Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Bauer's Mod-Phy 2e: Chapter 35: Relativity
Enviado por
thomaszoy zoyDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Bauer's Mod-Phy 2e: Chapter 35: Relativity
Enviado por
thomaszoy zoyDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Bauer/Westfall: University Physics, 2E
Chapter 35: Relativity
Bauer's Mod-Phy 2e
Concept Checks
35.1. c, d, e 35.2. a, c, d, e 35.3. e 35.4. a) True b) False c) True 35.5. a 35.6. b and c 35.7. b, c, d 35.8. a 35.9. d
Multiple-Choice Questions
35.1. a 35.2. d 35.3. c 35.4. d 35.5. a 35.6. d 35.7. c 35.8. c 35.9. a 35.10. c 35.11. c 35.12. b 35.13. d 35.14. d
Conceptual Questions
35.15. A direct corollary of Einstein’s special theory of relativity postulates that no entity or interaction in the
universe can propagate with a speed greater than the speed of light in vacuum. Therefore, instantaneous
effects of events at one point in space on another point in space are impossible. The translational motion
of a perfectly rigid object would imply that, by moving one end of the object, the other end of the object
would also move instantaneously, without any time delay. This contradicts Einstein’s theory.
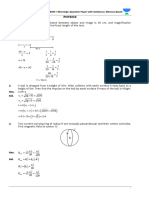
35.16. The y-axis is the time given in μs and the x-axis is the ‘distance’ ( x / c ) given in units of μs also, since the
speed of light can be written c =3.00 ⋅ 108 m/s = 3.00 ⋅ 10 0.300=
μs2 m/ km/μs. To hit the target, the world
line from t = −μs13 of the person (Eddie and/or Martin) must lie inside the past light cone of the target
at x = 0 and t = 0. As seen in the diagram, Eddie’s world line is inside the past light cone of the target
from t = −μs13 to t = −2 km / 0.3 km/
μs = − / 3 μs and so Eddie could hit the target. However, Martin’s
20
world line lies outside of the light cone for all time after t = −μs
13 and so he could not have hit the target.
Eddie and Martin find out the target has been hit at the point where their individual world lines intersect
the light cone from the target at the origin at some time after the target is hit at t = 0. As shown in the
diagram, Eddie finds out the target has been hit at t = 20 / 3μs and Martin finds out it has been hit at
t=
−5 km / 0.3 km/
μs =
− / 3 μs.
50
1324
Você também pode gostar
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterAinda não há avaliações
- Fiitjee: All India Test SeriesDocumento14 páginasFiitjee: All India Test SeriesJyothi BrothersAinda não há avaliações
- PHYSICS - (13th) Paper-1 TEST-6Documento7 páginasPHYSICS - (13th) Paper-1 TEST-6Raju SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Paper 1Documento6 páginasPaper 1wafi alAinda não há avaliações
- JEE Main 2003 Question Paper+Solution (Without Chemistry)Documento33 páginasJEE Main 2003 Question Paper+Solution (Without Chemistry)ShubhAinda não há avaliações
- You're Riding A Unicorn at 25 M/s and Come To A Uniform Stop at A Red Light 20 M Away. What's Your Acceleration?Documento4 páginasYou're Riding A Unicorn at 25 M/s and Come To A Uniform Stop at A Red Light 20 M Away. What's Your Acceleration?JP ResurreccionAinda não há avaliações
- Relativistic Astrophysics. 2009. Course Work 5. Solutions: X X 2 X X 2 2Documento5 páginasRelativistic Astrophysics. 2009. Course Work 5. Solutions: X X 2 X X 2 2ShootingStarPhotonsAinda não há avaliações
- PHYSICS - (13th) Paper-1 TEST-6Documento8 páginasPHYSICS - (13th) Paper-1 TEST-6Raju SinghAinda não há avaliações
- HW 1 SolutionsDocumento6 páginasHW 1 SolutionsMuzamil ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Em Waves JeeDocumento14 páginasEm Waves JeeTobiramaAinda não há avaliações
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology Opencourseware 8.03Sc Fall 2012 Problem Set #7 SolutionsDocumento8 páginasMassachusetts Institute of Technology Opencourseware 8.03Sc Fall 2012 Problem Set #7 Solutionsapolo1711Ainda não há avaliações
- Physics Details SolutionDocumento15 páginasPhysics Details SolutionkolodoloAinda não há avaliações
- Laws of Motion and FrictionDocumento136 páginasLaws of Motion and FrictionPriyankaMishra100% (1)
- AieeeDocumento218 páginasAieeesabhari_ram100% (3)
- 2008 Final Exam PaperDocumento9 páginas2008 Final Exam PaperKurisu KrisAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions To Problem Set 2Documento6 páginasSolutions To Problem Set 2KoraKaagazAinda não há avaliações
- HW 14 SolutionsDocumento8 páginasHW 14 SolutionsSeleneblueAinda não há avaliações
- Physics SolutionDocumento3 páginasPhysics SolutionShubhamKhannaAinda não há avaliações
- Phys101 - A6 - Lim - Module 1 - AssignmentDocumento16 páginasPhys101 - A6 - Lim - Module 1 - AssignmentJocel Erick P. LimAinda não há avaliações
- Gumawa - UA Instructional Class Activity in Classical Relativity Atomic PhenomenaDocumento4 páginasGumawa - UA Instructional Class Activity in Classical Relativity Atomic Phenomenajessrelle.gumawaAinda não há avaliações
- Keep 316Documento68 páginasKeep 316AdityaAinda não há avaliações
- Cantonment Public School and College, Saidpur (CQ)Documento4 páginasCantonment Public School and College, Saidpur (CQ)ismaelAinda não há avaliações
- Chap23 10Documento10 páginasChap23 10litrakhanAinda não há avaliações
- 351 - 13-03 - Gravitation and The Principle of Superposition - 05-16Documento5 páginas351 - 13-03 - Gravitation and The Principle of Superposition - 05-16Bradley NartowtAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Question PaperDocumento5 páginasPhysics Question Papervasudevan m.vAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions Code 0 JEEAdvanced2013 VMC SolvedDocumento28 páginasSolutions Code 0 JEEAdvanced2013 VMC SolvedShashank ShekharAinda não há avaliações
- BiologyDocumento23 páginasBiologyDevendra AryaAinda não há avaliações
- Exercise 26:: ∆ l=1 mω l AY m, A Y ∆ l ∝ωDocumento21 páginasExercise 26:: ∆ l=1 mω l AY m, A Y ∆ l ∝ωAbhishek PathakAinda não há avaliações
- 1.laser Diffraction PDFDocumento10 páginas1.laser Diffraction PDFyashika bairwaAinda não há avaliações
- Modern Physics 9p ECTSDocumento13 páginasModern Physics 9p ECTSMujahid khanAinda não há avaliações
- Mesl 3 Final Coaching SolutionDocumento11 páginasMesl 3 Final Coaching SolutionFf ElevenAinda não há avaliações
- EM Induction Experiment To Determine The Moment of A MagnetDocumento3 páginasEM Induction Experiment To Determine The Moment of A MagnetBhabeshSarangiAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Formula 105Documento1 páginaPhysics Formula 105pranodanAinda não há avaliações
- KinematicsDocumento65 páginasKinematicsGarlapati Srinivasa Rao100% (1)
- HW10 - GravitationDocumento6 páginasHW10 - GravitationBradley NartowtAinda não há avaliações
- JEE Main - 3 - JEE 2024 - SolutionsDocumento11 páginasJEE Main - 3 - JEE 2024 - Solutionskrishjhunjhunwala1254Ainda não há avaliações
- Physics Assignment 2Documento3 páginasPhysics Assignment 2Trí Võ PhạmAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1aDocumento22 páginasLecture 1aJingjing ChanAinda não há avaliações
- EMF63Documento1 páginaEMF63rupesh1000Ainda não há avaliações
- Aipmt 2010 ScreeningDocumento55 páginasAipmt 2010 ScreeningManjunath@116Ainda não há avaliações
- II 3 MagnetronDocumento8 páginasII 3 MagnetronNicolae ComanAinda não há avaliações
- Physical Optics Lecture MaterialsDocumento22 páginasPhysical Optics Lecture Materialsaryan kumarAinda não há avaliações
- E by M Thomson MethodDocumento9 páginasE by M Thomson MethodReddyvari Venugopal33% (3)
- Tugas Kuliah Asinkron MekanikaDocumento1 páginaTugas Kuliah Asinkron MekanikaAlfina Dewi hendryaniAinda não há avaliações
- Vidya Mandir Classes Study MaterialDocumento37 páginasVidya Mandir Classes Study Materialg_group43% (7)
- ch32 PDFDocumento14 páginasch32 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Morning Shift-1 (30!01!2024) FacultyDocumento7 páginasPhysics Morning Shift-1 (30!01!2024) FacultychennareddyvarshithreddyAinda não há avaliações
- MAY2003P3MSDocumento17 páginasMAY2003P3MSlifeinacsAinda não há avaliações
- Physics - Rigid Body Dynamics SolutionsDocumento2 páginasPhysics - Rigid Body Dynamics SolutionsPranavMachingal0% (1)
- NSEP Solved Paper 2011Documento31 páginasNSEP Solved Paper 2011ShubhamKhannaAinda não há avaliações
- CH 22 FDocumento21 páginasCH 22 FaklothAinda não há avaliações
- Answer: Given That F (X) 3X2+X 6+X We Have W (X)Documento3 páginasAnswer: Given That F (X) 3X2+X 6+X We Have W (X)علي محمودAinda não há avaliações
- Physical Optics-Part 1Documento33 páginasPhysical Optics-Part 1Mbrn AliAinda não há avaliações
- ECE230Documento3 páginasECE230KRISHNAPRIYAAinda não há avaliações
- Three Balls: Solution by David PetersonDocumento1 páginaThree Balls: Solution by David PetersonrakshitAinda não há avaliações
- PHY 151 Homework Practice Test Solutions 01Documento8 páginasPHY 151 Homework Practice Test Solutions 01Dnhdj JdhsjdAinda não há avaliações
- Part 1 - Physics: L B A G 2Documento7 páginasPart 1 - Physics: L B A G 2bindaaz301Ainda não há avaliações
- Atomic PhysicsDocumento18 páginasAtomic Physicskushwah_770145566Ainda não há avaliações
- Extract Pages From (Chun Yu.) Relativity and Cosmology (U.colorado LeDocumento18 páginasExtract Pages From (Chun Yu.) Relativity and Cosmology (U.colorado LeMizanur RahmanAinda não há avaliações
- HW&SM Herstein04Documento3 páginasHW&SM Herstein04thomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- (BAUER Phy - 2e) Solution Ch20 Prob 15to19Documento1 página(BAUER Phy - 2e) Solution Ch20 Prob 15to19thomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- HW&SM Herstein03Documento3 páginasHW&SM Herstein03thomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- HW&SM Herstein01Documento4 páginasHW&SM Herstein01thomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- HW&SM Herstein02Documento3 páginasHW&SM Herstein02thomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- An Example Shows How Important of Wavelength - (pt2/2)Documento1 páginaAn Example Shows How Important of Wavelength - (pt2/2)thomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- Assumption PDFDocumento1 páginaAssumption PDFthomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- Sol Self Test ExDocumento5 páginasSol Self Test Exthomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- Breviary Seis Thermgh Ch2 (Prob 13-15) ISMDocumento3 páginasBreviary Seis Thermgh Ch2 (Prob 13-15) ISMthomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- An Example Shows How Important of Wavelength - (pt1/2)Documento1 páginaAn Example Shows How Important of Wavelength - (pt1/2)thomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- Stainglass WorkshopDocumento21 páginasStainglass Workshopthomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- Jackson ClasED 3e Prob4 - 4Documento2 páginasJackson ClasED 3e Prob4 - 4thomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- Matrixsp2 PDFDocumento1 páginaMatrixsp2 PDFthomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- A Very Short Note On Vector Space - Page2/2Documento1 páginaA Very Short Note On Vector Space - Page2/2thomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- Bauer MOD PHY Ch35 (Prob27 31)Documento1 páginaBauer MOD PHY Ch35 (Prob27 31)thomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- CauchyBd PDFDocumento1 páginaCauchyBd PDFthomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- A Very Short Note On Vector Space - Page1/2Documento1 páginaA Very Short Note On Vector Space - Page1/2thomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- Bauer MOD PHY Ch35 (Prob17 22)Documento1 páginaBauer MOD PHY Ch35 (Prob17 22)thomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- Solution To Exercises, ManifoldsDocumento3 páginasSolution To Exercises, Manifoldsthomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- Solution To Exercises, ManifoldsDocumento3 páginasSolution To Exercises, Manifoldsthomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- Solution Tu's Manifolds Exer1 - 6Documento1 páginaSolution Tu's Manifolds Exer1 - 6thomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- Solution Tu's Manifolds Exer1 - 2Documento1 páginaSolution Tu's Manifolds Exer1 - 2thomaszoy zoyAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Force and Motion: Class-VII Physics Question BankDocumento21 páginas2 Force and Motion: Class-VII Physics Question BankGopa BhattacharyyaAinda não há avaliações
- Lab05 FizikDocumento22 páginasLab05 Fizikmemefizik0% (1)
- Physics NumericalDocumento2 páginasPhysics NumericalYash Mahajan100% (1)
- ANSWERS Worksheet Work-Kinetic Energy TheoremDocumento3 páginasANSWERS Worksheet Work-Kinetic Energy TheoremJohn DAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 9: PART A: Angle of Incidence Vs Angle of ReflectionDocumento2 páginasActivity 9: PART A: Angle of Incidence Vs Angle of Reflectionangelica calicaAinda não há avaliações
- DayStar Filters Magnesium Quark User ManualDocumento16 páginasDayStar Filters Magnesium Quark User ManualfredpbAinda não há avaliações
- Negative and Anomalous Refraction inDocumento166 páginasNegative and Anomalous Refraction inDaniel MoránAinda não há avaliações
- Exact Ray Tracing in MATLABDocumento9 páginasExact Ray Tracing in MATLABslysoft.20009951Ainda não há avaliações
- Velocity and AccelerationDocumento7 páginasVelocity and AccelerationFatinel EsicanAinda não há avaliações
- Catalogue - Ihara S300 R800 Spectrophotometers Press ReleaseDocumento2 páginasCatalogue - Ihara S300 R800 Spectrophotometers Press ReleaseAamirMalikAinda não há avaliações
- BE Physics-Solution PDFDocumento235 páginasBE Physics-Solution PDFRajeev PaudelAinda não há avaliações
- CLS Aipmt 19 20 XIII Phy Study Package 1 Level 1 Chapter 1Documento4 páginasCLS Aipmt 19 20 XIII Phy Study Package 1 Level 1 Chapter 1Optics Career Institute -OCI100% (1)
- The Microscope PowerpointDocumento26 páginasThe Microscope Powerpointapi-250530867Ainda não há avaliações
- Physical OpticsDocumento26 páginasPhysical OpticsLuo MarkAinda não há avaliações
- 9-7 Geometrical Vs Physical OpticsDocumento17 páginas9-7 Geometrical Vs Physical OpticsnidharshanAinda não há avaliações
- Gcse Physics Equations: ForcesDocumento1 páginaGcse Physics Equations: ForcesRanjan SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Hyperspectral Imaging: January 2018Documento6 páginasHyperspectral Imaging: January 2018Rania ZaatourAinda não há avaliações
- Electricity WorksheetsDocumento21 páginasElectricity WorksheetsMeagan JorgensonAinda não há avaliações
- Wavelength of Maximum AbsorbanceDocumento6 páginasWavelength of Maximum AbsorbanceNestor Kingking Jr.Ainda não há avaliações
- Brady Lecture 6Documento32 páginasBrady Lecture 6TygerGoose0% (1)
- PHY130 Exam#2 StudyGuideDocumento2 páginasPHY130 Exam#2 StudyGuideSagar GogiaAinda não há avaliações
- Comparison Between TEM and SEMDocumento5 páginasComparison Between TEM and SEManurag6866Ainda não há avaliações
- Complete MCQsDocumento42 páginasComplete MCQsKhawaja Hassam100% (1)
- Summative Test No. 4 Heat Light SoundDocumento1 páginaSummative Test No. 4 Heat Light SoundWinica Cagas100% (9)
- 04 - Electromagnetic Waves (Griffiths - Ch9)Documento95 páginas04 - Electromagnetic Waves (Griffiths - Ch9)Shobit JainAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Communications Questions and Answers - Absorption: Prev NextDocumento9 páginasOptical Communications Questions and Answers - Absorption: Prev NextKumar MukeshAinda não há avaliações
- Energies 16 01199 v2Documento20 páginasEnergies 16 01199 v2random randomAinda não há avaliações
- Fluorescence SpectrosDocumento5 páginasFluorescence SpectrosrutwickAinda não há avaliações
- Astm D1729-16Documento4 páginasAstm D1729-16Anonymous SYNFEw9h87% (15)
- Magnetic Particle Testing MethodDocumento6 páginasMagnetic Particle Testing Methodgbsubbu100% (4)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseNo EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (69)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceNo EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (51)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingNo EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (5)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)No EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (157)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesNo EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2193)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyAinda não há avaliações
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldNo EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (64)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessNo EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (6)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterNo EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (410)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeAinda não há avaliações
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowNo EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (49)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidNo EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1396)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldNo EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (54)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceNo EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (5)
- AP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNo EverandAP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeAinda não há avaliações
- Summary: American Prometheus: The Triumph and Tragedy of J. Robert Oppenheimer by Kai Bird & Martin J. Sherwin: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNo EverandSummary: American Prometheus: The Triumph and Tragedy of J. Robert Oppenheimer by Kai Bird & Martin J. Sherwin: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (3)
- A Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itNo EverandA Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (13)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldNo EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (60)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayNo EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (125)