Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Answer Key Structure and Function of Macromolecules
Enviado por
attoo0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
305 visualizações2 páginasTítulo original
Answer key Structure and function of macromolecules.docx
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
305 visualizações2 páginasAnswer Key Structure and Function of Macromolecules
Enviado por
attooDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
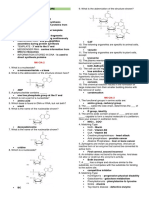
Chapter 5: Structure and function of macromolecules
Insert the number (1-15) from the choices below against the corresponding terms, in the spaces
provided.
1. Hydrolysis 2. Glucose 3. Nucleic acids. 4 Cellulose 5. Omega – 3 fatty acids
6. Glycosidic 7. Trans fats 8. Dehydration 9. Chitin 10. Hydrophobic 11. Lipids
12. Ester 13. Single bonds 14. Starch 15. Glycogen
Storage form of glucose in plants 14
Storage form of glucose in animals and humans 15
Structural polysaccharide in plants 4
Structural polysaccharide in animals 9
Four classes of large biological molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, 3
proteins, and ?
Process by which monomers are linked together to form 8
polymers
Process by which polymers are broken down into monomers 1
C6H12O6 2
Linkage between monomers in polysaccharides 6
10
Unique property of Lipids
Fats, phospholipids and steroids 11
Linkage in fats 12
Saturated fatty acids. 13
Hydrogenation of unsaturated fats results in 7
Provide protection against cardiovascular disease 5
1. Casein 2. Gene expression 3. Nucleoside 4. Chaperonins 5. Bioinformatics
6. Quarternary structure 7. Adipose cells 8. Guanine 9. Nucleotide
10. Secondary structure 11. Pyrimidines 12. Deoxyribose 13. Proteomics
14. Hemoglobin 15. Amino acids
Protein molecules that assist in the proper folding of other
protein molecules
4
Oxygen transporting protein
2
Two or more polypeptide chains form one macromolecule
6
B pleated sheet
3
Prediction of protein structure from amino acid sequences
5
Storage form of amino acids in milk
1
Fat is stored in these cells
7
Amino and carboxyl groups are found in
15
Nitrogenous base and a pentose sugar
10
Analysis of large sets of proteins including their sequences
13
Sugar molecule in DNA
12
Cytosine, thymidine and uracil
11
DNA directed synthesis of mRNA and through mRNA control of
protein synthesis
2
a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate group
9
Complementary base pairing: Adenine with ?
8
Você também pode gostar
- Macromolecules WorksheetDocumento4 páginasMacromolecules WorksheetYash PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Textbook of Biochemistry With Clinical Correlations 7th Edition 7th Edition Ebook PDFDocumento62 páginasTextbook of Biochemistry With Clinical Correlations 7th Edition 7th Edition Ebook PDFfannie.ball342100% (34)
- The Mystery of The Secret RoomDocumento3 páginasThe Mystery of The Secret RoomNur Farhana100% (2)
- BIO101 NotesDocumento12 páginasBIO101 NotesLora BellAinda não há avaliações
- Biochemistry For Medical Laboratory Science Course Outline 2018Documento4 páginasBiochemistry For Medical Laboratory Science Course Outline 2018Vincent Cuyuca100% (1)
- Chemistry Part 3 - BiochemistryDocumento16 páginasChemistry Part 3 - BiochemistryEJ Zoe ArturoAinda não há avaliações
- Protein ReviewerDocumento4 páginasProtein ReviewerMa Anna Cris LumongsudAinda não há avaliações
- Biological - MacromoleculesDocumento58 páginasBiological - Macromoleculesaaronnnjohnnnn20Ainda não há avaliações
- Biochem Lec 2Documento11 páginasBiochem Lec 2B-Panganiban, Cyrus SalvadorAinda não há avaliações
- Purine and Pyrimidine Nucleotide MetabolismDocumento13 páginasPurine and Pyrimidine Nucleotide Metabolism202210034Ainda não há avaliações
- L2 Fatty Acid MetabolismDocumento32 páginasL2 Fatty Acid Metabolismdunghd.ba12-056Ainda não há avaliações
- Essential Idea: Proteins Have A Very Wide Range of Functions in Living OrganismsDocumento29 páginasEssential Idea: Proteins Have A Very Wide Range of Functions in Living OrganismshzunigaAinda não há avaliações
- LG 4 Digestion and Human HealthDocumento148 páginasLG 4 Digestion and Human Health86t8gx9y8zAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 4 - Cell Transport MechanismDocumento74 páginasUnit 4 - Cell Transport MechanismIzzy Dynielle SolamilloAinda não há avaliações
- BiomoleculeDocumento8 páginasBiomoleculejimmy902437Ainda não há avaliações
- LipidsDocumento32 páginasLipidspnnavyaaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter - Muscle ProteinsDocumento18 páginasChapter - Muscle ProteinsSavitha ChellappanAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy (Protein)Documento3 páginasNutrition and Diet Therapy (Protein)Nairin W. EdzlaAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 3.4 - Nucleic Acid PDFDocumento28 páginasLecture 3.4 - Nucleic Acid PDFHedric VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Kaplan Biochem-QuizletDocumento1 páginaKaplan Biochem-QuizletAnjali PradhanAinda não há avaliações
- 2.4 Proteins: Essential Idea: Proteins Have A Very Wide Range of Functions in Living OrganismsDocumento31 páginas2.4 Proteins: Essential Idea: Proteins Have A Very Wide Range of Functions in Living OrganismsMubarak AlNaimiAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Activity No. 3 - REMEGIADocumento14 páginasLecture Activity No. 3 - REMEGIAMatthew Reyes RemegiaAinda não há avaliações
- TAGUM - Q2 - Biotech WS1Documento4 páginasTAGUM - Q2 - Biotech WS1Kryssa TagumAinda não há avaliações
- 2.4 Proteins Ib Biology PresentationDocumento33 páginas2.4 Proteins Ib Biology PresentationIker GAinda não há avaliações
- Webcontent 146 513 1 Biomolecules 20190926165314Documento2 páginasWebcontent 146 513 1 Biomolecules 20190926165314Abhishek Kumar VermaAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive Gland Enzymes Substrates Products Salivary Glands Gastric Glands PancreasDocumento1 páginaDigestive Gland Enzymes Substrates Products Salivary Glands Gastric Glands PancreasFebbio YoghatamaAinda não há avaliações
- Pato 1Documento1 páginaPato 1Febbio YoghatamaAinda não há avaliações
- Pato 1Documento1 páginaPato 1Febbio YoghatamaAinda não há avaliações
- Ans 5jan'10 Kul - Cell Membrane Channel and Transporter PSPD UNTADDocumento61 páginasAns 5jan'10 Kul - Cell Membrane Channel and Transporter PSPD UNTADAnonymous UYpbxWzAinda não há avaliações
- WK11 Cc-LecDocumento14 páginasWK11 Cc-LecAira UsiAinda não há avaliações
- Bio Chemistrycurriculum 1Documento11 páginasBio Chemistrycurriculum 1api-3728690Ainda não há avaliações
- Lec 6,7 Biological MacromoleculesDocumento32 páginasLec 6,7 Biological MacromoleculesEnmuskAinda não há avaliações
- St. Thomas Academy: Part A. Classify Each As A Carbohydrate, Protein, Lipid or Nucleic Acid (Only Used Once)Documento2 páginasSt. Thomas Academy: Part A. Classify Each As A Carbohydrate, Protein, Lipid or Nucleic Acid (Only Used Once)Kate Ashly Mae AteradoAinda não há avaliações
- Sr. No. Core Areas Percentage: BiochemistryDocumento9 páginasSr. No. Core Areas Percentage: BiochemistrymubinAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Activity No. 3 - Building Blocks of Plant LifeDocumento14 páginasLecture Activity No. 3 - Building Blocks of Plant LifeMatthew Reyes RemegiaAinda não há avaliações
- 12 - Nucleotide MetabolismDocumento53 páginas12 - Nucleotide MetabolismFrankenstein MelancholyAinda não há avaliações
- Stryer Table of ContentsDocumento5 páginasStryer Table of ContentsHannah Grace A PugalAinda não há avaliações
- Monomers Polymers/ Different Name Elements Examples / Real Life Examples / Real Life Use Special Characteristics Synthesis ReactionDocumento2 páginasMonomers Polymers/ Different Name Elements Examples / Real Life Examples / Real Life Use Special Characteristics Synthesis ReactionNxlaAinda não há avaliações
- Biological Molecules 1Documento29 páginasBiological Molecules 1hamdan.ishaq16Ainda não há avaliações
- Peptides and Proteins: Lec. 6: Mod. by Dr. Adam OsmanDocumento39 páginasPeptides and Proteins: Lec. 6: Mod. by Dr. Adam Osmanنجوي عبدالوهابAinda não há avaliações
- Test Blueprint Compre 2024Documento2 páginasTest Blueprint Compre 2024Immah PinedaAinda não há avaliações
- ProteinsDocumento12 páginasProteinsnmqq8k4vg8Ainda não há avaliações
- 2.4 ProteinsDocumento30 páginas2.4 ProteinsKatleho MokheleAinda não há avaliações
- Vitamin A - BIOT 203Documento21 páginasVitamin A - BIOT 203Soniya BastolaAinda não há avaliações
- Kisi2 BiochemDocumento4 páginasKisi2 Biochemcindy clarissaAinda não há avaliações
- BiochemDocumento1 páginaBiochemardusiasAinda não há avaliações
- UTF-8''U1 Chapter 3 The Chemical Building Blocks of LifeDocumento54 páginasUTF-8''U1 Chapter 3 The Chemical Building Blocks of Life1968405546Ainda não há avaliações
- Organic Compunds in The BodyDocumento1 páginaOrganic Compunds in The BodyNursakinah NajwahAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 MacromoleculesDocumento48 páginasChapter 5 MacromoleculesChaehyoung LimAinda não há avaliações
- Protein & Peptide Drug Delivery SystemDocumento12 páginasProtein & Peptide Drug Delivery SystemSandeep SainiAinda não há avaliações
- Chemicals of LifeDocumento43 páginasChemicals of LifeHamza AnwarAinda não há avaliações
- Essential Idea: Proteins Have A Very Wide Range of Functions in Living OrganismsDocumento38 páginasEssential Idea: Proteins Have A Very Wide Range of Functions in Living OrganismsAlvin JovanAinda não há avaliações
- BiomoleculesDocumento6 páginasBiomoleculesgeecyjane YguintoAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 6Documento29 páginasUnit 6Vaishnav SankarkAinda não há avaliações
- Unit One This or That 1Documento2 páginasUnit One This or That 1sushantAinda não há avaliações
- Part 1: Biomolecules Chart: Energy Source For The Cell Structural Support For Plant CellsDocumento6 páginasPart 1: Biomolecules Chart: Energy Source For The Cell Structural Support For Plant CellsJOHN CARLO ASTILLAAinda não há avaliações
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 9Documento11 páginasNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 9paulina ineduAinda não há avaliações
- Biomolecules Comprehensive2514897212738Documento15 páginasBiomolecules Comprehensive2514897212738DeepanshuAinda não há avaliações
- GRD271-Islamic EN-Lec11-Contributions-Part2Documento13 páginasGRD271-Islamic EN-Lec11-Contributions-Part2attooAinda não há avaliações
- Questions of Chapter 16: CorrelationDocumento17 páginasQuestions of Chapter 16: CorrelationattooAinda não há avaliações
- Hypothesis TestingDocumento14 páginasHypothesis TestingattooAinda não há avaliações
- GRD271-Islamic EN-Lec2-ShariaaDocumento24 páginasGRD271-Islamic EN-Lec2-ShariaaattooAinda não há avaliações
- Biostatistics Chapter 17Documento13 páginasBiostatistics Chapter 17attooAinda não há avaliações
- Radiography & Medical Imaging Science (Ultrasound Imaging)Documento25 páginasRadiography & Medical Imaging Science (Ultrasound Imaging)attooAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of Patient'S Safety: Basic Health Skills (GRU1251)Documento39 páginasPrinciples of Patient'S Safety: Basic Health Skills (GRU1251)attooAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 3 GallbladderDocumento59 páginasLecture 3 GallbladderattooAinda não há avaliações
- Health Law & Ethics Legal and Ethical Issues in Health Care: Basic Health Skills Ii (Gru1251)Documento59 páginasHealth Law & Ethics Legal and Ethical Issues in Health Care: Basic Health Skills Ii (Gru1251)attooAinda não há avaliações
- PleuraDocumento51 páginasPleuraattooAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2 Liver Focal PathologyDocumento52 páginasLecture 2 Liver Focal PathologyattooAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 7 Doppler and HaemodynamicsDocumento54 páginasLecture 7 Doppler and HaemodynamicsattooAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 5 Abdominal Wall and HerniasDocumento45 páginasLecture 5 Abdominal Wall and HerniasattooAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 4 Biliary TreeDocumento31 páginasLecture 4 Biliary TreeattooAinda não há avaliações
- Allen LM. Published Online:: August 31, 2012Documento1 páginaAllen LM. Published Online:: August 31, 2012attooAinda não há avaliações
- Allen LM. Published Online:: August 31, 2012Documento1 páginaAllen LM. Published Online:: August 31, 2012attooAinda não há avaliações
- Allen LM. Published Online:: August 31, 2012Documento1 páginaAllen LM. Published Online:: August 31, 2012attooAinda não há avaliações
- TretanivDocumento1 páginaTretanivattooAinda não há avaliações
- Major Depression: Mental Disorders (DSM) and International Classification of Diseases (ICD) Diagnostic CriteriaDocumento2 páginasMajor Depression: Mental Disorders (DSM) and International Classification of Diseases (ICD) Diagnostic CriteriaattooAinda não há avaliações
- Overview of Multiple Sclerosis: For Rehabilitation ProfessionalsDocumento53 páginasOverview of Multiple Sclerosis: For Rehabilitation ProfessionalsattooAinda não há avaliações
- JournalDocumento1 páginaJournalattooAinda não há avaliações
- BioDocumento1 páginaBioattooAinda não há avaliações
- General X-Ray ProjectionsDocumento19 páginasGeneral X-Ray ProjectionsattooAinda não há avaliações
- Hellinger, Bert - GenoGraph 2.1 ManualDocumento16 páginasHellinger, Bert - GenoGraph 2.1 ManualGladys Achurra DíazAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1. Introducing Second Language AcquisitionDocumento18 páginasLecture 1. Introducing Second Language AcquisitionДиляра КаримоваAinda não há avaliações
- 2019 National Innovation PoliciesDocumento98 páginas2019 National Innovation PoliciesRashmi SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Students' Rights: Atty. Mabelyn A. Palukpok Commission On Human Rights-CarDocumento15 páginasStudents' Rights: Atty. Mabelyn A. Palukpok Commission On Human Rights-Cardhuno teeAinda não há avaliações
- Animals Living in LithuaniaDocumento12 páginasAnimals Living in LithuaniaSuiliwasAinda não há avaliações
- NEGRETE vs. COURT OF FIRST INSTANCE OF MARINDUQUEDocumento1 páginaNEGRETE vs. COURT OF FIRST INSTANCE OF MARINDUQUELeo TumaganAinda não há avaliações
- Enter Pre NaurDocumento82 páginasEnter Pre NaurNeha singhalAinda não há avaliações
- Alb Ani A BrochureDocumento18 páginasAlb Ani A BrochurejskardaAinda não há avaliações
- RSC SCST Programme Briefing For Factories enDocumento4 páginasRSC SCST Programme Briefing For Factories enmanikAinda não há avaliações
- Sensitivity Training 2020 ErnieDocumento17 páginasSensitivity Training 2020 ErnieNeo MialaAinda não há avaliações
- ADVOCATE ACT - Smart Notes PDFDocumento30 páginasADVOCATE ACT - Smart Notes PDFAnonymous n7rLIWi7100% (2)
- Cell Theory Timeline Cut-Outs Wacky History ReviewDocumento3 páginasCell Theory Timeline Cut-Outs Wacky History Reviewapi-327145161Ainda não há avaliações
- Lpm2.1theoryDocumento85 páginasLpm2.1theoryvetprabu34Ainda não há avaliações
- Manusia LemahDocumento8 páginasManusia LemahKhoirul MubinAinda não há avaliações
- 2-Port Antenna Frequency Range Dual Polarization HPBW Adjust. Electr. DTDocumento5 páginas2-Port Antenna Frequency Range Dual Polarization HPBW Adjust. Electr. DTIbrahim JaberAinda não há avaliações
- Report Web AuditDocumento17 páginasReport Web Auditanupprakash36Ainda não há avaliações
- Cases Torts 7-29-17 DigestDocumento1 páginaCases Torts 7-29-17 Digestczabina fatima delicaAinda não há avaliações
- Knowledge About Visha - Upavisha & Metalic Preparations - Knowledge of Formulations Containing Visha - Upavisha & Rasa AushadhisDocumento154 páginasKnowledge About Visha - Upavisha & Metalic Preparations - Knowledge of Formulations Containing Visha - Upavisha & Rasa AushadhisPRASHNT SINGHAinda não há avaliações
- Amma Vun - Bala AshtagamDocumento4 páginasAmma Vun - Bala AshtagamSHIV RAMAinda não há avaliações
- IRS McqsDocumento7 páginasIRS McqsIbrahimGorgageAinda não há avaliações
- Axe in Pakistan PDFDocumento22 páginasAxe in Pakistan PDFAdarsh BansalAinda não há avaliações
- Kohn v. Hollywood Police, Einhorn, Knapp, Perez, Sheffel, Cantor, BlattnerDocumento30 páginasKohn v. Hollywood Police, Einhorn, Knapp, Perez, Sheffel, Cantor, Blattnerkohn5671Ainda não há avaliações
- Exam in Analytic Geometry With AnswersDocumento4 páginasExam in Analytic Geometry With Answersmvmbapple100% (6)
- Education Under The Philippine RepublicDocumento25 páginasEducation Under The Philippine RepublicShanice Del RosarioAinda não há avaliações
- Parkin 8e TIF Ch27Documento51 páginasParkin 8e TIF Ch27Pranta SahaAinda não há avaliações
- Human Computer Interaction LECTURE 1Documento19 páginasHuman Computer Interaction LECTURE 1mariya ali100% (2)
- Department of Education: Weekly Learning PlanDocumento4 páginasDepartment of Education: Weekly Learning PlanJanine Galas DulacaAinda não há avaliações
- Main CharacterDocumento5 páginasMain CharacterFluffy RabbitAinda não há avaliações
- WK5 SR MOD001074 Grundy 2006 PDFDocumento18 páginasWK5 SR MOD001074 Grundy 2006 PDFadwiyahAinda não há avaliações