Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
CBSE Class 6 Social Science Syllabus
Enviado por
Yaasir AliDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CBSE Class 6 Social Science Syllabus
Enviado por
Yaasir AliDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.
COM
Themes
VI
CLASS VI: OUR PASTS – I
Objectives
An Introduction to History Explain the specific nature of the discipline.
When, Where and How
(a) The time frame under study. (a) Familiarise the learner with the major developments
(b) The geographical framework. to be studied.
(c) Sources. (b) Develop an understanding of the significance of
geographical terms used during the time frame.
(c) Illustrate the sources used to reconstruct history.
The Earliest Societies
(a) Hunting and gathering as a way of life, its (a) Appreciate the skills and knowledge of hunter-
implications. gatherers.
(b) Introduction to stone tools and their use. (b) Identify stone artefacts as archaeological evidence, 165
(c) Case study: the Deccan. making deductions from them. Syllabus
for
The First Farmers and Herders Classes
(a) Implications of farming and herding. (a) Appreciate the diversity of early domestication. at the
Elementary
(b) Archaeological evidence for crops, animals, houses, (b) Identify the material culture generated by people Level
tools, pottery, burials, etc. in relatively stable settlements.
(c) Case study: the North-West, and North-East. (c) Understand strategies for analyzing these.
The First Cities
(a) The settlement pattern of the Harappan civilisation. (a) Appreciate the distinctive life in cities.
(b) Unique architectural features. (b) Identify the archaeological evidence of urban
(c) Craft production. centres.
(d) The meaning of urbanism. (c) Understand how this is used to reconstruct
(e) Case study: the North-West. processes such as craft production.
Different Ways of Life
(a) The Vedas and what they tell us. (a) Appreciate that different developments were taking
(b) A contemporary chalcolithic settlement. place in different parts of the subcontinent
(c) Case studies: the North-West and the Deccan. simultaneously.
(b) Introduce simple strategies of textual analysis.
(c) Reinforce the skills of archaeological analysis already
developed.
DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM
DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM
Themes Objectives
Early States
(a) Janapadas to Mahajanapadas (a) Introduce the concept of the state and its varieties.
(b) Case study: Bihar, Magadha and the Vajji (b) Understand the use of textual sources in this
confederacy. context.
New Ideas
(a) Upanisads. (a) Outline the basic tenets of these systems of
(b) Jainism. thought, and the context in which they developed
(c) Buddhism. and flourished.
(b) Introduce excerpts from sources relating to these
traditions.
The First Empire
(a) The expansion of the empire. (a) Introduce the concept of empire.
(b) Asoka (b) Show how inscriptions are used as sources.
Syllabus (c) Administration.
for
Classes Life in towns and villages
at the (a) The second urbanisation. (a) Demonstrate the variety of early urban centres—
Elementary
Level (b) Agricultural intensification. coastal towns, capitals, religious centres.
166 (c) Case study: Tamil Nadu. (b) Illustrate the use of archaeological material including
coins, sculpture, as well as textual sources to
reconstruct social and economic histories.
Contacts with Distant lands
(a) The Sangam texts and long distance exchange. (a) Introduce the idea of different contexts of contact
Suggested regions: the Tamil region, extending to between distant lands, and the motivating forces
south east Asia and the west. (including conquest).
(b) Conquerors from distant lands: north western and (b) Examine the implications of journeys within the
western India. subcontinent.
(c) The spread of Buddhism: north India to Central (c) Illustrate the use of textual and visual material for
Asia. reconstructing the histories of such contacts.
Political Developments
(a) Gupta empire and Harshavardhana. (a) Introduce the idea that strategies of expansion, and
(b) Pallavas and Chalukyas. their logic, differ.
DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM
DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM
Themes Objectives
(b) Explain the development of different
administrative systems.
(c) Understand how prasastis and caritas are used to
reconstruct political history.
Culture and Science
(a) Literature, including the Puranas, the epics, other (a) Develop a sense of appreciation of textual and
Sanskrit and Tamil works. visual traditions of the period.
(b) Architecture including early monasteries and (b) Introduce excerpts from texts and visual material
temples, sculpture, painting (Ajanta); for analysis and appreciation.
(c) Science.
DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM
DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM
GEOGRAPHY
Rationale
Geography is an integral component of social science. At this stage learners are introduced to the
basic concepts necessary for understanding the world in which they live. Geography will be
introduced to promote the understanding of interdependence of various regions and countries.
The child will be introduced to the contemporary issues such as global distribution of economic
resources, gender, marginalized group, and environment and on going process of globalisation.
The course at this stage comprises study of the earth as the habitat of humankind, study of
environment, resources and development at different scales local, regional/national and the world.
Objectives
The major objectives of the course are to:
1. develop an understanding about the earth as the habitat of humankind and other forms of
life.
2. initiate the learner into a study of her/his own region, state and country in the global context.
3. introduce the global distribution of economic resources and the on going process of
173
globalisation.
Syllabus
4. promote the understanding of interdependence of various regions and countries. for
Classes
VI
at the
Elementary
CLASS VI : THE EARTH - OUR HABITAT Level
Topics Objectives
Planet: Earth in the solar system. To understand the unique place of the earth in the
solar system, which provides ideal condition for all
forms of life, including human beings; (Periods-8)
Globe: the model of the earth, latitudes and longitudes; To understand two motions of the earth and their
motions of the earth rotation and revolution. effects; (Periods-12)
Maps: essential components of maps distance, To develop basic skills of map reading; (Periods-10)
directions and symbols.
Four realms of the earth: lithosphere, hydrosphere, To understand interrelationship of the realms of the
atmosphere and biosphere: continents and oceans. earth; (Periods-12)
DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM
DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM
Themes Objectives
Major relief features of the earth. To understand major landforms of the earth;
(Periods-10)
India in the world: physiographic divisions of India – To comprehend broad physiographic divisions of
mountains, plateaus and plains; climate; natural India;
vegetation and wild life; need for their conservation. To describe the influence of land, climate, vegetation
and wildlife on human life;
To appreciate the need for conserving natural
vegetation and wild life. (Periods-13)
Project/Activity
• Make a chart showing distance of the planets from the sun.
• Draw a sketch of your school and locate the following:
(i) the principal’s room
(ii) your classroom
Syllabus (iii) playground
for (iv) library
Classes • Show the major wildlife sanctuaries of your region on a political map of India.·
at the
Elementary • Arrange for a trip to a wildlife sanctuary or zoo.
Level Note: Any similar activities may be taken up.
174
DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM
DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM
SOCIAL AND POLITICAL LIFE
Rationale
At the elementary stage, the idea is to introduce students to various aspects of political, social and
economic life. This will be done through a preliminary focus on certain key concepts, knowledge
of which is essential to understand the functioning of Indian democracy. These concepts will be
explained using imaginary narratives that allow children to draw connections between these and
their everyday experiences. There will be no attempt made at this level to cover all aspects of
India’s democratic structure, but rather the effort is more to provide an overview with which the
child learns to critically engage by constructing herself as an interested citizen of a vibrant and on-
going democratic process. The focus on the real-life functioning of institutions and ideals is to
enable the child to grasp the deep interconnectedness between the political and social aspects of
her everyday life, as well as the impact of these two in the realm of economic decision-making.
Objectives
• To enable students to make connections between their everyday lives and the issues discussed
in the textbook; 177
• To have students imbibe the ideals of the Indian Constitution; Syllabus
• To have children gain a real sense of the workings of Indian democracy: its institutions and for
processes; Classes
• To enable students to grasp the interconnectedness between political, social and economic at the
Elementary
issues; Level
• To have them recognise the gendered nature of all of the issues raised;
• To have them develop skills to critically analyse and interpret political, social and economic
developments from the point of view of the marginalised;
• To have them recognise the ways in which politics affects their daily lives.
DIVERSITY AND INTERDEPENDENCE
VI
CLASS VI
Rationale
In the first year of the new subject area, ‘Social and Political Life’ the themes of diversity,
interdependence and conflict are to be focused on. This is done through first elucidating aspects
of social diversity through a discussion of linguistic diversity as well as the diversity of art forms.
In discussing these topics the idea is to celebrate diversity and interdependence while also highlighting
that this can be zone for conflict. The idea of government is introduced at this grade and then
elaborated upon through a discussion of the types of government at the local level, as well as
different aspects of their functioning. Through focusing chapters on concrete, though narrativised,
DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM
DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM
examples of land administration in the rural context and sanitation services in the urban one, the
attempt is to have the child gain an experiential understanding of the ways in which local government
functions. The last chapter through its focus on how people make a living in the rural and urban
context discusses issues of the diversity of livelihoods.
Objectives
The specific objectives of the course, where it is not clear from the rationale of the approach, are
indicated beside the themes to be taught in the course.
Themes Objectives
UNIT 1: Diversity To enable students to:
In this unit we focus on various aspects of diversity. • understand and appreciate various forms of
The first section begins by having the child recognise diversity in their everyday environments,
diversity as a fact of being human and understanding • develop a sensitivity towards pluralism and
diversity as different ways of doing the same thing. interdependence,
The second section builds on this by having the child • understand how prejudice can lead to discrimination,
Syllabus interrogate societal prejudices against diversity, • understand the difference between diversity and
for recognising that the self can be made up of multiple inequality,
Classes
at the identities and that the Constitution compels us to • recognise that there are multiple identities within
Elementary respect diversity. ourselves that we use in different contexts and that
Level Section 1 these can come into conflict with each other,
178 • Diversity as a fact of being human. • understand that the Constitution compels us to
• What diversity adds to our lives. respect diversity.
• Diversity in India.
Section 2
• Prejudice and discrimination.
• Inequality and discrimination.
• Recognition of multiple identities in oneself.
• The Constitution and respect for diversity.
UNIT 2: Government To enable students to:
This unit introduces the student to the idea of • gain a sense of why government is required,
government. The first section focuses on the need for • recognise the need for universal adult franchise,
it, the history of adult franchise, the various types of • appreciate need to make decisions with collective
governments that exist at present. The second section sanction,
discusses the key elements that influence the functioning • understand key elements that influence the
of democractic government. functioning of democracy.
DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM
DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM
Themes Objectives
Section 1
• The need for government.
• Decision-making and participation.
• The quest for universal adult franchise through
examples of the sufferagate movement and the anti-
apartheid struggle.
• Various forms of government and absence of
collective sanction.
Section 2
Key elements that influence the functioning of
democratic government:
• Participation and accountability.
• Resolution of Conflict.
• Concerns for Equality and Justice.
179
Syllabus
UNIT 3: Local Government To enable children to
for
This unit familiarises the student with both rural and • understand local level of government functioning, Classes
urban local government. It covers the Panchayati Raj, • understand the workings of the pnchayati raj and at the
rural administration and urban government and appreciate its importance, Elementary
Level
administration. The effort is to have the child draw • gain a sense of who performs what role within the
contrasts and comparisons between the ways in which local administration,
urban and rural local government function. • understand how the various levels of administration
Section 1 at the local level are interconnected,
Panchayati Raj • understand the intricacies involved in the local
• Description of panchayat including electoral process, administration’s provision of water.
decision making, implementation of decisions
• Role of a gram sabha
• Women and the panchayat
Section 2
Urban Local Government
• Municipal corporation elections, decision making
structures
• The provision of water and the work of the
municipal corporation
• Citizens protests to get their grievances addressed
DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM
DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM
Themes Objectives
Section 3
Rural Administration
• Focus on a land dispute and show the role of local
police and patwari.
• On land records and role of patwari.
• On the new inheritance law.
UNIT 4: Making a Living To enable students to:
This unit focuses on individuals earn a livelihood both • understand conditions that underline and impact
in the rural and the urban context. The rural context life strategies of various groups of people,
focuses on various types of farmers and the urban • understand that these conditions and opportunities
one on various types of occupations people engage in for making a living are not equally available to all.
to earn an income. The student should be able to
compare and contrast the urban and the rural context.
Section 1
Syllabus Rural Livelihoods
for • Various types of livelihoods prevalent in a village.
Classes • Different types of farmers: middle farmer, landless
at the labourers and large farmers.
Elementary
Level Section 2
180 Urban Livelihoods
• Difference between primary, secondary and tertiary
occupations.
• Descriptions of various types of lievelihoods
including vegetable vendor, domestic servant,
garment worker and bank employee.
• Differences between self-employed, regular
employment and wage employment.
• The interlinkage between rural and urban lives
through a discussion of migration.
DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM DOWNLOADED FROM WWW.STUDIESTODAY.COM
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Concrete Steel Brick Building Construction CalculatorDocumento12 páginasConcrete Steel Brick Building Construction CalculatorYaasir AliAinda não há avaliações
- Cement ConsumptionDocumento4 páginasCement ConsumptionKapil Verma100% (11)
- Final PortfolioDocumento33 páginasFinal PortfolioYaasir AliAinda não há avaliações
- Erco Catalogue 2020 enDocumento806 páginasErco Catalogue 2020 enYaasir AliAinda não há avaliações
- Natcon BrochureDocumento12 páginasNatcon BrochureYaasir AliAinda não há avaliações
- Avenues Mall Mosque - Zaha Hadid - Arch2ODocumento6 páginasAvenues Mall Mosque - Zaha Hadid - Arch2OYaasir AliAinda não há avaliações
- Bhong Mosque, Rahimyar Khan, PakistanDocumento26 páginasBhong Mosque, Rahimyar Khan, PakistanYaasir AliAinda não há avaliações
- Celcrete Floor System Details PDFDocumento14 páginasCelcrete Floor System Details PDFYaasir AliAinda não há avaliações
- York Curling Club Floor PlanDocumento1 páginaYork Curling Club Floor PlanYaasir AliAinda não há avaliações
- Celcrete Floor System Details PDFDocumento14 páginasCelcrete Floor System Details PDFYaasir AliAinda não há avaliações
- The Charles Wallace India Trust ScholarshipsDocumento4 páginasThe Charles Wallace India Trust ScholarshipsYaasir AliAinda não há avaliações
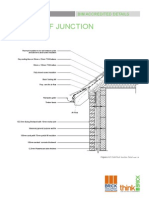
- BDA Cold Roof Junction Detail PageDocumento1 páginaBDA Cold Roof Junction Detail PageYaasir AliAinda não há avaliações
- Establishment ManualDocumento370 páginasEstablishment ManualYaasir AliAinda não há avaliações
- Gopal Prasad Yadav: Career SummaryDocumento2 páginasGopal Prasad Yadav: Career SummaryAnonymous ZSol6ZOHIpAinda não há avaliações
- Sri Bala Tripurasundari Khadgamala Stotram FinalDocumento3 páginasSri Bala Tripurasundari Khadgamala Stotram FinalSHIV RAMAinda não há avaliações
- Budhism AssignmentDocumento2 páginasBudhism Assignmentapi-528636235Ainda não há avaliações
- Kideny Chor New DraftDocumento38 páginasKideny Chor New DraftAbhilasha ShahAinda não há avaliações
- 11-03-19-CC Class Morning 1 - Advent of Lord Sri Caitanya Mahaprabhu - Radhanath Swami ISKCON ChowpattyDocumento17 páginas11-03-19-CC Class Morning 1 - Advent of Lord Sri Caitanya Mahaprabhu - Radhanath Swami ISKCON ChowpattyVOICE IIScAinda não há avaliações
- Oct'20 Mortgages Bank Type Customer Tel Value PayoutDocumento8 páginasOct'20 Mortgages Bank Type Customer Tel Value Payoutdfged54Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 34Documento23 páginasChapter 34Dāmodar DasAinda não há avaliações
- Florican EcologyDocumento15 páginasFlorican Ecologydhanapalg2010Ainda não há avaliações
- 9 Cities Sample DBDocumento86 páginas9 Cities Sample DBVikramAinda não há avaliações
- Breath and AumDocumento13 páginasBreath and AumExecutive Engineer kpid - bhujAinda não há avaliações
- India in MapsDocumento2 páginasIndia in Mapspreeti143Ainda não há avaliações
- SCHOOL & Institutes For Special Kids in MumbaiDocumento9 páginasSCHOOL & Institutes For Special Kids in MumbaiKamlesh Maheshwari100% (3)
- A Philosophy For Global Peace and HarmonyDocumento7 páginasA Philosophy For Global Peace and HarmonyGadhadhar GautamAinda não há avaliações
- 1857 Revolt - Final Study NotesDocumento22 páginas1857 Revolt - Final Study NotesVCrockzAinda não há avaliações
- Ancient Zen Koans From China - With Answers: Other CountriesDocumento15 páginasAncient Zen Koans From China - With Answers: Other CountriesFrancisco MedinaAinda não há avaliações
- Medi-Caps Institute of Management & Technology Medi-Caps Institute of Management & TechnologyDocumento12 páginasMedi-Caps Institute of Management & Technology Medi-Caps Institute of Management & TechnologyprinceAinda não há avaliações
- CBCS Syllabus - Final Updated - 02-09-16 - 2Documento12 páginasCBCS Syllabus - Final Updated - 02-09-16 - 2Saurabh YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Education DepartmentDocumento4 páginasEducation DepartmentDakshu SindhuAinda não há avaliações
- Merit - Journalism and Mass Comunication - General - 2020Documento23 páginasMerit - Journalism and Mass Comunication - General - 2020OENDRIL DASAinda não há avaliações
- ListDocumento22 páginasListSeema KumariAinda não há avaliações
- A Called For Alternative New Hermeneutical ApproachDocumento12 páginasA Called For Alternative New Hermeneutical ApproachMadhusudana Devi DasiAinda não há avaliações
- 2k12 Btech BoysDocumento6 páginas2k12 Btech BoysAshwaniBajajAinda não há avaliações
- Indian Agent Approval DataDocumento9 páginasIndian Agent Approval DataShivam SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Reflections of Social Theory in IndiaDocumento25 páginasReflections of Social Theory in IndiaAnjana RaghavanAinda não há avaliações
- CISF SenitelDocumento53 páginasCISF Senitelnitin ranaAinda não há avaliações
- Sri Hazur Sahib Maryada ParbodhDocumento185 páginasSri Hazur Sahib Maryada ParbodhSikh Texts100% (2)
- Shivananda Lahari (1-100) - Telugu Shlokas and English MeaningsDocumento82 páginasShivananda Lahari (1-100) - Telugu Shlokas and English MeaningsJanardhna KethaAinda não há avaliações
- SadhinchaneDocumento5 páginasSadhinchaneapi-3695801100% (2)
- The Stories of Lord Karthikeya-XiDocumento2 páginasThe Stories of Lord Karthikeya-XiRSPAinda não há avaliações
- Sanskrit Slokas CompiledDocumento3 páginasSanskrit Slokas Compiledsukanya_ravichandranAinda não há avaliações