Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Visual Pathway
Enviado por
mohhammadfaisaal0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
862 visualizações15 páginasssdfss
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentossdfss
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
862 visualizações15 páginasVisual Pathway
Enviado por
mohhammadfaisaalssdfss
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 15
Visual pathway
• Retina → Optic nerve →Optic chiasma
↓
Optic tract
↓
Lateral geniculate body
↓
geniculostriate tract
↓
Optic radiation
to visual sensory area
17,18&19
The retina
• Contains photoreceptors i.e.
Rods & cones
• Cones- around 7millions in
retina. Respond best in
bright light. Responsible for
sharp vision, discrimination
of colour. Most numerous in
Macula lutea
• Optic disc is devoid of
photoreceptors
• Rods are more in
number(100) million
• Predominate in peripheral
area
• Retina
Visual feld & retinal quadrent-
Head & eye are maintained in a fixed posture
• One eye is closed
• Area seen by the open eye constitute the
visual field of that eye
• Visual field of the two eye overlap to a great
extent
• On either side there is a small area which is
seen only by eye of that side.
• For convenience visual field is divided into
right & left halves
• For convenience
visual field is
divided into rt & lt
halves
• On retina image is
inverted
• Two halves of
retina are usually
referred
As nasal & temporal
halves
Optic nerve, optic chiasma & Optic tract
• Optic nerve is made up of axons of ganglion cells of
retina
• Fibers of the nerve arising from the four quadrants of
retina maintain the same relative position within the nerve
• Fibers from the macula are numerous & form
papillomacular bundle
• The fibers of the nasal half of each retina enter the optic
tract of the opposite side after crossing in the chiasma
• Fibers from the temporal half enter the optic tract of same
side
• Optic tract carries these fibers to lateral geniculate body
of the corresponding side
Lateral geniculate body-
• Part of metathalamus
• Grey matter is split into 6 layers
• Fibers from the same side eye end in
laminae 2, 3, & 5.
• Fibers from opposite side eye end in
1, 4 & 6
• Macular fiber end in central & posterior
part of body & this area is relatively
large
Geniculocalcarine tract & visual cortex
• Fibers arising from
geniculate body form
geniculocalcarine or
optic radiation
• These fiber pass
through retrolentiform
part of internal capsule
• Radiation end in visual
areas of cerebral
cortex (Area 17, 18 &
19)
• .
• Cortex receives
impulses from retinal
halves of the same
side( from opposite
halves of field of
vision)
• The cortical area of
macula is much larger
than that for the
peripheral area.
Reprenstation of visual fieldinthe
retinae, LGB & the visual cortex
• Applied - Loss of
vision in one half is
called hemianopia
• If the same half of the
visual field is lost in
both eyes it is called as
homonymous & if the
different half are lost
then it is called
heteronymous.
• Hemianopia is named
in relation to the visual
field & not to the retina
Auditory pathway
•
Vestibular nerve
Auditory radiation in internal
capsule
Auditory area on superolateral
surface of cerebral hemisphere
Você também pode gostar
- Anatomy of Visual Pathway, Field Defects AND Its Lesions.: By-Dr. Ruchi PherwaniDocumento43 páginasAnatomy of Visual Pathway, Field Defects AND Its Lesions.: By-Dr. Ruchi Pherwanisafasayed100% (1)
- Visual ND Pupillary PathwayDocumento43 páginasVisual ND Pupillary PathwayAdarsh KeshariAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Anatomy & Physiology of Eye For Ophthalmic NursesDocumento124 páginas1 Anatomy & Physiology of Eye For Ophthalmic NursesSMEY204100% (1)
- Visual PathwayDocumento24 páginasVisual PathwayAkshara Eye FoundationAinda não há avaliações
- Physiology of EyeDocumento96 páginasPhysiology of EyePhysiology by Dr RaghuveerAinda não há avaliações
- L 01 Ocular AnatomyDocumento13 páginasL 01 Ocular Anatomydoni anandaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of Eyelid: Presenter:-Dr. Vijayalaxmi Moderator:-Dr. SanjanaDocumento49 páginasAnatomy of Eyelid: Presenter:-Dr. Vijayalaxmi Moderator:-Dr. SanjanaRidhi Bhandari100% (1)
- Visual and Lacrimal AppratusDocumento45 páginasVisual and Lacrimal AppratusAzman Bin KadirAinda não há avaliações
- 734 Visual Pathway LesionsDocumento25 páginas734 Visual Pathway LesionsNarendra N NaruAinda não há avaliações
- 3.1 Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye - Nov. 3 - Dr. CastilloDocumento13 páginas3.1 Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye - Nov. 3 - Dr. CastilloHanako Sasaki AranillaAinda não há avaliações
- Eye AssessmentDocumento7 páginasEye AssessmentPuviyarasiAinda não há avaliações
- B06 Posterior SegmentDocumento22 páginasB06 Posterior SegmentMigs MedinaAinda não há avaliações
- The Pupillary Light Reflex PathwayDocumento5 páginasThe Pupillary Light Reflex PathwayNauli PanjaitanAinda não há avaliações
- Histology of Kidney, Ureter and Urinary BladderDocumento28 páginasHistology of Kidney, Ureter and Urinary Bladderkhairul_azhar_27Ainda não há avaliações
- Traktus UveaDocumento90 páginasTraktus UveaAudrey Ira Yunita100% (1)
- Electron Transport ChainDocumento11 páginasElectron Transport ChainSoofia SharifAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Skills Week 1Documento3 páginasClinical Skills Week 1Aishah SiddiqahAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of The OrbitDocumento43 páginasAnatomy of The OrbitHari KrishnanAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of RetinaDocumento39 páginasAnatomy of Retinadr_dev100% (1)
- Ocular EmergenciesDocumento4 páginasOcular EmergenciesJim Jose AntonyAinda não há avaliações
- Surgical Management of MyopiaDocumento23 páginasSurgical Management of MyopiaMohamed Ghanem100% (4)
- Cns PhysiologyDocumento152 páginasCns PhysiologyDr. Niyati Patel100% (1)
- Visual Pathway & Its LesionsDocumento24 páginasVisual Pathway & Its LesionsSyedaNaveenBatoolAinda não há avaliações
- Pre AnaestheticsDocumento69 páginasPre AnaestheticsPraney SlathiaAinda não há avaliações
- Pupillary PathwayDocumento21 páginasPupillary PathwaySurbhi BhartiAinda não há avaliações
- 13 Subjective RefractionDocumento19 páginas13 Subjective Refractionmuhammad farizAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of Eye: By: Dr. Lubna ShahDocumento36 páginasAnatomy of Eye: By: Dr. Lubna ShahRida ShahAinda não há avaliações
- CapsulotomyDocumento15 páginasCapsulotomyAdrian PearlAinda não há avaliações
- Ophthalmologic Exam PDFDocumento70 páginasOphthalmologic Exam PDFSamsam Almarez BacaltosAinda não há avaliações
- Epidural Hematoma Neuro SurgeryDocumento2 páginasEpidural Hematoma Neuro SurgeryA Novita Dewi AryantiAinda não há avaliações
- NCM 103 - Oxy RespiDocumento21 páginasNCM 103 - Oxy RespiMaureen Gonzalo-FlorendoAinda não há avaliações
- Nerve Muscle PhysiologyDocumento18 páginasNerve Muscle PhysiologyDr P N N Reddy100% (2)
- 4th Lecture On Physiology of Eye by Dr. RoomiDocumento36 páginas4th Lecture On Physiology of Eye by Dr. RoomiMudassar RoomiAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyesDocumento3 páginasAnatomy and Physiology of The EyesNkk Aqnd MgdnglAinda não há avaliações
- Extraocular Muscles Anatomy PDFDocumento2 páginasExtraocular Muscles Anatomy PDFCherylAinda não há avaliações
- Upper Motor Neuron PDFDocumento3 páginasUpper Motor Neuron PDFkevin_jawanAinda não há avaliações
- Motor TractDocumento4 páginasMotor TractRaden Achmad Candra PutraAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment of The Ear, Nose and ThroatDocumento40 páginasAssessment of The Ear, Nose and Throatsnickers_j100% (3)
- Visual Pathway - Neurology - Medbullets Step 1Documento5 páginasVisual Pathway - Neurology - Medbullets Step 1Andi.Roem_97Ainda não há avaliações
- Oculomotor Nerve: Arista Prima NDocumento7 páginasOculomotor Nerve: Arista Prima NArista Prima N100% (1)
- Auditory Pathway PDFDocumento3 páginasAuditory Pathway PDFShruthi DanielAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4. Muscular - System JeDocumento55 páginasChapter 4. Muscular - System JeIvonike Lim100% (2)
- Lect 2 Descending Motor IMPROVED PathwaysDocumento24 páginasLect 2 Descending Motor IMPROVED PathwaysMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- Error of RefractionDocumento37 páginasError of RefractionIka KrastanayaAinda não há avaliações
- Vascularization of Lower and Upper ExtermitesDocumento40 páginasVascularization of Lower and Upper Extermiteszainab sawan100% (1)
- Excitation of HeartDocumento17 páginasExcitation of HeartdevdsantoshAinda não há avaliações
- Roving Ring ScotomaDocumento3 páginasRoving Ring ScotomaDeboprasad DasAinda não há avaliações
- Case Presentation CataractDocumento19 páginasCase Presentation CataractRani GhereAinda não há avaliações
- Ring Enhancing LesionsDocumento50 páginasRing Enhancing LesionsVivek GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Encephalitis Is An Acute Inflammation of The Brain. Encephalitis With Meningitis IsDocumento4 páginasEncephalitis Is An Acute Inflammation of The Brain. Encephalitis With Meningitis IsDivya GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy 2 MnemonicsDocumento17 páginasAnatomy 2 MnemonicsRosalie Catalan EslabraAinda não há avaliações
- ANATOMY OF THE EYE (Organ of Vision) by DR Omeje EmmanuelDocumento31 páginasANATOMY OF THE EYE (Organ of Vision) by DR Omeje Emmanuelchidera100% (2)
- VENOUS DRAINAGE OoF HEAD AND NECKDocumento66 páginasVENOUS DRAINAGE OoF HEAD AND NECKBhanu PraseedhaAinda não há avaliações
- ErgDocumento84 páginasErgpartani_anand100% (1)
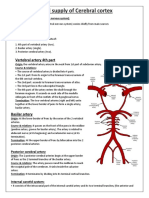
- Blood Supply of Cerebral CortexDocumento3 páginasBlood Supply of Cerebral CortexashrafAinda não há avaliações
- Cranial Nerve Exam in DetailDocumento36 páginasCranial Nerve Exam in DetailANIE100% (1)
- SCALP: (Keith L Moore)Documento5 páginasSCALP: (Keith L Moore)rajtanniruAinda não há avaliações
- Subject: Physiology Topic: Vision Physiology 1 Lecturer: Dr. Vic Mendoza DATE: MARCH, 2011Documento7 páginasSubject: Physiology Topic: Vision Physiology 1 Lecturer: Dr. Vic Mendoza DATE: MARCH, 2011Std DlshsiAinda não há avaliações
- Optic Nerve: Presented By: Aqsa Irfan Presented To: Dr. Sania ZehraDocumento21 páginasOptic Nerve: Presented By: Aqsa Irfan Presented To: Dr. Sania ZehraAqsaAinda não há avaliações
- VISUAL PATHWAY Lecture AMENDEDDocumento27 páginasVISUAL PATHWAY Lecture AMENDEDMarvel NnaemekaAinda não há avaliações
- Moh Faisal Sy Intam Sub Xwlcvs PLW Flight - OriginatingDocumento2 páginasMoh Faisal Sy Intam Sub Xwlcvs PLW Flight - OriginatingmohhammadfaisaalAinda não há avaliações
- Cover Refka DR WinarniDocumento2 páginasCover Refka DR WinarnimohhammadfaisaalAinda não há avaliações
- The Implementation of Issuance Service of Birth and Death Certificates Indepartment of Population and Civil Registrar of Merauke District PDFDocumento5 páginasThe Implementation of Issuance Service of Birth and Death Certificates Indepartment of Population and Civil Registrar of Merauke District PDFmohhammadfaisaalAinda não há avaliações
- Cover Refka DR WinarniDocumento2 páginasCover Refka DR WinarnimohhammadfaisaalAinda não há avaliações
- DiagnosticDocumento4 páginasDiagnosticmohhammadfaisaalAinda não há avaliações
- Referat Antropologi ForensikDocumento40 páginasReferat Antropologi ForensikmohhammadfaisaalAinda não há avaliações
- DifficultDocumento4 páginasDifficultmohhammadfaisaalAinda não há avaliações
- Herpes DR EdhaDocumento15 páginasHerpes DR EdhamohhammadfaisaalAinda não há avaliações
- DiagnosticDocumento4 páginasDiagnosticmohhammadfaisaalAinda não há avaliações
- Cover Refka DR WinarniDocumento2 páginasCover Refka DR WinarnimohhammadfaisaalAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 11Documento3 páginasLesson 11mohhammadfaisaalAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 10 - Why The Idea of A Fluid?Documento6 páginasLesson 10 - Why The Idea of A Fluid?mohhammadfaisaalAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 6 - Magnetism, Hypnosis and SomnambulismDocumento6 páginasLesson 6 - Magnetism, Hypnosis and SomnambulismmohhammadfaisaalAinda não há avaliações
- Final LessonDocumento3 páginasFinal LessonmohhammadfaisaalAinda não há avaliações
- The Concepts and Principles of Equity and HealthDocumento18 páginasThe Concepts and Principles of Equity and HealthPaulo César López BarrientosAinda não há avaliações
- MKF Tool HelpDocumento6 páginasMKF Tool HelpRob GoetzAinda não há avaliações
- A Book of Beasts PDFDocumento32 páginasA Book of Beasts PDFbrad drac100% (2)
- LP.-Habitat-of-Animals Lesson PlanDocumento4 páginasLP.-Habitat-of-Animals Lesson PlanL LawlietAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study Method: Dr. Rana Singh MBA (Gold Medalist), Ph. D. 98 11 828 987Documento33 páginasCase Study Method: Dr. Rana Singh MBA (Gold Medalist), Ph. D. 98 11 828 987Belur BaxiAinda não há avaliações
- Failure of Composite Materials PDFDocumento2 páginasFailure of Composite Materials PDFPatrickAinda não há avaliações
- How To Manage Asthma: A GuideDocumento44 páginasHow To Manage Asthma: A GuideSrinivas YerriboinaAinda não há avaliações
- Molina Vs de La Riva 6 Phil 12 INOKDocumento2 páginasMolina Vs de La Riva 6 Phil 12 INOKErick Jay InokAinda não há avaliações
- Gullivers TravelDocumento3 páginasGullivers TravelRanen Das MishukAinda não há avaliações
- PREETI and RahulDocumento22 páginasPREETI and Rahulnitinkhandelwal2911Ainda não há avaliações
- Teaching and Assessment of Literature Studies and CA LitDocumento9 páginasTeaching and Assessment of Literature Studies and CA LitjoshuaalimnayAinda não há avaliações
- Kravitz Et Al (2010)Documento5 páginasKravitz Et Al (2010)hsayAinda não há avaliações
- Eaap Critical Approaches SamplesDocumento2 páginasEaap Critical Approaches SamplesAcsana LucmanAinda não há avaliações
- Marriage and Divorce Conflicts in The International PerspectiveDocumento33 páginasMarriage and Divorce Conflicts in The International PerspectiveAnjani kumarAinda não há avaliações
- WhatsApp Chat With MiniSoDocumento28 páginasWhatsApp Chat With MiniSoShivam KumarAinda não há avaliações
- The Cave Tab With Lyrics by Mumford and Sons Guitar TabDocumento2 páginasThe Cave Tab With Lyrics by Mumford and Sons Guitar TabMassimiliano MalerbaAinda não há avaliações
- DBS AR 2019 Final Final PDFDocumento371 páginasDBS AR 2019 Final Final PDFDevi Nurusr100% (1)
- IC HDL Lab ManualDocumento82 páginasIC HDL Lab ManualRakshitha AngelAinda não há avaliações
- Overpressure Prediction From PS Seismic DataDocumento10 páginasOverpressure Prediction From PS Seismic DataSevinj HumbatovaAinda não há avaliações
- Operations Research Letters: Meichun Lin, Woonghee Tim Huh, Guohua WanDocumento8 páginasOperations Research Letters: Meichun Lin, Woonghee Tim Huh, Guohua WanQuỳnh NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- AMBROSE PINTO-Caste - Discrimination - and - UNDocumento3 páginasAMBROSE PINTO-Caste - Discrimination - and - UNKlv SwamyAinda não há avaliações
- m100 Resume Portfolio AssignmentDocumento1 páginam100 Resume Portfolio Assignmentapi-283396653Ainda não há avaliações
- M40 Mix DesignDocumento2 páginasM40 Mix DesignHajarath Prasad Abburu100% (1)
- 4 Problem GamblingDocumento14 páginas4 Problem GamblingLee Jia HuiAinda não há avaliações
- Universal Prayers IIDocumento3 páginasUniversal Prayers IIJericho AguiatanAinda não há avaliações
- Sales Purchases Returns Day BookDocumento8 páginasSales Purchases Returns Day BookAung Zaw HtweAinda não há avaliações
- Essay On Earth QuakeDocumento7 páginasEssay On Earth Quakexlgnhkaeg100% (2)
- Stability Result 15275 MT - Initial StowageDocumento1 páginaStability Result 15275 MT - Initial StowageLife with Our planetAinda não há avaliações
- Potential Nursing Diagnosis Problem Fdar / NCP: Activity # 2Documento2 páginasPotential Nursing Diagnosis Problem Fdar / NCP: Activity # 2Karl KiwisAinda não há avaliações
- Chryso CI 550Documento2 páginasChryso CI 550Flavio Jose MuhaleAinda não há avaliações