resources
proof.
e.g access to specialist safety
How would
Equipment - 8 you define a health and safety 6. Stress.
COMMITMENT
culture?
1.
8. Lack
Fit of leadership
for place/environment
Individual factors: and leadership
from
(C.A.M.P) from
management management
Additionally specific? 6. Security
ERGONOMICS:
Employers
Fatigue working (signThe it and study outofprocedures
the relationship - I.D) between
to sharethe riskworker, the work they ar
People (S.K.E.T) Competence - 4
7.
2.Presence
7. Welfare of blameclosely
facilities culture together may need assessments to ensure
Verbal
8.
PEER
3. Drugs
Health positives:
group and
and alcohol
pressure:
safety Extentofallowed
receiving to drivethan
lower knowledge,
priority badexperience
behaviour
other business issues that bring
What Competence:
1.
1. Accident
It's quick Is
rates the combo skills, and training
What acronym
Employees
are the
the do you
working
factors associate
close
that together
could with
resultsafety
share Workload:
4.related
what?
Also
9.
inhealth
the1. diferent
Training
deterioration
High
Use of behaviour?
staf Amount,
and time
education
turnover
of health
surveys/Discussion rate,and
schedules deadlines
(positive)
safety
groups of
so 2 contractorswork
culture?
to degree
establish aren't
why toinwhich isdont
each others
workers under waytheir direct
appreciate theco
What are
J.O.I. -acronym
What
5
indicators
I (C.A.M.P) do -you
used
Partassociate
5 to assess 2.
with safety2.
Absenteeism,
and
Allows
CONSULTATION
5.related
Lack
safety
of
culture?
additional
behaviour?
worker
either
and
not
information
worker
consultation
willing, or not able to work
to be transmitted i.e tone, facial expressions
involvement and bp
J.O.I. - J Attitude:
3. Staf
Environment: A persons
turnover. (Low
Air, space, point - of
Good. view
lighting, High or -
noise,way
Poor) of looking
temperature at something.
andtalks.
humidity How they think a
Health
2. Safety and safety
awareness behaviour influenced by physical factors:
4
Perception of risk: A way a person interprets4. Influence
Written
information Negatives: peerscampaign
ofdetected (peerby group
their
using
senses.
posters
pressure. Some
and toolbox
Social group
hazards areform group
notrisks
detected behaviour.
by human Socs
J.O.I. - O COMMUNICATION:
1. Education and Health- workers
training and safety messages
educated in and information
hazards and associated
Part 1 Motivation:
1. Takes
Displays
1.
3. Size
Develop
time A to
andtraining persons
write
controls: drive towards
Their design,
programmes
a goal; The
poorly awareness
increases
thing that
designs canofcontribute makes
hazards
them
to human
and
do errorthim
consequence
with
what
2. High
Management
2. Language impact intervention
commitment
barrier may (shock tactics) - workers shown
and leadership: blindness). Sensory impairment also pictures of injuries cau
Perception
Part 2 of hazards can be efected by sensory 2.
3. Weight
Resources: impairment
Enforcement Availability
- (partial
Workers ofexist
sightedness/colour
equipment,
are forced machine
to use guardguards,
by P.P.E and allocating
supervision and time for
Workers
3. Highlight
Strength
Having often
amanagement
positive behavesafety unsafely
culture NOT
stems simply
from because
having they are wilful,
competent staf. but becauseEve
discipline. th
J.O.I. - I (C.A.M.P) - Part 3 4. Consultation
Having
Written hazards
positives: and using
involvement safety
demonstrates signs,
in paint
decision
a 'visible' (yellow
making
commitmentand
process black)
to- for
Workers
health low objects
get
and e.g
ownersh
safety
What other factors distort perception? 5 Items Disciplinary
4. Age procedures:
Outline ways of improving
J.O.I. - I (C.A.M.P) - Part 4 health and safety1. Primary
culture
Therefore ways
ofany anof improving
organisation.
reward scheme health
Partin a1and safety related
workplace intended behaviour
to improve and subsequent saf
In what ways can you improve worker perception 5.
1.
All Permanent
Gender
The
stafof
Emergency
5.
1. Ensure
Behaving
Understand:
company
(S.K.E.T) record
types:
hazards?
adequate
correctly
safety
to6carry policy
lighting out work
themselves safety and without risk to health.safety must be c
Outline ways of improving health and
What physical factors influence health and safety safety2.
1.
6.
2. Cheap
culture
'Minor'
Medical to
of
behaviour?
Employees distribute
breaks
an
history organisation.
in
liability to
health
6 insurance wideand
Partaudience
safety
2 procedure are often efectively dealt with inf
(Management commitment to leadership) 1. 2.
1.
3.
Fire
Often
Their
The negative
involvement
hazards
Emergency
culture
and
procedures risksin occur
inherentif worker
day-to-day in feels
management
their workdictatedof to. and safety e.g attending
health
Outline
Survey /ways of improving
Discussion health and safety2.
- (S.H.R.E.D) Employers
6.
3. culture
Bomb
Remove
Taking of responsibility
threatanin organisation.
distractions
part safety e.gensurePart
noise workers
3audits
(result incompetent
worker nottohearing carry out tasks safely.
warning alarms) or e
(Disciplinary procedures) 2.
4.
3.
The
Graphic
E.g correct
negatives:
a supervisor
Recent
Spillage accident
of
rulesfails
hazardous
andtotours
statistics follow
chemical
and
precautionsa safe to apply
system of work and instructs staf to cut corne
Outline
4 ways of improving health and safety3. To
4. culture
avoid
Enforcing this,
ofonlyanitorganisation.
is important to
Part actively
4 encourage worker interest andoccur
ownership b
What
(Having items are present
competent staf)on a notice board? 1. 5. Foreseeable
Convey
First aidboth,
Identity
Having
4. Release room:ofcompanyemergencies
simple
safety
manages
toxic gas
safety
messages
representatives rules
and actions
(and staf competence and firstto take should
aiders these events
checked (relevant qualifications or me
3
4 Principles for delivering media for communication 2.
1. Expensive
Centrally
Having
5. Severe appropriateto
located
weather buy or
in produce
area
procedures
orEmployer that can be accessed
for by
discussions the emergency
flooding talking directly to each worker is efective in- Efective
in place of such services
situations
(Co-operation and consultation) Direct
Extra
2. Clean, consultation:
training after:
adequately heated, lit direct safety implicationa small
5
4 Increase
First
F.E.P
1. New
aiders
Furthermore, efectiveness
Provision
employees provision (inductionof anyventilated
in house training
training)
and wellhas on tas
(Verbal, written and graphic) there are positives Graphic
3.
1. The and
Provided
Appropriate
Number
Arrangements positives:
negatives
with
organisations
of use
workers
for for
a contacting
hand
of all.
health
eye
on was
site station,
and
catching safety
emergency hot
methods and
policy cold running
(impact
services colours) water, table a chair and
4 1. Notice
ViaNo
2. worker boards
representatives: Setting up a health and safety committee (key manage
What ways can you improve efectiveness of1. 2.a=Job
Fire
Use change
language
and
noticeboard?
'localtalks
Distribution or
emergency
lighting'
of promotion
barriers
workers toprocedures
keep boardwhere illuminated
What
2 will the worker understand once theyF2. 3.
2.
3.
Toolbox
are Facilities
Process
trained?
Conveys
First aid
First
Position
Shift aid -
change
equipment appropriate
message
facilities
in
patterns high in andproduction
to
traffic
(adequate a location
wide
personnel
areas
cover audience
(messall hall,
shifts,
first aid treatment can be given
toilet)
weekends and nightshift)
Emergency
Broadcasting
3 types include
methods what? Appropriate
3.
E =Posters
Equipment
4. Location
New and
technologyarrangements:
video
- Appropriately
introduced stocked first aid kits and other equipment as necess
5 As
4.
1. a minimum:
Allocate
First aid
Communication of welfare
responsibility
cover during facilities
equipment for updating
absences (Holidays/illness)
4.
P
5.
1 =Memes
Personnel
New
fully and
legislation
stocked - email
Staf with appropriate training to deliver first aid
Typical
5 content of a general induction training 5.
5. Accident
2. course
Contact
Worker andfirst
include?
details
handbooks
aid kitreporting
incident for small,procedures
low risk workplace
What
8 circumstances will trigger extra training? 6. General
First aid safety
coverage rules (e.g smoking area)
Emergency
5 procedures reduces severity of risk P.P.P
These all bring there
When determining first aid personnel numbers, Multiple
7. Specific
1. P.P.Ewhat
Responsible first
requirements
is aid
hazards
to bekits,
individuals in own
considered?
the hazardsat various locations in larger workplace
positioned
workplace
with necessary information and knowledge to make call.
First
4 aid
Induction room
takes should
place be?
when workers join an8. organisation
Intro
placetoto risk asR.A's,
theyS.S.O.W's,
are at riskP.T.W from systems
day 1. What are they?
There
Provision
3
should be
of first aid = (F.E.P) arrangements 2.
appropriate in Accident
Preserve
eyewash
history
lifedeal
stations
with foreseeable incidents.
Exact
2 nature of first aid training normally determined 3.
In Presence byoflocal
many deterioration
Prevent instances vulnerable
legislation
the workers
emergency
of health of services
casualty can provide more efective response if g
Refresher training is=usually Resuscitation
mandatory for first
4. Workaiders pattern equipment
as skills andfade shiftoversystems
time of through
workers lack of practice
Purpose of first aid
First aid equipment includes? (P.P.P) Promote
Emergency recovery
showers
5. Geographical location of workplace
4 (depending
First aid coverage of specific hazards)
considerations? Stretchers
6 Where there may not be emergency services close by- on site nurses and doctors
d. Consultation for development/implementation of policies and procedures necessary for building.
body
dcontractor
ursequipment.
relating to health and safety
Subsequent corrective action taken)
rking to the agree'd health and safety standards
with
ialistthe workplace
safety advice then awareness of issue and appropriate response can be raised
t
ween
sharethe riskworker, the work
assessments they areboth
to ensure doing and the environment
organisations are aware of in which
possiblethey are doing
impact of useit.ofMain reasonsand
equipment = Comfort, safety
substances so and
that productivity
activities can
behaviour
other
xperiencebusiness
and issues that brings a person to a level where they are able to perform to an acceptable standard whilst being aware of their
training
een'ttoin
why which isdont
each others
workers under their direct
way
appreciate thecontrol or imposed
presence externally
of particular hazards then set about dealing with the issues by:
work
d i.e tone, facial expressions and body language.
ng at something.
ure andtalks.
humidity How they think and feel about it. Changing attitude is notoriously difficult therefore use methods such as: (H.E.E.C.)
toolbox
group form group behaviour. Social pressure exerted forcing individuals to comply with group behaviour)
nd information
azards andmakes
risks them
associated withthey
machines
hing
s canofthat
contribute do what
to human error i.e do. and
displays why guards
diferent to vieware
andneeded.
critical displays out of operations normal F.O.V
ness
ers shown hazards and
pictures consequences.
of injuries caused by failure to use guard. This may change attitude quickly.
ards,
by theyP.P.E and
supervision allocating
andbut time
discipline. for training in Health and safety
use
gngcompetent are wilful,
staf. becauseEventually it will
they perceive becomeand
a reward habit.
think the risk is worth the reward (There unsafe behaviour is incentivised)
ow and black)
process
mmitment for low
to- health
Workers andobjects
get e.g the edge of steps
ownership
safety
ted
nded behaviour
to improve and subsequent safety culture of an organisation.
hout risk to health.safety must be carefully thought through to ensure it incentivises correct behaviour
are often efectively dealt with informally e.g (discussion and coaching). However in case of breach resulting in endangerment of safety to e
ted to. and safety e.g attending safety meetings
of health
entnottohearing
carry out tasks safely.
warning alarms) or excessive heat (causing fatigue)
ork and instructs staf to cut corners in order to save time.
ehould
worker interest
these eventsandoccur
ownership by involving them in decision making process (primarily through consultation)
cked (relevant qualifications or memberships to professional bodies is important)
by the of
ssions emergency services
such situations - Efective means improving organisations health and safety culture.
ach worker is efective in a small organisation and in large workplaces.
it
as direct safety implication on tasks carried out from day-to-day in the organisation.
running water, table a chair and a clinica; waste bin as a minimum
nd safety committee (key management and representatives meet regularly to discuss health and safety matters and resolve issues).
treatment can be given
tsndsandand nightshift)
other equipment as necessary
s)
deliver first aid
place
onsand
on in larger workplace
knowledge to make call.
ovide more efective response if given critical information quickly
e by- on site nurses and doctors should be used.
ort, safety
stances so and
that productivity
activities can be co-ordinated.
whilst being aware of their own limitations. Experience or qualifications alone does not make somebody competent. They need a combina
ds such as: (H.E.E.C.)
V
aviour is incentivised)
endangerment of safety to employees and others disciplinary is used.
and resolve issues).
mpetent. They need a combination of both
Você também pode gostar
- Helmet Importance in Health and Safety DepartmentDocumento21 páginasHelmet Importance in Health and Safety DepartmentrumanAinda não há avaliações
- 20 Revision Questions With Model AnswersDocumento33 páginas20 Revision Questions With Model AnswersHossamKandilAinda não há avaliações
- Nebosh Certificate Course NotesDocumento62 páginasNebosh Certificate Course NotesMinnie ALAinda não há avaliações
- IGC1 PP March 201023112011481322 PDFDocumento2 páginasIGC1 PP March 201023112011481322 PDFAsim50% (2)
- Element 1Documento60 páginasElement 1naidu952290% (10)
- The Beard of A Muslim PDFDocumento25 páginasThe Beard of A Muslim PDFNasirAbbasAinda não há avaliações
- Tire Retreading & RepairDocumento31 páginasTire Retreading & RepairrumanAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Activity ID Activity Name Remaining BL Project Start BL Project FinishDocumento4 páginasActivity ID Activity Name Remaining BL Project Start BL Project FinishDeviPrasadNathAinda não há avaliações
- Reading Diagnostic Test n2Documento5 páginasReading Diagnostic Test n2Cleo TokongAinda não há avaliações
- Virginia's Rare Animals GuideDocumento83 páginasVirginia's Rare Animals Guidezineil BlackwoodAinda não há avaliações
- Delhi Public School Ghatkesar Friday: Daily Time TableDocumento1 páginaDelhi Public School Ghatkesar Friday: Daily Time TableranjithophirAinda não há avaliações
- Creative Minds and CraftsDocumento162 páginasCreative Minds and CraftsLogan Mckee100% (7)
- Ludo Present Tenses Fun Activities Games Games Grammar Drills - 95023Documento1 páginaLudo Present Tenses Fun Activities Games Games Grammar Drills - 95023Claudia JimenezAinda não há avaliações
- Mismatch Defect in ERW Steel Tubes: September 2014Documento5 páginasMismatch Defect in ERW Steel Tubes: September 2014Riza KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Abeeb Salaam - Gangs in Kano, NigeriaDocumento11 páginasAbeeb Salaam - Gangs in Kano, Nigeriapraveenswami100% (1)
- Eastern Mindoro College Child Development CourseDocumento2 páginasEastern Mindoro College Child Development CourseJaymar MagtibayAinda não há avaliações
- Shareholders AgreementDocumento12 páginasShareholders Agreementmetareason100% (1)
- Veritas Command Line SyntaxDocumento6 páginasVeritas Command Line SyntaxSalma KhatoonAinda não há avaliações
- G8 DLL Health-2Documento6 páginasG8 DLL Health-2MARGIE BOGANOTAN100% (1)
- 8 DischargeDocumento33 páginas8 DischargelelsocAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 StsDocumento16 páginasChapter 1 Stsfelize padlla100% (4)
- Freepik BrandBook 07092023Documento84 páginasFreepik BrandBook 07092023Sai MoonAinda não há avaliações
- Inphusion HX: Color Additive For Hot Mix AsphaltDocumento1 páginaInphusion HX: Color Additive For Hot Mix AsphaltRed RedAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Notes PGS 505Documento79 páginasLecture Notes PGS 505miftha faizAinda não há avaliações
- Medado and DacanayDocumento6 páginasMedado and DacanayDatu TahilAinda não há avaliações
- Qualitative StudyDocumento7 páginasQualitative Studyapi-303681050Ainda não há avaliações
- Appendix 12.7.0 Fortinet Corporate ProfileDocumento8 páginasAppendix 12.7.0 Fortinet Corporate ProfileYan Naing ThwinAinda não há avaliações
- Kabbalah For Complete Life ManagementDocumento177 páginasKabbalah For Complete Life ManagementRudy Tombeng Lopez100% (2)
- Cognitive Academic Language Learning Approach: CALLA's Basic PremisesDocumento2 páginasCognitive Academic Language Learning Approach: CALLA's Basic PremisesDani SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- 1101 Lab 4 - Circular MotDocumento18 páginas1101 Lab 4 - Circular MotYi Wei OngAinda não há avaliações
- Chevron SealDocumento7 páginasChevron Sealwenny_tpdAinda não há avaliações
- Student Welcome PackDocumento24 páginasStudent Welcome PackKaden MaysAinda não há avaliações
- Come, Holy SpiritDocumento1 páginaCome, Holy SpiritNguyễn TrinhAinda não há avaliações
- SSC Imd Electronics 1Documento25 páginasSSC Imd Electronics 1kartikAinda não há avaliações
- Tarnished Queen - Nicole FoxDocumento396 páginasTarnished Queen - Nicole Foxyourmom33% (3)
- A Study of The Sewn Plank Boats of Goa IndiaDocumento11 páginasA Study of The Sewn Plank Boats of Goa IndiaKrishna L.R.Ainda não há avaliações
- RAICES LawsuitDocumento25 páginasRAICES LawsuitJohn MoritzAinda não há avaliações