Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Aparte Del Aisc 358
Enviado por
Cristian SandovalDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Aparte Del Aisc 358
Enviado por
Cristian SandovalDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Prequalified Seismic:Sept.
6, 2011 9/6/11 1:18 PM Page 3
9.2–3
CHAPTER 2
DESIGN REQUIREMENTS
2.1. SPECIAL AND INTERMEDIATE MOMENT FRAME
CONNECTION TYPES
The connection types listed in Table 2.1 are prequalified for use in connecting beams
to column flanges in special moment frames (SMF) and intermediate moment frames
(IMF) within the limitations specified in this Standard.
2.2. CONNECTION STIFFNESS
All connections contained in this Standard shall be considered fully restrained (Type
FR) for the purpose of seismic analysis.
2.3. MEMBERS
The connections contained in this Standard are prequalified in accordance with the
requirements of the AISC Seismic Provisions when used to connect members meet-
ing the limitations of Sections 2.3.1 or 2.3.2, as applicable.
1. Rolled Wide-Flange Members
Rolled wide-flange members shall conform to the cross section profile limitations
applicable to the specific connection in this Standard.
2. Built-up Members
Built-up members having a doubly symmetric, I-shaped cross section shall meet the
following requirements:
(1) Flanges and webs shall have width, depth and thickness profiles similar to rolled
wide-flange sections meeting the profile limitations for wide-flange sections
applicable to the specific connection in this Standard, and
(2) Webs shall be continuously connected to flanges in accordance with the require-
ments of Sections 2.3.2a or 2.3.2b, as applicable.
Prequalified Connections for Special and Intermediate Steel Moment Frames
for Seismic Applications, 2010, incl. Supplement No. 1
AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF STEEL CONSTRUCTION
Prequalified Seismic:Sept. 6, 2011 9/6/11 1:18 PM Page 4
9.2–4 MEMBERS [Sect. 2.3.
TABLE 2.1.
Prequalified Moment Connections
Connection Type Chapter Systems
Reduced beam section (RBS) 5 SMF, IMF
Bolted unstiffened extended end plate (BUEEP) 6 SMF, IMF
Bolted stiffened extended end plate (BSEEP) 6 SMF, IMF
Bolted flange plate (BFP) 7 SMF, IMF
Welded unreinforced flange-welded web (WUF-W) 8 SMF, IMF
Kaiser bolted bracket (KBB) 9 SMF, IMF
ConXtech ConXL moment connection (ConXL) 10 SMF, IMF
2a. Built-up Beams
The web and flanges shall be connected using complete-joint-penetration (CJP)
groove welds with a pair of reinforcing fillet welds within a zone extending from the
beam end to a distance not less than one beam depth beyond the plastic hinge loca-
tion, Sh, unless specifically indicated in this Standard. The minimum size of these
fillet welds shall be the lesser of 5/16 in. (8 mm) and the thickness of the beam web.
Exception: This provision shall not apply where individual connection prequalifica-
tions specify other requirements.
2b. Built-up Columns
Built-up columns shall conform to the provisions of subsections (1) through (4), as
applicable. Built-up columns shall satisfy the requirements of the AISC Specification
except as modified in this Section. Transfer of all internal forces and stresses between
elements of the built-up column shall be through welds.
(1) I-Shaped Columns
The elements of built-up I-shaped columns shall conform to the requirements of
the AISC Seismic Provisions.
Within a zone extending from 12 in. (300 mm) above the upper beam flange to
12 in. (300 mm) below the lower beam flange, unless specifically indicated in
this Standard, the column webs and flanges shall be connected using CJP groove
welds with a pair of reinforcing fillet welds. The minimum size of the fillet welds
shall be the lesser of 5/16 in. (8 mm) and the thickness of the column web.
(2) Boxed Wide-Flange Columns
The wide-flange shape of a boxed wide-flange column shall conform to the
requirements of the AISC Seismic Provisions.
The width-to-thickness ratio, b/t, of plates used as flanges shall not exceed,
0.6 E Fy , where b shall be taken as not less than the clear distance between
plates.
The width-to-thickness ratio, h/tw, of plates used only as webs shall conform to
the requirements of the AISC Seismic Provisions.
Prequalified Connections for Special and Intermediate Steel Moment Frames
for Seismic Applications, 2010, incl. Supplement No. 1
AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF STEEL CONSTRUCTION
Prequalified Seismic:Sept. 6, 2011 9/6/11 1:18 PM Page 39
9.2–39
CHAPTER 7
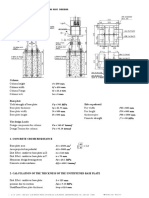
BOLTED FLANGE PLATE (BFP)
MOMENT CONNECTION
7.1. GENERAL
Bolted flange plate (BFP) moment connections utilize plates welded to column
flanges and bolted to beam flanges. The top and bottom plates must be identical.
Flange plates are welded to the column flange using complete-joint-penetration
(CJP) groove welds and beam flange connections are made with high-strength bolts.
The beam web is connected to the column flange using a bolted shear tab with bolts
in short-slotted holes. Details for this connection type are shown in Figure 7.1. Initial
yielding and plastic hinge formation are intended to occur in the beam in the region
near the end of the flange plates.
7.2. SYSTEMS
Bolted flange plate connections are prequalified for use in special moment frame
(SMF) and intermediate moment frame (IMF) systems within the limitations of these
provisions.
Exception: Bolted flange plate connections in SMF systems with concrete structural
slabs are only prequalified if the concrete structural slab is kept at least 1 in. (25 mm)
from both sides of both column flanges. It is permissible to place compressible mate-
rial in the gap between the column flanges and the concrete structural slab.
Fig. 7.1. Bolted flange plate moment connection.
Prequalified Connections for Special and Intermediate Steel Moment Frames
for Seismic Applications, 2010, incl. Supplement No. 1
AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF STEEL CONSTRUCTION
Prequalified Seismic:Sept. 6, 2011 9/6/11 1:18 PM Page 40
9.2–40 PREQUALIFICATION LIMITS [Sect. 7.3.
7.3. PREQUALIFICATION LIMITS
1. Beam Limitations
Beams shall satisfy the following limitations:
(1) Beams shall be rolled wide-flange or welded built-up I-shaped members con-
forming to the requirements in Section 2.3.
(2) Beam depth is limited to a maximum of W36 (W920) for rolled shapes. Depth of
built-up sections shall not exceed the depth permitted for rolled wide-flange
shapes.
(3) Beam weight is limited to a maximum of 150 lb/ft (224 kg/m).
(4) Beam flange thickness is limited to a maximum of 1 in. (25 mm).
(5) The clear span-to-depth ratio of the beam is limited as follows:
(a) For SMF systems, 9 or greater.
(b) For IMF systems, 7 or greater.
(6) Width-to-thickness ratios for the flanges and web of the beam shall conform to
the requirements of the AISC Seismic Provisions.
(7) Lateral bracing of beams shall be provided as follows:
Lateral bracing of beams shall conform to the requirements of the AISC Seismic
Provisions. To satisfy the requirements of Chapter E of the AISC Seismic
Provisions for lateral bracing at plastic hinges, supplemental lateral bracing shall
be provided at both the top and bottom beam flanges, and shall be located a dis-
tance of d to 1.5d from the bolt farthest from the face of the column. No
attachment of lateral bracing shall be made within the protected zone.
Exception: For both SMF and IMF systems, where the beam supports a concrete
structural slab that is connected along the beam span between protected zones
with welded shear connectors spaced at a maximum of 12 in. (300 mm) on cen-
ter, supplemental top and bottom flange bracing at plastic hinges is not required.
(8) The protected zone consists of the flange plates and the portion of the beam
between the face of the column and a distance equal to the beam depth beyond
the bolt farthest from the face of the column.
2. Column Limitations
(1) Columns shall be any of the rolled shapes or welded built-up sections permitted
in Section 2.3.
(2) The beam shall be connected to the flange of the column.
(3) Rolled shape column depth shall be limited to W36 (W920) maximum when a
concrete structural slab is provided. In the absence of a concrete structural slab,
the rolled shape column depth is limited to W14 (W360) maximum. Flanged
Prequalified Connections for Special and Intermediate Steel Moment Frames
for Seismic Applications, 2010, incl. Supplement No. 1
AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF STEEL CONSTRUCTION
Você também pode gostar
- Asci 358-18 2.3Documento2 páginasAsci 358-18 2.3Jan stevens Vargas cardonaAinda não há avaliações
- ANSI-AISC 358-20 - C7SA - InglésDocumento7 páginasANSI-AISC 358-20 - C7SA - InglésmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- Norma Aisc 341 (Capítulo E)Documento22 páginasNorma Aisc 341 (Capítulo E)ElmerAinda não há avaliações
- Stress Analysis of Reduced Beam Section ConnectionsDocumento10 páginasStress Analysis of Reduced Beam Section Connectionskukuh kurniawan dwi sungkonoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 9Documento24 páginasChapter 9alcaponeAinda não há avaliações
- ANSI-AISC 358-20 - C7SB - InglésDocumento7 páginasANSI-AISC 358-20 - C7SB - InglésmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- 001-Behaviour of Reduced Beam Section Moment Connection With Refernce To Continuity Plates State Od Art ReviewDocumento10 páginas001-Behaviour of Reduced Beam Section Moment Connection With Refernce To Continuity Plates State Od Art ReviewSwati KulkarniAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 10 (B) - DR S K Garg On Ductile Detailing of Steel BridgesDocumento20 páginasLecture 10 (B) - DR S K Garg On Ductile Detailing of Steel BridgesSulabh GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- OCBFDocumento3 páginasOCBFJeffH100% (1)
- Short Course IMF and SMF ConnectionDocumento53 páginasShort Course IMF and SMF ConnectionNugraha BintangAinda não há avaliações
- PSCC PolesDocumento13 páginasPSCC PolesChaitanya Bhargav KotikeAinda não há avaliações
- Beam-column joint design provisionsDocumento9 páginasBeam-column joint design provisionsSanjeev MishraAinda não há avaliações
- 2006 Beam Column Joint ICJDocumento9 páginas2006 Beam Column Joint ICJvishalgoreAinda não há avaliações
- Structural Design Requirements for Steel Moment Frame ConnectionsDocumento4 páginasStructural Design Requirements for Steel Moment Frame ConnectionsDavidQAinda não há avaliações
- Cement Concrete PoleDocumento30 páginasCement Concrete PoleGeno AgneAinda não há avaliações
- Conxtech Conxl Moment Connection: 10.1. GENERALDocumento24 páginasConxtech Conxl Moment Connection: 10.1. GENERALPaola DoradoAinda não há avaliações
- AISC 2022-Capitulo JDocumento36 páginasAISC 2022-Capitulo JLeonardo ReynaAinda não há avaliações
- Clause For Seismic DesignDocumento10 páginasClause For Seismic DesignFarhanah Binti FaisalAinda não há avaliações
- 14 PSC Poles Spec No 39Documento7 páginas14 PSC Poles Spec No 39sonu200186100% (1)
- ER-5861 SSDA Slotted Web Beam-To-Column Steel Moment Frame ConnectionDocumento6 páginasER-5861 SSDA Slotted Web Beam-To-Column Steel Moment Frame Connectioncancery0707Ainda não há avaliações
- Drift Control Deep Beam-To-Deep Column Special Moment Frames Dengan Sambungan RbsDocumento8 páginasDrift Control Deep Beam-To-Deep Column Special Moment Frames Dengan Sambungan RbsAyulestariSimamoraAinda não há avaliações
- 5.9 Backing: AWS D1.1/D1.1M:2015 Clause 5. FabricationDocumento1 página5.9 Backing: AWS D1.1/D1.1M:2015 Clause 5. FabricationRohit KambleAinda não há avaliações
- Ur s12 Rev5 pdf1332Documento6 páginasUr s12 Rev5 pdf1332Maan MrabetAinda não há avaliações
- Module 9-Ductile Frame BuildingsDocumento20 páginasModule 9-Ductile Frame BuildingsThomas John Doblas AgrabioAinda não há avaliações
- IS 800:2007 Section 12 Design and Detailing for Earthquake LoadsDocumento21 páginasIS 800:2007 Section 12 Design and Detailing for Earthquake LoadsAnshul SoniAinda não há avaliações
- Connections, Joints, and Fasteners: 7.1. ScopeDocumento4 páginasConnections, Joints, and Fasteners: 7.1. ScopeQuốc KhánhAinda não há avaliações
- Designing Composite Box Flanges for BridgesDocumento28 páginasDesigning Composite Box Flanges for BridgesMehedi HasanAinda não há avaliações
- Suspended Lay in Panel Ceiling Details - 2019 California Building CodeDocumento71 páginasSuspended Lay in Panel Ceiling Details - 2019 California Building CodeStevieAinda não há avaliações
- Removable Temporary Ground Anchor BookletDocumento12 páginasRemovable Temporary Ground Anchor BookletRajesh KyasanipalleyAinda não há avaliações
- Metallic Coated Stranded Steel Core For Aluminum Conductors, Steel Reinforced (ACSR)Documento3 páginasMetallic Coated Stranded Steel Core For Aluminum Conductors, Steel Reinforced (ACSR)alanetnAinda não há avaliações
- Benchmark Study of A Bolted Flange Plate Moment Connection: Prepared For Idea StaticaDocumento17 páginasBenchmark Study of A Bolted Flange Plate Moment Connection: Prepared For Idea Staticabramo96Ainda não há avaliações
- Acoustical ceiling suspension systemsDocumento6 páginasAcoustical ceiling suspension systemsEnque01Ainda não há avaliações
- Astm C-645Documento7 páginasAstm C-645sabbirAinda não há avaliações
- Pages From AISC 341Documento2 páginasPages From AISC 341vijaykumarzAinda não há avaliações
- Nonstructural Steel Framing Members: Standard Specification ForDocumento6 páginasNonstructural Steel Framing Members: Standard Specification ForJesús Luis Arce GuillermoAinda não há avaliações
- Docking/Drain Plug and Boss Assemblies (Metric) : Standard Specification ForDocumento3 páginasDocking/Drain Plug and Boss Assemblies (Metric) : Standard Specification ForEduardoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter Five, Plate GirdersDocumento21 páginasChapter Five, Plate GirdersZeleke TaimuAinda não há avaliações
- Capitulo 6 (358-10)Documento5 páginasCapitulo 6 (358-10)tzawar mishkeAinda não há avaliações
- Astm CDocumento16 páginasAstm Csolrac4371100% (2)
- Earthquake Resistant Design of Structures for DuctilityDocumento10 páginasEarthquake Resistant Design of Structures for DuctilityYeni TewatiaAinda não há avaliações
- ST5101-Advance Concrete StructuresDocumento16 páginasST5101-Advance Concrete Structuresraj25% (4)
- Weld Access Hole (AISC 360 Section J1.6&7)Documento1 páginaWeld Access Hole (AISC 360 Section J1.6&7)Jovito EdillonAinda não há avaliações
- Design FRP Bar PDFDocumento58 páginasDesign FRP Bar PDFTrầmLãngAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Design of Steel and Concrete Composite StructuresDocumento19 páginasAdvanced Design of Steel and Concrete Composite StructuresCristian BlanaruAinda não há avaliações
- Guidance Note Shear Connectors No. 2.11: ScopeDocumento4 páginasGuidance Note Shear Connectors No. 2.11: ScopeDesigns3 ShreeprefabAinda não há avaliações
- Details of Fillet Welds D15M-D15-2002 - Section - 2.1Documento40 páginasDetails of Fillet Welds D15M-D15-2002 - Section - 2.1drac_dracAinda não há avaliações
- Moment Coupler - Codal RequirementsDocumento3 páginasMoment Coupler - Codal Requirementskvamshi_1971Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter M - Design of Fabrication and ErectionDocumento5 páginasChapter M - Design of Fabrication and ErectionGirl Who LivedAinda não há avaliações
- Ductile Detailing Useful ReferencesDocumento6 páginasDuctile Detailing Useful ReferencesMandar NadgaundiAinda não há avaliações
- Astm A363Documento3 páginasAstm A363Adolfo Luis Avila Murcia100% (1)
- 1917101-Advanced Concrete and Steel StructuresDocumento18 páginas1917101-Advanced Concrete and Steel StructuresDeepakAinda não há avaliações
- 10.1 General: Building Code Requirements For Structural Concrete, American Concrete InstituteDocumento8 páginas10.1 General: Building Code Requirements For Structural Concrete, American Concrete InstituteParth DaxiniAinda não há avaliações
- Seismic Performance of Reinforced Concrete Slab-Column Connections With Thin Plate StirrupsDocumento9 páginasSeismic Performance of Reinforced Concrete Slab-Column Connections With Thin Plate StirrupsangthiankongAinda não há avaliações
- Designed and Detailed According To IS 456 As An Ordinary Moment Resisting Frame Also Called Ordinary Concrete FrameDocumento3 páginasDesigned and Detailed According To IS 456 As An Ordinary Moment Resisting Frame Also Called Ordinary Concrete FrameAnonymous Gye18jAinda não há avaliações
- AISC 341 Section 9Documento9 páginasAISC 341 Section 9Quốc KhánhAinda não há avaliações
- Astm C1433M 01Documento6 páginasAstm C1433M 01Eyas hamadAinda não há avaliações
- C933 PDFDocumento2 páginasC933 PDFDIAZCORDOBAAinda não há avaliações
- Esr 1227Documento26 páginasEsr 1227murdicksAinda não há avaliações
- Ensuring ductility in RC designDocumento5 páginasEnsuring ductility in RC designTabrez AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignNo EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Structural Analysis of Steel TowersDocumento11 páginasStructural Analysis of Steel TowersGunabalasingam JeneevanAinda não há avaliações
- C39C39M 36505Documento8 páginasC39C39M 36505Cristian SandovalAinda não há avaliações
- Beam Design Formulas With Shear and MomentDocumento20 páginasBeam Design Formulas With Shear and MomentMuhammad Saqib Abrar100% (8)
- 1 Placa BaseDocumento4 páginas1 Placa BaseCristian SandovalAinda não há avaliações
- Steel To Concrete Joints Design-Manual II enDocumento292 páginasSteel To Concrete Joints Design-Manual II enSujeevan Tharmakulasingam100% (2)
- Elastic Stresses in Composite SectionsDocumento39 páginasElastic Stresses in Composite Sectionsjshgfukwekkfu100% (1)
- Loading, and Preliminary Design Considerations For Tall Guyed TowersDocumento9 páginasLoading, and Preliminary Design Considerations For Tall Guyed TowersCristian SandovalAinda não há avaliações
- Astm A6 Am PDFDocumento64 páginasAstm A6 Am PDFCristian SandovalAinda não há avaliações
- Barth Nsba Wsbs LRFDDocumento52 páginasBarth Nsba Wsbs LRFDCristian SandovalAinda não há avaliações
- 221 Guide For Writing A ThesisDocumento42 páginas221 Guide For Writing A ThesisJack DoverAinda não há avaliações
- Fatigue DesignDocumento56 páginasFatigue Designg401992Ainda não há avaliações
- Barth Nsba Wsbs LRFDDocumento52 páginasBarth Nsba Wsbs LRFDCristian SandovalAinda não há avaliações
- Two Span Continuous Steel GirderDocumento130 páginasTwo Span Continuous Steel Girderiv54Ainda não há avaliações
- New Fatigue Provisions For The Design of Crane Runway GirdersDocumento9 páginasNew Fatigue Provisions For The Design of Crane Runway Girdersdicktracy11Ainda não há avaliações
- Ben-Dor 2000 - Analytical Solution For Penetration by Rigid Conical Impactors Using CaviDocumento5 páginasBen-Dor 2000 - Analytical Solution For Penetration by Rigid Conical Impactors Using CaviCristian SandovalAinda não há avaliações
- CAPWAP Description WebinarDocumento41 páginasCAPWAP Description WebinarCristian SandovalAinda não há avaliações
- Pdi CapwapDocumento2 páginasPdi CapwapCristian SandovalAinda não há avaliações
- An Innovative Approach To Evaluate The Behaviour of Vertically Loaded Pile Groups Based On Elastic TheoryDocumento10 páginasAn Innovative Approach To Evaluate The Behaviour of Vertically Loaded Pile Groups Based On Elastic TheoryCristian SandovalAinda não há avaliações
- I BeamDocumento9 páginasI BeamRinjal BanerjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Rules For The Certification and ConstructionDocumento244 páginasRules For The Certification and Constructionanno_xAinda não há avaliações
- Torsional PropertiesDocumento19 páginasTorsional PropertiesAndrés Felipe HernándezAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed Design of Single-Storey Steel Portal FramesDocumento135 páginasDetailed Design of Single-Storey Steel Portal FramespodderickAinda não há avaliações
- Wind Load Provisions ASCE7 - 05Documento60 páginasWind Load Provisions ASCE7 - 05mgp82100% (2)
- Offshore Helideck Design GuidelinesDocumento307 páginasOffshore Helideck Design Guidelinestambok100% (1)
- Analisis Estructural Por DesempeñoDocumento15 páginasAnalisis Estructural Por DesempeñoJulio Cesar GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- AMCRPS HP Bearing Piles Execution DetailsDocumento9 páginasAMCRPS HP Bearing Piles Execution DetailsCristian SandovalAinda não há avaliações
- CH 6 066 002Documento7 páginasCH 6 066 002Cristian SandovalAinda não há avaliações
- Bolton 1986 - The Strength and Dilatancy of SandsDocumento14 páginasBolton 1986 - The Strength and Dilatancy of SandsCristian SandovalAinda não há avaliações
- Pile Driving ResistanceDocumento7 páginasPile Driving ResistanceCristian SandovalAinda não há avaliações
- Ratio Analysis of PIADocumento16 páginasRatio Analysis of PIAMalik Saad Noman100% (5)
- Laryngeal Diseases: Laryngitis, Vocal Cord Nodules / Polyps, Carcinoma LarynxDocumento52 páginasLaryngeal Diseases: Laryngitis, Vocal Cord Nodules / Polyps, Carcinoma LarynxjialeongAinda não há avaliações
- Revit 2010 ESPAÑOLDocumento380 páginasRevit 2010 ESPAÑOLEmilio Castañon50% (2)
- Reading Comprehension Exercise, May 3rdDocumento3 páginasReading Comprehension Exercise, May 3rdPalupi Salwa BerliantiAinda não há avaliações
- Guia de Usuario GPS Spectra SP80 PDFDocumento118 páginasGuia de Usuario GPS Spectra SP80 PDFAlbrichs BennettAinda não há avaliações
- The Dominant Regime Method - Hinloopen and Nijkamp PDFDocumento20 páginasThe Dominant Regime Method - Hinloopen and Nijkamp PDFLuiz Felipe GuaycuruAinda não há avaliações
- Alignment of Railway Track Nptel PDFDocumento18 páginasAlignment of Railway Track Nptel PDFAshutosh MauryaAinda não há avaliações
- Inventory ControlDocumento26 páginasInventory ControlhajarawAinda não há avaliações
- Philippine Population 2009Documento6 páginasPhilippine Population 2009mahyoolAinda não há avaliações
- Weone ProfileDocumento10 páginasWeone ProfileOmair FarooqAinda não há avaliações
- NABARD road inspection report formatDocumento24 páginasNABARD road inspection report formatSrinivas PAinda não há avaliações
- Consumers ' Usage and Adoption of E-Pharmacy in India: Mallika SrivastavaDocumento16 páginasConsumers ' Usage and Adoption of E-Pharmacy in India: Mallika SrivastavaSundaravel ElangovanAinda não há avaliações
- Job Order Costing: Patrick Louie E. Reyes, CTT, Micb, Rca, CpaDocumento45 páginasJob Order Costing: Patrick Louie E. Reyes, CTT, Micb, Rca, CpaClaudette Clemente100% (1)
- Form 709 United States Gift Tax ReturnDocumento5 páginasForm 709 United States Gift Tax ReturnBogdan PraščevićAinda não há avaliações
- Done - NSTP 2 SyllabusDocumento9 páginasDone - NSTP 2 SyllabusJoseph MazoAinda não há avaliações
- PNBONE_mPassbook_134611_6-4-2024_13-4-2024_0053XXXXXXXX00 (1) (1)Documento3 páginasPNBONE_mPassbook_134611_6-4-2024_13-4-2024_0053XXXXXXXX00 (1) (1)imtiyaz726492Ainda não há avaliações
- Mobile ApplicationDocumento2 páginasMobile Applicationdarebusi1Ainda não há avaliações
- Baobab MenuDocumento4 páginasBaobab Menuperseverence mahlamvanaAinda não há avaliações
- Pfr140 User ManualDocumento4 páginasPfr140 User ManualOanh NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Breaking NewsDocumento149 páginasBreaking NewstigerlightAinda não há avaliações
- Philippine Army BDU BidDocumento2 páginasPhilippine Army BDU BidMaria TeresaAinda não há avaliações
- Role of PAODocumento29 páginasRole of PAOAjay DhokeAinda não há avaliações
- Methods to estimate stakeholder views of sustainabilityDocumento7 páginasMethods to estimate stakeholder views of sustainabilityAlireza FatemiAinda não há avaliações
- Special Power of Attorney: Benedict Joseph M. CruzDocumento1 páginaSpecial Power of Attorney: Benedict Joseph M. CruzJson GalvezAinda não há avaliações
- Cot 2Documento3 páginasCot 2Kathjoy ParochaAinda não há avaliações
- Cover Letter PDFDocumento1 páginaCover Letter PDFAli EjazAinda não há avaliações
- Kathy Davis - Dancing Tango - Passionate Encounters in A Globalizing World-New York University Press (2015)Documento236 páginasKathy Davis - Dancing Tango - Passionate Encounters in A Globalizing World-New York University Press (2015)Csongor KicsiAinda não há avaliações
- Prac Res Q2 Module 1Documento14 páginasPrac Res Q2 Module 1oea aoueoAinda não há avaliações
- 1st SemDocumento3 páginas1st SemARUPARNA MAITYAinda não há avaliações