Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Cabigao, Abigail A. APRIL 4, 2018 Bsba - 3 Natsci 2
Enviado por
Stefani Ann Cabalza0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
8 visualizações3 páginasThe document summarizes the functions of the pituitary gland and its hormones. The anterior pituitary gland secretes hormones that control functions of the thyroid, adrenals, ovaries/testes, breasts, and growth. These include ACTH, TSH, LH, FSH, prolactin, GH, and MSH. The posterior pituitary gland secretes ADH and oxytocin which control water balance and uterine/breast functions.
Descrição original:
marketing
Título original
CABIGAO
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThe document summarizes the functions of the pituitary gland and its hormones. The anterior pituitary gland secretes hormones that control functions of the thyroid, adrenals, ovaries/testes, breasts, and growth. These include ACTH, TSH, LH, FSH, prolactin, GH, and MSH. The posterior pituitary gland secretes ADH and oxytocin which control water balance and uterine/breast functions.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
8 visualizações3 páginasCabigao, Abigail A. APRIL 4, 2018 Bsba - 3 Natsci 2
Enviado por
Stefani Ann CabalzaThe document summarizes the functions of the pituitary gland and its hormones. The anterior pituitary gland secretes hormones that control functions of the thyroid, adrenals, ovaries/testes, breasts, and growth. These include ACTH, TSH, LH, FSH, prolactin, GH, and MSH. The posterior pituitary gland secretes ADH and oxytocin which control water balance and uterine/breast functions.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 3
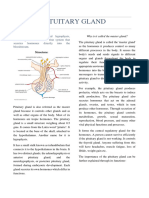
CABIGAO, ABIGAIL A.
APRIL 4, 2018
BSBA – 3 NATSCI 2
1. Anterior 1. Adrenocorticotroph 1. Adrenals Stimulates the adrenal gland to
ic hormone (ACTH)
Pituitary 2. Thyroid produce a hormone called
2. Thyroid-stimulating
Gland hormone (TSH) 3-4. Ovaries cortisol. ACTH is also known as
3. Luteinising hormone (women) corticotrophin.
(LH)
Testes (men) Stimulates the thyroid gland to
4. Follicle-stimulating
hormone (FSH) 5. Breasts secrete its own hormone, which is
5. Prolactin (PRL) 6. All cells in the called thyroxine. TSH is also
6. Growth hormone
(GH) body known as thyrotrophin.
7. Melanocyte- 7. none Controls reproductive
stimulating
functioning and sexual
hormone (MSH)
characteristics. Stimulates the
ovaries to produce oestrogen
and progesterone and the testes
to produce testosterone and
sperm. LH and FSH are known
collectively as gonadotrophins.
LH is also referred to as interstitial
cell stimulating hormone (ICSH) in
males.
Stimulates the breasts to produce
milk. This hormone is secreted in
large amounts during pregnancy
and breast feeding, but is
present at all times in both men
and women.
Stimulates growth and repair.
Research is currently being
carried out to identify the
functions of GH in adult life.
Exact role in humans is unknown.
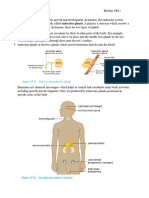
2. Posterior 1. Anti-diuretic 1. Kidneys Controls the blood fluid and
hormone (ADH)
Pituitary 2. Uterus mineral levels in the body by
2. Oxytocin
Gland affecting water retention by the
kidneys. This hormone is also
known vasopressin or argenine
vasopressin (AVP).
Affects uterine contractions in
pregnancy and birth and
subsequent release of breast
milk.
Breasts
3. Pineal
Gland
4. Thyroid
Gland
5. Parathyroid
Gland
6. Thymus
7. Pancreas
8. Adrenal
Cortex
9. Adrenal
Medulla
10. Ovaries
11. Testis
Você também pode gostar
- Sodium and PotassiumDocumento7 páginasSodium and PotassiumLUALHATI VILLASAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report Assistant Endocrine SystemDocumento7 páginasLab Report Assistant Endocrine SystemJohn Louis AguilaAinda não há avaliações
- Calc Tekniks Part 2Documento4 páginasCalc Tekniks Part 2Stefani Ann CabalzaAinda não há avaliações
- Notes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemDocumento3 páginasNotes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemAlven ReyAinda não há avaliações
- Local Media2182658933713495317Documento129 páginasLocal Media2182658933713495317JAYMAYMA ELGARIOAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrine System Functions & GlandsDocumento11 páginasEndocrine System Functions & Glandssaeed qurashiAinda não há avaliações
- Body Systems (Grade 6) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeachingDocumento1 páginaBody Systems (Grade 6) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeachingshuganesh82% (11)
- Science: Third QuarterDocumento10 páginasScience: Third Quarterrig guel100% (1)
- 1 PPT Endocrine SystemDocumento30 páginas1 PPT Endocrine SystemBianca ManimtimAinda não há avaliações
- The Endocrine SystemDocumento18 páginasThe Endocrine SystemPhea VillarealAinda não há avaliações
- A Research On The Relationship Between Ejaculation and Serum Testosterone Level in MenDocumento5 páginasA Research On The Relationship Between Ejaculation and Serum Testosterone Level in MenAnonymous XsYOMYarrvAinda não há avaliações
- Science5 DLP Q2Documento173 páginasScience5 DLP Q2Shie Pante100% (9)
- Science 9: Quarter 3: Role of HormonesDocumento2 páginasScience 9: Quarter 3: Role of Hormonescrizlie enotAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrine SystemDocumento73 páginasEndocrine SystemIsabel Higgins100% (4)
- Calc Tekniks For ProgressionDocumento5 páginasCalc Tekniks For ProgressionStefani Ann CabalzaAinda não há avaliações
- 3rd Quarter Science Module 1Documento13 páginas3rd Quarter Science Module 1Vincq100% (2)
- Making Babies: The Definitive Guide to Improving Your Fertility and Reproductive HealthNo EverandMaking Babies: The Definitive Guide to Improving Your Fertility and Reproductive HealthAinda não há avaliações
- Laporan Pendahuluan Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)Documento14 páginasLaporan Pendahuluan Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)Jali24Ainda não há avaliações
- NCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Documento3 páginasNCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Jum ChumAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan On Pituitary Gland (Endocrine SystemDocumento37 páginasLesson Plan On Pituitary Gland (Endocrine SystemRosalyn Angcay Quintinita100% (1)
- Topic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesDocumento18 páginasTopic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesHaris AliAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezDocumento144 páginasEndocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezTrixie Rose Ebona CortezAinda não há avaliações
- hORmones in Plants Class Note Class 10 ...Documento4 páginashORmones in Plants Class Note Class 10 ...AceHunterAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 UNIT IIDocumento10 páginasChapter 2 UNIT IIAyen LatosaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Assignmnet 12Documento3 páginasChapter 1 Assignmnet 12nabihazonabAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 3.3 The Endocrine System - 084504Documento1 páginaActivity 3.3 The Endocrine System - 084504Megan WolvesAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrine SystemDocumento4 páginasEndocrine SystemKirsten GomezAinda não há avaliações
- HSBDocumento2 páginasHSBAreefa MohamedAinda não há avaliações
- AnaPhy Lec - Endocrine SystemDocumento2 páginasAnaPhy Lec - Endocrine SystemReigh DakotaAinda não há avaliações
- No Gland Hormone Its Function Pituitary GlandDocumento3 páginasNo Gland Hormone Its Function Pituitary GlandKush KesharwaniAinda não há avaliações
- q3 Module Edited w1-7Documento21 páginasq3 Module Edited w1-7Regine DigamonAinda não há avaliações
- Pituitary Gland 1Documento3 páginasPituitary Gland 1iiout346Ainda não há avaliações
- Name of The GlandDocumento3 páginasName of The GlandSajeevAinda não há avaliações
- Task 3Documento15 páginasTask 3maryamshahzad489Ainda não há avaliações
- Glands SummaryDocumento3 páginasGlands SummaryRokaia RagehAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrine System HandoutDocumento3 páginasEndocrine System Handoutker KerAinda não há avaliações
- Gr10 Endocrine SystemDocumento5 páginasGr10 Endocrine SystemDomuAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesDocumento10 páginasEndocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesHabi JabiAinda não há avaliações
- Q3 Activity 2 Endocrine SystemDocumento3 páginasQ3 Activity 2 Endocrine Systempt09651934948Ainda não há avaliações
- ENDOCRIONOLOGYDocumento15 páginasENDOCRIONOLOGYmoepiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Biology: Analysing The Role of Hormone in HumansDocumento8 páginasChapter 1 Introduction To Biology: Analysing The Role of Hormone in HumansHamirah Abd HamidAinda não há avaliações
- Biochemistry of HormonesDocumento26 páginasBiochemistry of HormonesZayan Haider0% (1)
- BSA 1C 10-26-2021 Endocrine SystemDocumento38 páginasBSA 1C 10-26-2021 Endocrine SystemAngelika ButaslacAinda não há avaliações
- 3 +endocrine+systemDocumento41 páginas3 +endocrine+systemDew JirawatAinda não há avaliações
- Module 20 Hook Activity Hormones Functions 1. Hormones of ThyroidDocumento2 páginasModule 20 Hook Activity Hormones Functions 1. Hormones of ThyroidDuchess Juliane Jose MirambelAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrine SystemDocumento7 páginasEndocrine SystemIvy Jana BelenAinda não há avaliações
- Sigh EndsDocumento3 páginasSigh Endsmacy kang (maceeeeh)Ainda não há avaliações
- Role of HormonesDocumento23 páginasRole of HormonesJhuvy C. TigbaoAinda não há avaliações
- Term Paper : Isabela State UniversityDocumento9 páginasTerm Paper : Isabela State UniversityFlor SagnipAinda não há avaliações
- Sci10 Q3 Mod1 The Endocrine System Glands and Their HormonesDocumento3 páginasSci10 Q3 Mod1 The Endocrine System Glands and Their Hormonestomman warmanAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrine SystemDocumento2 páginasEndocrine SystemJason MacatuggalAinda não há avaliações
- Targets From Previous Lesson Learning ObjectivesDocumento9 páginasTargets From Previous Lesson Learning ObjectivesTom MaguireAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Education: Learning Activity Worksheets (LAW) General Biology 2 Grade 12Documento5 páginasDepartment of Education: Learning Activity Worksheets (LAW) General Biology 2 Grade 12Maria Bettina DizonAinda não há avaliações
- Adobe Scan Jan 13, 2024Documento3 páginasAdobe Scan Jan 13, 2024Abhijeet KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrine SystemDocumento4 páginasEndocrine SystemKAUSTUBH SAWANTAinda não há avaliações
- Reproductive Hormones and PregnancyDocumento14 páginasReproductive Hormones and PregnancycharmaineAinda não há avaliações
- Big Picture F: MetalanguageDocumento13 páginasBig Picture F: Metalanguagejohanna deguzmanAinda não há avaliações
- Science - LensDocumento8 páginasScience - LensAte DannyAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrine SystemDocumento14 páginasEndocrine SystemEdsel Ian S. FuentesAinda não há avaliações
- 7.1 Human Endocrine System - MEMO - ONE PAGER 2020Documento1 página7.1 Human Endocrine System - MEMO - ONE PAGER 2020Rudzi UdziAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrine SystemDocumento3 páginasEndocrine SystemDearly Niña OsinsaoAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrine SystemDocumento5 páginasEndocrine SystemCHIQUI JIMENEZAinda não há avaliações
- evaluatedSLK On The Endocrine SystemDocumento14 páginasevaluatedSLK On The Endocrine SystemMilagrosBautistaAinda não há avaliações
- 5M: Care of Clients With Hormonal Disturbances: Endocrine SystemDocumento19 páginas5M: Care of Clients With Hormonal Disturbances: Endocrine SystemEmmanuelle Soroño AmoresAinda não há avaliações
- Group 6 (Sas 16-20)Documento7 páginasGroup 6 (Sas 16-20)jovan teopizAinda não há avaliações
- GQA Science10 - Q3 - Wk1 2 - Endocrine and Reproductive System - GQA .LRQADocumento17 páginasGQA Science10 - Q3 - Wk1 2 - Endocrine and Reproductive System - GQA .LRQALevi AckermanAinda não há avaliações
- Anaphy Lecture Activity 10 Endocrine SystemDocumento5 páginasAnaphy Lecture Activity 10 Endocrine SystemJohnAinda não há avaliações
- (Peque) Menstrual Cycle Activity 2Documento2 páginas(Peque) Menstrual Cycle Activity 2SamSam PequeAinda não há avaliações
- Slu Online Enrollment Guide: STEP 2: Click Sign in With GoogleDocumento11 páginasSlu Online Enrollment Guide: STEP 2: Click Sign in With GoogleStefani Ann CabalzaAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment MathDocumento6 páginasAssignment MathStefani Ann CabalzaAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Taps, Splices and Joints of ConductorDocumento10 páginasTypes of Taps, Splices and Joints of ConductorStefani Ann CabalzaAinda não há avaliações
- Tabs (From Zee)Documento4 páginasTabs (From Zee)Stefani Ann CabalzaAinda não há avaliações
- Nomograph: Centrifugation BiochemistryDocumento1 páginaNomograph: Centrifugation BiochemistryStefani Ann CabalzaAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Site Development PlanDocumento1 página2 Site Development PlanStefani Ann CabalzaAinda não há avaliações
- CoulsonDocumento5 páginasCoulsonStefani Ann CabalzaAinda não há avaliações
- BOD DO SAG Curve PDFDocumento19 páginasBOD DO SAG Curve PDFStefani Ann CabalzaAinda não há avaliações
- Definitions of LevelDocumento10 páginasDefinitions of LevelStefani Ann CabalzaAinda não há avaliações
- Create A Java Program That Will Compute For The Sum of The 1st 50 NumbersDocumento8 páginasCreate A Java Program That Will Compute For The Sum of The 1st 50 NumbersStefani Ann CabalzaAinda não há avaliações
- Formulas For Thermodynamics 1Documento2 páginasFormulas For Thermodynamics 1Stefani Ann CabalzaAinda não há avaliações
- Ref Sonographic Evaluation of Thyroid Size 2019Documento5 páginasRef Sonographic Evaluation of Thyroid Size 2019Daniel Alejandro CastrilloAinda não há avaliações
- Insulinas de OsmosisDocumento3 páginasInsulinas de OsmosisDennise A. Hernández JuárezAinda não há avaliações
- Hormones and The Endocrine System - Johns Hopkins MedicineDocumento5 páginasHormones and The Endocrine System - Johns Hopkins MedicineAnjaliAinda não há avaliações
- The Chakras: Seventh Chakra (Crown)Documento4 páginasThe Chakras: Seventh Chakra (Crown)Nabuco FilmesAinda não há avaliações
- Q. What Is The Difference Between Myxedema and Hypothyroidism?Documento4 páginasQ. What Is The Difference Between Myxedema and Hypothyroidism?Wan Razin Wan HassanAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Management of Woman With GDMDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Management of Woman With GDMkimglaidyl bontuyanAinda não há avaliações
- Subcutaneous FatDocumento7 páginasSubcutaneous FatAres Santiago R. NoguedaAinda não há avaliações
- The Ketogenic Diet & Insulin ResistanceDocumento2 páginasThe Ketogenic Diet & Insulin ResistanceSaurabh Pandey0% (1)
- MEDITECH-GAINZLAB (Caro Jimenez)Documento4 páginasMEDITECH-GAINZLAB (Caro Jimenez)Lean Spinetta100% (1)
- Semis 2 - Drugs Acting On The Endocrine System 2Documento11 páginasSemis 2 - Drugs Acting On The Endocrine System 2Amiel Francisco Reyes100% (1)
- Iris A4 PosterDocumento2 páginasIris A4 PosterAndrea Gil Flaño0% (1)
- Crash Course Anatomy and Physiology EndoccrineDocumento9 páginasCrash Course Anatomy and Physiology EndoccrineReem SleemAinda não há avaliações
- Insulin ResistanceDocumento29 páginasInsulin Resistanceahmed AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- DLL Sci Q2 W2Documento12 páginasDLL Sci Q2 W2Raymund DelfinAinda não há avaliações
- (1479683X - European Journal of Endocrinology) ENDOCRINE OBESITY - Pituitary Dysfunction in ObesityDocumento14 páginas(1479683X - European Journal of Endocrinology) ENDOCRINE OBESITY - Pituitary Dysfunction in ObesityAnonymous nRufcMpvNAinda não há avaliações
- General Adaptation Syndrome TheoriesDocumento4 páginasGeneral Adaptation Syndrome TheoriesHema JothyAinda não há avaliações
- Ata Hyperthyroidism BrochureDocumento3 páginasAta Hyperthyroidism BrochureKumalaAudiKusumaAinda não há avaliações
- Surgery Acute Kidney Injury 10-06-21Documento49 páginasSurgery Acute Kidney Injury 10-06-21Muhammad ArsalAinda não há avaliações
- PhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 3Documento3 páginasPhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 3PabloAndresPalaciosAgilaAinda não há avaliações
- Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections,: Lecture by Edward J. ZaliskoDocumento87 páginasCampbell Biology: Concepts & Connections,: Lecture by Edward J. ZaliskoLawiswisAinda não há avaliações
- ADA GuidlinesDocumento154 páginasADA GuidlinesJazmin AguillonAinda não há avaliações
- Pancreas: Anatomy, Diseases and Health Implications: September 2012Documento53 páginasPancreas: Anatomy, Diseases and Health Implications: September 2012DrFarah Emad AliAinda não há avaliações
- PALMCODocumento15 páginasPALMCOBelinderjit KaurAinda não há avaliações
- Hiperpotasemia KDIGODocumento20 páginasHiperpotasemia KDIGOAndy MaciasAinda não há avaliações